Abstract
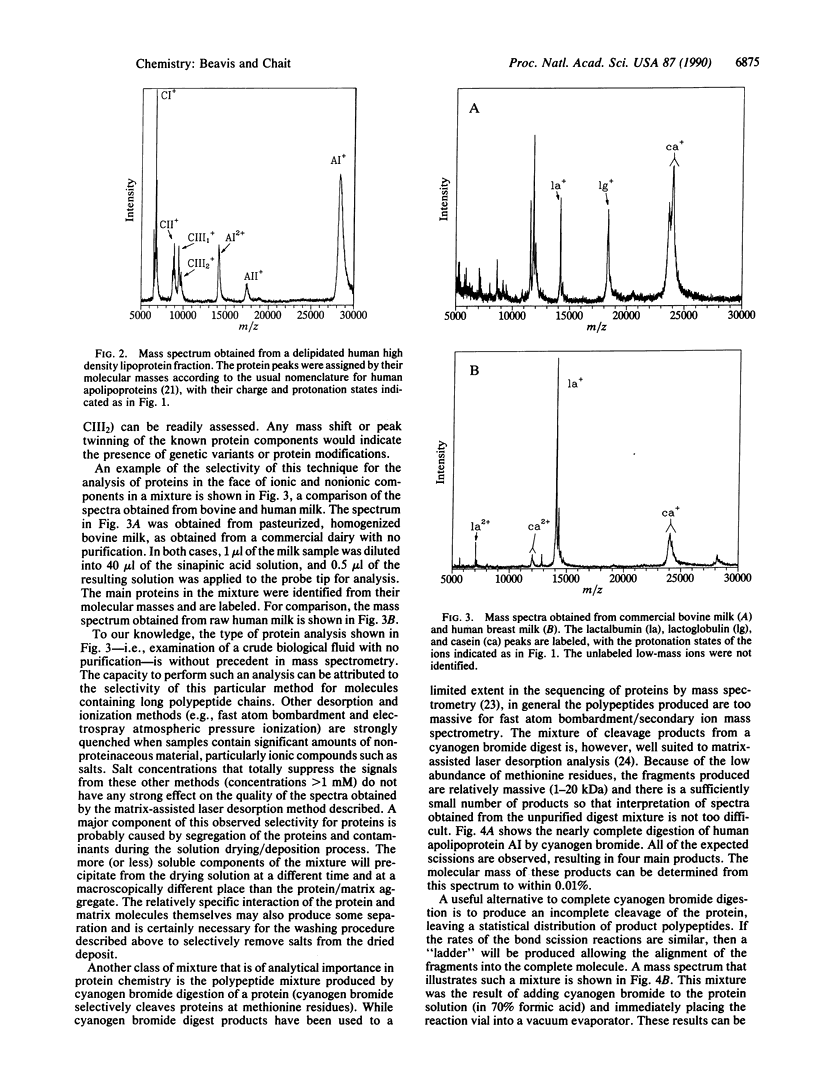
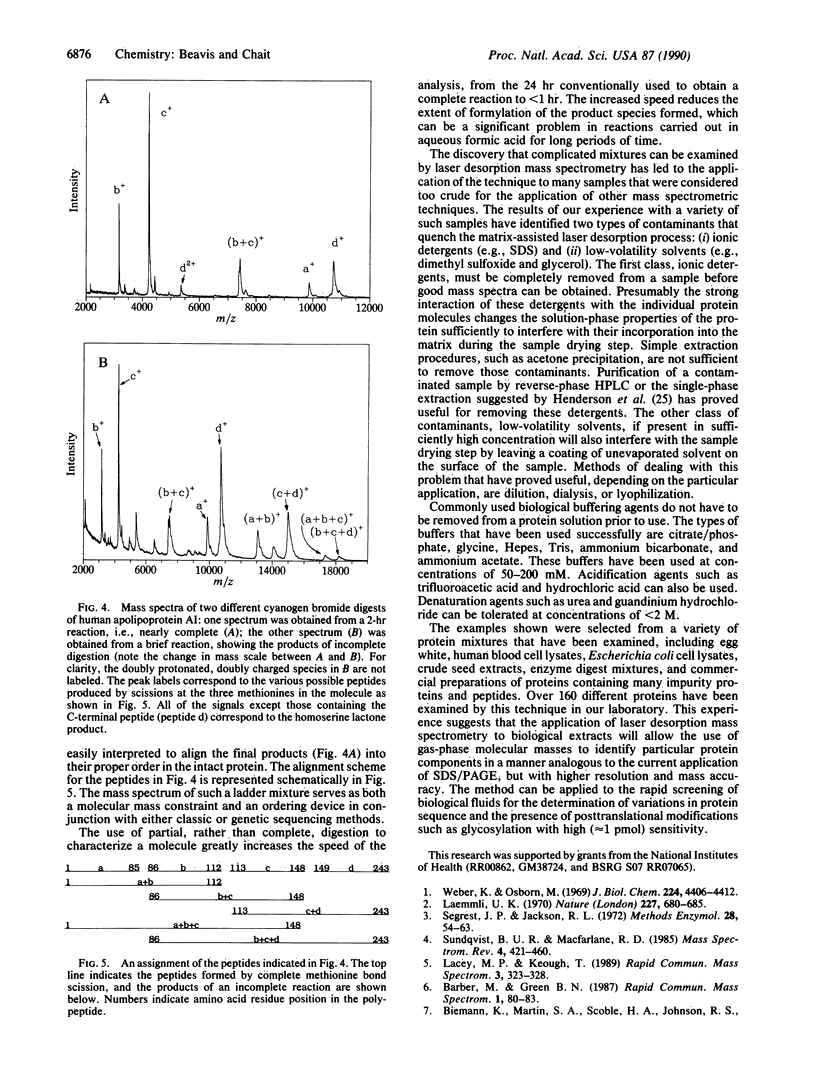
We have developed a method for determining the molecular masses of proteins in complex mixtures by mass spectrometry. The method has the capacity to examine the components of mixtures without using any chromatographic separation steps and will tolerate relatively large amounts of buffers and inorganic contaminants. It allows the simultaneous determination of protein molecular masses from 1 to 40 kDa with an accuracy of +/- 0.01% and above 40 kDa with reduced accuracy. The lower limit for practical detection of a protein is a concentration of approximately 0.1 microM, and less than 1 microliter of such a solution is consumed. The analysis is very fast: less than 15 min is necessary to perform the complete analysis, including sample preparation, introduction into the mass spectrometer, mass spectrum collection, and data reduction. The mass spectrum that is obtained does not require elaborate interpretation because there is no fragmentation of the ionized protein (or protein subunit) molecule. Therefore, there is a one-to-one correspondence between the peaks in the mass spectrum and the proteins present in the original mixture. The spectra assume the appearance of chromatograms, with the abscissa being mass-to-charge ratio rather than chromatographic retention time.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber M., Green B. N. The analysis of small proteins in the molecular weight range 10-24 kDa by magnetic sector mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1987 Sep;1(5):80–83. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290010505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavis R. C., Chait B. T. Cinnamic acid derivatives as matrices for ultraviolet laser desorption mass spectrometry of proteins. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1989 Dec;3(12):432–435. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290031207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavis R. C., Chait B. T. Factors affecting the ultraviolet laser desorption of proteins. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1989 Jul;3(7):233–237. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290030708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavis R. C., Chait B. T. Matrix-assisted laser-desorption mass spectrometry using 355 nm radiation. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1989 Dec;3(12):436–439. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290031208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton E. A., Eisenberg S., Breslow J. L. Elevated high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels correlate with decreased apolipoprotein A-I and A-II fractional catabolic rate in women. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):262–269. doi: 10.1172/JCI114149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey T. R., Bonner R. F., Shushan B. I., Henion J. The determination of protein, oligonucleotide and peptide molecular weights by ion-spray mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1988 Nov;2(11):249–256. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290021111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn J. B., Mann M., Meng C. K., Wong S. F., Whitehouse C. M. Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules. Science. 1989 Oct 6;246(4926):64–71. doi: 10.1126/science.2675315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Jr, Pownall H. J., Havel R. J. Introduction to the plasma lipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:3–41. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Konigsberg W. A micromethod for complete removal of dodecyl sulfate from proteins by ion-pair extraction. Anal Biochem. 1979 Feb;93(1):153–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry K. D., Williams E. R., Wang B. H., McLafferty F. W., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F. Fourier-transform mass spectrometry of large molecules by electrospray ionization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9075–9078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karas M., Hillenkamp F. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10,000 daltons. Anal Chem. 1988 Oct 15;60(20):2299–2301. doi: 10.1021/ac00171a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H. D., Wiltfang J., Karas M., Neuhoff V., Hilschmann N. Gas-phase sequencing after electroblotting on polyvinylidene difluoride membranes assigns correct molecular weights to myoglobin molecular weight markers. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90161-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey M. P., Keough T. Plasma-desorption mass spectrometry of intact enzymes and proenzymes. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1989 Sep;3(9):323–328. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290030914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. W., Trimble R. B., Wirth D. F., Hering C., Maley F., Maley G. F., Das R., Gibson B. W., Royal N., Biemann K. Primary structure of the Streptomyces enzyme endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7577–7583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salehpour M., Perera I., Kjellberg J., Hedin A., Islamian M. A., Håkansson P., Sundqvist B. U. Laser-induced desorption of proteins. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1989 Aug;3(8):259–263. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290030804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. D., Loo J. A., Edmonds C. G., Barinaga C. J., Udseth H. R. New developments in biochemical mass spectrometry: electrospray ionization. Anal Chem. 1990 May 1;62(9):882–899. doi: 10.1021/ac00208a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



