Abstract
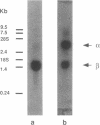
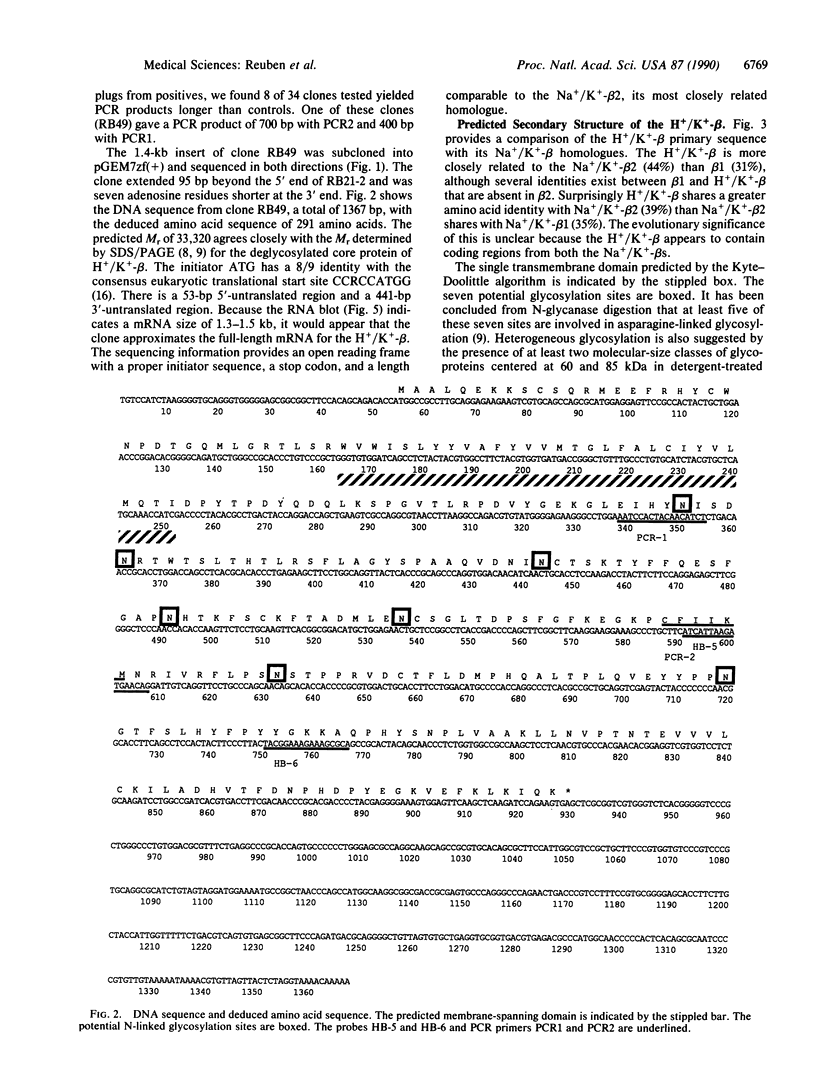
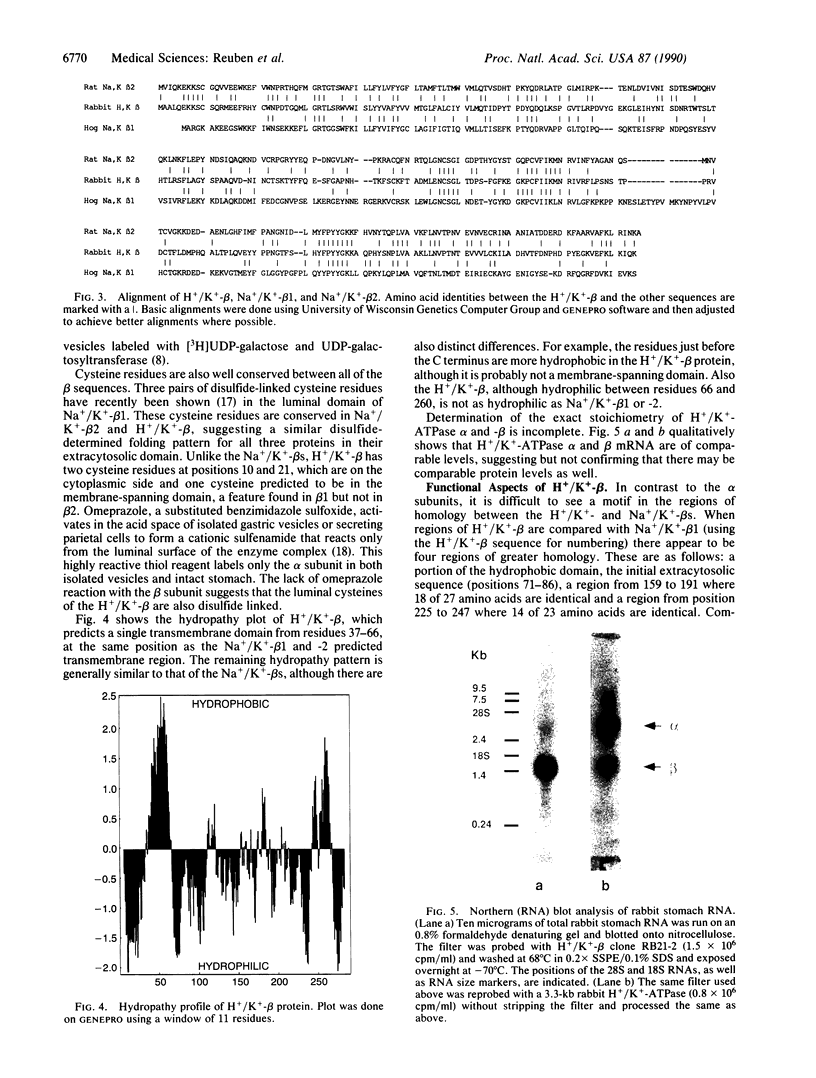
The catalytic subunit of the H+/K(+)-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.1.3) has 62% identity to the alpha, or catalytic subunit, of the Na+/K(+)-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.1.37); however, a homologous beta subunit was unknown until recently. Removal of the carbohydrate from purified hog H+/K(+)ATPase vesicles reveals a 35-kDa peptide that, when fragmented with protease V8, gives sequences homologous to both beta 1 and beta 2 subunits of the Na+/K(+)-ATPase. cDNA clones for a beta subunit of the gastric H+/K(+)-ATPase were isolated from a rabbit stomach cDNA library by using degenerate 17-mer oligonucleotide probes made to the protease V8-treated peptides. An open reading frame (54-926) encodes a predicted 291-amino acid peptide with Mr = 33,320, which exhibits 31% and 44% homologies to the Na+/K+)-ATPase beta 1 and Na+/K(+)-ATPase beta 2 proteins, respectively. A Kyte-Doolittle hydropathy plot predicts a single N-terminal transmembrane domain with a small hydrophobic region near the C terminus. The presumed extracytosolic domain contains seven potential N-linked glycosylation sites and six out of nine cysteines. Northern (RNA) blot analysis of stomach RNA with the rabbit H+/K(+)-ATPase beta probe identifies a single mRNA of 1.3-1.5 kilobases, similar in concentration to the alpha subunit mRNA. The presence of a defined gastric H+/K(+)-ATPase beta subunit extends the homology between H+/K(+)-ATPase and the Na+/K(+)-ATPase subclass of phosphoenzyme transport ATPases and distinguishes them from the monomeric Ca2+ and proton pump subclasses.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman P., Mårdh S., Norberg L., Karlsson F. A. Parietal cell antibodies in pernicious anemia inhibit H+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase, the proton pump of the stomach. Gastroenterology. 1989 Jun;96(6):1434–1438. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloor S., Antonicek H., Sweadner K. J., Pagliusi S., Frank R., Moos M., Schachner M. The adhesion molecule on glia (AMOG) is a homologue of the beta subunit of the Na,K-ATPase. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):165–174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldkorn I., Gleeson P. A., Toh B. H. Gastric parietal cell antigens of 60-90, 92, and 100-120 kDa associated with autoimmune gastritis and pernicious anemia. Role of N-glycans in the structure and antigenicity of the 60-90-kDa component. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18768–18774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K., Perez G., Anderson D., Gutierrez C., Munson K., Hersey S. J., Kaplan J. H., Sachs G. Location of the carbohydrates present in the HK-ATPase vesicles isolated from hog gastric mucosa. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 23;29(3):701–706. doi: 10.1021/bi00455a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson F. A., Burman P., Löf L., Mårdh S. Major parietal cell antigen in autoimmune gastritis with pernicious anemia is the acid-producing H+,K+-adenosine triphosphatase of the stomach. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):475–479. doi: 10.1172/JCI113344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Molecular considerations relevant to the mechanism of active transport. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):201–204. doi: 10.1038/292201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda M., Ishizaki J., Futai M. cDNA cloning and sequence determination of pig gastric (H+ + K+)-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):203–209. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Vasallo P., Dackowski W., Emanuel J. R., Levenson R. Identification of a putative isoform of the Na,K-ATPase beta subunit. Primary structure and tissue-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4613–4618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. P., Farley R. A. Beta subunit of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase contains three disulfide bonds. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 13;29(6):1524–1532. doi: 10.1021/bi00458a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto C. T., Karpilow J. M., Smolka A., Forte J. G. Isolation and characterization of gastric microsomal glycoproteins. Evidence for a glycosylated beta-subunit of the H+/K(+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Mar 1;1037(3):360–372. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(90)90038-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs G., Carlsson E., Lindberg P., Wallmark B. Gastric H,K-ATPase as therapeutic target. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1988;28:269–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.28.040188.001413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Lane L. K., Lingrel J. B. Amino-acid sequence of the beta-subunit of the (Na+ + K+)ATPase deduced from a cDNA. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):429–431. doi: 10.1038/321429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Lingrel J. B. Molecular cloning of the rat stomach (H+ + K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16788–16791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamofing D., Rossier B. C., Geering K. Role of the Na,K-ATPase beta-subunit in the cellular accumulation and maturation of the enzyme as assessed by glycosylation inhibitors. J Membr Biol. 1988 Aug;104(1):69–79. doi: 10.1007/BF01871903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]