Abstract
Background
This study examined Sal-like protein (SALL)3 methylation profiles of head and neck cancer (HNSCC) patients at diagnosis and follow-up and evaluated their prognostic significance and value as a biomarker. SALL3 expression was examined in a panel of cell lines by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The methylation status of the SALL3 promoter was examined by quantitative methylation-specific PCR.
Results
SALL3 promoter methylation was associated with transcriptional inhibition and was correlated with disease recurrence in 64.8% of cases, with an odds ratio of 1.914 (95% confidence interval: 1.157–3.164; P = 0.011) by multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression analysis. SALL3 promoter hypermethylation showed highly discriminatory receiver operator characteristic curve profiles that clearly distinguished HNSCC from adjacent normal mucosal tissue, and was correlated with reduced disease-free survival (DFS) (log-rank test, P = 0.01). Hypermethylation of tumor-related genes was higher among patients with SALL3 methylation than among those without methylation (P < 0.001). Furthermore, SALL3 hypermethylation was associated with expression of TET1, TET2, and DNMT3A genes.
Conclusions
This study suggests that CpG hypermethylation is a likely mechanism of SALL3 gene inactivation, supporting the hypothesis that the SALL3 gene may play a role in the tumorigenesis of HNSCC and may serve as an important biomarker.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13148-017-0363-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: SALL3, Hypermethylation, Tumor-suppressor genes, Head and neck cancer, Biomarker, Real-time PCR
Background
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a broad disease that encompasses epithelial malignancies arising in the paranasal sinuses, nasal cavity, oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx [1]. Risk factors for HNSCC development include tobacco use, alcohol consumption, sexual promiscuity, and human papilloma virus (HPV) infection [2, 3]. At least 50% of patients with locally advanced HNSCC develop local or distant failure, which is usually detected within the first 2 years of treatment [1]. To improve patient outcomes, it is necessary to identify reliable biomarkers that provide sufficient prognostic power for effective clinical management of this disease [3, 4].
Spalt like transcription factor 3 (SALL3) encodes a C2H2-type zinc-finger protein in a family of evolutionarily conserved genes present in species such as Drosophila, Caenorhabditis elegans, and vertebrates [5]. Recent studies have investigated the association between SALL3 expression and carcinogenesis. One group demonstrated that SALL3 was silenced by DNA methylation and that the protein interacts with DNA methyltransferases 3 alpha (DNMT3A) in hepatocellular carcinoma [6]; another report showed that SALL3 hypermethylation reduced the level of SALL3 mRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma [7]; and aberrant hypermethylation of SALL3 along with HPV infection was found to contribute to carcinogenesis in cervical cancer [8].
Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) on chromosome 18q, which is observed in a large proportion of HNSCC cases, is associated with advanced stage and decreased survival [9, 10], suggesting that one or more genes on this chromosome are important for tumorigenesis [9, 11]. The missing portion of 18q23 can vary from 53% (D18S461) to 75% (D18S70), and encompasses the SALL3 and galanin receptor type I (GALR1) locus [12]. Our preliminary analyses have indicated that methylation-induced GALR1 gene silencing is a critical event in HNSCC progression [13] associated with LOH of 18q [12], and that activation of GALR1 signaling suppresses tumor cell proliferation [14]. The findings are consistent with the notion that inactivation or loss of one or more genes on 18q contributes to aggressive tumor behavior in HNSCC.
SALL3 promoter hypermethylation has been linked to loss of gene expression; we speculated that this a critical event in the development of HNSCC. To test this hypothesis, we investigated the methylation status of SALL3 in 165 HNSCC cases at diagnosis and during follow-up to assess its clinical significance and potential as a prognostic biomarker for tumor recurrence and patient survival. We suggest that methylation-induced silencing of SALL3 facilitates methylation of tumor-related genes, leading to de novo DNA methylation of DNMT3s and ten-eleven translocation (TET) family genes that potentiates enzymatic conversion of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC).
Methods
Tumor samples and cell lines
A total of 236 primary HNSCC specimens were obtained during surgery at the Department of Otolaryngology of Hamamatsu University School of Medicine. Clinical information including age, gender, tumor location, smoking status, alcohol consumption, tumor size, lymph node status, and tumor stage was obtained from clinical records. Tumor stage was adapted to the 7th edition of the TNM system. The mean patient age was 65.4 years (range 32–93 years), and the male: female ratio was 198:38. Primary tumors were located in the oral cavity (n = 73), hypopharynx (n = 61), larynx (n = 52), oropharynx (n = 41), and nasal cavity (n = 9). The primary endpoints of this study were disease-free survival (DFS). A total of 165 primary HNSCC patients were surveilled for up to 3 years after initial treatment. Patients provided written, informed consent for participation in the study and the protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Boards at the Hamamatsu University School of Medicine. DNA and cDNA from 11 University of Michigan squamous cell carcinoma (UM-SCC) cell lines, 99 F fibroblasts, and HOK-16B cells were provided by Dr. Thomas E. Carey of the University of Michigan. Normal human keratinocytes (NHK) were a gift from Dr. No Hee Park of the University of California at Los Angeles School of Dentistry [15]. For reactivation of SALL3 expression, cultures were incubated for 48 h with 5-azacytidine (15 μg/ml, A2385; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor [13].
Bisulfite modification and quantitative methylation-specific PCR (qMSP)
Bisulfite modification of genomic DNA was carried out as previously described. [16] SALL3 promoter methylation was assessed by qMSP with the TP800 Thermal Cycler Dice Real-Time System (Takara Bio, Otsu, Japan) using the primer sequences shown in Additional file 1: Table S1. SALL3 CpG islands and regions analyzed by qMSP are shown in Fig. 1a. We tested three different primer sets to identify the pair that would most reliably predict DNA methylation. SALL3 region 1, 2, and 3 primers amplified sequences upstream of, around, and downstream of the transcription start site (TSS), respectively (i.e., P1, P2, and P3, respectively). A standard curve was generated using serial dilutions of EpiScope Methylated HeLa genomic DNA (3520; Takara), with fully methylated (FM) DNA used as a control. The normalized methylation value (NMV) was defined as follows: NMV = (SALL3-S/SALL3-FM)/(ACTB-S/ACTB-FM), where SALL3-S and SALL3-FM represent SALL3 methylation levels in sample and universal methylated DNAs, respectively, and ACTB-S and ACTB-FM correspond to β-actin in sample and universal methylated DNAs, respectively [17]. For amplification reactions, 2 μL (0.01 μg/μL) of bisulfite treatment of genomic DNA, 12.5 μL of SYBR® Premix DimerEraser TM Perfect Real Time (TaKaRa, Tokyo, Japan), and 0.5 μL (10 μM) of each primer were added to a final volume of 25 μL. The PCR conditions were as follows: one denaturing cycle at 95 °C for 10 s, followed by 40 cycles of denaturing at 95 °C for 5 s, and annealing/extension at 58 °C for 30 s (two-step reaction). Dissociation curves are carried out at the end of a PCR experiment by following a 3-step procedure (Additional file 2: Figure S1).
Fig. 1.
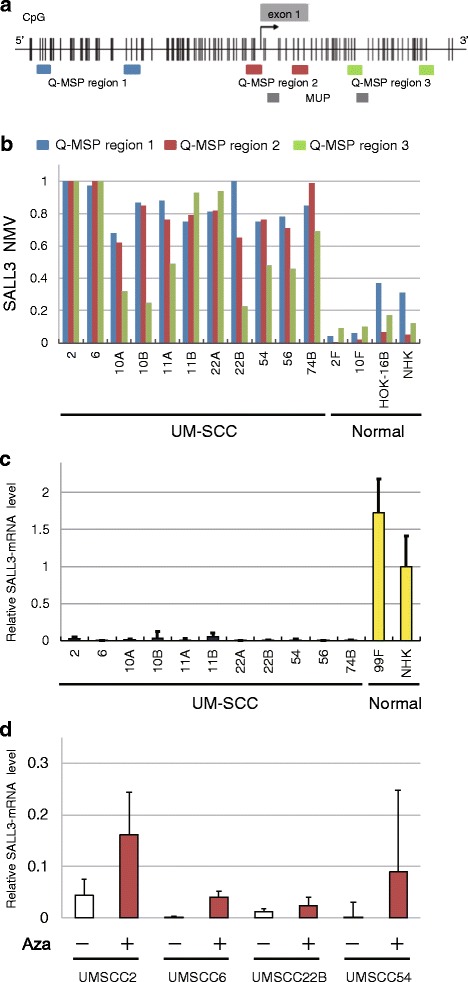
Schematic representation of SALL3 gene methylation analysis by qMSP and evaluation of SALL3 expression by qRT-PCR in UM-SCC cell lines. a Colored boxes indicate the three regions examined by qMSP (P1, blue box; P2, red box; P3, green box). Grayed boxes indicate the regions examined by MUP. The bent arrow indicates the TSS. CpG sites are indicated by black vertical lines. The gray box denotes the exon 1. b qMSP of the SALL3 promoter region in HNSCC cell lines. Genomic DNA of non-malignant cells was included as a control (P1, blue box; P2, red box; P3, green box). c Relative mRNA expression level of SALL3, as determined by qRT-PCR in 11 UM-SCC and two normal cell lines. d Effect of 5-azacytidine on SALL3 expression in four cell lines with densely methylated SALL3, as evaluated by qRT-PCR. Controls were cells were similarly treated but without 5-azacytidine
MSP/unmethlylation-specific PCR (UMSP) analysis and methylation-unspecific qPCR (MUP) assay
Bisulfite-treated DNA was PCR-amplified using two MSP/UMSP primer and MUP primer pairs targeting the SALL3 gene promoter region; the sequences are provided in Additional file 1: Table S1. The PCR conditions were 94 °C for 5 min; 39 cycles at 94 °C for 30 s, 58 °C (MSP primer for methylated DNA detection) or 54 °C (UMSP primer for unmethylated DNA detection) for 30 s, and 72 °C for 40 s; and 72 °C for 5 min. The 106-bp PCR products were separated by gel electrophoresis on a 9% polyacrylamide gel and visualized by staining with ethidium bromide.
Methylation analysis by droplet digital (dd) PCR
SALL3 methylation was confirmed using qMSP P2 primers and the QX200 Droplet Digital PCR system (1864001JA; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA); the reaction was run in duplicate and samples were transferred one column at a time to an 8-channel Droplet Generator Cartridge (1864008; Bio-Rad). Droplet Generator Oil (1863005; Bio-Rad) was then added, and droplets were produced using a QX200 Droplet Generator (1864002; Bio-Rad). After amplification, the PCR plate was placed in the QX200 Droplet Reader (1864003; Bio-Rad) and droplets were subsequently confirmed as being either positive or negative for fluorescence/amplification. Data were analyzed using QuantaSoft software (18640011; BioRad).
RNA extraction and quantitative reverse transcription (qRT-)PCR of SALL3, DNMT3A, DNMT3B, TET1, TET2, and TET3
Total RNA was isolated with RNeasy Plus Mini kit (74134; Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA), and cDNA was synthesized with ReverTra Ace qPCR RT kit (FSQ-101; Toyobo, Osaka, Japan). [17] Primer sequences are shown in Additional file 1: Table S1. Target mRNA expression was compared between samples by normalization to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) mRNA expression.
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data
DNA methylation and mRNA expression data for invasive HNSCC were collected in July 2016 from MethHC, a database of DNA methylation and gene expression in human cancer (http://methhc.mbc.nctu.edu.tw/php/index.php) [18]. DNA methylation data obtained using the Infinium HumanMethylation450 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) are shown as β values.
Analysis of high-risk HPV status
The HPV status was evaluated using the HPV Typing Set (Takara Bio., Tokyo, Japan), a PCR primer set specifically designed to identify HPV genotypes −16, −18, −31, −33, −35, −52, and −58 in genomic DNA. The PCR HPV Typing Set method was performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The PCR products were separated using 9% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and stained with ethidium bromide.
Data analysis and statistics
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed using NMVs for the 36 HNSCC specimens and adjacent normal mucosal tissue samples. Differences in SALL3 methylation levels between tumor and normal tissues were compared by the paired t test. A Spearman correlation analysis was performed to evaluate interactions between SALL3 expression and methylation of each primer set. The association between discrete variables and SALL3 methylation was tested by Fisher’s exact probability and Student t tests. DFS curves were constructed by the Kaplan-Meier method and were evaluated by the log-rank test. Cox’s proportional hazards regression analysis for age, gender, smoking status, alcohol consumption, tumor stage, and SALL3 methylation status was performed to determine the multivariate predictive value of prognostic factors. Differences were considered as significant when the probability was less than 0.05. Statistical analyses were performed using Stat-Mate IV (ATMS Co., Tokyo, Japan).
Results
SALL3 expression in UM-SCC cells is correlated with promoter methylation
To determine whether the SALL3 promoter is methylated in HNSCC, qMSP analysis was carried out on three regions of bisulfite-treated DNA from UM-SCC cell lines, fibroblasts, and NHKs. In all cancer cell lines with reduced SALL3 expression, the NMV of SALL3 was higher than that in normal cell lines (Fig. 1b); moreover, the absence of SALL3 expression was associated with hypermethylation. In contrast, normal fibroblasts and NHKs were SALL3-positive (Fig. 1c). Treatment with 5-azacytidine resulted in upregulation of SALL3 (Fig. 1d).
SALL3 promoter methylation status was analyzed in 36 cancerous and paired noncancerous mucosae by qMSP. Promoter methylation levels were represented by NMVs, which is the ratio of methylated DNA at the target sequence in each specimen to fully methylated control DNA. SALL3 methylation status was assessed using three sets of primers (P1: median NMV = 0.269 vs. 0.030, P < 0.001; P2: median NMV = 0.285 vs. 0.056, P < 0.001; P3: median NMV = 0.314 vs. 0.058, P < 0.001) (Fig. 2a, c, e). The ROC curves showed similar areas under the curve (AUC) (P1: 0.7407, P2: 0.7863, and P3: 0.7832) (Fig. 2b, d, f). The Spearman analysis revealed that SALL3 expression in 83 HNSCC cases and paired normal tissue was negatively correlated with P1 NMV (ρ = −0.1882, P = 0.0160), P2 NMV (ρ = −0.2835, P = 0.0019), and P3 NMV (ρ = −0.192, P = 0.0211) (Additional file 3: Figure S2A–C). P2 showed the maximum AUC and Spearman’s rho. The cutoff NMV (0.11) for P2 was identified from the ROC curve to maximize sensitivity (58.3%) and specificity (91.7%) (Fig. 2d).
Fig. 2.
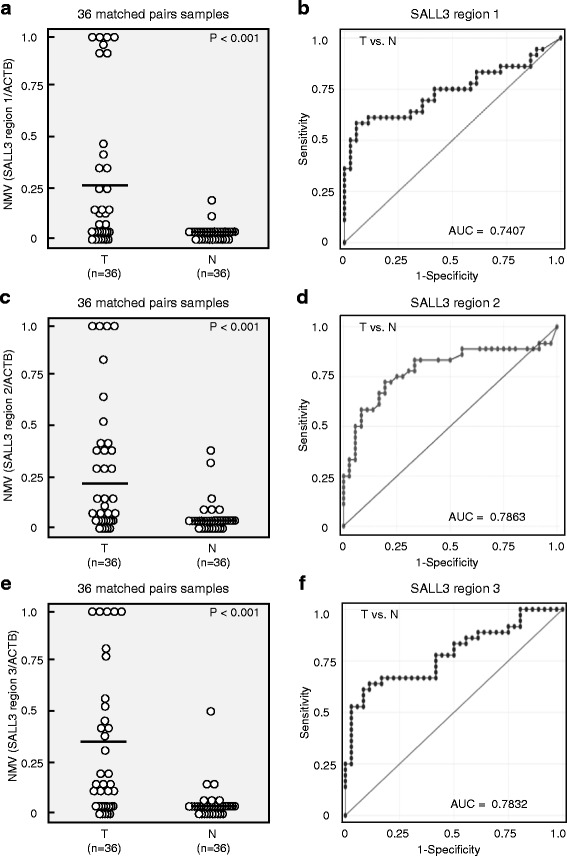
Pattern of methylation in matched pairs of head and neck tumors and adjacent normal mucosal tissues, and ROC curve analysis of NMV. a SALL3-P1 NMVs of head and neck tumors were higher than those of adjacent normal mucosal tissues (P < 0.001). b Area under the ROC curve (AUROC) for SALL3-P1 was 0.7407. c A higher frequency and degree of SALL3-P2 methylation was observed in head and neck tumors than in matched normal mucosae (P < 0.001). d AUROC value for SALL3-P2 was 0.7863. At the cutoff value of 0.11, sensitivity was 58.3% and specificity was 91.7%. e SALL3-P3 NMVs of head and neck tumors were higher than those of paired adjacent normal mucosae (P < 0.001) f AUROC value for SALL3-P3 was 0.7832
SALL3 methylation status in tumor samples
Among 236 DNA samples from untreated primary tumors examined with P2, a specimen was classified as methylated when the NMV exceeded 0.11. The SALL3 promoter was methylated in 153/236 (64.8%) cases and unmethylated in 83/236 (35.2%) cases. There was no association between SALL3 promoter hypermethylation and other clinical characteristics (Table 1, Additional file 4: Figure S3).
Table 1.
SALL3 gene methylation status in primary samples of HNSCC
| Patient and tumor characteristics (n = 236) | Methylation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Present (n = 153) | Absent (n = 83) | P value | |
| Agea | |||
| 70 and older (82) | 56 | 26 | 0.475 |
| Under 70 (154) | 97 | 57 | |
| Sexa | |||
| Male (198) | 126 | 72 | 0.460 |
| Female (38) | 27 | 11 | |
| Smoking statusa | |||
| Smoker (174) | 116 | 58 | 1 |
| Nonsmoker (62) | 37 | 25 | |
| Alcohol intakea | |||
| Ever (172) | 112 | 60 | 1 |
| Never (64) | 41 | 23 | |
| Tumor sizea | |||
| T1-2 (109) | 71 | 38 | 1 |
| T3-4 (127) | 82 | 45 | |
| Lympho-node statusa | |||
| N0 (102) | 67 | 35 | 0.891 |
| N+ (134) | 86 | 48 | |
| Stagea | |||
| I, II, III (105) | 68 | 37 | 1 |
| IV (131) | 85 | 46 | |
| HPV status | |||
| Positive (29) | 18 | 11 | 1 |
| Negative (199) | 130 | 69 | |
| Indeterminate (8) | |||
aFisher’s exact probability test
SALL3 promoter methylation predicts poor patient outcome
Kaplan–Meier plots revealed that methylation of SALL3 and other genes in 165 tumors were related to DFS duration in some patients (log-rank test, P = 0.01) (Fig. 3a). SALL3 methylation status in patients with T1 and T2, without lymph node metastasis, or Stage I and II tumors was not related to outcome (Fig. 3b, d, f). Patients with T3 and T4, lymph node metastasis, and Stage III and IV tumors had decreased DFS as compared to those without SALL3 methylation (P = 0.024, P = 0.029, and P = 0.008, respectively) (Fig. 3c, e, g). Kaplan-Meier survival curves using median methylation as a cut-off was not statistically significant (Additional file 5: Figure S4A, B). In other words, patients with advanced cancer had worse prognosis. In addition, results of the multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression analysis—which included age, gender, alcohol consumption, smoking status, and tumor stage—indicated that survival rates were 1.914 times lower in patients with SALL3 gene methylation than in those without methylation (P = 0.011) (Table 2). Furthermore, Cox’s proportional hazards regression analysis including HPV status was lower in patients with SALL3 gene methylation than in those without methylation (P = 0.009) (Additional file 6: Table S2). These results indicate that SALL3 promoter methylation is a predictor of poor outcome in HNSCC patients.
Fig. 3.
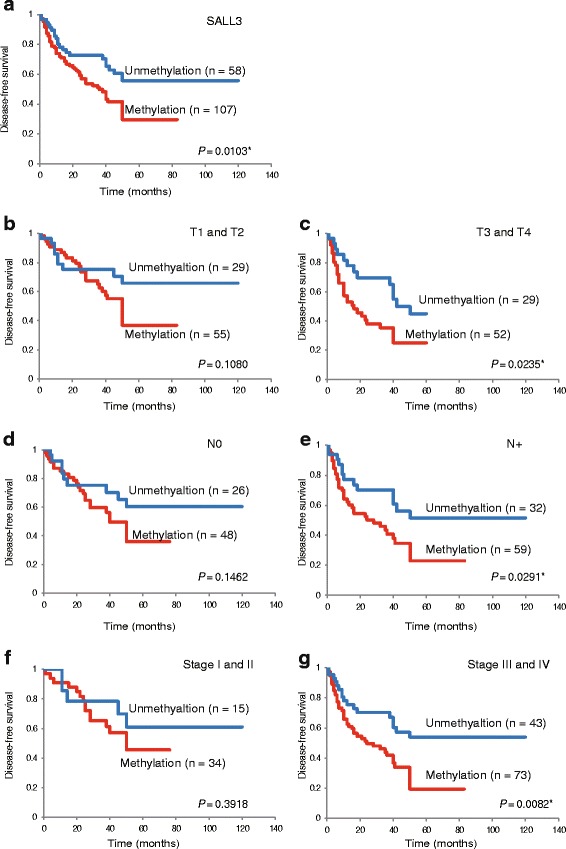
Kaplan-Meier survival curves for HNSCC patients. DFS for (a) all 165 HNSCC cases, (b) tumor size in T1 and T2 cases (n = 84), (c) tumor size T3 and T4 cases (n = 81), (d) lymph node status N0 cases (n = 74), (e) lymph node status N+ cases (n = 91), (f) stage I and II cases (n = 49), and (g) stage III and IV cases (n = 116). Gray and black lines indicate patients without and with methylation, respectively
Table 2.
Multivariate analysis of factors affecting survival using Cox proportional hazards model in 165 HNSCC patients
| Disease-free survival | ||
|---|---|---|
| Variables | HR (95% CI) | P |
| Age | ||
| 70 and older vs. <70 | 1.062 (0.659–1.711) | 0.8038 |
| Gender | ||
| Male vs. female | 1.170 (0.644–2.125) | 0.6064 |
| Alcohol exposure | ||
| Ever vs. never | 1.015 (0.565–1.823) | 0.9606 |
| Smoking status | ||
| Smoker vs. nonsmoker | 1.339 (0.752–2.383) | 0.3216 |
| Stage | ||
| I, II, III, vs. IV | 2.356 (1.480–3.751) | 0.0003* |
| SALL3 methylation | ||
| Yes vs. no | 1.914 (1.157–3.164) | 0.0114* |
HR hazard ratio, 95% CI 95% confidence interval
SALL3 promoter methylation is associated with HNSCC by MSP/UMSP, ddMSP analyses and methylation-unspecific qPCR (MUP) assay
Primary tumor samples were tested with both sets of primers (MSP and UMSP) for P2. All 12 samples that showed promoter hypermethylation by qMSP (Samples 5, 6, 14, 37, 39, 40, 43. 46, 55, 59, 61, and 64) had predominantly methylated alleles (Additional file 7: Figure S5A). Cancerous and paired noncancerous mucosae were also analyzed by the ddMSP assay; the results showed that all cancerous samples (T) in which SALL3 methylation was detected by qMSP showed positive signals. On the other hand, most noncancerous mucosa samples (N) showed no SALL3 methylation (Additional file 7: Figure S5B). A MUP assay targeting a CpG-free gene locus close to SALL3 as a reference assay showed positive signals (Additional file 7: Figure S5C).
Methylated SALL3 along with other molecular markers is associated with patient survival
We evaluated the methylation status of deleted in colorectal cancer (DCC), galanin receptor (GALR)1, p16, Ras association domain family 1 isoform A, E-cadherin (CDH1), H-cadherin (CDH13), O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT), and death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) genes, which are involved in methylation. SALL3 methylation was correlated with GALR1, CDH1, CDH13, and DAPK methylation (P < 0.001, P = 0.002, P = 0.005, and P < 0.001, respectively) (Additional file 8: Table S3). Hypermethylation of tumor-related genes was higher among patients with SALL3 methylation than among those without methylation (P < 0.001) (Additional file 9: Figure S6).
SALL3 methylation level and TET and DNMT3 expression in HNSCC specimens
We examined TETI, TET2, TET3, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B mRNA levels by qRT-PCR. TET1, TET2, and DNMT3A expression was associated with SALL3 methylation levels (P = 0.011, 0.015, and 0.027, respectively) (Fig. 4a, b, d). However, TET3 and DNMT3B expression was not associated with SALL3 methylation level (P = 0.064 and P = 0.645, respectively) (Fig. 4c, e).
Fig. 4.
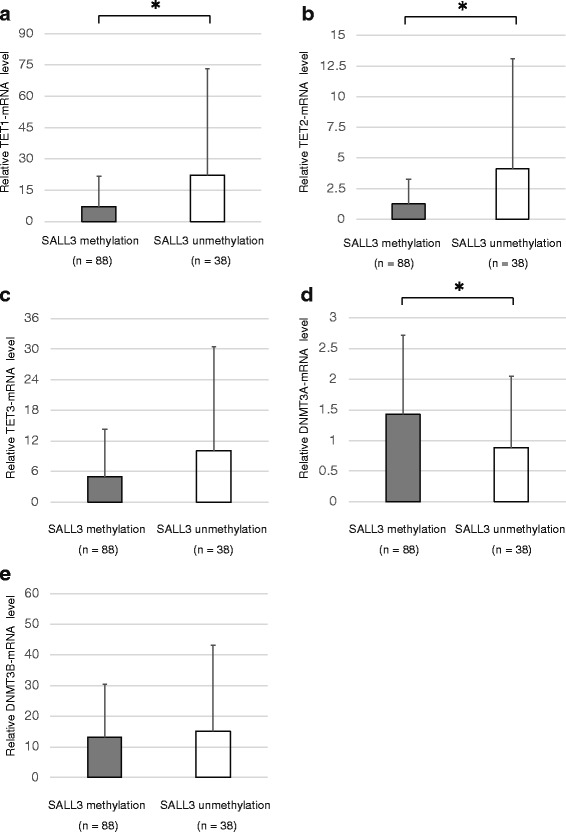
Correlation between SALL3 methylation status and TET and DNMT3 mRNA expression in HNSCC patients. a TET1 expression. b TET2 expression. c TET3 expression. d DNMT3A expression. e DNMT3B expression
External validation of TCGA data
HNSCC data from TCGA were examined for SALL3 DNA methylation. SALL3 methylation showed an average β value of 0.350 in the HNSCC TCGA cohort as compared to 0.098 in normal samples (P < 0.001, Student’s t test) (Additional file 10: Figure S7A). Consistent with our data, there was a strong negative correlation between SALL3 DNA methylation and expression (Additional file 10: Figure S7B). Together with our previous finding that the region around the TSS of the SALL3 gene exhibits promoter activity, these results suggest that HNSCC is characterized by epigenetic silencing of SALL3 via promoter hypermethylation. Furthermore, SALL3 DNA methylation was significantly associated with age and smoking status (P = 0.007 and P = 0.030, respectively) (Additional file 11: Table S4).
Moreover, using mRNA expression data, p16-negative tumors were significantly lower SALL3 mRNA expression than p16-positive tumors (5.23 ± 15.94 vs. 63.39 ± 117.38, P < 0.001) (Additional file 12: Table S5). Kaplan–Meier analysis revealed that the SALL3 methylation and expression levels were not significantly associated with the overall survival. (Additional file 13: Figure S8) Furthermore, the methylation status of the other eight individual genes was not associated with outcome (Additional file 14: Figure S9).
Discussion
Clarifying the epigenetic regulation of SALL3 can provide insights into the mechanisms of tumorigenesis and the risk of disease recurrence. To this end, the present study investigated SALL3 promoter methylation profiles in 236 HNSCC patient tissues. We found that hypermethylation of CpG islands in the SALL3 promoter was independently associated with aggressive tumor behavior, suggesting that SALL3 acts as a tumor suppressor gene and can serve as a prognostic biomarker in HNSCC.
SALL3 encodes a spalt-like homeoprotein containing double zinc-finger domains. The SALL3 locus on human chromosome 18q23 is likely included in 18q deletion syndrome [19]. In mouse, Sall3 heterozygous knockouts (Sall3 +/−) are indistinguishable from wild-type littermates and are fertile, while homozygous mutants (Sall3 −/−) fail to survive after 12 h of extrauterine life [20]. Absence of Sall3 may lead to palate deficiency, cranial nerve abnormalities, and perinatal lethality [20]. In humans, this deletion is associated with hearing loss, cardiac defects, mental retardation, midfacial hypoplasia, delayed growth, and limb abnormalities [21, 22].
Three additional SALL genes have been identified thus far: SALL1 on chromosome 16q12.1, SALL2 on chromosome 14q11.2, and SALL4 on chromosome 20q13.2 [20]. SALL1 hypermethylation has been described in several malignancies, including non-small cell lung cancer, prostate tumors [23], chronic lymphocytic leukemia [24], and acute lymphoblastic leukemia [25]. SALL2 binds to the neurotrophin receptor and regulates neuronal development [26]. LOH in the region of 14q12 harboring the SALL2 gene and SALL2 promoter methylation have been reported in ovarian cancer [27]. SALL4 is important for maintaining a pluripotent state in mouse embryonic stem cells [28–30], and hypomethylation of the promoter is a common event in myelodysplastic syndrome [31]. The presence of epigenetic repressors and/or the enzymatic activities of DNMT, methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 2, and histone deacetylase 1 are associated with SALL4 repression [32].
Exposure to carcinogens such as HPV, tobacco, and alcohol is associated with epigenetic gene inactivation in human cancers, including head and neck cancer [33]. Recently, oncogenic viruses such as HPV and Epstein-Barr and hepatitis viruses were found to induce oncogenic changes to the DNA methylome by increasing the expression and activity of DNMT3A [34–36]. DNMTs play an important role in genomic integrity, disruption of which may result in chromosomal instability and tumor progression [37]. DNMT levels—especially those of DNMT3A and DNMT3B—are often increased in various cancer tissues and cell lines, which may partly account for the hypermethylation of CpG-rich regions in tumor suppressor gene promoters in various malignancies [38]. More recently, methyl donor depletion significantly increased expression of DNMT3A, TET, and key pro-apoptotic genes such as DAPK [39].
TET proteins regulate the dynamic conversion of cytosine (C), 5mC, and 5hmC, and consequently, the balance between DNA methylation and demethylation [40]. Missense and truncating mutations in TET genes are present in nearly all solid tumor types at a relatively low frequency [41]. It was recently reported that TET2 expression is lower in esophageal SCC than in normal epithelium and associated with 5-hmC expression; it was speculated that TET2 is more significant in esophageal SCC development than TET1 and TET3 [42]. There is little known about the role of TET family genes in HNSCC.
The DNA methylation profile of a cell is maintained by both the DNA methylation and demethylation pathways [43]. DNA methylation and demethylation occurs either passively or actively. Alterations in 5mC writers, readers, and modifiers that affect their level, all potential mechanisms contributing to altered chromatin composition and structure as well as genome activity and stability and contribute to an overwhelming variety of human diseases [44].
SALL3 is silenced by DNA methylation and the protein directly interacts with DNMT3A in human hepatocellular carcinoma; SALL3 inactivation by DNA methylation was found to accelerate aberrant DNA methylation [6]. Furthermore, suppressed expression of histone methyltransferases, which in turn resulted in a decrease of di- and trimethylated H3K9 around SALL3 genes’ promoter [45]. HPV infection was positively associated with hypermethylation of the SALL3 promoter, and SALL3 mRNA level was lower in HPV-positive as compared to -negative cervical cancer tissues [8]. SALL3 hypermethylation has been reported in several cancers, including in cervical [8] and breast [46] cancers and hepatocellular carcinoma [7]. Thus, detecting aberrant SALL3 methylation can serve as a means of identifying patients at high risk of relapse.
This study suggests that CpG hypermethylation is a likely mechanism of SALL3 gene inactivation, supporting the hypothesis that the SALL3 gene may play a role in the tumorigenesis of HNSCC and may serve as an important biomarker. We demonstrated for the first time that SALL3 mRNA is downregulated in HNSCC owing to DNA methylation; this may be a critical event in HNSCC progression that is associated with DFS. Indeed, SALL3 promoter methylation was increased in tumor tissue as compared to that in noncancerous mucosae from the same patient. SALL3 promoter methylation was associated with disease recurrence. Moreover, transcriptional inactivation of SALL3 was associated with aberrant methylation of other tumor-related genes and TET1, TET2, and DNMT3A levels in HNSCC. Our findings suggest that these methylation markers can be used in clinical practice to identify patients that may benefit from adjuvant therapy after initial surgical treatment; however, this must be confirmed in additional prospective studies in other HNSCC patient groups.
Conclusion
The present study showed that the SALL3 promoter methylation profile appears to be an important marker predicting the clinical outcome of HNSCC. This demonstrates that molecular stratification may predict cancer progression. These findings can benefit HNSCC screening and surveillance algorithms.
Additional files
Q-MSP primer, MSP/UMSP primers, MUP primer, and Q-RT primer list (DOCX 30 kb).
Standard curve plot showing Ct versus initial quantity and dissociation curves. (A) Efficiency of primers of SALL3 gene checked for methylation quantification using dilutions of universal methylated DNAs control. (B) Dissociation curves are carried out at the end of a PCR experiment by following a 3-step procedure (EPS 1413 kb).
Spearman rank correlation between SALL3 expression and promoter methylation status using three SALL3 primer sets.(A) SALL3 mRNA expression was inversely correlated with SALL3-P1 hypermethylation (correlation coefficient = 0.1882, P = 0.0160). (B) SALL3-P2, correlation coefficient = 0.2835, P = 0.0019. (C) SALL3-P3, correlation coefficient = 0.192, P = 0.0211. The Spearman rank correlation for SALL3 obtained using the SALL3-P2 primer pair was used to maximize the correlation coefficient (EPS 1299 kb).
Comparison of normalized methylation value (NMV) amongst selected clinical parameters. The mean NMVs for the different groups were compared by using Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05 (EPS 952 kb).
Kaplan-Meier survival curves for HNSCC patients using median methylation as a cut-off. (A) DFS for all 165 HNSCC cases, high methylation group versus low methylation group. (B) Combined analyses of SALL3 methylation status and HPV status; Hme, high methylation; Lme, low methylation; HPV (+), HPV positive; HPV (−), HPV negative (EPS 797 kb).
Multivariate analysis of factors affecting survival using Cox proportional hazards model in 157 HNSCC patients (DOCX 15 kb).
MSP/UMSP, ddPCR assays and MUP assay. (A) Representative results from the MSP/UMSP assay of SALL3 expression in primary HNSCC showing methylated samples (no. 5, 6, 14, 37, 39, 40, 43, 46, 55, 59, 61, and 64). (B) Representative ddMSP results for tumor (T) and normal (N) samples. (C) Representative MUP results for tumor (T) samples (EPS 1790 kb).
SALL3 Gene Methylation Status in Primary Samples of HNSCC with the methylation of other eight genes (DOCX 21 kb).
Correlation with other tumor-related genes. Comparison of methylation rates in eight genes along with SALL3 in primary HNSCC (EPS 609 kb).
SALL3 DNA methylation and expression data for HNSCC from TCGA database. (A) SALL3 DNA methylation profiles of HNSCC and normal tissue samples (P < 0.001). (B) Spearman rank correlation coefficient () and P values are shown. An inverse correlation was observed between SALL3 methylation and expression in HNSCC (EPS 1321 kb).
SALL3 Gene Methylation levels in TCGA cohort of HNSCC (DOCX 21 kb).
SALL3 mRNA levels in TCGA cohort of HNSCC (DOCX 23 kb).
Overall survival based on SALL3 gene signatures in the TCGA cohort using median methylation as a cut-off. (A) SALL3 DNA methylation profiles of HNSCC. (B) SALL3 mRNA expression profiles of HNSCC. Patients were divided into 2 groups. (EPS 884 kb)
Overall survival curves of other tumor-related genes in the TCGA cohort using median methylation as a cut-off. Overall survival curves of (A) DCC, (B) GALR1, (C) p16, (D) RASSF1A, (E) E-cadherin, (F) H-cadherin, (G) MGMT and (H) DAPK. Patients were divided into two groups (EPS 1548 kb).
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Yuko Mohri for technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (nos. 26462599, 26462600, 16 K11228, and 16 K20239) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets obtained and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
KM contributed to the conceptualization and methodology of the study. YM and TK contributed to the software of the study and vaildation of the study. AI contributed to the validation of the study. DM contributed to the formal analysis of the study. TK and SE contributed to the investigation of the study. HM contributed to the resources of the study. HM and MM wrote the manuscript. KM wrote the original draft. TK reviewed and edited the manuscript., KM visualized the study. HM supervised the study. KM was in charge of the project administration. KM acquired the funding. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was obtained from all patients.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
These tissue samples were obtained with informed written consent following protocols approved by the research ethics board of the Hamamatsu University School of Medicine.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- ACTB
β-actin
- ddPCR
Droplet digital PCR
- DFS
Disease-free survival
- DNMT3
DNA methyltransferases 3
- GALR1
Galanin receptor type I
- GAPDH
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- HNSCC
Head and neck squamous cell cancer
- HPV
Human papilloma virus
- LOH
Loss of heterozygosity
- NHK
Normal human keratinocytes
- NMV
Normalized methylation value
- qMSP
Quantitative methylation-specific PCR
- ROC
Receiver operating characteristic
- SALL3
Sal-like protein 3
- TCGA
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- TET
Ten-eleven translocation
- TSS
Transcription start site
- UMSP
Unmethlylation-specific PCR
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13148-017-0363-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
References
- 1.Argiris A, Karamouzis MV, Raben D, Ferris RL. Head and neck cancer. Lancet. 2008;371(9625):1695–709. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60728-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kumar B, Cordell KG, Lee JS, Worden FP, Prince ME, Tran HH, Wolf GT, Urba SG, Chepeha DB, Teknos TN, et al. EGFR, p16, HPV Titer, Bcl-xL and p53, sex, and smoking as indicators of response to therapy and survival in oropharyngeal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(19):3128–37. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.12.7662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Choong N, Vokes E. Expanding role of the medical oncologist in the management of head and neck cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58(1):32–53. doi: 10.3322/CA.2007.0004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brock MV, Hooker CM, Ota-Machida E, Han Y, Guo M, Ames S, Glockner S, Piantadosi S, Gabrielson E, Pridham G, et al. DNA methylation markers and early recurrence in stage I lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(11):1118–28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0706550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sweetman D, Munsterberg A. The vertebrate spalt genes in development and disease. Dev Biol. 2006;293(2):285–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shikauchi Y, Saiura A, Kubo T, Niwa Y, Yamamoto J, Murase Y, Yoshikawa H. SALL3 interacts with DNMT3A and shows the ability to inhibit CpG island methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29(7):1944–58. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00840-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yang XX, Sun JZ, Li FX, Wu YS, Du HY, Zhu W, Li XH, Li M. Aberrant methylation and downregulation of sall3 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(21):2719–26. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i21.2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wei X, Zhang S, Cao D, Zhao M, Zhang Q, Zhao J, Yang T, Pei M, Wang L, Li Y, et al. Aberrant Hypermethylation of SALL3 with HPV Involvement Contributes to the Carcinogenesis of Cervical Cancer. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0145700. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pearlstein RP, Benninger MS, Carey TE, Zarbo RJ, Torres FX, Rybicki BA, Dyke DL. Loss of 18q predicts poor survival of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1998;21(4):333–9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2264(199804)21:4<333::AID-GCC7>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ, Brakenhoff RH. The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11(1):9–22. doi: 10.1038/nrc2982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Frank CJ, McClatchey KD, Devaney KO, Carey TE. Evidence that loss of chromosome 18q is associated with tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1997;57(5):824–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Takebayashi S, Ogawa T, Jung KY, Muallem A, Mineta H, Fisher SG, Grenman R, Carey TE. Identification of new minimally lost regions on 18q in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2000;60(13):3397–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Misawa K, Ueda Y, Kanazawa T, Misawa Y, Jang I, Brenner JC, Ogawa T, Takebayashi S, Grenman RA, Herman JG, et al. Epigenetic inactivation of galanin receptor 1 in head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(23):7604–13. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kanazawa T, Iwashita T, Kommareddi P, Nair T, Misawa K, Misawa Y, Ueda Y, Tono T, Carey TE. Galanin and galanin receptor type 1 suppress proliferation in squamous carcinoma cells: activation of the extracellular signal regulated kinase pathway and induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Oncogene. 2007;26(39):5762–71. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Park NH, Min BM, Li SL, Huang MZ, Cherick HM, Doniger J. Immortalization of normal human oral keratinocytes with type 16 human papillomavirus. Carcinogenesis. 1991;12(9):1627–31. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.9.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Misawa Y, Misawa K, Kanazawa T, Uehara T, Endo S, Mochizuki D, Yamatodani T, Carey TE, Mineta H. Tumor suppressor activity and inactivation of galanin receptor type 2 by aberrant promoter methylation in head and neck cancer. Cancer. 2014;120(2):205–13. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Misawa K, Mochizuki D, Imai A, Endo S, Mima M, Misawa Y, Kanazawa T, Carey TE, Mineta H. Prognostic value of aberrant promoter hypermethylation of tumor-related genes in early-stage head and neck cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(18):26087–98. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huang WY, Hsu SD, Huang HY, Sun YM, Chou CH, Weng SL, Huang HD. MethHC: a database of DNA methylation and gene expression in human cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(Database issue):D856–61. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kohlhase J, Hausmann S, Stojmenovic G, Dixkens C, Bink K, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Altmann M, Engel W. SALL3, a new member of the human spalt-like gene family, maps to 18q23. Genomics. 1999;62(2):216–22. doi: 10.1006/geno.1999.6005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Parrish M, Ott T, Lance-Jones C, Schuetz G, Schwaeger-Nickolenko A, Monaghan AP. Loss of the Sall3 gene leads to palate deficiency, abnormalities in cranial nerves, and perinatal lethality. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(16):7102–12. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.16.7102-7112.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Strathdee G, Sutherland R, Jonsson JJ, Sataloff R, Kohonen-Corish M, Grady D, Overhauser J. Molecular characterization of patients with 18q23 deletions. Am J Hum Genet. 1997;60(4):860–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dostal A, Nemeckova J, Gaillyova R. The 18q deletion syndrome and analysis of the critical region for orofacial cleft at 18q22.3. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2009;37(5):272–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2008.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hill VK, Hesson LB, Dansranjavin T, Dallol A, Bieche I, Vacher S, Tommasi S, Dobbins T, Gentle D, Euhus D, et al. Identification of 5 novel genes methylated in breast and other epithelial cancers. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:51. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tong WG, Wierda WG, Lin E, Kuang SQ, Bekele BN, Estrov Z, Wei Y, Yang H, Keating MJ, Garcia-Manero G. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling of chronic lymphocytic leukemia allows identification of epigenetically repressed molecular pathways with clinical impact. Epigenetics. 2010;5(6):499–508. doi: 10.4161/epi.5.6.12179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kuang SQ, Tong WG, Yang H, Lin W, Lee MK, Fang ZH, Wei Y, Jelinek J, Issa JP, Garcia-Manero G. Genome-wide identification of aberrantly methylated promoter associated CpG islands in acute lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2008;22(8):1529–38. doi: 10.1038/leu.2008.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pincheira R, Baerwald M, Dunbar JD, Donner DB. Sall2 is a novel p75NTR-interacting protein that links NGF signalling to cell cycle progression and neurite outgrowth. EMBO J. 2009;28(3):261–73. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bandera CA, Takahashi H, Behbakht K, Liu PC, LiVolsi VA, Benjamin I, Morgan MA, King SA, Rubin SC, Boyd J. Deletion mapping of two potential chromosome 14 tumor suppressor gene loci in ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1997;57(3):513–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yang J, Gao C, Chai L, Ma Y. A novel SALL4/OCT4 transcriptional feedback network for pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 2010;5(5):e10766. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang J, Tam WL, Tong GQ, Wu Q, Chan HY, Soh BS, Lou Y, Yang J, Ma Y, Chai L, et al. Sall4 modulates embryonic stem cell pluripotency and early embryonic development by the transcriptional regulation of Pou5f1. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(10):1114–23. doi: 10.1038/ncb1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhou Q, Chipperfield H, Melton DA, Wong WH. A gene regulatory network in mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(42):16438–43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701014104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lin J, Qian J, Yao DM, Qian W, Yang J, Wang CZ, Chai HY, Ma JC, Deng ZQ, Li Y, et al. Aberrant hypomethylation of SALL4 gene in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk Res. 2013;37(1):71–5. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2012.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yang J, Corsello TR, Ma Y. Stem cell gene SALL4 suppresses transcription through recruitment of DNA methyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(3):1996–2005. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.308734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rubenstein LM, Smith EM, Pawlita M, Haugen TH, Hamsikova E, Turek LP. Human papillomavirus serologic follow-up response and relationship to survival in head and neck cancer: a case-comparison study. Infect Agent Cancer. 2011;6:9. doi: 10.1186/1750-9378-6-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sartor MA, Dolinoy DC, Jones TR, Colacino JA, Prince ME, Carey TE, Rozek LS. Genome-wide methylation and expression differences in HPV(+) and HPV(−) squamous cell carcinoma cell lines are consistent with divergent mechanisms of carcinogenesis. Epigenetics. 2011;6(6):777–87. doi: 10.4161/epi.6.6.16216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kaneda A, Matsusaka K, Aburatani H, Fukayama M. Epstein-Barr virus infection as an epigenetic driver of tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2012;72(14):3445–50. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fan H, Cui Z, Zhang H, Mani SK, Diab A, Lefrancois L, Fares N, Merle P, Andrisani O. DNA demethylation induces SALL4 gene re-expression in subgroups of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with Hepatitis B or C virus infection. Oncogene. 2017;36(17):2435–45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Jin B, Robertson KD. DNA methyltransferases, DNA damage repair, and cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;754:3–29. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-9967-2_1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Subramaniam D, Thombre R, Dhar A, Anant S. DNA methyltransferases: a novel target for prevention and therapy. Front Oncol. 2014;4:80. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hearnden V, Powers HJ, Elmogassabi A, Lowe R, Murdoch C. Methyl-donor depletion of head and neck cancer cells in vitro establishes a less aggressive tumour cell phenotype. Eur J Nutr. 2017. doi:10.1007/s00394-017-1411-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 40.Lian H, Li WB, Jin WL. The emerging insights into catalytic or non-catalytic roles of TET proteins in tumors and neural development. Oncotarget. 2016;7(39):64512–25. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rasmussen KD, Helin K. Role of TET enzymes in DNA methylation, development, and cancer. Genes Dev. 2016;30(7):733–50. doi: 10.1101/gad.276568.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Murata A, Baba Y, Ishimoto T, Miyake K, Kosumi K, Harada K, Kurashige J, Iwagami S, Sakamoto Y, Miyamoto Y, et al. TET family proteins and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6(27):23372–82. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ludwig AK, Zhang P, Cardoso MC. Modifiers and Readers of DNA Modifications and Their Impact on Genome Structure, Expression, and Stability in Disease. Front Genet. 2016;7:115. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.van der Wijst MG, Venkiteswaran M, Chen H, Xu GL, Plosch T, Rots MG. Local chromatin microenvironment determines DNMT activity: from DNA methyltransferase to DNA demethylase or DNA dehydroxymethylase. Epigenetics. 2015;10(8):671–6. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1062204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wu LP, Wang X, Li L, Zhao Y, Lu S, Yu Y, Zhou W, Liu X, Yang J, Zheng Z, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor depsipeptide activates silenced genes through decreasing both CpG and H3K9 methylation on the promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(10):3219–35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01516-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Andersson E, Dahmcke CM, Steven K, Larsen LK, Guldberg P. Filtration Device for On-Site Collection, Storage and Shipment of Cells from Urine and Its Application to DNA-Based Detection of Bladder Cancer. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0131889. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Q-MSP primer, MSP/UMSP primers, MUP primer, and Q-RT primer list (DOCX 30 kb).
Standard curve plot showing Ct versus initial quantity and dissociation curves. (A) Efficiency of primers of SALL3 gene checked for methylation quantification using dilutions of universal methylated DNAs control. (B) Dissociation curves are carried out at the end of a PCR experiment by following a 3-step procedure (EPS 1413 kb).
Spearman rank correlation between SALL3 expression and promoter methylation status using three SALL3 primer sets.(A) SALL3 mRNA expression was inversely correlated with SALL3-P1 hypermethylation (correlation coefficient = 0.1882, P = 0.0160). (B) SALL3-P2, correlation coefficient = 0.2835, P = 0.0019. (C) SALL3-P3, correlation coefficient = 0.192, P = 0.0211. The Spearman rank correlation for SALL3 obtained using the SALL3-P2 primer pair was used to maximize the correlation coefficient (EPS 1299 kb).
Comparison of normalized methylation value (NMV) amongst selected clinical parameters. The mean NMVs for the different groups were compared by using Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05 (EPS 952 kb).
Kaplan-Meier survival curves for HNSCC patients using median methylation as a cut-off. (A) DFS for all 165 HNSCC cases, high methylation group versus low methylation group. (B) Combined analyses of SALL3 methylation status and HPV status; Hme, high methylation; Lme, low methylation; HPV (+), HPV positive; HPV (−), HPV negative (EPS 797 kb).
Multivariate analysis of factors affecting survival using Cox proportional hazards model in 157 HNSCC patients (DOCX 15 kb).
MSP/UMSP, ddPCR assays and MUP assay. (A) Representative results from the MSP/UMSP assay of SALL3 expression in primary HNSCC showing methylated samples (no. 5, 6, 14, 37, 39, 40, 43, 46, 55, 59, 61, and 64). (B) Representative ddMSP results for tumor (T) and normal (N) samples. (C) Representative MUP results for tumor (T) samples (EPS 1790 kb).
SALL3 Gene Methylation Status in Primary Samples of HNSCC with the methylation of other eight genes (DOCX 21 kb).
Correlation with other tumor-related genes. Comparison of methylation rates in eight genes along with SALL3 in primary HNSCC (EPS 609 kb).
SALL3 DNA methylation and expression data for HNSCC from TCGA database. (A) SALL3 DNA methylation profiles of HNSCC and normal tissue samples (P < 0.001). (B) Spearman rank correlation coefficient () and P values are shown. An inverse correlation was observed between SALL3 methylation and expression in HNSCC (EPS 1321 kb).
SALL3 Gene Methylation levels in TCGA cohort of HNSCC (DOCX 21 kb).
SALL3 mRNA levels in TCGA cohort of HNSCC (DOCX 23 kb).
Overall survival based on SALL3 gene signatures in the TCGA cohort using median methylation as a cut-off. (A) SALL3 DNA methylation profiles of HNSCC. (B) SALL3 mRNA expression profiles of HNSCC. Patients were divided into 2 groups. (EPS 884 kb)
Overall survival curves of other tumor-related genes in the TCGA cohort using median methylation as a cut-off. Overall survival curves of (A) DCC, (B) GALR1, (C) p16, (D) RASSF1A, (E) E-cadherin, (F) H-cadherin, (G) MGMT and (H) DAPK. Patients were divided into two groups (EPS 1548 kb).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets obtained and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.


