Abstract
Specifically targeting genomic rearrangements and mutations in tumor cells has remained an elusive goal in cancer therapy. Here, we use Cas9-based genome editing to introduce the gene for the pro-drug converting enzyme ‘herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase’ (HSV1-tk) into the genome of cancer cells that carry unique sequences resulting from genome rearrangements. Specifically, we targeted the breakpoints of TMEM135-CCDC67 and MAN2A1-FER fusions in human prostate cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in mouse xenografts. We designed one adenovirus to deliver the nickase Cas9D10A and gRNAs targeting the breakpoint sequences and another to deliver an EGFP-HSV1-tk construct flanked by sequences homologous to those surrounding the breakpoint. Infection with both viruses resulted in breakpoint-dependent expression of EGFP-tk and ganciclovir-mediated apoptosis. When mouse xenografts were treated with adenoviruses and ganciclovir, all animals showed reduction of tumor burden with no mortality over the observation period. Our results suggest that Cas9-mediated suicide gene insertion might be a viable genotype-specific therapy for cancer.
Genome instability and the resulting chromosomal rearrangements and mutations I are hallmarks of cancer. Some of these rearrangements are re-occurring as they are either cancer drivers or provide other evolutionary advantages to cancer cells that carry them. For example, we recently identified a panel of fusion genes that are present in most recurrent and lethal prostate cancers1. Targeting chromosomal breakpoints that create these common fusion genes would provide a genotype specific approach to treat human cancers.
One technology that can be used to target specific sequences in the genome is Cas9-based genome editing. Cas9, a component of the Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated (Cas) prokaryotic immune system2, is a DNA endonuclease that can be targeted to a specific 20 base-pair DNA sequence by a single guide RNA (sgRNA)4,3. A D10A mutation in the catalytic domain of Cas9 converts it to nickase that produces single strand breaks at the target DNA4.
Nicking genomic DNA can be used to precisely introduce sequences into a specific genomic locus using the cellular homology directed repair (HDR) pathway. Introducing two nicks in close proximity (double nicking) in target DNA increases the efficiency of introducing sequences 50–1500 fold5 with an off-target rate as low as 1/10,000. Such specificity makes somatic genomic targeting a viable approach in treating human diseases, especially neoplasms carrying fusion genes that do not exist in the normal cells.
Thymidine kinase from Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 phosphorylates thymidine (HSV1-tk) to thymidine monophosphate which is the building block for DNA synthesis. However, the substrate specificity of HSV1-tk is somewhat different from mammalian counterpart such that it also phosphorylates a synthetic nucleoside homologue ganciclovir (pro-drug)6, that is not recognized by mammalian thymidine kinase. This results in accumulation of ganciclovir monophosphate in mammalian cells expressing HSV1-tk when treated with ganciclovir. Ganciclovir monophosphate is converted to triphosphate form by two other kinases7. Ganciclovir triphosphate blocks DNA synthesis through elongation termination. Mammalian cells negative for HSV1-tk, on the other hand, is immune from such effect due to their inability to phosphorylate ganciclovir.
In this report, we showed that by using Cas9D10A-mediated genome editing, we have successfully inserted Herpes Simplex Virus 1 thymidine kinase (HSV1-tk) into the chromosomal breakpoints of the fusion genes TMEM135-CCDC67 and MAN2A1-FER. Treatment of tumors harboring these chromosome breakpoints with ganciclovir after introduction of HSV1-tk led to cell death in cell culture and to a reduction of tumor size and mortality in mice xenografted with human prostate and liver cancers.
Results
Strategy to insert HSV1-tk into the fusion gene breakpoint
One reoccurring fusion genes discovered in prostate cancer is between transmembrane protein 135 (TMEM135) and coiled-coil domain containing 67 (CCDC67)1,8,9. The fusion gene is created by a 6 Mbp deletion in the region of chromosome 11q14.2-21. The deletion joins intron 13 of TMEM135 with intron 9 of CCDC67 in chromosome 11 (figure 1a) creating a unique sequence breakpoint not present in normal tissues, which provides a unique target in cancer cells for therapeutic intervention.
Figure 1. Schema of strategy to introduce EGFP-tk into the breakpoint of TMEM135-CCDC67 fusion gene.
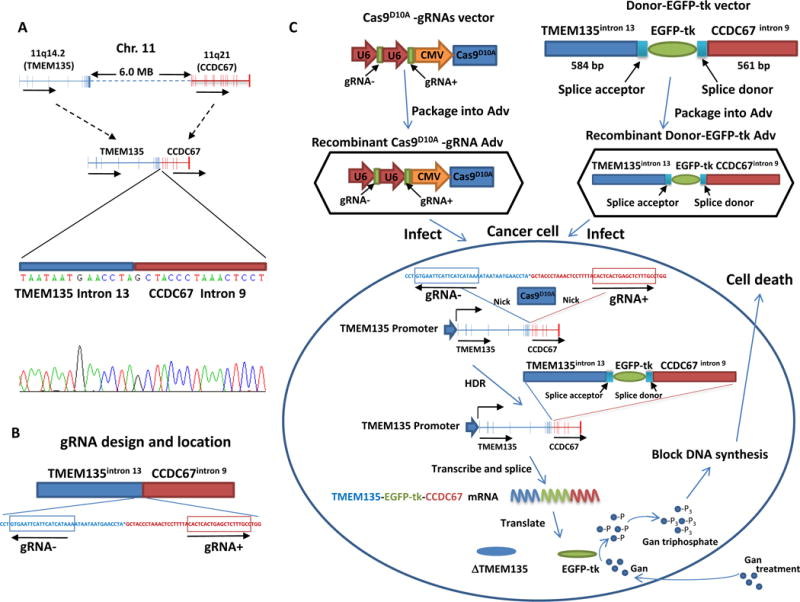
(A) Diagram representation of TMEM135 and CCDC67 recombination in Chr.11and Sanger sequencing of TMEM135-CCDC67 chromosome breakpoint. Direction of transcription is indicated by arrow. (B) Diagram of the gRNA design and location. The locations of gRNA− and gRNA+ are indicated by boxes. The directions of gRNA are indicated by arrows. (C) Stepwise schematic diagram of genome therapy strategy to introduce EGFP-tk into the breakpoint of TMEM135-CCDC67. These gRNAs were ligated with Cas9D10A into VQAd5-CMV shuttle vector and recombined into pAd5 virus. Separately, 584 bp of TMEM135 intron 13 sequence and 561 bp of CCDC67 intron 9 sequence are designed to sandwich a promoterless EGFP-tk cDNA, ligated into PAdlox shuttle vector and recombined into adenovirus. A splice acceptor and a splice donor from exon 14 of TMEM135 are inserted between TMEM135 intron 13 and EGFP-tk, and between EGFP-tk and CCDC67 intron 9, respectively, to allow proper EGFP-tk RNA splicing to occur. Cells containing TMEM135-CCDC67 chromosome breakpoint are infected with these recombinant viruses. After nicking at the sites corresponding to gRNA sequences by Cas9D10A, donor DNA containing EGFP-tk is integrated into the breakpoint region of TMEM135-CCDC67 through homology directed recombination (HDR). The integrated EGFP-tk is transcribed by the fusion head gene (TMEM135) promoter in these cells, spliced and translated into protein product of EGFP-tk, which in turn blocks DNA synthesis by converting ganciclovir (Gan) to ganciclovir triphosphate.
To target at this joining sequence, we designed two sgRNAs each complementary to one of the regions flanking the chromosomal breakpoint on opposite strands (figure 1b). These gRNAs and Cas9D10A were ligated into VQAd5-CMV shuttle vector and recombined into pAD5 adenovirus to create pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNATMEM135int13-gRNACCDC67int9. To provide a potential lethal gene for targeted cancer cells, cDNA of HSV-1 tk was ligated with enhanced green fluorescence protein (EGFP) cDNA in frame to create a chimeric gene EGFP-tk. The chimeric cDNA is promoterless but contains full open-reading frame and ribosomal binding site for independent translation initiation. To provide homologous sequences that can engage the HDR pathway, the construct was then ligated with 584 bp of intron 13 sequence of TMEM135 at the 5′ end and 561 bp of intron 9 sequence of CCDC67 at the 3′ end. These sequences were subsequently ligated into PAdlox shuttle vector and recombined into adenovirus to create pAD-TMEM135int13-EGFP-tk-CCDC67int9.
Targeting TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint in vitro
To examine whether the designed gRNAs are adequate for recruiting Cas9 to produce DNA breaks at the targeted DNA, in vitro cleavage assays were performed on pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9 plasmids using recombinant S. pyogenes Cas9 and gRNA generated by in vitro transcription. As shown in figure 2A, both gRNA− and gRNA+ cleaved the linearized pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9 at the correct locations and generated the expected 4317 and 3206 bp fragments for gRNA−, and 4414 and 3109 bp for gRNA+.
Figure 2. EGFP-tk integration and expression in cells expressing TMEM135-CCDC67 fusion breakpoint transcript.
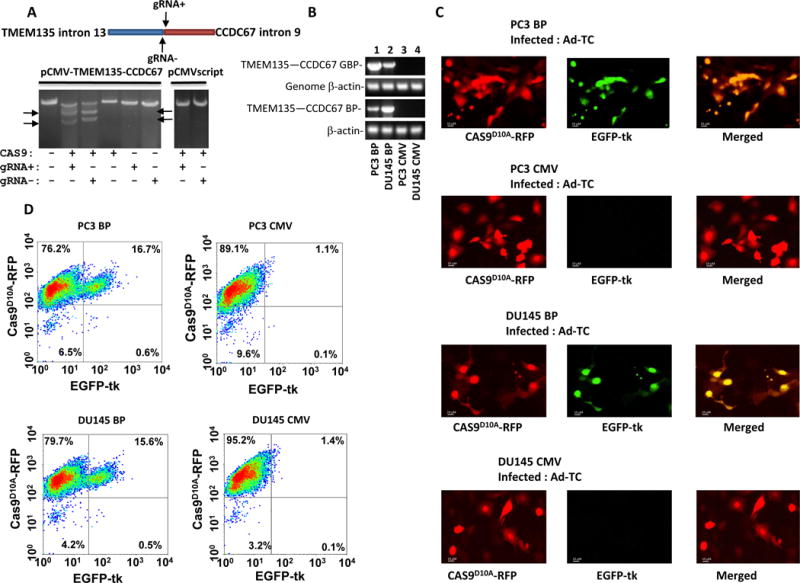
(A) gRNA mediated cleavage of pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9. In vitro cleavage assays were performed on PVUI linearized pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9 vector using recombinant Cas9, S. pyogenes and in vitro transcribed gRNA− or gRNA+ as indicated. The cleavage generated 4317 and 3206 bp fragments of pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9 vector for gRNA−, and 4414 and 3109 bp for gRNA+, indicated by arrows. (B) Genome integration and expression of TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9 breakpoint in PC3 and DU145 cells. Top panel: PCR products of TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9 breakpoint from the genome of indicated cells; Second from the top: PCR products of genomic β-actin from the genome of indicated cells. Third from the top: RT-PCR products of TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9 breakpoint from the mRNA of the indicated cells. Bottom panel: RT-PCR products of β-actin from the mRNA of the indicated cells. PC3 BP denotes PC3 cells transfected with pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9; DU145 BP denotes DU145 cells transfected with pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9; PC3 CMV denotes PC3 transfected with pCMVscript; DU145 CMV denotes DU145 cells transfected with pCMVscript. Primer sequences are listed in Supplementary table 2. (C) Infection of PC3 or DU145 cells containing TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint led to expression of EGFP-tk. PC3 or DU145 cells transformed with pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9 were infected with pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNATMEM135int13-gRNACCDC67int9 and pAD-TMEM135int13-EGFP-tk-CCDC67int9 (Ad-TC). Expression of Cas9D10A-RFP is indicated by red fluorescence, while expression EGFP-tk is indicated by green. PC3 or DU145 cells transformed with pCMVscript were used as controls. Selected images were shown. (D) Quantification of EGFP-tk integration/expression by flow cytometry as of (C).
We next tested whether pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNATMEM135int13-gRNACCDC67int9/pAD-TMEM135int13-EGFP-tk-CCDC67int9 (Ad-TC) induce integration of EGFP-tk into the TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint of the cancer genome. We first artificially introduced a TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint into prostate cancer cell lines PC3 and DU145 by transfecting a pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9 plasmid such that the integrated vector would transcribe a RNA containing TMEM133-CCDC67 breakpoint under the CMV IE94 promoter (figure 2B). Clones of transformed PC3 cells were selected to quantify for the copy number of TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint relative to that of β-actin in the genome. A clone (PC3 BP) that was estimated to contain one copy of TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint per genome was selected based on the ratio of TMEM135-CCDC67 RNA to β-actin (~1:4, PC3 cells are hyperploid for the chromosome region containing β-actin) (Supplementary figure 1)10,11. Similar selection was also applied to select a DU145 clone (DU145 BP) that contains TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint.
When PC3 BP cells were infected with Ad-TC, EGFP-tk expression was identified in cells (green fluorescence) that also expressed Cas9 D10A -RFP (red fluorescence), whereas little EGFP-tk expression was found in cells that had minimal Cas9D10A-RFP expression (figure 2C and D, table 1), suggesting that the integration of EGFP-tk into the genome and the expression of EGFP-tk protein are dependent on Cas9D10A-RFP and the specific gRNAs. Similar finding were also observed in DU145 BP cells. By contrast, neither PC3 nor DU145 cells transformed with pCMVscript displayed significant expression of EGFP-tk (figure 2C and D, table 1), suggesting that no integration of EGFP-tk occurred when TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint was absent. These results indicate that integration of EGFP-tk into the breakpoint of TMEM135-CCDC67 using Cas9D10A is highly specific. Few off-target events occurred as by FACS quantification.
Table 1.
Chromosome breakpoint dependent integration and expression of EGFP-tk
| Samples | Treatment | Cas9D10A-RFP+/EGFP-tk+ | Cas9D10A-RFP+/EGFP-tk− | Cas9D10A-RFP-/EGFP-tk+ | Cas9D10A-RFP-/EGFP-tk− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC3 BP | Ad-TC* | 16.9%±2.2 | 76.6%±3.5 | 0.5%±0.2 | 6.4%±0.5 |
| PC3 CMV | Ad-TC* | 1.0%±0.3 | 90.2%±5.6 | 0.2%±0.1 | 8.4%±1.5 |
| DU145 BP | Ad-TC* | 16.0%±1.7 | 80.1%±4.3 | 0.4%±0.1 | 4.4%±0.8 |
| DU145 CMV | Ad-TC* | 1.2%±0.3 | 95.7%±5.1 | 0.1%±0.1 | 3.1%±0.4 |
| HUH7 | Ad-MF** | 27.3%±2.8 | 69.8%±3.3 | 0.1%±0.1 | 1.6%±0.2 |
| HEP3B | Ad-MF** | 1.1%±0.4 | 96%±1.5 | 0.1%±0.1 | 2.8%±0.6 |
| HUH7 | Ad-TC* | 0.5%±0.1 | 97.8%±1.7 | 0.1%±0.1 | 1.4%±0.2 |
- Treatment includes pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNATMEM135int13-gRNACCDC67int9 and pAD-TMEM135int13-EGFP-tk-CCDC67int9 at 10 multiplicity of infection.
- Treatment includes pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNAMAN2A1int13-gRNAFERint14 and pAD-MAN2A1int13-EGFP-tk-FERint14 at 10 multiplicity of infection.
BP=pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9.
CMV=pCMVscript.
To examine whether cancer cells expressing EGFP-tk are susceptible to anti-Herpes drug such as ganciclovir, PC3 or DU145 cells expressing TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint were infected with Ad-TC. These cells were exposed to various concentrations of ganciclovir. As shown in figure 3A, at 0.075 μg/ml of ganciclovir, the killing of PC3 or DU145 cells reached 50% of its maximal level, and at 5 μg/ml, the killing was at the peak. At 5 μg/ml of ganciclovir, apoptosis of PC3 or DU145 cells containing the TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint and infected with Ad-TC was clearly visualized (figure 3B and Supplementary table 1). No significant cell death was found for cells containing no TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint, even though they were equally infected with these viruses and exposed to high concentrations of ganciclovir (up to 100 μg/ml, figure 3A and B). These findings indicate that the killing of cancer cells by ganciclovir is breakpoint dependent and is highly specific.
Figure 3. Treatment with nucleotide analogue ganciclovir kills cancer cells expressing EGFP-tk.
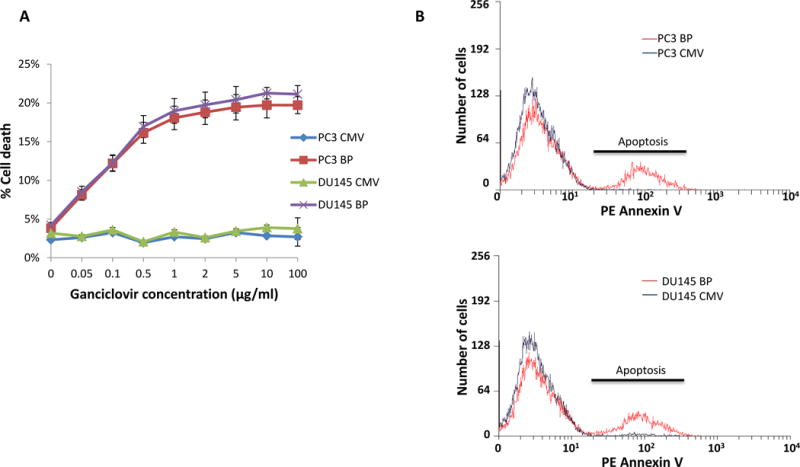
(A) PC3 or DU145 cells containing TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint were infected with pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNATMEM135int13-gRNACCDC67int9/pAD-TMEM135int13-EGFP-tk-CCDC67int9 (Ad-TC). These cells were then incubated with various concentrations of ganciclovir for 24 hours. Cell deaths were then quantified with phycoerythrin labeled Annexin V through flow cytometer. PC3 or DU145 cells harboring no TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint were used as controls. PC3 BP denotes PC3 cells transfected with pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9; DU145 BP denotes DU145 cells transfected with pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9; PC3 CMV denotes PC3 transfected with pCMVscript; DU145 CMV denotes DU145 cells transfected with pCMVscript. (B) Representative sample of cell death induced by ganciclovir on cells infected with Ad-TC, and treated with 5 μg/ml ganciclovir. PC3 or DU145 cells harboring no TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint were used as controls. Apoptosis was indicated by Annexin V staining. PC3 BP denotes PC3 cells transfected with pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9; DU145 BP denotes DU145 cells transfected with pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9; PC3 CMV denotes PC3 transfected with pCMVscript; DU145 CMV denotes DU145 cells transfected with pCMVscript.
Partial remission of xenografted tumors by genome targeting
To examine whether such breakpoint dependent killing of cancer cells can be used as a treatment for cancer, PC3 or DU145 cells containing TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint were xenografted into the subcutaneous regions of SCID mice. The xenografted tumors were allowed to grow for 3 weeks to reach ~700 mm3 in size. These mice were then infected with Ad-TC (5×1010 pfu), and treated with ganciclovir (80 mg/kg) 3 times a week through intraperitoneal injection. As shown in figure 4A, mice xenografted with PC3 or DU145 cancer cells containing TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint experienced exponential growth of tumor if they were not treated with ganciclovir. By contrast, if the tumors were treated with both Ad-TC and ganciclovir, the mice experienced up to 30% shrinking of the tumor volumes. Integration of TMEM135int13-EGFP-tk-CCDC67int9, expression of EGFP-tk and apoptosis were detected in PC3 or DU145 cells that contained TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint and treated with the recombinant viruses (Supplementary figure 2). There was no incidence of metastasis detected in mice treated with Ad-TC and ganciclovir. However, PC3 or DU145 cells containing no TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint had 33–50% metastasis rate even treated with the recombinant viruses and ganciclovir (figure 4B). Mice xenografted with PC3 or DU145 cells that contain TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint and treated with the recombinant viruses and ganciclovir had no associated mortality, whereas all control treated mice died by the 8th week of tumor cells xenografting (figure 4C).
Figure 4. Treatment of ganciclovir induced partial remission of xenografted prostate cancers in SCID mice.
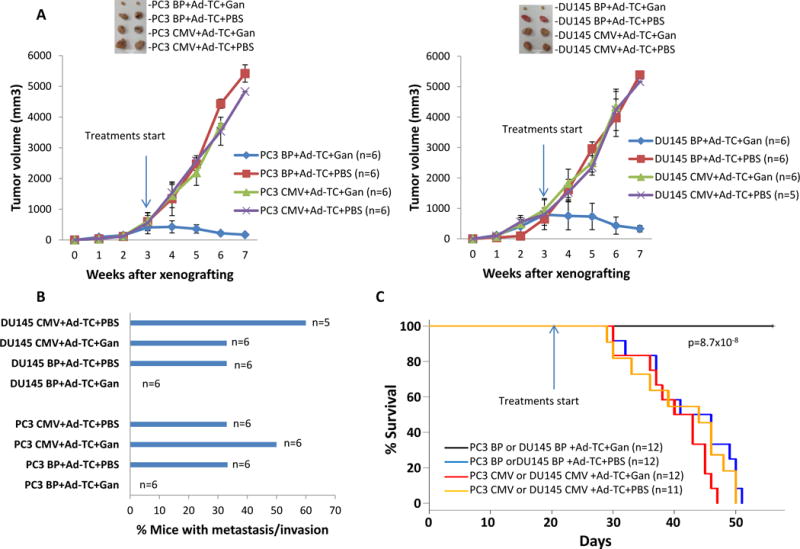
(A) PC3 cells harboring TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint were xenografted into the subcutaneous regions of SCID mice. These tumors were allowed to grow for 3 week before the treatment. The indicated drugs were applied through intraperitoneal injections 3 times a week until all the mice from control treatments died off. The tumor volumes were measured weekly. PC3 BP denotes PC3 cells transformed with pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9; PC3 CMV denotes PC3 cells transformed with pCMVscript; Ad-TC denotes treatment of pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNATMEM135int13-gRNACCDC67int9 and pAD-TMEM135int13-EGFP-tk-CCDC67int9; Gan denotes Ganciclovir; PBS denotes phosphate buffer saline. (B) DU145 cells harboring TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint were xenografted into the subcutaneous regions of SCID mice. These tumors were allowed to grow for 3 week before the treatment. The indicated drugs were applied through intraperitoneal injections 3 times a week until all the mice from control treatments died off. The tumor volumes were measured weekly. DU145 BP denotes DU145 cells transformed with pCMV-TMEM135int13-CCDC67int9; DU145 CMV denotes DU145 cells transformed with pCMVscript; Ad-TC denotes treatment of pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNATMEM135int13-gRNACCDC67int9 and pAD-TMEM135int13-EGFP-tk-CCDC67int9; Gan denotes Ganciclovir; PBS denotes phosphate buffer saline. (C) Mice treated with TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint therapy are free of cancer metastasis. (D) Mice treated TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint therapy had no mortality.
Targeting MAN2A1-FER breakpoint in HUH7 cells
Screening of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HUH7 showed that it expresses MAN2A1-FER, one of the fusion genes we discovered previously in prostate cancers2, and both MAN2A1-FER mRNA and protein were detected in this cell line (figure 5A and B). A genome breakpoint was identified between intron 13 of MAN2A1 and intron 14 of FER in HUH7 cells12. The chimera protein retains intact tyrosine kinase domain from FER but loses the SH2 domain that regulates the kinase activity.
Figure 5. Genome therapy targeting at MAN2A1-FER breakpoint.
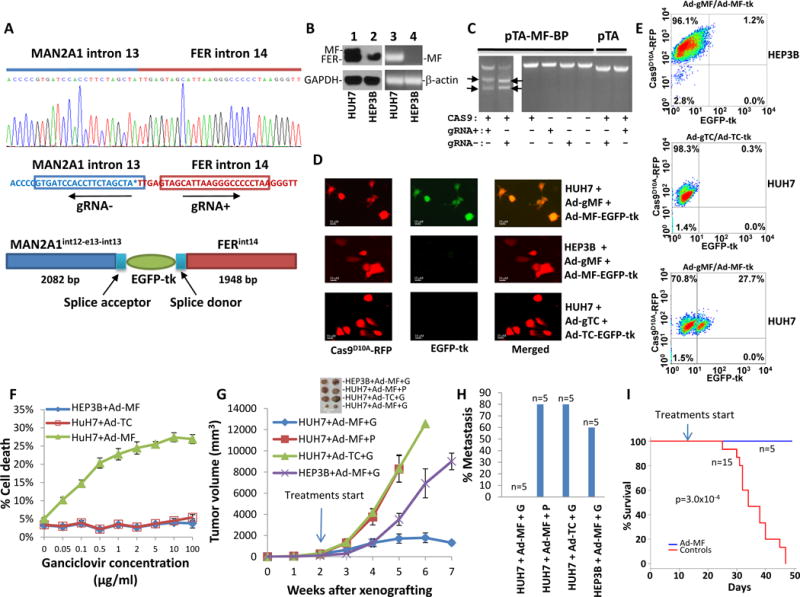
(A) Design of gRNA and recombination donor adenoviruses for MAN2A1-FER fusion gene. Upper panel: Sanger sequencing diagram of MAN2A1-FER chromosome breakpoint of HUH7 cells; Middle panel: Design of gRNA for pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNAMAN2A1int13-gRNAFERint14; Lower panel: Design of homologous DNA sequences and EGFP-tk for pAD-MAN2A1int13-EGFP-tk-FERint14. The splicing acceptor and donor sequences correspond to the juncture sequences of intron13-exon 14 of MAN2A1and exon15-intron 15 of FER. (B) Expression of MAN2A1-FER in HUH7 cells. Lanes 1 and 2: immunoblots of protein extracts from HUH7 and HEP3B cells with antibodies specific for FER or GAPDH. MAN2A1-FER (MF) and FER protein are indicated. Lanes 3 and 4: RT-PCR of RNA from HUH7 and HEP3B cells with primers specific for MAN2A1-FER (MF) or β-actin. (C) In vitro cleavage assays were performed on BamH1 linearized pTA-MAN2A1int13-FERint14 vector using recombinant Cas9, S. pyogenes and in vitro transcribed gRNA− or gRNA+ as indicated. The cleavage generated 2446 and 1944 bp fragments of pTA-MAN2A1int13-FERint14 vector for gRNA−, and 2484 and 1906 bp for gRNA+. (D) Infection of HUH7 or HEP3B cells led to expression of EGFP-tk in HUH7 but not HEP3B cells. HUH7 and HEP3B cells were infected with pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNAMAN2A1int13-gRNAFERint14 (ad-gMF) and pAD-MAN2A1int13-EGFP-tk-FERint14 (Ad-MF-EGFP-tk). Expression of Cas9D10A-RFP is indicated by red fluorescence, while expression EGFP-tk is indicated by green. HUH7 cells infected with pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNATMEM135int13-gRNACCDC67int9 (Ad-gTC) and pAD-TMEM135int13-EGFP-tk-CCDC67int9 (Ad-TC-EGFP-tk) were used as specificity control. Selected images were shown. (E) Quantification of EGFP-tk integration/expression by flow cytometry as of (D). (F) Killing of HUH7 cells with ganciclovir. HUH7 or HEP3B cells were infected with pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNAMAN2A1int13-gRNAFERint14/pAD-MAN2A1int13-EGFP-tk-FERint14 (Ad-MF). These cells were then incubated with various concentrations of ganciclovir for 24 hours. Cell deaths were then quantified with phycoerythrin labeled Annexin V through flow cytometer. HUH7 cells infected with pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNATMEM135int13-gRNACCDC67int9/pAD-TMEM135int13-EGFP-tk-CCDC67int9 (Ad-TC) were used as specificity controls. (G) HUH7 and HEP3B cells were xenografted into the subcutaneous regions of SCID mice. These tumors were allowed to grow for 2 weeks before the treatment. These mice were treated with the indicated viruses plus ganciclovir (G, 80mg/kg) or PBS (P). The indicated drugs were applied through intraperitoneal injections 3 times a week until all the mice from control treatments died off. The tumor volumes were measured weekly. (H) Mice treated with MAN2A1-FER breakpoint therapy are free of cancer metastasis. (I) Mice treated MAN2A1-FER breakpoint therapy had no mortality.
To evaluate the applicability of genome therapy targeting at cancer cells with native fusion gene breakpoint, we designed a pair of gRNAs specific for intron 13 of MAN2A1 and intron 14 of FER (figure 5A). The gRNAs and Cas9D10A was packaged into adenovirus to create pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNAMAN2A1int13-gRNAFERint14. This recombinant virus was co-infected with a “donor” recombinant adenovirus containing the sequences flanking the nick-sites (pAD-MAN2A1int13-EGFP-tk-FERint14). This “donor” virus also contains splicing sequences corresponding to acceptor of intron 14 of MAN2A1 and donor of intron 15 of FER, respectively, so that EGPF-tk is interrupted into the mRNA of MAN2A1-FER. The results showed that up to 27% of HUH7 cells infected with these viruses expressed EGFP-tk (figure 5D and E) in vitro, whereas similar infection of HEP3B cells, which are negative for MAN2A1-FER fusion, with these viruses induced minimal fluorescent protein expression. When HUH7 cells, which are negative for TMEM135-CCDC67 fusion, were infected with adenoviruses specific for TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint, there is little expression of EGFP-tk (figure 5D and E). These results confirm the specificity of our genome targeting.
When HUH7 cells were infected with pAD5-Cas9D10A-gRNAMAN2A1int13-gRNAFERint14/pAD-MAN2A1int13-EGFP-tk-FERint14 (Ad-MF) and treated with various concentrations of ganciclovir, up to 27% cells died at 10 μg/ml of ganciclovir, whereas HEP3B cells infected with the same viruses had minimal cell death even at high concentrations of ganciclovir. When HUH7 cells were infected with Ad-TC and treated with ganciclovir, there is no appreciable increase of cell death, clearly indicating that cell death induced by ganciclovir is MAN2A1-FER breakpoint dependent.
To examine the effectiveness of targeting MAN2A1-FER in vivo, SCID mice were xenografted with HUH7 and HEP3B cells, and treated with recombinant viruses and ganciclovir 2 weeks after the xenografting (tumor size 244 mm3 on average). The mice xenografted with HUH7 cells and treated with Ad-MF and ganciclovir experienced up to 29% reduction of tumor size from the peak, and had no notable metastasis or mortality in the observation period 8 weeks. By contrast, the mice xenografted with HUH7 cells treated with ganciclovir and Ad-TC, the adenoviruses specific for TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint not carried by the HUH7 cells, experienced an average 39 fold increase of tumor size. Four of 5 of these mice had metastasis in lung and liver and all 5 mice had died at 40 days after xenografting. Similar rates of death, metastases and increase of tumor volume also occurred in mice treated with AD-MF and PBS. Treatment of mice xenografted with HEP3B, a hepatocellular cancer cell line negative for MAN2A1-FER fusion, with Ad-MF and ganciclovir was similarly ineffective. These results indicate that therapy targeting at cancer genome is highly specific and effective.
Fusion gene breakpoint targeting is highly specific
The fusion gene breakpoint targeting approach employed here appears highly specific, with average functional off-target rates being 1.3% in both PC3 and DU145 cells (EGFP-tk+ cells/Cas9D10A-RFP+ cells in PC3 CMV or DU145 CMV cells, table 1) and less than 1% for HUH7 (EGFP-tk+ cells/Cas9D10A-RFP+ cells in HUH7 treated with adeno-TC, table 1) and HEP3B cells (EGFP-tk+ cells/Cas9D10A-RFP+ cells in HUH7 treated with adeno-MF, table 1). These off-target rates were largely confirmed by sequencing quantification methods: Off-target rates ranged from <0.1% to 2.5% in 100 million reads, including samples from in vitro tissue culture experiments, xenografted cancers and liver samples from mice that were treated with the recombinant viruses (Supplementary tables 3–6). On-target integration rates in vitro based on sequencing range from 15.9% to 25.5%, whereas rates for xenografted tumors range from 21.1% to 33.5%. The higher integration rates in xenografted tumors probably reflect repeat application of the recombinant adenoviruses.
Discussion
Chromosome rearrangement and deletion creates many cancer specific fusion genes9. These fusions either generate genes that acquire additional functions to drive cancer progression or destroy genes that block the oncogenic progression. TMEM135-CCDC7 is an example of latter such that the fusion eliminates the open-reading frame of CCDC67, a putative cancer suppressor and truncates 65 amino acids off the C-terminus of TMEM135, a protein widely expressed in most tissues but with unknown function. On the other hand, MAN2A1-FER fusion probably belongs to the first category due to elimination of SH2 domain of FER that may lead to constitutive activation of FER tyrosine kinase12. The impact of fusion genes on the function of gene products that are involved could be dramatic due to creation of a new protein or generation of truncations of protein domains9,13,14. The presence of chromosome rearrangement-based fusion genes is one of the hallmarks of human malignancies13,14 and targeting fusion -breakpoints may be highly cancer cell specific.
The recent advance in precision cleavage of DNA by bacterial CRISPR/Cas system makes it possible to target specific genome sequence with relatively high efficiency. Our gRNA target designs produces two nicks at different strands 69 bp apart for TMEM135-CCDC67 breakpoint and 37 bp apart for MAN2A1-FER breakpoint. It is unlikely that these nicks would generate a double stranded DNA break. As a result, these DNA damages are likely repaired by homologous recombination process rather than by non-homologous end-joining. Our results are consistent with several other studies that CRISPR/Cas-mediated homologous recombination rates can reach levels of up to 20–30%15–17.
To our knowledge, it has not been shown previously that CRISPR/Cas Cas-mediated genome editing can be applied to specifically target genomic alterations in cancer genomes with a recombination rate sufficient to achieve partial remission of xenograft tumors. The The precision specificity and EGFP-tk integration rate of the genome therapy might make it possible to apply this approach to clinical setting. Future developments that enhance the integration rate of the targeting cassette into the genome target site may be helpful in enhancing the efficiency of the genome therapy. It should be noted that the donor sequences of adenoviral GFP-tk genome are outside the gRNA target sites, and thus, the viruses do not contain target sequences recognizable by gRNA/Cas9 activity. The recombination rate between the 2 viruses is probably low. In over 300,000 reads of integrated EGFP-tk sequencing (Supplementary Tables 5–7), we did not find any recombination read between EGPFP-tk and Cas9.
The current therapeutic approach to human cancer heavily relies on interception of signaling pathways that drive cancer growth. However, such approach invariably leads to drug tolerance and refractory to drug treatment as cancer genome adjusts its gene expression pattern and develops new pathways to growth due to new mutations to bypass the signaling blockade. The subsequent application of second tier chemotherapy may impact both cancer and normal tissues, and thus generally produces poor therapeutic outcomes. The genome approach may have substential advantage over chemotherapy because it is specific for the cancer genome sequence, and it kills cancer cells regardless whether the mutations are cancer drivers or not. It is possible that additional new mutations and fusion genes will be generated under the pressure of cancer therapy. In principle, additional vectors can be designed to target these genomic lesions and maybe even lead to an increase in the integration rate due to multiple integrations in one cell (Supplementary table 7). It remains to be seen if such an adaptive strategy will be feasible in the clinic. When cancer is presented with multiple populations of cancer cells with several different fusion gene targets, these targets can be targeted simultaneously using genome targeting scheme. Furthermore, our approach is not limited using HSV-tk in the therapeutic cassette but can use wide spectrum of gene device, such as immunogens from viruses or toxins from plants or bacteria. When necessary, genome targeting can be combined with other cancer therapeutic treatment, such as tumor immunotherapy, signaling molecule targeting, etc, to achieve better therapeutic results.
In our initial studies, we did not observe appreciable cytotoxic side-effect of these recombinant viruses in either cell culture or animal model. The integration of EGFP-tk can be monitored by fluorescence imaging. In addition, in the event of unwanted integration into the genome of healthy cells of critical location, the integrated EGFP-tk can be retrieved by cre expression. The recombinant adenoviruses used in the study are defective for replication and self-propagation, and stay episomal in healthy cells18. In addition, other carriers, such as non-viral vectors that efficiently transduce the targeting DNA into the cancer cells could be used as alternative to the recombinant adenoviruses, if they are proven better carriers in terms of efficiency and safety. As chromosome breakpoint for fusion gene may vary among individuals, genome targeting strategy needs individualization. The genome approach shown in this report should in principle be applicable for most human cancers carrying fusion genes and with improved targeting specificity of the genome editing tools even smaller mutations might become targetable.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Songyang Zheng for technical support. This work was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute (RO1 CA098249 to JHL), Department of Defense (W81XWH-16-1-0364) and a grant from University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute.
Footnotes
Ed Sum: Insertion of the sequence encoding herpes simplex virus 1 thymidine kinase at the breakpoint of fusion genes in cancer cells causes cell death and regression of mouse xenograft tumors
All authors declare no conflict of financial interest for this study.
References
- 1.Yu YP, et al. Novel fusion transcripts associate with progressive prostate cancer. The American journal of pathology. 2014;184:2840–2849. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.06.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mojica FJ, Diez-Villasenor C, Garcia-Martinez J, Soria E. Intervening sequences of regularly spaced prokaryotic repeats derive from foreign genetic elements. Journal of molecular evolution. 2005;60:174–182. doi: 10.1007/s00239-004-0046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Esvelt KM, Smidler AL, Catteruccia F, Church GM. Concerning RNA-guided gene drives for the alteration of wild populations. eLife. 2014:e03401. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jinek M, et al. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science (New York, NY) 2012;337:816–821. doi: 10.1126/science.1225829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ran FA, et al. Double nicking by RNA-guided CRISPR Cas9 for enhanced genome editing specificity. Cell. 2013;154:1380–1389. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Smith KO, Galloway KS, Kennell WL, Ogilvie KK, Radatus BK. A new nucleoside analog, 9-[[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxyl]methyl]guanine, highly active in vitro against herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy. 1982;22:55–61. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Van Rompay AR, Johansson M, Karlsson A. Phosphorylation of nucleosides and nucleoside analogs by mammalian nucleoside monophosphate kinases. Pharmacol Ther. 2000;87:189–198. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(00)00048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yu YP, et al. Genomic Copy Number Variations in the Genomes of Leukocytes Predict Prostate Cancer Clinical Outcomes. PloS one. 2015;10:e0135982. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Luo JH, et al. Discovery and Classification of Fusion Transcripts in Prostate Cancer and Normal Prostate Tissue. The American journal of pathology. 2015 doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ohnuki Y, Marnell MM, Babcock MS, Lechner JF, Kaighn ME. Chromosomal analysis of human prostatic adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer research. 1980;40:524–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bernardino J, et al. Characterization of chromosome changes in two human prostatic carcinoma cell lines (PC-3 and DU145) using chromosome painting and comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer genetics and cytogenetics. 1997;96:123–128. doi: 10.1016/s0165-4608(96)00258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen ZH, et al. MAN2A1-FER Fusion Gene Is Expressed by Human Liver and Other Tumor Types and Has Oncogenic Activity in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2017 doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.12.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81683-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yu C, et al. Small molecules enhance CRISPR genome editing in pluripotent stem cells. Cell stem cell. 2015;16:142–147. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hsu PD, et al. DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nature biotechnology. 31:827–832. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cong L, et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science (New York, NY) 339:819–823. doi: 10.1126/science.1231143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kozarsky KF, Wilson JM. Gene therapy: adenovirus vectors. Current opinion in genetics & development. 1993;3:499–503. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90126-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


