Abstract
Background
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether polymyxin B hemoperfusion (PMX-HP) improves the survival of patients with septic shock.
Methods
This was a retrospective, multicenter study conducted on patients treated during a 3-year period. We performed propensity-score analyses of the Japan Septic Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (JSEPTIC DIC) study database. The study included data on 1723 patients with septic shock aged 16 years or older. Furthermore, we divided patients into to PMX-HP- and non-PMX-HP-treated groups. The primary endpoint was all-cause hospital mortality; secondary endpoints included intensive care unit (ICU) mortality and number of ICU-free days (ICUFDs) in the first 28 days.
Results
Of 1,723 eligible patients, 522 had received PMX-HP. Propensity score matching created 262 matched pairs (i.e., 262 patients in each of the non-PMX-HP and PMX-HP groups). The proportion of all-cause hospital mortality was significantly lower in the PMX-HP group than in the non-PMX-HP group (32.8% vs. 41.2%; odds ratio (OR): 0.681; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.470–0.987; P = 0.042). The number of ICUFD in the first 28 days was significantly higher in the PMX-HP group than in the non-PMX-HP group (18 (0-22) vs. 14 (0-22) days, respectively; P = 0.045). On the other hand, there was no significant difference in ICU mortality between the two groups (21.8% vs. 24.4%; OR: 0.844; CI: 0.548–1.300; P = 0.443).
Conclusions
Our results strongly suggest that PMX-HP reduces all-cause hospital mortality and length of ICU stay in patients with septic shock.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13054-017-1712-3) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Polymyxin B hemoperfusion, Septic shock, Propensity score matching, Intensive care unit-free days, Mortality
Background
Despite the availability of modern antibiotics and resuscitation therapies, sepsis is a leading cause of death in critically ill patients [1]. Treatment of patients with septic shock is a major challenge for physicians. To improve clinical management and outcome of critically ill patients, the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines were published approximately a decade ago and were most recently revised in 2012 [2].
Endotoxin, a lipopolysaccharide derived from the outer membranes of gram-negative rods (GNRs), is a key factor in the sepsis cascade because it triggers a series of inflammatory reactions that lead to organ dysfunction [3, 4]. Because high serum concentrations of endotoxin are closely linked to increased risk of multiple organ failure and death [5, 6], endotoxin is considered a therapeutic target in treating sepsis [7]. Polymyxin B direct hemoperfusion (PMX-HP) removes plasma endotoxins and is considered an effective treatment for sepsis [8]. Moreover, Totsugawa et al. [9] reported that PMX-HP not only removes plasma endotoxins, but also causes a drastic decrease in the doses of inotropic agents and a shortening of the duration of mechanical ventilation in patients with severe sepsis and/or septic shock from gram-positive cocci (GPC). Moreover, Yamato et al. [10] reported that treatment with a combination of PMX-HP and recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin (rhsTM) significantly improves survival rates after septic shock with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) due to GPC or GNR infections. These results suggest that PMX-HP has a survival benefit not only in patients with GNR infections, but also in those with GPC-induced events. Two randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of abdominal septic shock have been reported to date. One is the EUPHAS trial [11], which reported a significant reduction in the 28-day mortality rate with PMX-HP in comparison with conventional treatment (32% vs. 53%; hazard ratio (HR): 0.36; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.16–0.80; P = 0.01). In contrast, in the ABDOMIX RCT [12] there was no significant difference in the 28-day mortality rate between PMX-HP and conventional treatment (27.7% vs. 19.5%, respectively; P = 0.14). Therefore, it remains unclear whether PMX-HP produces a survival benefit in patients with abdominal septic shock. Furthermore, no studies have compared the usefulness of PMX-HP for various infection sites and different types of septic shock-causing pathogens as well as GNRs.
Therefore, we conducted this retrospective study in a large number of Japanese multi-intensive care unit (ICU) patients with septic shock arising from various sites of infection and types of pathogens to determine the efficacy of PMX-HP in reducing mortality using propensity score analysis.
Methods
Study design, setting, and selection of participants
This retrospective, observational study used the dataset of the Japan Septic Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (JSEPTIC DIC) study, which was conducted in 42 ICUs in 40 institutions in Japan (Additional files 1 and 2) and was approved by the Institutional Review Boards of all participating hospitals. The JSEPTIC DIC study aimed to evaluate anti-DIC drugs in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock who were admitted to ICUs between January 2011 and December 2013 [13, 14]. Because this database had already been anonymized for individual patient data and institutions, the Institutional Review Board waived the need for review of this post-hoc study. However, we did not input patient personal data such as name or medical ID number at each facility in order to adhere strictly to the anonymity of patients. Included patients were those aged ≥16 years who had been admitted to the study ICUs between January 2011 and December 2013 for treatment of severe sepsis or septic shock, as defined by the International Sepsis Definitions Conference [15].
Data collection
In this study, the following information was collected from the JSEPTIC DIC study dataset: age, sex, body weight (BW), type of ICU, route of admission to the ICU, ICU policy, number of ICU beds, pre-existing organ dysfunction, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score [16], total Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score [17], systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) score [18], Japanese Association for Acute Medicine (JAAM) DIC score [19], primary infection site, microorganisms responsible for sepsis, laboratory tests (white blood cell count (WBC), platelet count, hemoglobin (Hb) and prothrombin time-international normalized ratio (PT-INR)) at the time of admission, packed red blood cells (PRBC) administered, surgical interventions at the infection site, anti-DIC drugs (rhsTM, antithrombin (AT) III products, protease inhibitors, or heparinoids), intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), low-dose steroids, and renal replacement therapy (RRT) for renal or non-renal indications, and PMX-HP during the first week after ICU admission. Furthermore, all-cause hospital mortality, ICU mortality, and length of ICU stay were collected for evaluation of the endpoints. We defined the ICU policy as follows: open ICU was defined as all patients admitted to the ICU were managed by each department of doctors; closed ICU was defined as all patients admitted to the ICU were managed by intensivists or anesthesiologists or emergency doctors.
Patient selection
Patients with SOFA cardiovascular scores <3 and those who did not receive catecholamines upon ICU admission were excluded because they did not fit the criteria for septic shock. Furthermore, patients for whom the following data were missing were excluded: BW, SOFA score, WBC, Hb, platelet count, and PT-INR. Eligible patients were then allocated to PMX-HP and non-PMX-HP groups.
PMX-HP
PMX-HP was performed with an adsorbent column designed for clinical use that contained 5 mg of PMX per gram of polystyrene fiber (Toray Industries, Tokyo, Japan) [20, 21]. This device was approved in 1994 and is widely used for treating severe sepsis in clinical settings in Japan [22].
Endpoints
The primary endpoint of this study was all-cause hospital mortality, and the secondary endpoints ICU mortality and ICU-free days (ICUFDs). ICUFDs were calculated as follows: ICUFDs = 0 if the patient died during the first 28 days; ICUFDs = (28 − x) if the patient survived more than 28 days, where x is the number of days spent in the ICU; and ICUFDs = (28 − y) if the patient had been transferred to another hospital before 28 days had elapsed, where y is the number of days spent in the ICU.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as number (%) for categorical variables, mean ± standard deviation (SD) for normally distributed variables, and median (first quartile to third quartile) for non-normally distributed variables. One-to-one nearest neighbor matching without replacement was performed between the PMX-HP and non-PMX-HP groups based on the estimated propensity scores for each patient. To estimate the propensity score, a logistic regression model was fitted for patients who had undergone PMX-HP treatment as a function of patient and ICU characteristics, including age, sex, BW, type of ICU, route of admission to the ICU, ICU policy, number of ICU beds, pre-existing organ dysfunction, APACHE II score, total SOFA, a SIRS score <2 vs. ≥2 [18], JAAM DIC score ≥4 vs. <4 [19], primary infection site, microorganisms responsible for sepsis, laboratory tests (WBC, platelet count, Hb concentration, and PT-INR), PRBC administration, surgical interventions at the infection site, anti-DIC drugs (rhsTM, AT III products, protease inhibitors, or heparinoids), IVIG, low-dose steroids, and RRT for renal or non-renal indications. A caliper width equal to 0.01 of the standard deviation of the logit of the propensity score was used. The standardized difference was used to evaluate covariate balance. An absolute standardized difference of >10% signifies a meaningful imbalance [23].
To evaluate differences between the PMX-HP and non-PMX-HP groups, categorical variables were compared by logistic regression, whereas continuous variables were compared by Student’s t tests or Wilcoxon test. ICU and hospital mortality rates were analyzed using conditional logistic regression, including the group (PMX-HP vs. non-PMX-HP) as a covariate and the matched set as a stratum. A signed rank test was used to compare the ICUFDs between groups. SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) was used for all analyses.
Results
Patients
This study enrolled 3,195 patients over the observational period, 1,363 of whom did not have septic shock and were excluded, as were 109 patients for whom the required data were unavailable. Finally, the 1,723 eligible patients were categorized into the PMX-HP (n = 522) or non-PMX-HP (control group; n = 1,201) groups, from which 262 propensity score-matched pairs were generated (Fig. 1). The C statistic indicated that the goodness of fit was 0.849 in the propensity score model.
Fig. 1.
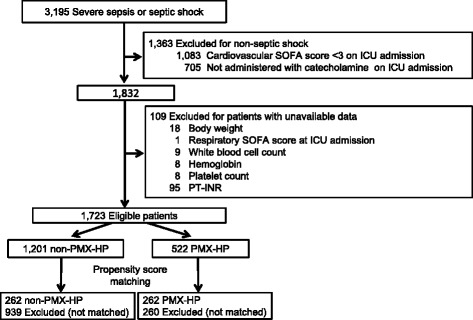
Patient selection schema. ICU intensive care unit, PMX-HP polymyxin B hemoperfusion, PT-INR prothrombin time-international normalized ratio, SOFA Sequential Organ Failure Assessment
The baseline characteristics of the unmatched PMX-HP and non-PMX-HP groups and those of the propensity score-matched groups are shown in Tables 1 and 2. When the unmatched groups were compared, ICU type (emergency center or surgical ICU), route of admission to the ICU, ICU policy, number of ICU beds, pre-existing organ dysfunction, SOFA score, JAAM DIC, primary infection site, microorganism, WBC, platelet counts, Hb, PT-INR, PRBC, surgical intervention, and other therapeutic interventions (rhsTM, AT III concentrate, protease inhibitors, IVIG, low-dose steroids, RRT, and non-renal RRT) differed significantly between the two groups. After propensity score matching, the baseline patient characteristics were well balanced between the groups, the standardized differences being ≤0.1.
Table 1.
Relevant patient characteristics according to study group
| Variables | Unmatched group | Matched group | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All patients (n = 1,723) |
non-PMX-HP (n = 1,201) |
PMX-HP (n = 522) |
SD | P value | All patients (n = 524) |
non-PMX-HP (n = 262) |
PMX-HP (n = 262) |
SD | P value | |
| Age, years | 69.7 (13.8) | 69.5 (14.0) | 70.0 (13.1) | 0.036 | 0.502 | 69.9 (13.1) | 70.3 (13.4) | 69.4 (12.8) | 0.070 | 0.422 |
| Male, n (%) | 1019 (59.1) | 705 (58.7) | 314 (60.2) | 0.030 | 0.574 | 304 (58.0) | 150 (57.3) | 154 (58.8) | 0.031 | 0.723 |
| Body weight, kg | 56.6 (14.1) | 56.6 (14.5) | 56.6 (13.4) | 0.007 | 0.903 | 56.5 (14.6) | 56.0 (14.4) | 57.0 (14.8) | 0.064 | 0.465 |
| Emergency center ICU, n (%) | 729 (42.3) | 486 (40.5) | 243 (46.6) | 0.123 | 0.019 | 239 (45.6) | 121 (46.2) | 118 (45.0) | 0.023 | 0.793 |
| Admission route to the ICU, n (%) | ||||||||||
| Emergency department | 735 (42.7) | 543 (45.2) | 192 (36.8) | 0.172 | 0.000 | 215 (41.0) | 109 (41.6) | 106 (40.5) | 0.023 | 0.790 |
| Other hospital | 423 (24.6) | 287 (23.9) | 136 (26.1) | 0.050 | 0.339 | 121 (23.1) | 62 (23.7) | 59 (22.5) | 0.027 | 0.756 |
| Hospital ward | 565 (32.8) | 371 (30.9) | 194 (37.2) | 0.133 | 0.011 | 188 (35.9) | 91 (34.7) | 97 (37.0) | 0.048 | 0.585 |
| ICU policy, n (%) | ||||||||||
| Open ICU | 549 (31.9) | 387 (32.2) | 162 (31.0) | 0.026 | 0.628 | 160 (30.5) | 74 (28.2) | 86 (32.8) | 0.100 | 0.255 |
| Closed ICU | 897 (52.1) | 637 (53.0) | 260 (49.8) | 0.065 | 0.217 | 281 (53.6) | 147 (56.1) | 134 (51.1) | 0.100 | 0.255 |
| Others | 277 (16.1) | 177 (14.7) | 100 (19.2) | 0.118 | 0.022 | 83 (15.8) | 41 (15.6) | 42 (16.0) | 0.011 | 0.905 |
| Number of ICU beds, number | 12 (8–18) | 12 (10–19) | 10 (7–12) | 0.429 | <0.001 | 10.5 (8–16) | 12 (8–15) | 10 (7–16) | 0.041 | 0.361 |
| Pre-existing organ dysfunction, n (%) | ||||||||||
| Liver insufficiency | 83 (4.8) | 49 (4.1) | 34 (6.5) | 0.109 | 0.032 | 30 (5.7) | 12 (4.6) | 18 (6.9) | 0.099 | 0.262 |
| Chronic respiratory disorder | 66 (3.8) | 46 (3.8) | 20 (3.8) | 0.000 | 1.000 | 18 (3.4) | 6 (2.3) | 12 (4.6) | 0.126 | 0.158 |
| Chronic heart failure | 99 (5.7) | 68 (5.7) | 31 (5.9) | 0.012 | 0.821 | 29 (5.5) | 13 (5.0) | 16 (6.1) | 0.050 | 0.567 |
| Chronic hemodialysis | 149 (8.6) | 99 (8.2) | 50 (9.6) | 0.047 | 0.365 | 53 (10.1) | 25 (9.5) | 28 (10.7) | 0.038 | 0.664 |
| Immunocompromised | 299 (17.4) | 218 (18.2) | 81 (15.5) | 0.070 | 0.185 | 83 (15.8) | 43 (16.4) | 40 (15.3) | 0.031 | 0.720 |
| None | 1,108 (64.3) | 773 (64.4) | 335 (64.2) | 0.004 | 0.941 | 338 (64.5) | 177 (67.6) | 161 (61.5) | 0.128 | 0.145 |
| Severity | ||||||||||
| APACHE II score | 25.4 (8.9) | 25.2 (8.9) | 25.9 (8.9) | 0.083 | 0.115 | 25.2 (9.2) | 25.5 (8.9) | 25.0 (9.5) | 0.060 | 0.493 |
| SOFA score | 11.5 (3.5) | 11.2 (3.5) | 12.0 (3.5) | 0.246 | <0.001 | 11.6 (3.4) | 11.7 (3.4) | 11.5 (3.4) | 0.067 | 0.442 |
| SIRS positivea, n (%) | 1,654 (96.0) | 1151 (95.8) | 503 (96.4) | 0.027 | 0.611 | 499 (95.2) | 253 (96.6) | 246 (93.9) | 0.126 | 0.157 |
| JAAM DIC positiveb, n (%) | 1,092 (63.4) | 723 (60.2) | 369 (70.7) | 0.222 | <0.001 | 345 (65.8) | 176 (67.2) | 169 (64.5) | 0.056 | 0.519 |
Data are presented as mean (standard deviation), median (first quartile to third quartile), or number (percentage)
aSIRS criteria ≥2
bJAAM DIC score ≥4
APACHE Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation, DIC disseminated intravascular coagulation, ICU intensive care unit, JAAM Japanese Association for Acute Medicine, PMX-HP polymyxin B hemoperfusion, SD standardized difference, SIRS systemic inflammatory response syndrome, SOFA Sequential Organ Failure Assessment
Table 2.
Characteristics of patients, laboratory findings, and treatment for sepsis according to study group
| Variables | Unmatched group | Matched group | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All patients (n = 1,723) |
non-PMX-HP (n = 1,201) |
PMX-HP (n = 522) |
SD | P value | All patients (n = 524) |
non-PMX-HP (n = 262) |
PMX-HP (n = 262) |
SD | P value | |
| Primary infection site, n (%) | ||||||||||
| Abdomen | 618 (35.9) | 321 (26.7) | 297 (56.9) | 0.642 | <0.001 | 226 (43.1) | 113 (43.1) | 113 (43.1) | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Lung/thorax | 385 (22.3) | 323 (26.9) | 62 (11.9) | 0.387 | <0.001 | 93 (17.7) | 47 (17.9) | 46 (17.6) | 0.010 | 0.909 |
| Urinary tract | 268 (15.6) | 189 (15.7) | 79 (15.1) | 0.017 | 0.751 | 97 (18.5) | 46 (17.6) | 51 (19.5) | 0.049 | 0.574 |
| Bone/soft tissue | 192 (11.1) | 147 (12.2) | 45 (8.6) | 0.119 | 0.029 | 52 (9.9) | 28 (10.7) | 24 (9.2) | 0.051 | 0.559 |
| Cardiovascular | 31 (1.8) | 27 (2.2) | 4 (0.8) | 0.122 | 0.043 | 7 (1.3) | 3 (1.1) | 4 (1.5) | 0.033 | 0.705 |
| Central nervous system | 26 (1.5) | 25 (2.1) | 1 (0.2) | 0.179 | 0.019 | 1 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.4) | 0.088 | – |
| Catheter-related | 30 (1.7) | 27 (2.2) | 3 (0.6) | 0.142 | 0.024 | 6 (1.1) | 4 (1.5) | 2 (0.8) | 0.072 | 0.421 |
| Others | 34 (2.0) | 27 (2.2) | 7 (1.3) | 0.068 | 0.219 | 8 (1.5) | 3 (1.1) | 5 (1.9) | 0.062 | 0.481 |
| Unknown | 139 (8.1) | 115 (9.6) | 24 (4.6) | 0.195 | 0.001 | 34 (6.5) | 18 (6.9) | 16 (6.1) | 0.031 | 0.723 |
| Microorganisms, n (%) | ||||||||||
| Gram-negative bacteria | 656 (38.1) | 429 (35.7) | 227 (43.5) | 0.159 | 0.002 | 230 (43.9) | 113 (43.1) | 117 (44.7) | 0.031 | 0.725 |
| Gram-positive coccus | 402 (23.3) | 311 (25.9) | 91 (17.4) | 0.207 | <0.001 | 105 (20.0) | 50 (19.1) | 55 (21.0) | 0.048 | 0.585 |
| Fungus | 23 (1.3) | 18 (1.5) | 5 (1.0) | 0.049 | 0.373 | 8 (1.5) | 5 (1.9) | 3 (1.1) | 0.062 | 0.481 |
| Mixed infection | 232 (13.5) | 142 (11.8) | 90 (17.2) | 0.154 | 0.003 | 72 (13.7) | 39 (14.9) | 33 (12.6) | 0.067 | 0.447 |
| Others | 29 (1.7) | 20 (1.7) | 9 (1.7) | 0.005 | 0.930 | 9 (1.7) | 3 (1.1) | 6 (2.3) | 0.088 | 0.323 |
| Unknown | 371 (21.5) | 272 (22.6) | 99 (19.0) | 0.091 | 0.088 | 100 (19.1) | 52 (19.8) | 48 (18.3) | 0.039 | 0.657 |
| Laboratory tests on admission to the ICU | ||||||||||
| WBC, 109/L | 10.8 (3.6–17.7) | 11.8 (5.0–18.1) | 7.4 (2.2–16.1) | 0.188 | <0.001 | 10.4 (3.4–18.5) | 11.6 (4.6–18.1) | 9.7 (2.7–18.8) | 0.012 | 0.195 |
| Platelet counts, 109/L | 108 (58–174) | 113 (60–186) | 99 (53–154) | 0.189 | <0.001 | 100 (54–164) | 92 (52–162) | 108 (57–167) | 0.100 | 0.126 |
| Hb, g/L | 10.5 (2.5) | 10.6 (2.5) | 10.4 (2.4) | 0.099 | 0.063 | 10.4 (2.5) | 10.3 (2.7) | 10.5 (2.4) | 0.081 | 0.355 |
| PT-INR | 1.4 (1.2–1.7) | 1.4 (1.2–1.6) | 1.5 (1.3–1.8) | 0.122 | <0.001 | 1.4 (1.3–1.8) | 1.4 (1.2–1.8) | 1.4 (1.3–1.8) | 0.091 | 0.477 |
| PRBC administration, n (%) | 889 (51.6) | 546 (45.5) | 343 (65.7) | 0.416 | <0.001 | 313 (59.7) | 159 (60.7) | 154 (58.8) | 0.039 | 0.656 |
| Surgical intervention, n (%) | 795 (46.1) | 450 (37.5) | 345 (66.1) | 0.598 | <0.001 | 289 (55.2) | 146 (55.7) | 143 (54.6) | 0.023 | 0.792 |
| Other therapeutic intervention, n (%) | ||||||||||
| rhsTM | 571 (33.1) | 329 (27.4) | 242 (46.4) | 0.401 | <0.001 | 203 (38.7) | 101 (38.5) | 102 (38.9) | 0.008 | 0.929 |
| AT III concentrate | 653 (37.9) | 353 (29.4) | 300 (57.5) | 0.591 | <0.001 | 241 (46.0) | 121 (46.2) | 120 (45.8) | 0.008 | 0.930 |
| Protease inhibitors | 209 (12.1) | 117 (9.7) | 92 (17.6) | 0.231 | <0.001 | 64 (12.2) | 33 (12.6) | 31 (11.8) | 0.023 | 0.790 |
| Heparinoids | 69 (4.0) | 44 (3.7) | 25 (4.8) | 0.056 | 0.275 | 23 (4.4) | 11 (4.2) | 12 (4.6) | 0.019 | 0.831 |
| IVIG | 619 (35.9) | 360 (30.0) | 259 (49.6) | 0.410 | <0.001 | 224 (42.7) | 117 (44.7) | 107 (40.8) | 0.077 | 0.377 |
| Low-dose steroid | 568 (33.0) | 333 (27.7) | 235 (45.0) | 0.365 | <0.001 | 196 (37.4) | 101 (38.5) | 95 (36.3) | 0.047 | 0.588 |
| RRT | 627 (36.4) | 352 (29.3) | 275 (52.7) | 0.489 | <0.001 | 245 (46.8) | 121 (46.2) | 124 (47.3) | 0.023 | 0.793 |
| Non-renal indication RRT | 189 (11.0) | 45 (3.7) | 144 (27.6) | 0.694 | <0.001 | 53 (10.1) | 26 (9.9) | 27 (10.3) | 0.013 | 0.885 |
Data are presented as mean (standard deviation), median (first quartile to third quartile), or number (percentage)
AT antithrombin, Hb hemoglobin, IVIG intravenous immunoglobulins, PMX-HP polymyxin B hemoperfusion, PRBC packed red blood cells, PT-INR prothrombin time-international normalized ratio, rhsTM recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin, RRT renal replacement therapy, SD standardized difference, WBC white blood cell count
Endpoints
The overall all-cause hospital mortality was 37.0% (637/1,723). There was no significant difference in all-cause hospital mortality between the two unmatched groups (PMX-HP vs. non-PMX-HP: 37.9% vs. 36.6%, respectively; odds ratio (OR): 1.061; 95% CI: 0.858–1.312; P = 0.585). However, a significant difference was observed between the two groups after propensity-score matching (PMX-HP vs. non-PMX-HP: 32.8% vs. 41.2%, respectively; OR: 0.681; 95% CI: 0.470–0.987; P = 0.042). Additionally, in the propensity-score matched groups, number of ICUFDs in the first 28 days was significantly greater in the PMX-HP group than in the non-PMX-HP group (18 (0–22) vs. 14 (0–22) days, respectively; P = 0.045). On the other hand, there was no significant difference in ICU mortality between the two groups (21.8% vs. 24.4%, respectively; OR: 0.844; 95% CI: 0.548–1.300; P = 0.443) (Table 3).
Table 3.
Mortality and number of IUCFDs in the propensity-matched groups analyses
| Variables | Unmatched group | Matched group | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| non-PMX-HP (n = 1201) | PMX-HP (n = 522) | OR | Difference | 95% CI | P value | non-PMX-HP (n = 262) | PMX-HP (n = 262) | OR | Difference | 95% CI | P value | |
| All-cause hospital mortality, n (%) | 439 (36.6) | 198 (37.9) | 1.061 | (0.858–1.312) | 0.585 | 108 (41.2) | 86 (32.8) | 0.681 | (0.470–0.987) | 0.042 | ||
| ICU mortality, n (%) | 268 (22.3) | 128 (24.5) | 1.131 | (0.889–1.440) | 0.317 | 64 (24.4) | 57 (21.8) | 0.844 | (0.548–1.300) | 0.443 | ||
| 28 ICUFDs (days) | 16 (0–23) | 15 (0–21) | 0.0 | (0.0–0.0) | 0.255 | 14 (0–22) | 18 (0–22) | 1.5 | (0.0–3.5) | 0.045 | ||
Data are presented as median (first quartile to third quartile) or number (percentage)
In the unmatched group, categorical variables were compared by logistic regressions, and continuous variables were compared by Wilcoxon tests and Hodges-Lehmann estimates were presented for difference and 95% CI. In the matched group, all-cause hospital mortality and ICU mortality were analyzed by conditional logistic regression including PMX-DHP as a covariate and matched-set as a stratum, and ICUFDs were analyzed by signed rank test and Hodges-Lehmann estimate was presented for difference and 95% CI
CI confidence interval, ICU intensive care unit, ICUFDs ICU-free days, OR odds ratio, PMX-HP polymyxin B hemoperfusion
Discussion
Our study included the largest number of patients with septic shock until now across 42 Japanese ICUs. PMX-HP has been accepted by the Japanese national health insurance program since 1994 [20]; more than 100,000 patients have received this treatment since then [24]. In Japan, PMX-HP is generally administered for severe sepsis or septic shock due to GNR infection (or suspected infection). In this study, we enrolled patients with septic shock associated with various sites of infection and pathogens; our data revealed that all-cause hospital mortality was significantly lower and there were significantly more ICUFDs in the PMX-HP group than in the non-PMX-HP group. Additionally, this is the first study to show a survival benefit of PMX-HP in patients with septic shock at various sites of infection and pathogens; these data are thus very noteworthy. Because various baseline characteristics differed between the PMX-HP (n = 522) and non-PMX-HP (n = 1201) groups, comparing all data for these two regimens would not be valid. Therefore, to adjust for differing baseline characteristics, we extracted 262 comparable subjects from each group by propensity score matching. Almost all baseline characteristics were homogenous between the resultant groups, making a comparison between them valid. Thus, the most valid conclusions can be derived from comparing the PMX-HP (n = 262) and non-PMX-HP (n = 262) groups.
Cruz et al. [11] have reported that PMX-HP produces improvements in mortality, as well as in cardiac index, mean arterial pressure, inotropic score, vasopressor dependency index, and mean PaO2/FiO2 ratio. Moreover, a recent large retrospective study [25] showed that PMX-HP treatment reduces 28-day mortality in high-risk patients with septic shock complicated by continuous RRT-requiring acute kidney injury (the 28-day mortality was 40.2% (393/978) in the PMX-HP group and 46.8% (458/978) in the non-PMX-HP group; P = 0.003). In contrast, using propensity-matched analysis of data from Japanese Diagnosis Procedure Combination (DPC) databases, Iwagami et al. [22] reported no significant survival benefit in patients with postoperative abdominal septic shock (the 28-day mortality was 17.1% (101/590) in the PMX-HP group and 16.3% (96/590) in the non-PMX-HP group; P = 0.696). However, their DPC database [22] did not incorporate the scoring systems generally used in critically ill patients (such as the APACHE II, SOFA, JAAM DIC, and SIRS scores). Therefore, we could not determine the severity of the patients’ conditions in their study. Additionally, they accepted patients who had received noradrenaline and/or dopamine on day 0 as possibly having septic shock. However, Hashiguchi and Iba [26] highlighted a lower 28-day mortality rate in their study than in previous studies [11, 27]. Because the JSEPTIC DIC study database does not supply 28-day mortality, we were unable to evaluate this variable. However, in our study, the mean APACHE II score was over 25 on entry and the overall all-cause hospital mortality rate was approximately 37% (194/524) in the matched group. Therefore, we strongly suspect that this discrepancy in mortality rates is attributable to differences in severity of illness between our study subjects and previous studies; that is, patients enrolled in the Iwagami et al. [22] study were possibly less severely ill than our patients. Furthermore, the hospital mortality rate was very high in both groups in this study. However, a previous Japanese cohort study reported a similar hospital mortality from septic shock (41.5%, 117/282) [28].
Regarding the curative effects of PMX-HP, a meta-analysis by Cruz et al. [29] reported that PMX-HP treatment is associated with an increase in mean arterial pressure of 19 mm Hg (95% CI: 15–22 mmHg; P < 0.001) and a decrease in dopamine/dobutamine dose of 1.8 μg/kg per minute (95% CI: 0.4–3.3 μg/kg per minute; P = 0.01). Furthermore, the mean PaO2/FiO2 ratio reportedly increases by 32 units (95% CI: 23–41 units; P < 0.001). These data suggest that PMX-HP improves patient hemodynamics and oxygenation. In our study, the PMX-HP group had significantly more ICUFDs in the first 28 days than the non-PMX-HP group; this result may be attributable to clinical effects similar to those reported by Cruz et al. [29].
In this study, organisms were isolated from a relatively high proportion of patients and subjected to microbiologic testing. In the previous Japanese Sepsis Registry database [30] a high percentage of patients had blood cultures (81.4%). Additionally, in the JSEPTIC DIC study, blood cultures were performed in 94% of patients [14]. Thus, microbiological tests can usually be performed in patients with sepsis in Japanese ICUs in accordance with the Japanese guidelines for the management of sepsis [31]. Moreover, we enrolled patients with various sites of infection and types of pathogen. Patients with GPC infection comprised 20.0% (205/524) of the matched group. Nevertheless, all-cause hospital mortality was significantly better in the PMX-HP group than in the non-PMX-HP group. PMX-HP was originally developed for removal of endotoxin and used to treat GNR-induced septic shock. However, our results suggest that PMX-HP also has a beneficial effect on GPC-induced septic shock. PMX-HP is reportedly able to adsorb endogenous cannabinoids such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol [32], as well as activated monocytes [33]. The interaction of cannabinoids with vascular cannabinoid receptors leads to the hypotension that occurs in hemorrhagic or endotoxic shock [34–36]. Moreover, sepsis-induced immunoparalysis appears to play a key role in sepsis-induced morbidity and mortality [37]. One of the most important biomarkers of immunoparalysis is the human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR on the cell surface of monocytes (mHLA-DR), which is correlated with mortality [38, 39]. Ono et al. [40] reported that mHLA-DR was markedly decreased in patients with septic shock, and that this decrease was significantly reversed after PMX-HP treatment (P < 0.01). They thus concluded that PMX-HP may be a new strategy for helping patients to recover from immunoparalysis in septic conditions. In addition to endotoxin adsorption, adsorption of mediators such as endogenous cannabinoids or recovery from immunoparalysis may have contributed to the improvement in hospital mortality identified in this present study. In contrast, the JSEPTIC DIC study database does not contain information on cause of death and there is no clear explanation for the reported discrepancy between ICU mortality and all-cause hospital mortality. Hotchkiss et al. [41] reported development of immunoparalysis in later phases of sepsis. Hence, even though PMX-HP is an acute intervention, the hospital mortality (longer term mortality) observed in the present study may represent a significant improvement.
Some limitations of our study deserve consideration. First, this study was retrospective. Second, we did not consider the number of times (once or twice), the duration, or the initiation time of PMX-HP administration after ICU admission. Third, we did not examine long-term prognosis (such as 60-day or 90-day mortality). Fourth, a new definition of sepsis was published in 2016 [42]. Because the JSEPTIC DIC study was planned in November 2015, we used the 2001 consensus sepsis definition [15] in this study. Finally, we were unable to determine the exact timing of the various therapeutic interventions. However, because other therapeutic interventions and PMX-HP are usually performed simultaneously upon admission to the ICU, we considered it acceptable to use therapeutic interventions when estimating propensity scores. Because of these limitations, further studies (particularly RCTs) are required to more reliably ascertain the survival benefit of PMX-HP. In fact, the efficacy of PMX-HP treatment for septic shock is currently being investigated in the USA and Canada [43]; the results of these trials are eagerly anticipated.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that PMX-HP is associated with reduced all-cause hospital mortality and number of ICUFDs in patients with septic shock caused by various pathogens and with various sites of infection.
Key messages
Despite the availability of modern antibiotics and resuscitation therapies, sepsis is a leading cause of death in critically ill patients.
Endotoxin, a lipopolysaccharide derived from the outer membranes of gram-negative rods, is a key factor in the sepsis cascade and high serum concentrations of endotoxin are closely linked to increased risk of multiple organ failure and death.
Polymyxin B direct hemoperfusion (PMX-HP) removes plasma endotoxins and is considered an effective treatment for sepsis.
The aim of this study was to investigate the usefulness of PMX-HP for various infection sites and different types of septic shock caused by not only gram-negative rods but other pathogens.
This study included the largest number of patients with septic shock until now across 42 Japanese ICUs.
PMX-HP is associated with reduced all-cause hospital mortality and number of ICU free days in patients with septic shock caused by various pathogens and with various sites of infection.
Additional files
List of participating institutions (DOC 39 kb).
Characteristics of the intensive care units (ICUs). Data are presented as number (percentage) (DOC 29 kb).
Acknowledgements
We thank all collaborators of the JSEPTIC DIC study for collecting the data: Shinjiro Saito and Shigehiko Uchino (Intensive Care Unit, Department of Anesthesiology, Jikei University School of Medicine); Daisuke Kudo (Division of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine); Toshihiko Mayumi (Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental Health); Takeo Azuhata (Division of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Acute Medicine, Nihon University School of Medicine); Fumihito Ito (Department of Emergency & Critical Care Medicine, Ohta General Hospital Foundation Ohta Nishinouchi Hospital); Shodai Yoshihiro (Pharmaceutical Department, JA Hiroshima General Hospital); Hayakawa Katsura (Department of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Saitama Red Cross Hospital); Tsuyoshi Nakashima (Department of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Wakayama Medical University); Takayuki Ogura (Department of Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Medicine, Advanced Medical Emergency Department and Critical Care Center, Japan Red Cross Maebashi Hospital); Eiichiro Noda (Emergency and Critical Care Center, Kyushu University Hospital); Yoshihiko Nakamura (Department of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Fukuoka University Hospital); Ryosuke Sekine (Emergency Department, Ibaraki Prefectural Central Hospital); Kazuma Yamakawa and Yoshiaki Yoshikawa (Department of Emergency and Critical Care, Osaka General Medical Center); Motohiro Sekino (Division of Intensive Care, Nagasaki University Hospital); Keiko Ueno (Department of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Tokyo Medical University, Hachioji Medical Center); Yuko Okuda (Anesthesiology, Kyoto First Red-cross hospital); Masayuki Watanabe (Intensive Care Unit, Saiseikai Yokohamasi Tobu Hospital); Akihito Tampo (Department of Emergency Medicine, Asahikawa Medical University); Nobuyuki Saito (Shock and Trauma Center, Nippon Medical School Chiba Hokusoh Hospital); Yuya Kitai (Emergency Medicine, Kameda Medical Center); Kohei Takimoto and Hiroki Takahashi (Department of Traumatology and Acute Critical Medicine, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine); Iwao Kobayashi (Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Asahikawa Red Cross Hospital); Yutaka Kondo (Department of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, University of the Ryukyus); Masamitsu Sanui, Yusuke Iizuka, and Wataru Matsunaga (Department of Anesthesia and Critical Care Medicine, Saitama Medical Center Jichi Medical University); Sho Nachi (Advanced Critical Care Center, Gifu University Hospital); Toru Miike (Emergency and Critical Care Center, Saga University Hospital); Hiroshi Takahashi (Division of Cardiovascular Disease, Steel Memorial Muroran Hospital); Shuhei Takauji (Department of Emergency Medicine and Critical Care, Sapporo City General Hospital); Kensuke Umakoshi (Division of Emergency Medicine, Ehime University Hospital); Takafumi Todaka (Intensive Care Unit, Tomishiro Central Hospital); Hiroshi Kodaira (Department of Emergency Medicine, Akashi City Hospital); Kohkichi Andoh (Critical Care Department, Sendai City Hospital); Takehiko Kasai (Emergency Department, Hakodate Municipal Hospital); Yoshiaki Iwashita (Emergency and Critical Care Center, Mie University Hospital); Hideaki Arai (Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental Health Hospital); Masato Murata (Department of Emergency Medicine, Gunma University); Masahiro Yamane (Department of Anesthesia and Intensive Care, KKR Sapporo Medical Center); Kazuhiro Shiga (Emergency and Critical Care Center, Seirei Mikatahara General Hospital); and Naoto Hori (Intensive Care Unit, Hyogo College of Medicine).
Funding
There were no external sources of funding for this retrospective study.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the JSEPTIC DIC group but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, and so are not publicly available. Data are, however, available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of the JSEPTIC DIC group.
Authors’ contributions
YN, TK, MH, and HI had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. YN, TK, FK, MH, KH, YK, RY, TN, and MM contributed to the conception and design of the study and take responsibility for the accuracy of the data analysis. YN, FK, TK, and HI contributed to data acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. YN and HI contributed to drafting the manuscript. YN, FK, and HI contributed to the statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The JSEPTIC DIC study was conducted in 42 ICUs of 40 institutions in Japan (Additional file 1), and was approved by the Institutional Review Boards of each hospital. The boards waived the requirement for informed consent because of the retrospective nature of the JSEPTIC DIC study. Since this database was already anonymized for individual patient data and institutions, the Institutional Review Board waived the need for review of this post-hoc study. However, we did not input patient personal data such as name or medical ID number at each facility in order to adhere strictly to the anonymity of patients.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- APACHE
Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation
- AT
Antithrombin
- BW
Body weight
- CI
Confidence interval
- DIC
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- DPC
Diagnosis procedure combination
- GNR
Gram-negative rod
- GPC
Gram-positive cocci
- Hb
Hemoglobin
- HLA
Human leukocyte antigen
- HR
Hazard ratio
- ICU
Intensive care unit
- ICUFDs
ICU-free days
- IVIG
Intravenous immunoglobulin
- JAAM
Japanese Association for Acute Medicine
- JSEPTIC DIC
The Japan Septic Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
- OR
Odds ratio
- PMX-HP
Polymyxin B hemoperfusion
- PRBC
Packed red blood cells
- PT-INR
Prothrombin time-international normalized ratio
- RCT
Randomized controlled trial
- rhsTM
Recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin
- RRT
Renal replacement therapy
- SIRS
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- SOFA
Sequential Organ Failure Assessment
- WBC
White blood cell count
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13054-017-1712-3) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
Yoshihiko Nakamura, Email: pdmxy827@yahoo.co.jp.
Taisuke Kitamura, Email: taisukekitamura@gmail.com.
Fumiaki Kiyomi, Email: fumkiyomi@adm.fukuoka-u.ac.jp.
Mineji Hayakawa, Email: mineji@dream.com.
Kota Hoshino, Email: hoshinoqq@yahoo.co.jp.
Yasumasa Kawano, Email: kawano0301@cis.fukuoka-u.ac.jp.
Reiko Yamasaki, Email: qp.reiko.19811104@gmail.com.
Takeshi Nishida, Email: bushinishitaxi007@gmail.com.
Mariko Mizunuma, Email: numariko625@gmail.com.
Hiroyasu Ishikura, Email: ishikurah@fukuoka-u.ac.jp.
Japan Septic Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (JSEPTIC DIC) study group:
Shinjiro Saito, Shigehiko Uchino, Daisuke Kudo, Toshihiko Mayumi, Takeo Azuhata, Fumihito Ito, Shodai Yoshihiro, Hayakawa Katsura, Tsuyoshi Nakashima, Takayuki Ogura, Eiichiro Noda, Yoshihiko Nakamura, Ryosuke Sekine, Kazuma Yamakawa, Yoshiaki Yoshikawa, Motohiro Sekino, Keiko Ueno, Yuko Okuda, Masayuki Watanabe, Akihito Tampo, Nobuyuki Saito, Yuya Kitai, Kohei Takimoto, Hiroki Takahashi, Iwao Kobayashi, Yutaka Kondo, Masamitsu Sanui, Yusuke Iizuka, Wataru Matsunaga, Sho Nachi, Toru Miike, Hiroshi Takahashi, Shuhei Takauji, Kensuke Umakoshi, Takafumi Todaka, Hiroshi Kodaira, Kohkichi Andoh, Takehiko Kasai, Yoshiaki Iwashita, Hideaki Arai, Masato Murata, Masahiro Yamane, Kazuhiro Shiga, and Naoto Hori
References
- 1.Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–10. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200107000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:580–637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.da Silva AM T, Kaulbach HC, Chuidian FS, Lambert DR, Suffredini AF, Danner RL. Brief report: shock and multiple-organ dysfunction after self-administration of Salmonella endotoxin. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1457–60. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305203282005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.van Deventer SJ, Buller HR, ten Cate JW, Aarden LA, Hack CE, Sturk A. Experimental endotoxemia in humans: analysis of cytokine release and coagulation, fibrinolytic, and complement pathways. Blood. 1990;76:2520–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Opal SM, Scannon PJ, Vincent JL, White M, Carroll SF, Palardy JE, et al. Relationship between plasma levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS-binding protein in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:1584–9. doi: 10.1086/315093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Marshall JC, Foster D, Vincent JL, Cook DJ, Cohen J, Dellinger RP, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of endotoxemia in critical illness: results of the MEDIC study. J Infect Dis. 2004;190:527–34. doi: 10.1086/422254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Opal SM, Gluck T. Endotoxin as a drug target. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:S57–64. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200301001-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tani T, Hanasawa K, Kodama M, Imaizumi H, Yonekawa M, Saito M, et al. Correlation between plasma endotoxin, plasma cytokines, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 activities in septic patients. World J Surg. 2001;25:660–8. doi: 10.1007/s002680020028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Totsugawa T, Kuinose M, Yoshitaka H, Tsushima Y, Ishida A, Chikazawa G, et al. Intraoperative direct hemoperfusion with a polymyxin-B immobilized fiber column for treatment of infective endocarditis. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;59:98–104. doi: 10.1007/s11748-010-0700-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yamato M, Minematsu Y, Fujii J, Mori K, Minato T, Miyagawa S, et al. Effective combination therapy of polymyxin-B direct hemoperfusion and recombinant thrombomodulin for septic shock accompanied by disseminated intravascular coagulation: a historical controlled trial. Ther Apher Dial. 2013;17:472–6. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.12112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cruz DN, Antonelli M, Fumagalli R, Foltran F, Brienza N, Donati A, et al. Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in abdominal septic shock: the EUPHAS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;301:2445–52. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Payen DM, Guilhot J, Launey Y, Lukaszewicz AC, Kaaki M, Veber B, et al. Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in patients with septic shock due to peritonitis: a multicenter randomized control trial. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41:975–84. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-3751-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hayakawa M, Yamakawa K, Saito S, Uchino S, Kudo D, Iizuka Y, Sanui M, Takimoto K, Mayumi T, Ono K, Japan Septic Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (JSEPTIC DIC) study group Recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin and mortality in sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation. A multicentre retrospective study. Thromb Haemost. 2016;115:1157–66. doi: 10.1160/TH15-12-0987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hayakawa M, Saito S, Uchino S, Yamakawa K, Kudo D, Iizuka Y, Sanui M, Takimoto K, Mayumi T, Azuhata T, Ito F, Yoshihiro S, Hayakawa K, Nakashima T, Ogura T, Noda E, Nakamura Y, Sekine R, Yoshikawa Y, Sekino M, Ueno K, Okuda Y, Watanabe M, Tampo A, Saito N, Kitai Y, Takahashi H, Kobayashi I, Kondo Y, Matsunaga W, Nachi S, Miike T, Takahashi H, Takauji S, Umakoshi K, Todaka T, Kodaira H, Andoh K, Kasai T, Iwashita Y, Arai H, Murata M, Yamane M, Shiga K, Hori N. Characteristics, treatments, and outcomes of severe sepsis of 3195 ICU-treated adult patients throughout Japan during 2011–2013. J Intensive Care. 2016;4:44. doi: 10.1186/s40560-016-0169-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:1250–6. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000050454.01978.3B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985;13:818–29. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198510000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonca A, Bruining H, et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22:707–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01709751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, et al. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992;101:1644–55. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.6.1644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gando S, Iba T, Eguchi Y, Ohtomo Y, Okamoto K, Koseki K, et al. A multicenter, prospective validation of disseminated intravascular coagulation diagnostic criteria for critically ill patients: comparing current criteria. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:625–31. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000202209.42491.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shoji H. Extracorporeal endotoxin removal for the treatment of sepsis: endotoxin adsorption cartridge (Toraymyxin) Ther Apher Dial. 2003;7:108–14. doi: 10.1046/j.1526-0968.2003.00005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Aoki H, Kodama M, Tani T, Hanasawa K. Treatment of sepsis by extracorporeal elimination of endotoxin using polymyxin B-immobilized fiber. Am J Surg. 1994;167:412–7. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(94)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Iwagami M, Yasunaga H, Doi K, Horiguchi H, Fushimi K, Matsubara T, et al. Postoperative polymyxin B hemoperfusion and mortality in patients with abdominal septic shock: a propensity-matched analysis. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:1187–93. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Austin PC. The use of propensity score methods with survival or time-to-event outcomes: reporting measures of effect similar to those used in randomized experiments. Stat Med. 2014;33:1242–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.5984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ronco C, Klein DJ. Polymyxin B hemoperfusion: a mechanistic perspective. Crit Care. 2014;18:309. doi: 10.1186/cc13912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Iwagami M, Yasunaga H, Noiri E, Horiguchi H, Fushimi K, Matsubara T, et al. Potential survival benefit of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in septic shock patients on continuous renal replacement therapy: a propensity-matched analysis. Blood Purif. 2016;42:9–17. doi: 10.1159/000444474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hashiguchi N, Iba T. Is postoperative polymyxin B hemoperfusion for abdominal septic shock really ineffective? Crit Care Med. 2014;42:e596–7. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vincent JL, Laterre PF, Cohen J, Burchardi H, Bruining H, Lerma FA, et al. A pilot-controlled study of a polymyxin B-immobilized hemoperfusion cartridge in patients with severe sepsis secondary to intra-abdominal infection. Shock. 2005;23:400–5. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000159930.87737.8a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ogura H, Gando S, Saitoh D, Takeyama N, Kushimoto S, Fujishima S, Mayumi T, Araki T, Ikeda H, Kotani J, Miki Y, Shiraishi S, Suzuki K, Suzuki Y, Takuma K, Tsuruta R, Yamaguchi Y, Yamashita N, Aikawa N, Japanese Association for Acute Medicine Sepsis Registry (JAAMSR) Study Group Epidemiology of severe sepsis in Japanese intensive care units: a prospective multicenter study. J Infect Chemother. 2014;20:157–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2013.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cruz DN, Perazella MA, Bellomo R, de Cal M, Polanco N, Corradi V, et al. Effectiveness of polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column in sepsis: a systematic review. Crit Care. 2007;11:R47. doi: 10.1186/cc5780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fujishima S, Gando S, Saitoh D, Mayumi T, Kushimoto S, Shiraishi S, Ogura H, Takuma K, Kotani J, Ikeda H, Yamashita N, Suzuki K, Tsuruta R, Takeyama N, Araki T, Suzuki Y, Miki Y, Yamaguchi Y, Aikawa N, Japanese Association for Acute Medicine Sepsis Registry (JAAM SR) Study Group A multicenter, prospective evaluation of quality of care and mortality in Japan based on the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines. J Infect Chemother. 2014;20:115–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2013.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Oda S, Aibiki M, Ikeda T, Imaizumi H, Endo S, Ochiai R, Kotani J, Shime N, Nishida O, Noguchi T, Matsuda N, Hirasawa H, Sepsis Registry Committee of The Japanese Society of Intensive Care Medicine The Japanese guidelines for the management of sepsis. J Intensive Care. 2014;2:55. doi: 10.1186/s40560-014-0055-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wang Y, Liu Y, Sarker KP, Nakashima M, Serizawa T, Kishida A, et al. Polymyxin B binds to anandamide and inhibits its cytotoxic effect. FEBS Lett. 2000;470:151–5. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nishibori M, Takahashi HK, Katayama H, Mori S, Saito S, Iwagaki H, et al. Specific removal of monocytes from peripheral blood of septic patients by polymyxin B-immobilized filter column. Acta Med Okayama. 2009;63:65–9. doi: 10.18926/AMO/31855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stein EA, Fuller SA, Edgemond WS, Campbell WB. Physiological and behavioural effects of the endogenous cannabinoid, arachidonylethanolamide (anandamide), in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1996;119:107–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15683.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Varga K, Wagner JA, Bridgen DT, Kunos G. Platelet- and macrophage-derived endogenous cannabinoids are involved in endotoxin-induced hypotension. FASEB J. 1998;12:1035–44. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.12.11.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lake KD, Compton DR, Varga K, Martin BR, Kunos G. Cannabinoid-induced hypotension and bradycardia in rats mediated by CB1-like cannabinoid receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997;281:1030–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hamers L, Kox M, Pickkers P. Sepsis-induced immunoparalysis: mechanisms, markers, and treatment options. Minerva Anestesiol. 2015;81:426–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Landelle C, Lepape A, Voirin N, Tognet E, Venet F, Bohe J, et al. Low monocyte human leukocyte antigen-DR is independently associated with nosocomial infections after septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2010;36:1859–66. doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-1962-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Monneret G, Lepape A, Voirin N, Bohe J, Venet F, Debard AL, et al. Persisting low monocyte human leukocyte antigen-DR expression predicts mortality in septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2006;32:1175–83. doi: 10.1007/s00134-006-0204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ono S, Tsujimoto H, Matsumoto A, Ikuta S, Kinoshita M, Mochizuki H. Modulation of human leukocyte antigen-DR on monocytes and CD16 on granulocytes in patients with septic shock using hemoperfusion with polymyxin B-immobilized fiber. Am J Surg. 2004;188:150–6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2003.12.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hotchkiss RS, Coopersmith CM, McDunn JE, Ferguson TA. The sepsis seesaw: tilting toward immunosuppression. Nat Med. 2009;15:496–7. doi: 10.1038/nm0509-496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Klein DJ, Foster D, Schorr CA, Kazempour K, Walker PM, Dellinger RP. The EUPHRATES trial (Evaluating the Use of Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion in a Randomized controlled trial of Adults Treated for Endotoxemia and Septic shock): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2014;15:218. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
List of participating institutions (DOC 39 kb).
Characteristics of the intensive care units (ICUs). Data are presented as number (percentage) (DOC 29 kb).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the JSEPTIC DIC group but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, and so are not publicly available. Data are, however, available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of the JSEPTIC DIC group.


