Abstract
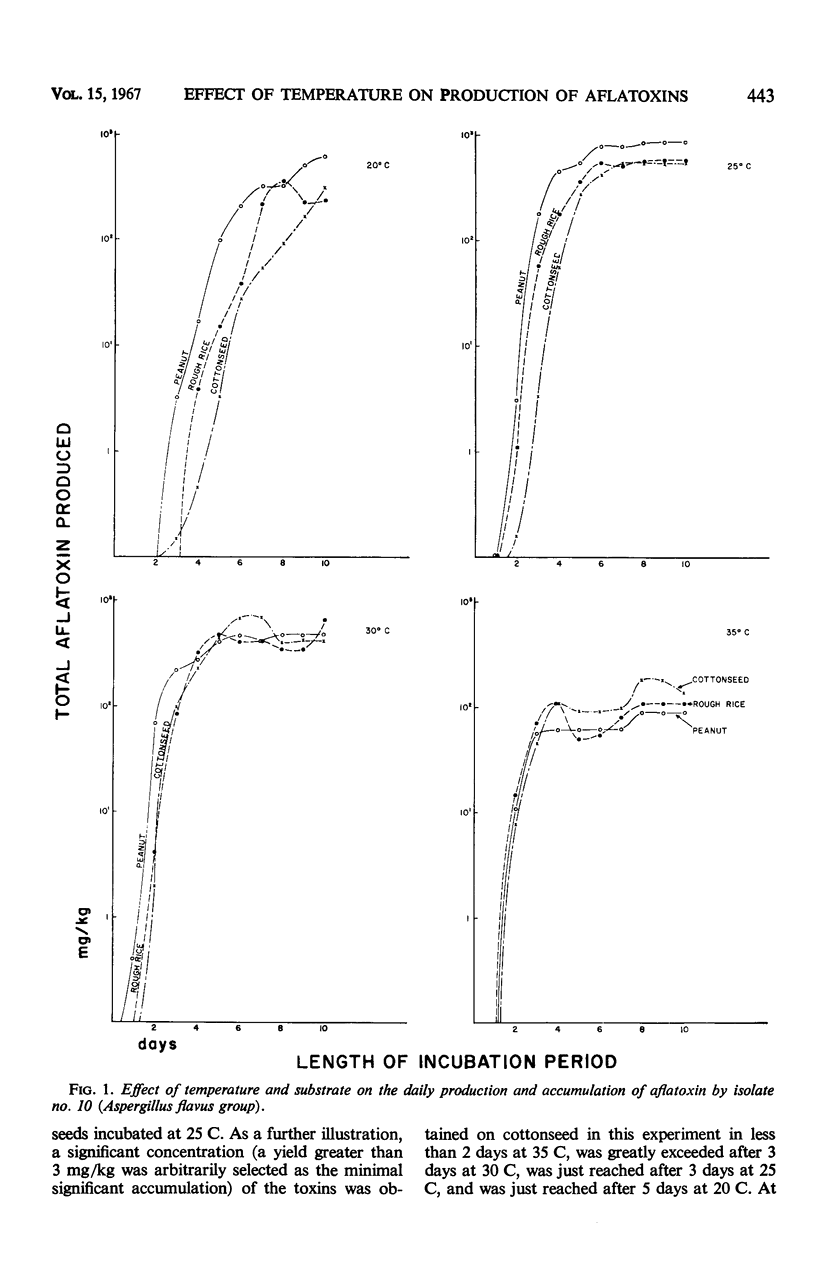
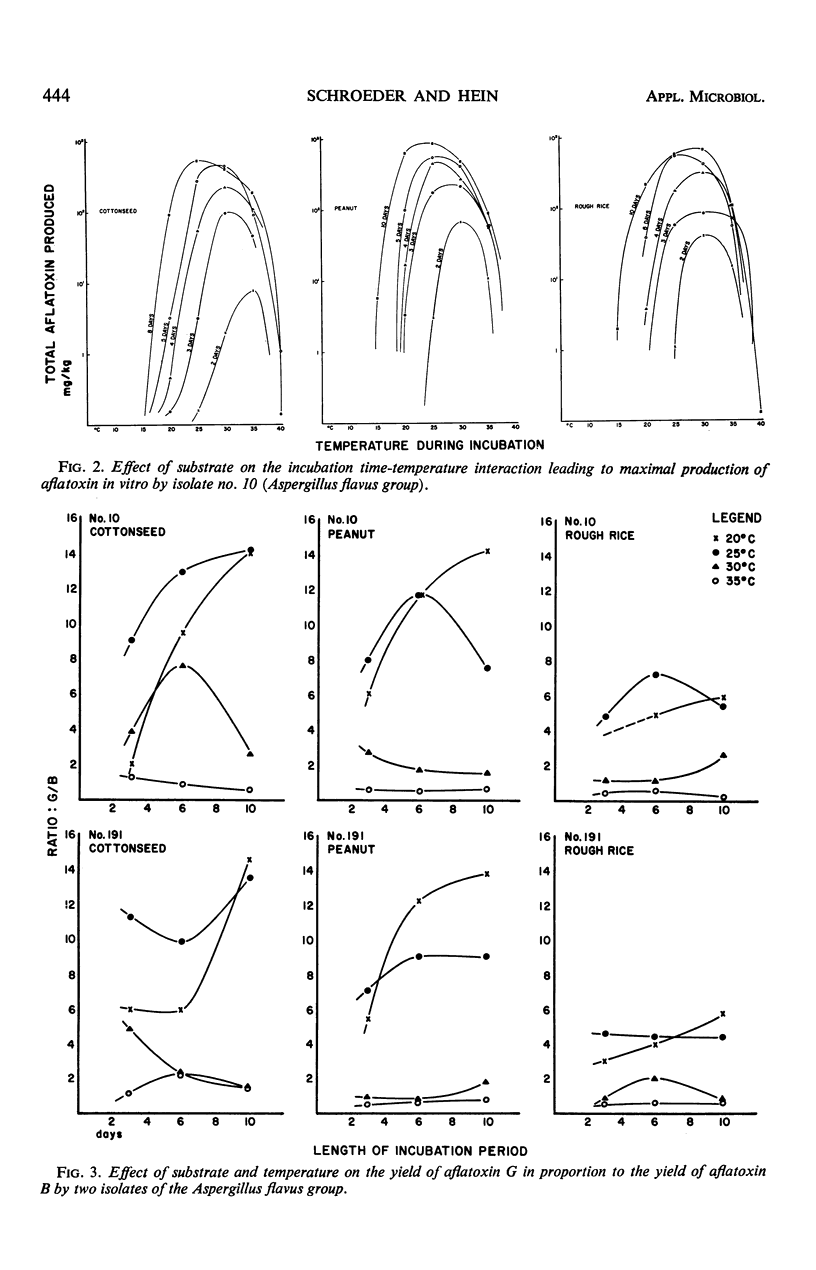
The production or accumulation of aflatoxins in vitro by four isolates on three substrates (acid-delinted cottonseed, shelled Spanish peanut, and rough rice) was studied in relation to temperature in the range of 10 to 40 C. Within the first 10 days after inoculation, the optimal temperature range for aflatoxin production was between 20 and 35 C. Only small amounts of the toxins were produced at 10 and 40 C. Within the optimal temperature range, the time required for toxin production and for significant accumulation decreased as the temperature increased. More aflatoxin G was produced or accumulated in relation to aflatoxin B at low temperatures (within the optimal range), and the G aflatoxins were metabolized more rapidly at the higher temperatures.
Full text
PDF
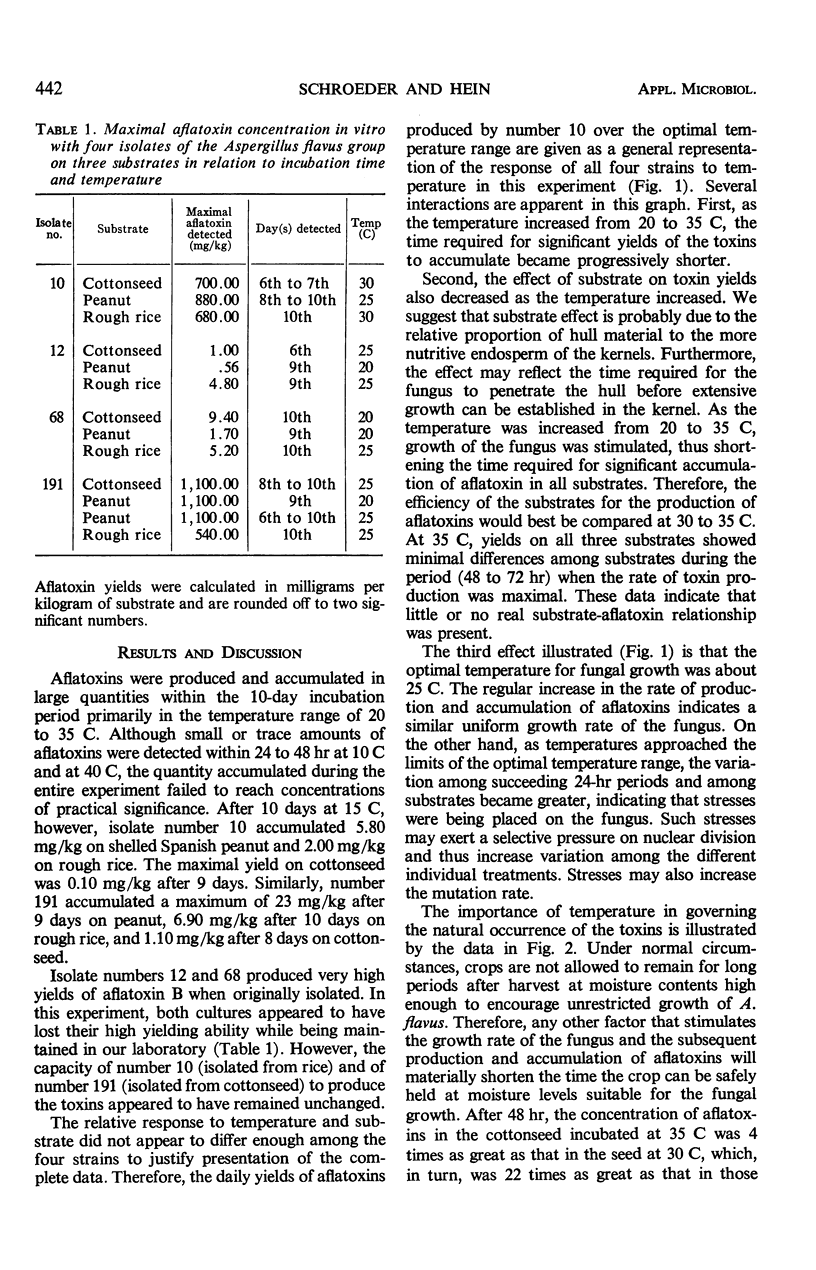

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashworth L. J., Jr, Schroeder H. W., Langley B. C. Aflatoxins: Environmental Factors Governing Occurrence in Spanish Peanuts. Science. 1965 May 28;148(3674):1228–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3674.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONS W. A., Jr, GOLDBLATT L. A. THE DETERMINATION OF AFLATOXINS IN COTTONSEED PRODUCTS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jun;42:471–475. doi: 10.1007/BF02540087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W. Effect of corn steep liquor on mycelial growth and aflatoxin production in Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):381–385. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.381-385.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taber R. A., Schroeder H. W. Aflatoxin-producing potential of isolates of the Aspergillus flavus-oryzae group from peanuts (Arachis hypogaea). Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jan;15(1):140–144. doi: 10.1128/am.15.1.140-144.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wogan G. N. Chemical nature and biological effects of the aflatoxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):460–470. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.460-470.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]