Abstract
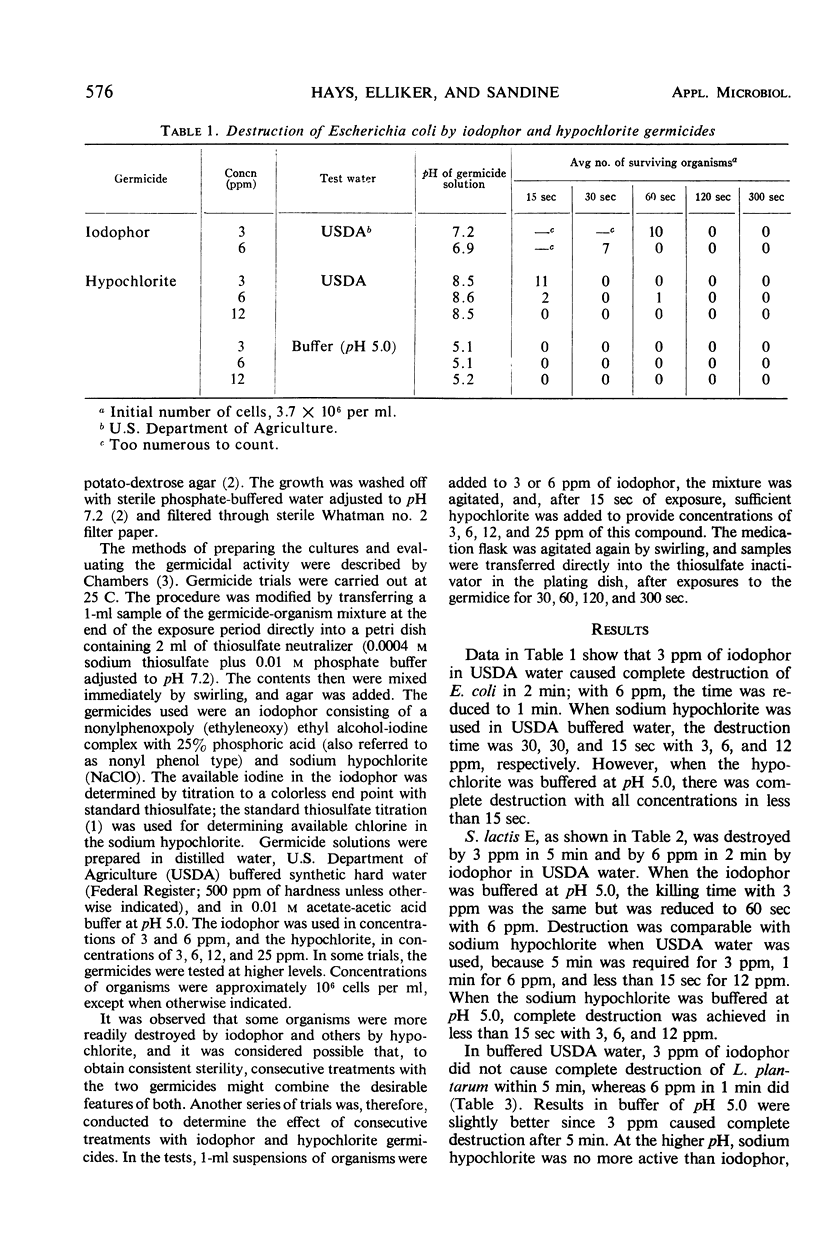
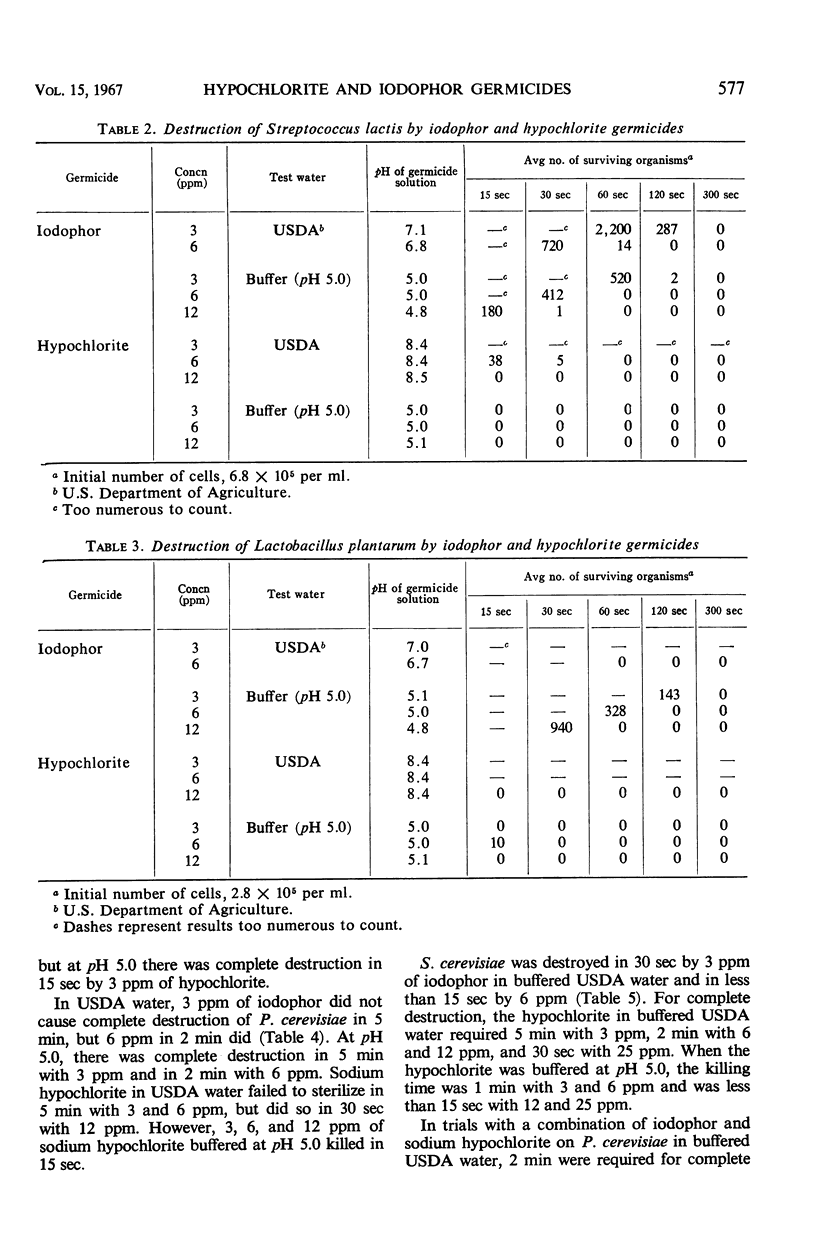
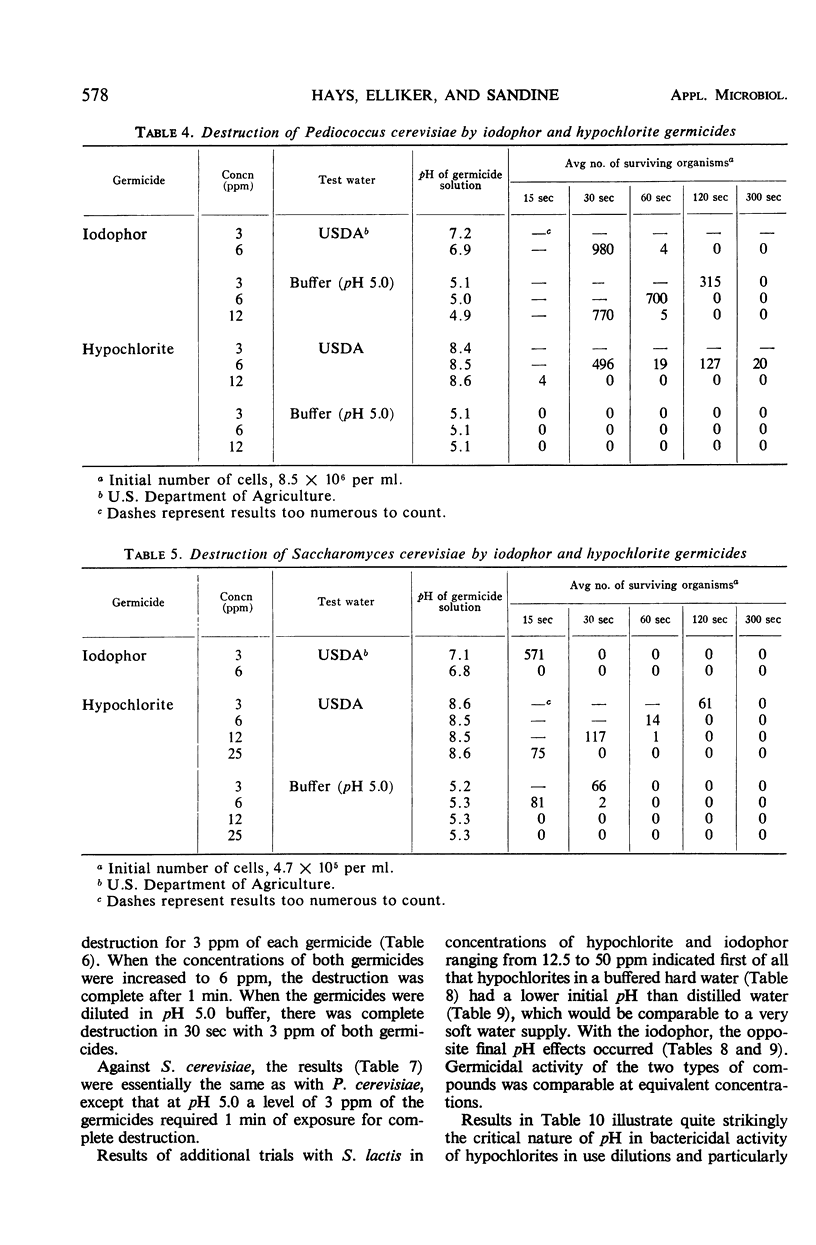
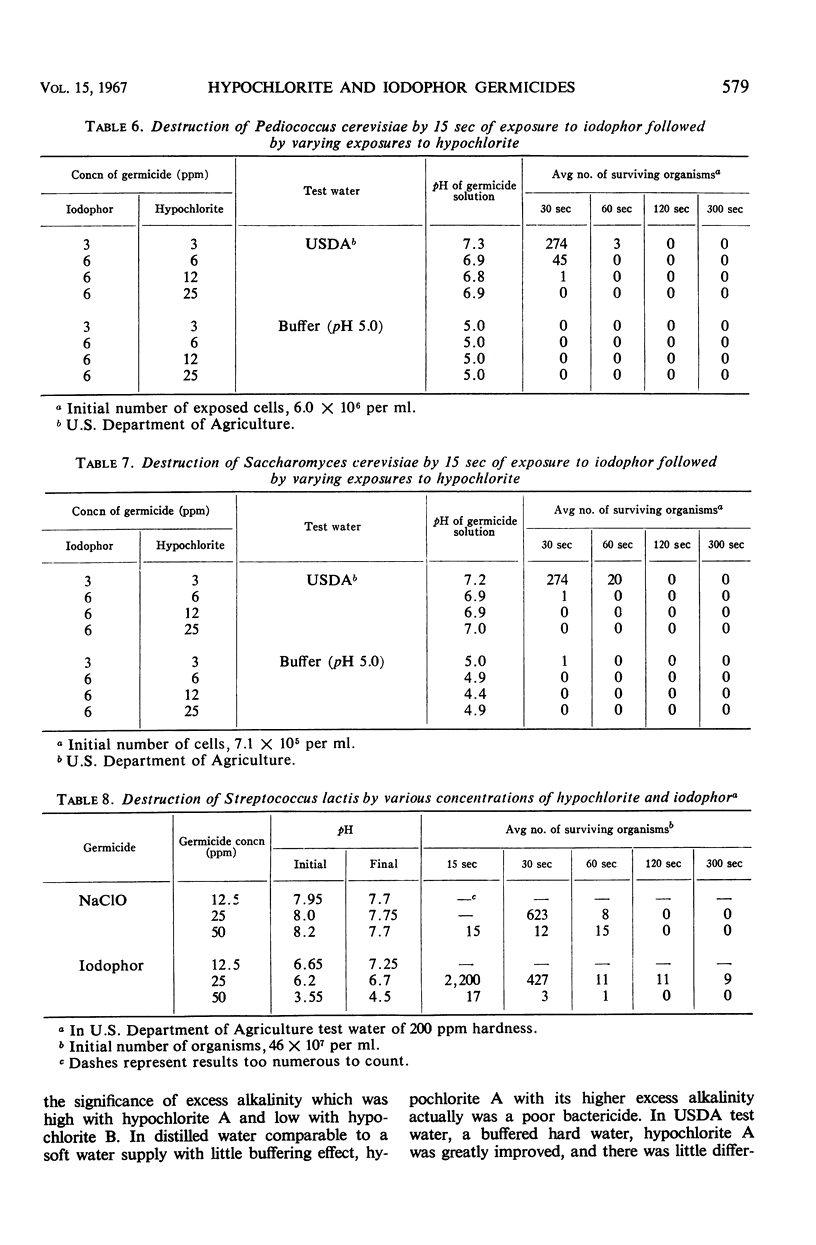
Hypochlorite and iodophor germicides were evaluated for their ability to destroy a variety of organisms at levels approximating those used for final sanitizing rinse for dairy and food equipment and beverage bottles (3 to 50 ppm). Test organisms included Escherichia coli, Streptococcus lactis, Lactobacillus plantarum, Pediococcus cerevisiae, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The hypochlorites and iodophors demonstrated approximate rates of destruction at equivalent concentrations for the bacterial species tested, except where the hypochlorite contained excess alkalinity. The hypochlorite responded more readily to a downward shift to a pH of 5.0 than did the iodophor. Excess alkalinity of the hypochlorite significantly affected its bactericidal activity. The iodophor exhibited a consistently greater rate of destruction of yeast cells than the hypochlorite. Successive treatment with low levels of iodophor (6 ppm) followed by a hypochlorite (12 to 25 ppm) resulted in a high level of destruction of all test organisms. Possibilities for employing these measures in a sanitizing rinse of bottles for maximal destruction of organisms were discussed. Among the test organisms, S. lactis showed a comparatively high resistance and was a useful organism for comparing the halogen preparations.
Full text
PDF