Abstract
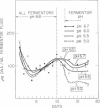
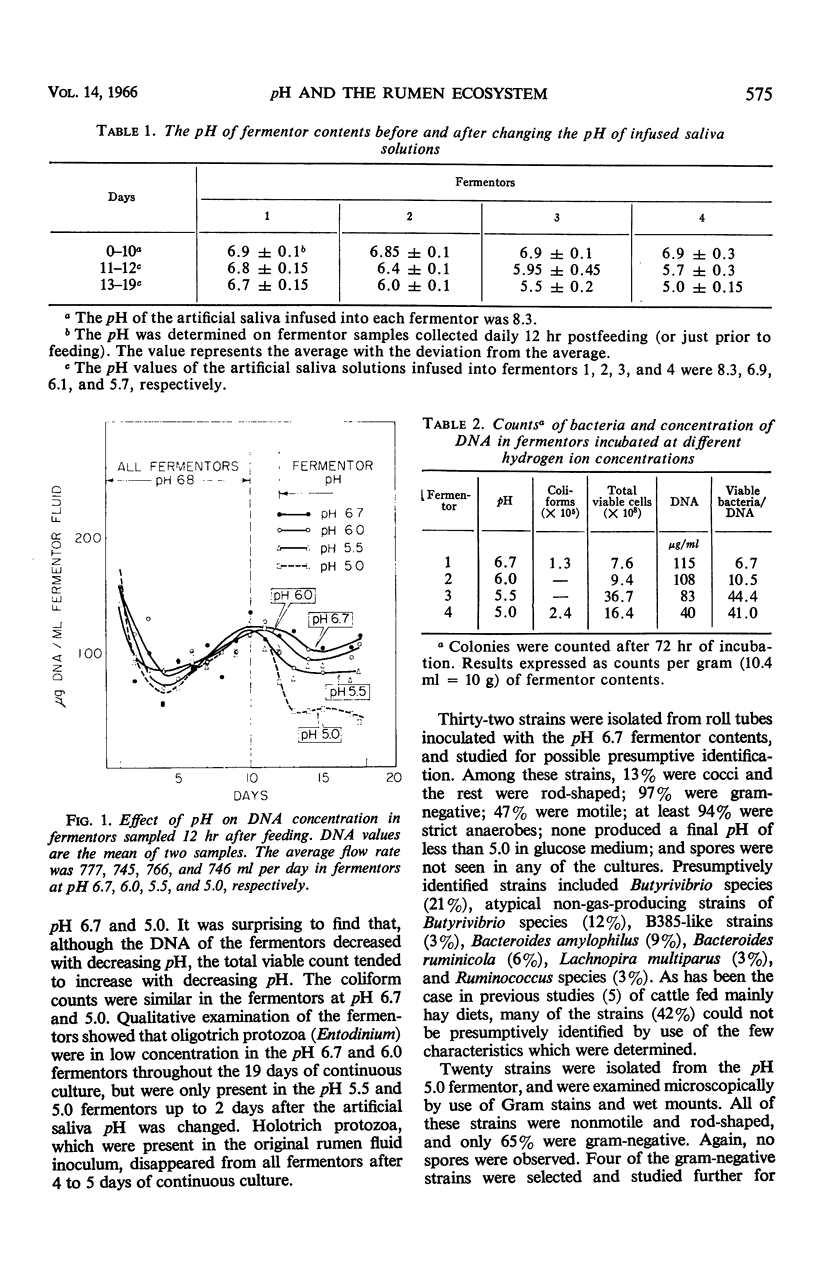
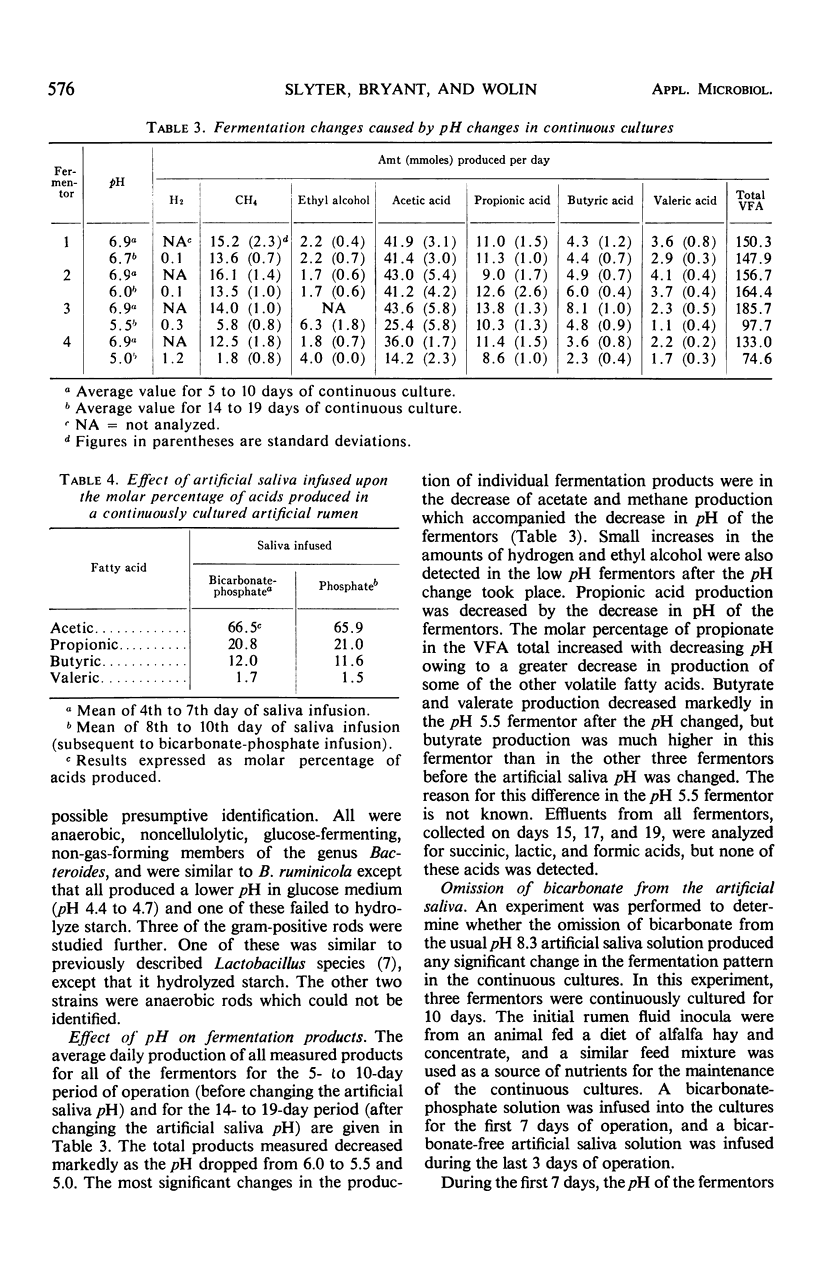
The effect of pH on rumen fermentation and microbial population was studied in a continuously cultured rumen ecosystem. A marked decrease in the production of volatile fatty acids and methane from alfalfa hay occurred when the cultures were maintained at pH values below 6.0. The decrease in acetate and methane production was greater than that of propionate production. The culture maintained at pH 6.7 contained the types of bacteria often found in high concentration in the rumen, whereas the culture maintained at pH 5.0 had a high percentage of bacteria which could not be identified with the major rumen bacteria found in rumens of animals fed alfalfa hay. Replacement of the bicarbonate-phosphate buffer used to maintain fermentor pH at 6.7 with phosphate alone did not greatly alter the fermentation products produced from a hay-concentrate substrate.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG D. G., BLAXTER K. L., GRAHAM N. M. The heat increments of mixtures of steam-volatile fatty acids in fasting sheep. Br J Nutr. 1957;11(4):392–408. doi: 10.1079/bjn19570061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARMSTRONG D. G., BLAXTER K. L. The heat increment of steam-volatile fatty acids in fasting sheep. Br J Nutr. 1957;11(3):247–272. doi: 10.1079/bjn19570044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALCH D. A., ROWLAND S. J. Volatile fatty acids and lactic acid in the rumen of dairy cows receiving a variety of diets. Br J Nutr. 1957;11(3):288–298. doi: 10.1079/bjn19570046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P. Bacterial species of the rumen. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Sep;23(3):125–153. doi: 10.1128/br.23.3.125-153.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., ROBINSON I. M., LINDAHL I. L. A note on the flora and fauna in the rumen of steers fed a feedlot bloat-provoking ration and the effect of penicillin. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Nov;9:511–515. doi: 10.1128/am.9.6.511-515.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladen H. A., Bryant M. P., Doetsch R. N. A Study of Bacterial Species from the Rumen Which Produce Ammonia from Protein Hydrolyzate. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Mar;9(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/am.9.2.175-180.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. B. The relative rates of absorption of the volatile acids from the rumen and their relationship to ketosis. Cornell Vet. 1951 Apr;41(2):115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall E. I. Studies on ruminant saliva. 1. The composition and output of sheep's saliva. Biochem J. 1948;43(1):99–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUFENER W. H., Jr, NELSON W. O., WOLIN M. J. Maintenance of the rumen microbial population in continuous culture. Appl Microbiol. 1963 May;11:196–201. doi: 10.1128/am.11.3.196-201.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLYTER L. L., NELSON W. O., WOLIN M. J. MODIFICATIONS OF A DEVICE FOR MAINTENANCE OF THE RUMEN MICROBIAL POPULATION IN CONTINUOUS CULTURE. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:374–377. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.374-377.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]