Abstract
A system for studying the effects of relative humidity (RH) and temperature on biological aerosols, utilizing a modified toroid for a static aerosol chamber, is described. Studies were conducted at 23 C and at three RH levels (10, 35, and 90%) with four viruses (Newcastle disease virus, infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus, vesicular stomatitis virus, and Escherichia coli B T3 bacteriophage). Virus loss on aerosol generation was consistently lower at 90% than at 10 or 35% RH. When stored at 23 C, Newcastle disease virus and vesicular stomatitis virus survived best at 10% RH. Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus and E. coli B T3 bacteriophage survived storage at 23 C best at 90% RH.
Full text
PDF

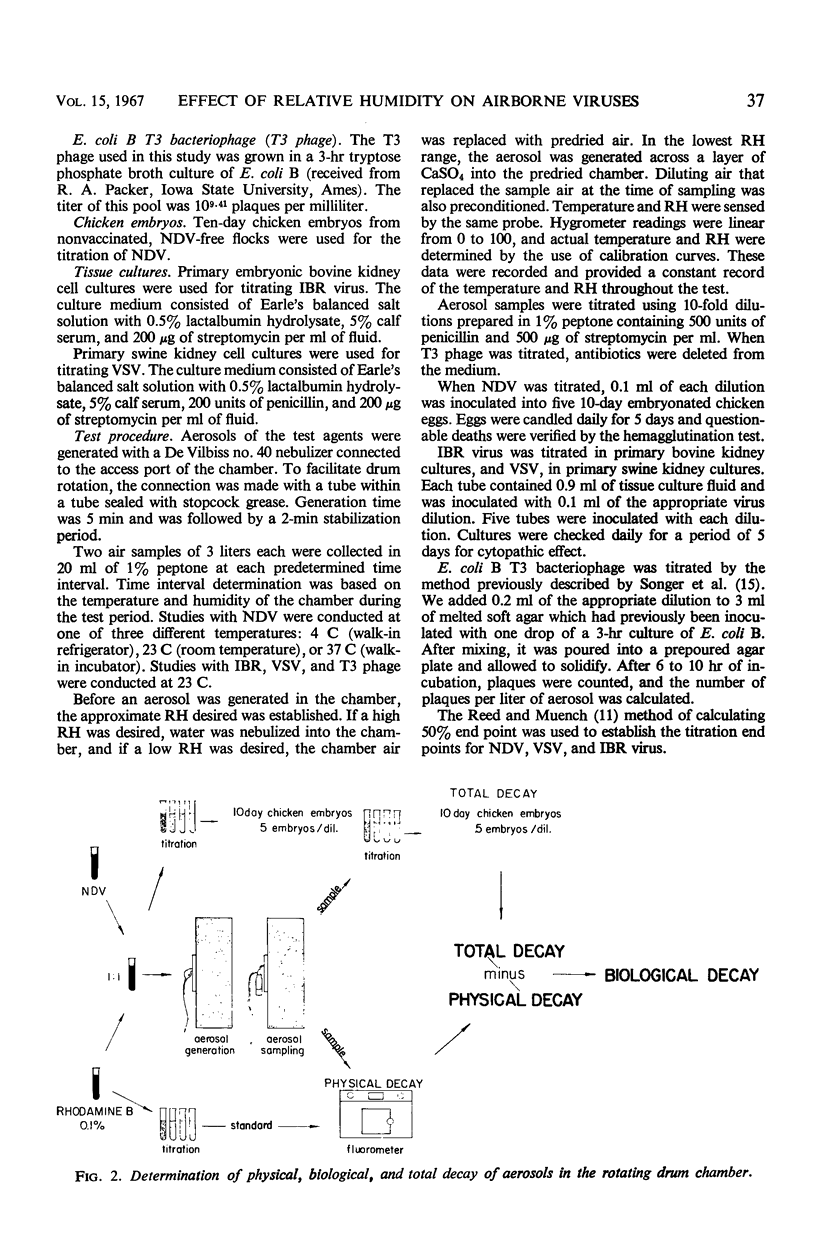

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FERRY R. M., MAPLE T. G. Studies of the loss of viability of stored bacterial aerosols. I. Micrococcus candidus. J Infect Dis. 1954 Sep-Oct;95(2):142–159. doi: 10.1093/infdis/95.2.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG L. J., WATKINS H. M., BOERKE E. E., CHATIGNY M. A. The use of a rotating drum for the study of aerosols over extended periods of time. Am J Hyg. 1958 Jul;68(1):85–93. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODLOW R. J., LEONARD F. A. Viability and infectivity of microorganisms in experimental airborne infection. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Sep;25:182–187. doi: 10.1128/br.25.3.182-187.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARPER G. J. Airborne micro-organisms: survival tests with four viruses. J Hyg (Lond) 1961 Dec;59:479–486. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400039176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEMMES J. H., WINKLER K. C., KOOL S. M. Virus survival as a seasonal factor in influenza and polimyelitis. Nature. 1960 Oct 29;188:430–431. doi: 10.1038/188430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHECHMEISTER I. L., GOLDBERG L. J. Studies on the experimental epidemiology of respiratory infections. II. Observations on the behavior of aerosols of Streptococcus zooepidemicus. J Infect Dis. 1950 Sep-Oct;87(2):117–127. doi: 10.1093/infdis/87.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHECHMEISTER I. L. Studies on the experimental epidemiology of respiratory infections. III. Certain aspects of the behavior of type A influenza virus as an air-borne cloud. J Infect Dis. 1950 Sep-Oct;87(2):128–132. doi: 10.1093/infdis/87.2.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SONGER J. R., SULLIVAN J. F., HURD J. W. TESTING AIR-FILTERING SYSTEMS. I. PROCEDURE FOR TESTING HIGH-EFFICIENCY AIR FILTERS ON EXHAUST SYSTEMS. Appl Microbiol. 1963 Sep;11:394–397. doi: 10.1128/am.11.5.394-397.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB S. J. Factors affecting the viability of air-borne bacteria. II. The effect of chemical additives on the behavior of air-borne cells. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Feb;6:71–87. doi: 10.1139/m60-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB S. J. Factors affecting the viability of air-borne bacteria. III. The role of bonded water and protein structure in the death of air-borne cells. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Feb;6:89–105. doi: 10.1139/m60-011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFE E. K., Jr Quantitative characterization of aerosols. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Sep;25:194–202. doi: 10.1128/br.25.3.194-202.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells W. F., Zappasodi P. THE EFFECT OF HUMIDITY ON BETA STREPTOCOCCI (GROUP C) ATOMIZED INTO AIR. Science. 1942 Sep 18;96(2490):277–278. doi: 10.1126/science.96.2490.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




