Abstract
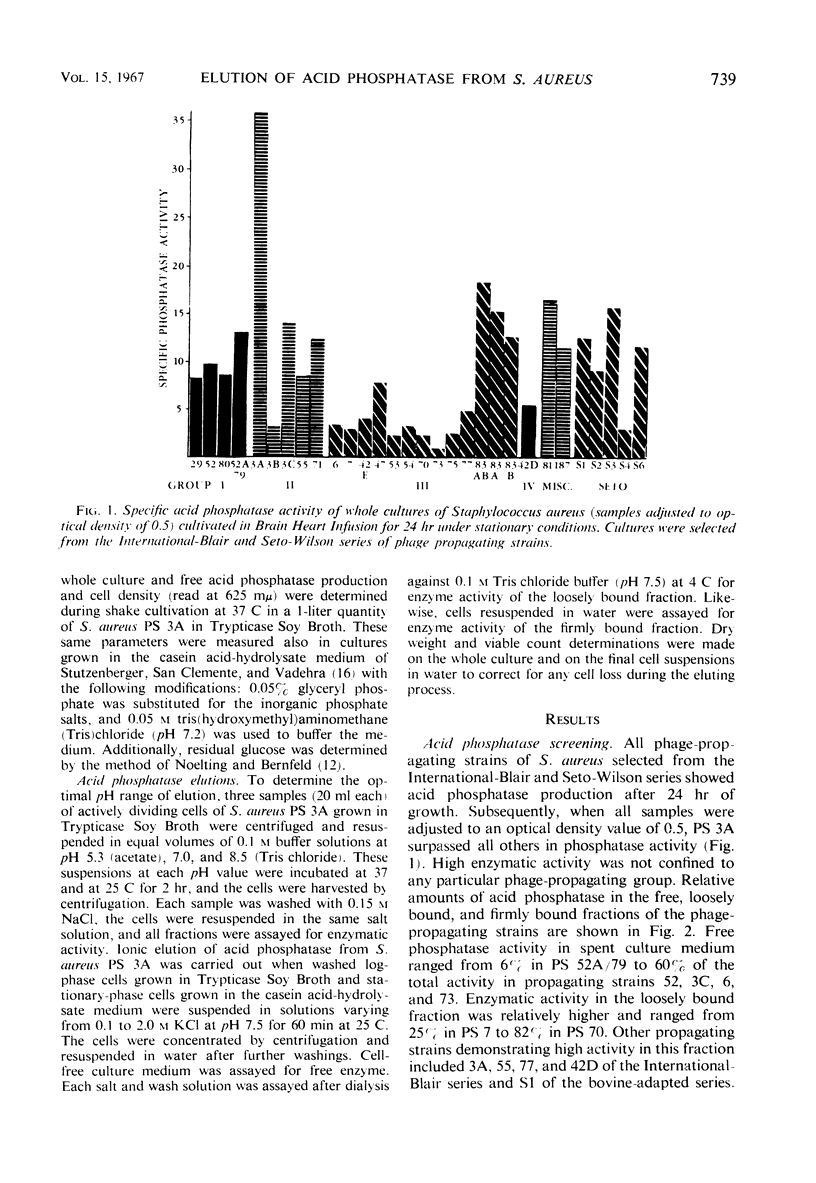
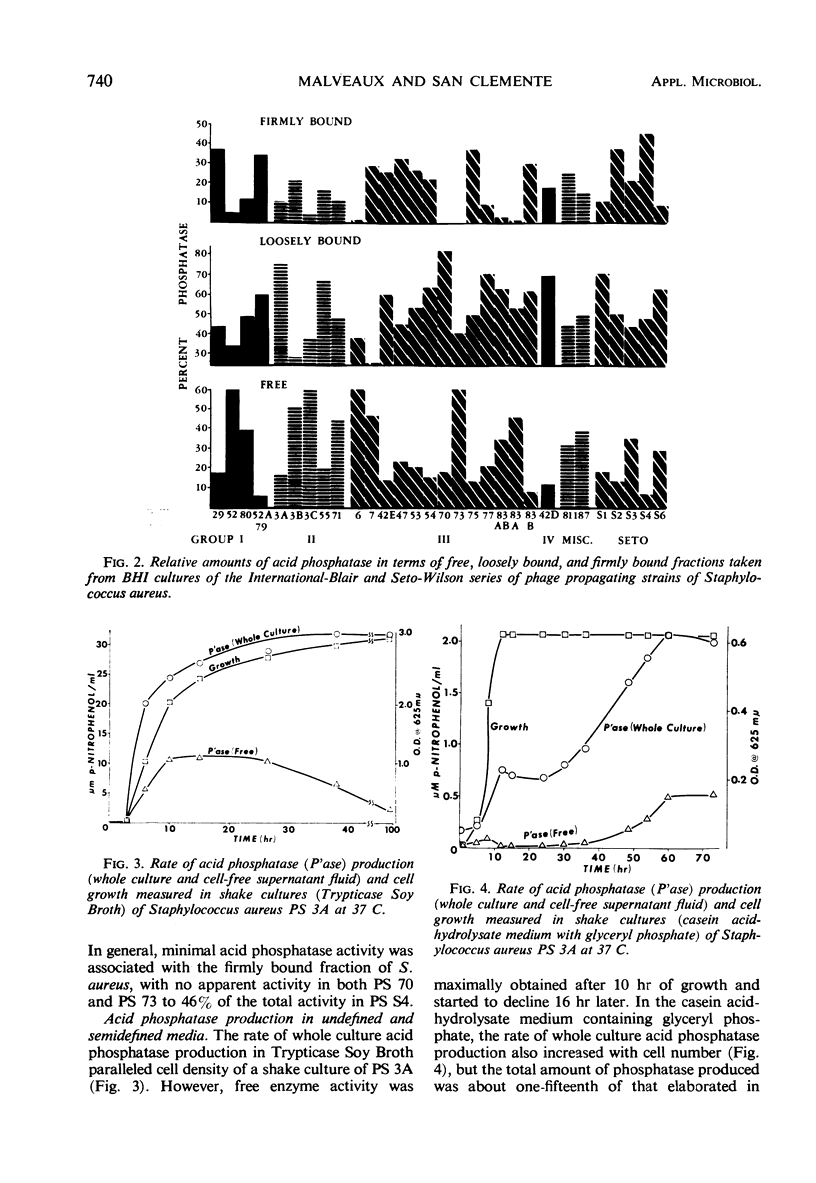
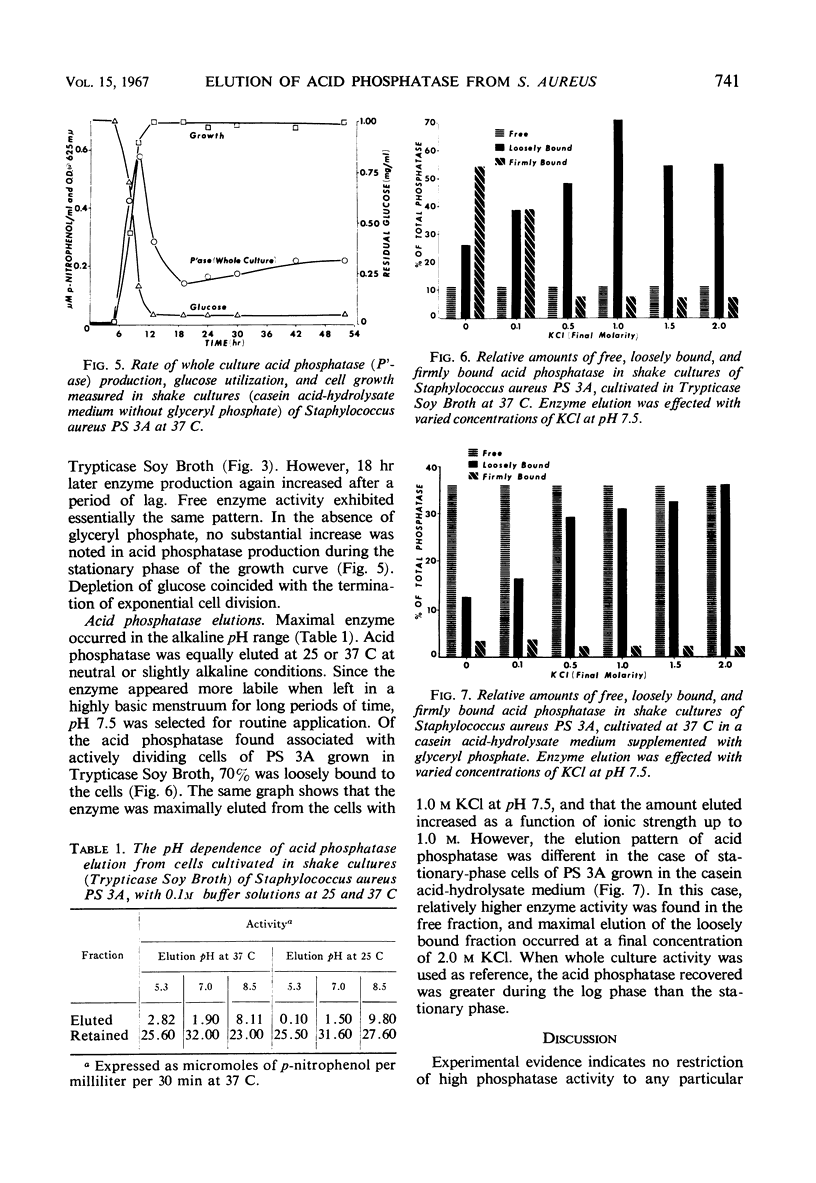
Strains of Staphylococcus aureus from the International-Blair and the Seto-Wilson series of phage propagating strains were examined for acid phosphatase activity. This enzyme was found to occur in varying amounts in three different fractions: free (6 to 60%), loosely bound (25 to 82%), and firmly bound (0 to 46%). Propagating strain 3A, because of its high activity, was chosen for further study. The rate of enzyme production paralleled cell growth in Trypticase Soy Broth, but followed a biphasic pattern in a semisynthetic casein acid-hydrolysate medium with glyceryl phosphate. Maximal elution of acid phosphatase in the loosely bound fraction, presumably from the surface of cells, occurred in the alkaline pH range. From log-phase cells, elution was maximally effected with buffered 1.0 M KCl (pH 7.5), but stationary-phase cells required twice the concentration of KCl.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNES E. H., MORRIS J. F. A quantitative study of the phosphatase activity of Micrococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):100–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.100-104.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAIR J. E., CARR M. The techniques and interpretation of phage typing of staphylococci. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Apr;55:650–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORSTPAUWELS G. W. THE ABSENCE OF A CORRELATION BETWEEN THE EXTERNAL PHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY OF YEAST AND PHOSPHATE UPTAKE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 9;93:659–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G., Horecker B. L. Fructose-1, 6-diphosphatase and acid hexose phosphatase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):837–842. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.837-842.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUO M. H., BLUMENTHAL H. J. Purification and properties of an acid phosphomonoesterase from Neurospora crassa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 2;52:13–29. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90899-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. A general theory of membrane transport from studies of bacteria. Nature. 1957 Jul 20;180(4577):134–136. doi: 10.1038/180134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Structure and function in microorganisms. Biochem Soc Symp. 1959;16:73–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. On the surface localization of enzymes in E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Oct 14;17(3):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS H. J. The formation of extracellular enzymes by staphylococci. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1956 Aug 31;65(3):132–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1956.tb36631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETO J. T., WILSON J. B. Bacteriophage typing of micrococci of bovine origin. Am J Vet Res. 1958 Jan;19(70):241–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutzenberger F. J., Clemente C. L., Vadehra D. V. Nephelometric assay of staphylococal coagulase. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1005-1009.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRIANI A. Influence of inorganic phosphate in the formation of phosphatases by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:460–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimberg R., Orton W. L. Elution of Acid Phosphatase from the Cell Surface of Saccharomyces mellis by Potassium Chloride. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):82–94. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.82-94.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimberg R., Orton W. L. Elution of exocellular enzymes from Saccharomyces fragilis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.1-13.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von HOFSTEN Acid phosphatase and the growth of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Mar 18;48:171–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90529-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von HOFSTEN, PORATH J. Purification and some properties of an acid phosphatase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;64:1–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90754-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


