Abstract
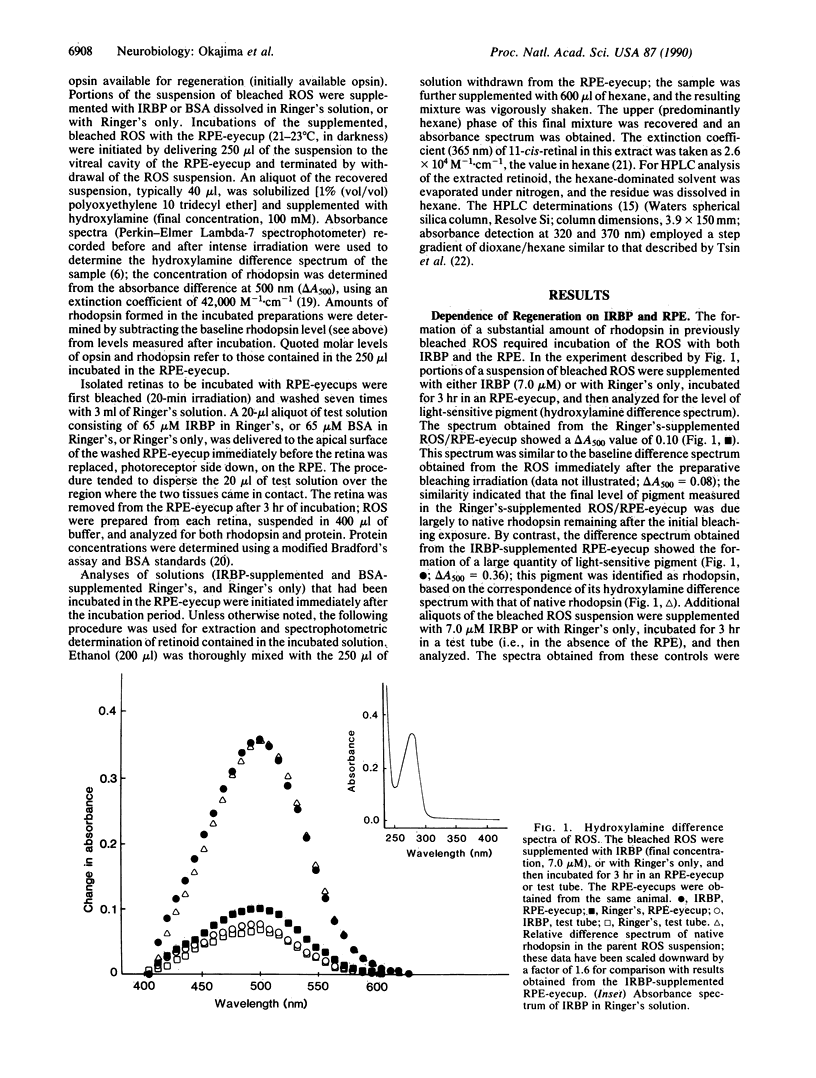
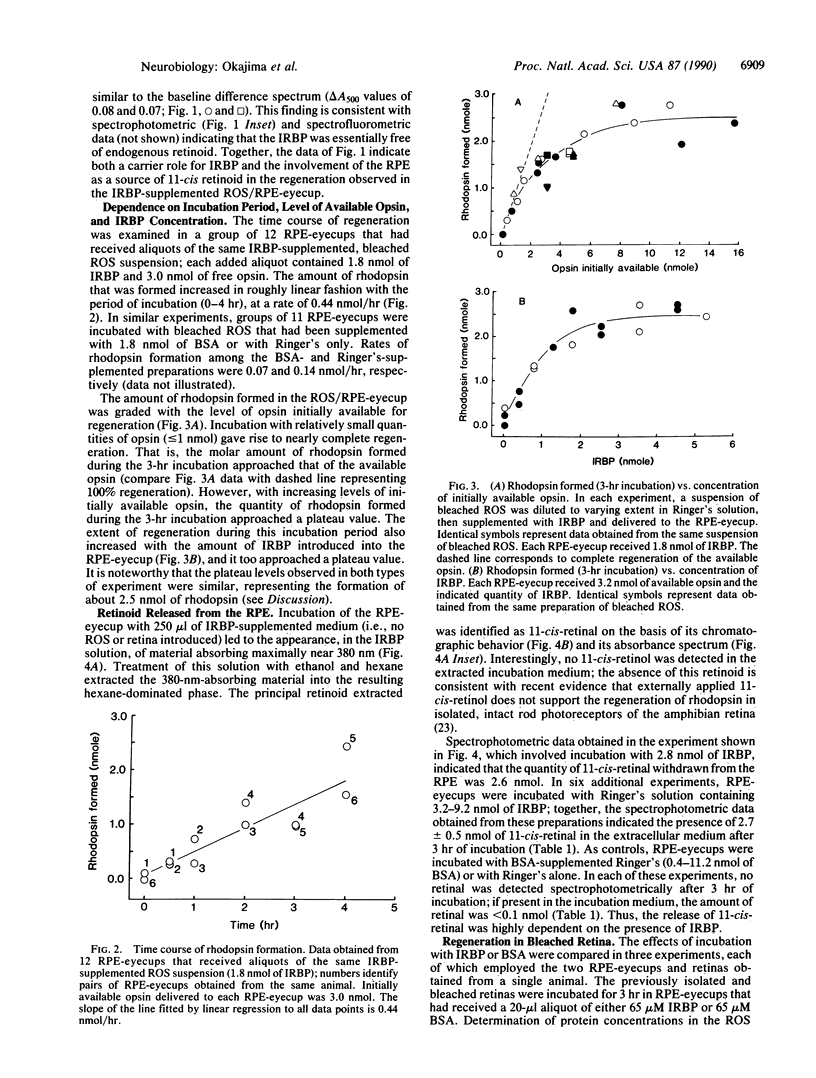
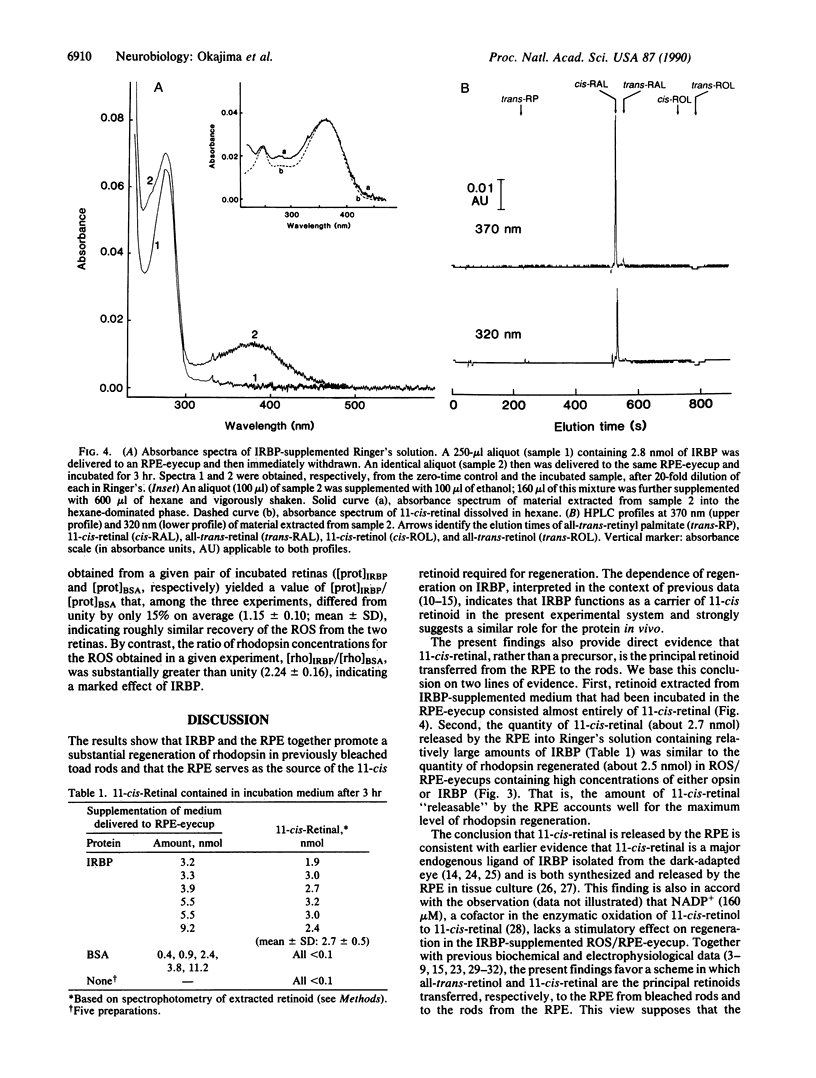
Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) has been hypothesized to function as an intercellular shuttle in the vertebrate eye, serving to transport retinoids between the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and photoreceptors in the process by which visual pigment is regenerated after photolysis. This hypothesis was tested in preparations utilizing the toad (Bufo marinus) eye and purified, initially ligand-free IRBP obtained from the bovine eye. Rod outer segments (ROS) or neural retinas were isolated and bleached, then incubated with native RPE (RPE-eyecup) in the presence or absence of IRBP. The amount of rhodopsin present after incubation was determined by spectrophotometric analysis and compared with that in control preparations receiving bovine serum albumin or Ringer's solution only. Supplementation with IRBP enhanced the formation of rhodopsin in both the ROS/RPE-eyecup and retina/RPE-eyecup preparations. Regeneration in ROS/RPE-eyecups receiving IRBP (1.8 nmol) increased in a roughly linear manner with the period of incubation (0-4 hr), at a rate of 0.44 nmol/hr. The extent of regeneration was graded with the quantities of IRBP and opsin introduced into the RPE-eyecup. With increasing amounts of IRBP (up to 5.2 nmol) or of initially available opsin (up to 15.6 nmol), the amount of rhodopsin formed (3-hr incubation) approached the same plateau value, about 2.5 nmol. Analysis of IRBP-supplemented Ringer's solution incubated in the RPE-eyecup showed 11-cis-retinal to be virtually the only retinoid withdrawn from the RPE. With large quantities of IRBP (3.2-9.2 nmol), the amount of 11-cis-retinal (2.7 +/- 0.5 nmol) withdrawn from the RPE during a 3-hr incubation was similar to the plateau value of rhodopsin formed in the ROS/RPE-eyecup. No 11-cis-retinal was observed in albumin-supplemented Ringer's solution (0.4-11.2 nmol of bovine serum albumin) or in Ringer's alone after similar incubation in the RPE-eyecup. The results suggest that an IRBP-mediated transfer of 11-cis-retinal from the RPE to the rods supports rhodopsin regeneration in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler A. J., Martin K. J. Retinol-binding proteins in bovine interphotoreceptor matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 29;108(4):1601–1608. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann C. Kinetics of slow thermal reactions during the bleaching of rhodopsin in the perfused frog retina. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):643–663. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein P. S., Law W. C., Rando R. R. Isomerization of all-trans-retinoids to 11-cis-retinoids in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges C. D. Rhodopsin regeneration in rod outer segments: utilization of 11-cis retinal and retinol. Exp Eye Res. 1977 Jun;24(6):571–580. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(77)90114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges C. D. Vitamin A and the role of the pigment epithelium during bleaching and regeneration of rhodopsin in the frog eye. Exp Eye Res. 1976 May;22(5):435–455. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(76)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brin K. P., Ripps H. Rhodopsin photoproducts and rod sensitivity in the skate retina. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jan;69(1):97–120. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Pinto L. H. Ionic mechanism for the photoreceptor potential of the retina of Bufo marinus. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):575–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deigner P. S., Law W. C., Cañada F. J., Rando R. R. Membranes as the energy source in the endergonic transformation of vitamin A to 11-cis-retinol. Science. 1989 May 26;244(4907):968–971. doi: 10.1126/science.2727688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD R., DOWLING J. E. Formation and utilization of 11-cis vitamin A by the eye tissues during light and dark adaptation. Nature. 1962 Jan 27;193:341–343. doi: 10.1038/193341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. T., Massey J. B., Pownall H. J., Anderson R. E., Hollyfield J. G. Mechanism of vitamin A movement between rod outer segments, interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein, and liposomes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):928–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hárosi F. I. Absorption spectra and linear dichroism of some amphibian photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Sep;66(3):357–382. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. J., Crouch R. K., Wiggert B., Cornwall M. C., Chader G. J. Retinoid requirements for recovery of sensitivity after visual-pigment bleaching in isolated photoreceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9606–9610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Y. L., Wiggert B., Liu Y. P., Chader G. J. Interphotoreceptor retinol-binding proteins: possible transport vehicles between compartments of the retina. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):848–849. doi: 10.1038/298848a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Z. S., Fong S. L., Bridges C. D. Retinoids bound to interstitial retinol-binding protein during light and dark-adaptation. Vision Res. 1989;29(12):1699–1709. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(89)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou G. I., Bridges C. D., Fong S. L., Alvarez R. A., Gonzalez-Fernandez F. Vitamin A transport between retina and pigment epithelium--an interstitial protein carrying endogenous retinol (interstitial retinol-binding protein). Vision Res. 1982;22(12):1457–1467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(82)90210-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima T. I., Pepperberg D. R., Ripps H., Wiggert B., Chader G. J. Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein: role in delivery of retinol to the pigment epithelium. Exp Eye Res. 1989 Oct;49(4):629–644. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(89)80059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepperberg D. R., Brown P. K., Lurie M., Dowling J. E. Visual pigment and photoreceptor sensitivity in the isolated skate retina. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Apr;71(4):369–396. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.4.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman J. I., Nodes B. R., Pepperberg D. R. Utilization of retinoids in the bullfrog retina. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Dec;80(6):885–913. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.6.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer B., Wiggert B., Lee L., Zonnenberg B., Newsome D., Chader G. The presence of a soluble interphotoreceptor retinol-binding protein (IRBP) in the retinal interphotoreceptor space. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Dec;117(3):333–341. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041170308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond T. M., Wiggert B., Robey F. A., Nguyen N. Y., Lewis M. S., Lee L., Chader G. J. Isolation and characterization of monkey interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein, a unique extracellular matrix component of the retina. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):787–793. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saari J. C., Teller D. C., Crabb J. W., Bredberg L. Properties of an interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein from bovine retina. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):195–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsin A. T., Alvarez R. A., Fong S. L., Bridges C. D. Use of high-performance liquid chromatography in the analysis of retinyl and 3,4-didehydroretinyl compounds in tissue extracts of bullfrog tadpoles and goldfish. Vision Res. 1984;24(12):1835–1840. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(84)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald G. CAROTENOIDS AND THE VISUAL CYCLE. J Gen Physiol. 1935 Nov 20;19(2):351–371. doi: 10.1085/jgp.19.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald G. Molecular basis of visual excitation. Science. 1968 Oct 11;162(3850):230–239. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3850.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee R., Liebman P. A. Light-activated phosphodiesterase of the rod outer segment. Kinetics and parameters of activation and deactivation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8902–8909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman W. F. The distribution and proportions of vitamin A compounds during the visual cycle in the rat. Vision Res. 1974 Sep;14(9):795–802. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(74)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



