Abstract
A new antibiotic, designated LL-A491, was isolated by butanol extraction and crystallization from beers of an unidentified streptomycete, Lederle culture A491. LL-A491 was primarily active against gram-positive bacteria and was related to monazomycin. A tentative molecular formula of C72±2 H144±8 O25±1 N for the antibiotic, based on analyses of the crystalline hydrochloride, picrate, and picrolonate salts, is considerably larger than that proposed for monazomycin, from which LL-A491 was not differentiated by paper chromatography. Analysis of the amorphous polyacetate ester suggested 15 to 16 acetylable groups. Upon hydrolysis, LL-A491 liberated ammonia and a reducing sugar which appeared to be mannose. LL-A491 was dextrorotatory, [α]D25 + 14°, and exhibited only end absorption in the ultraviolet region.
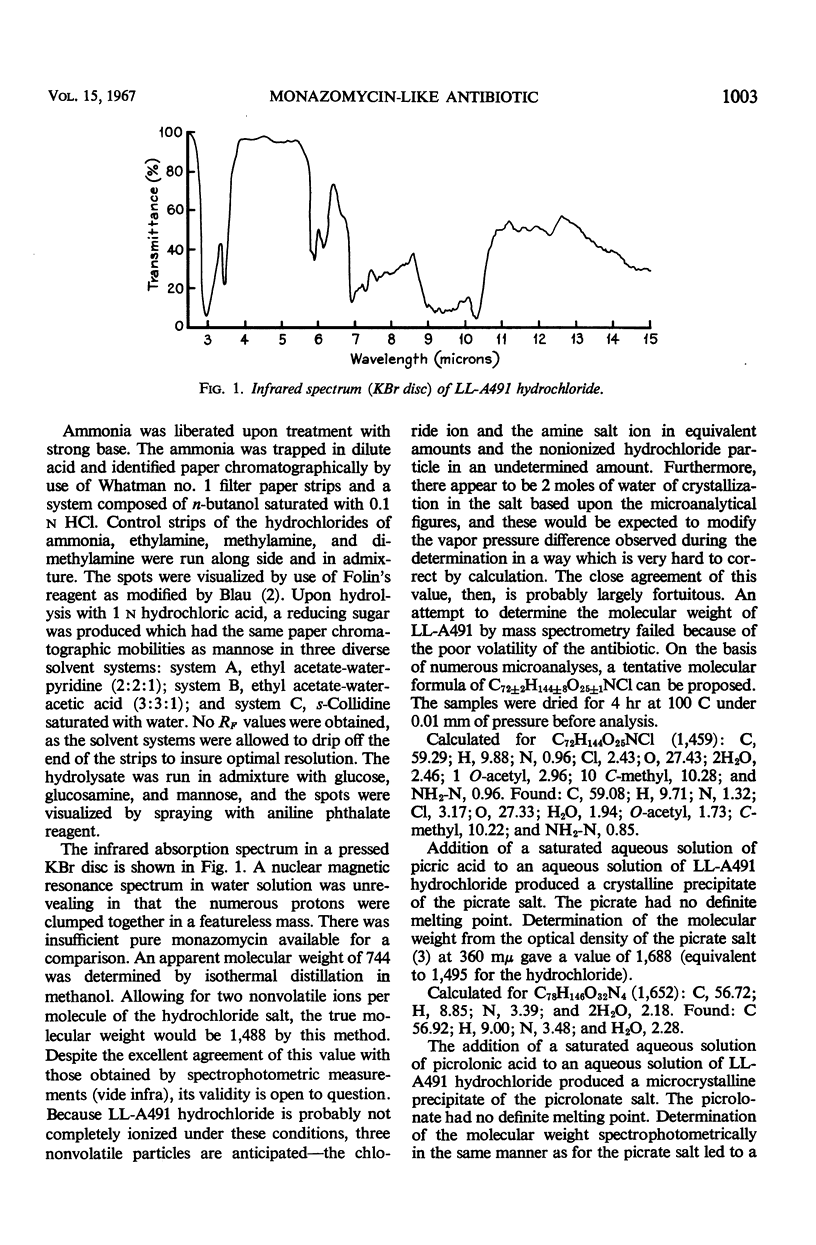
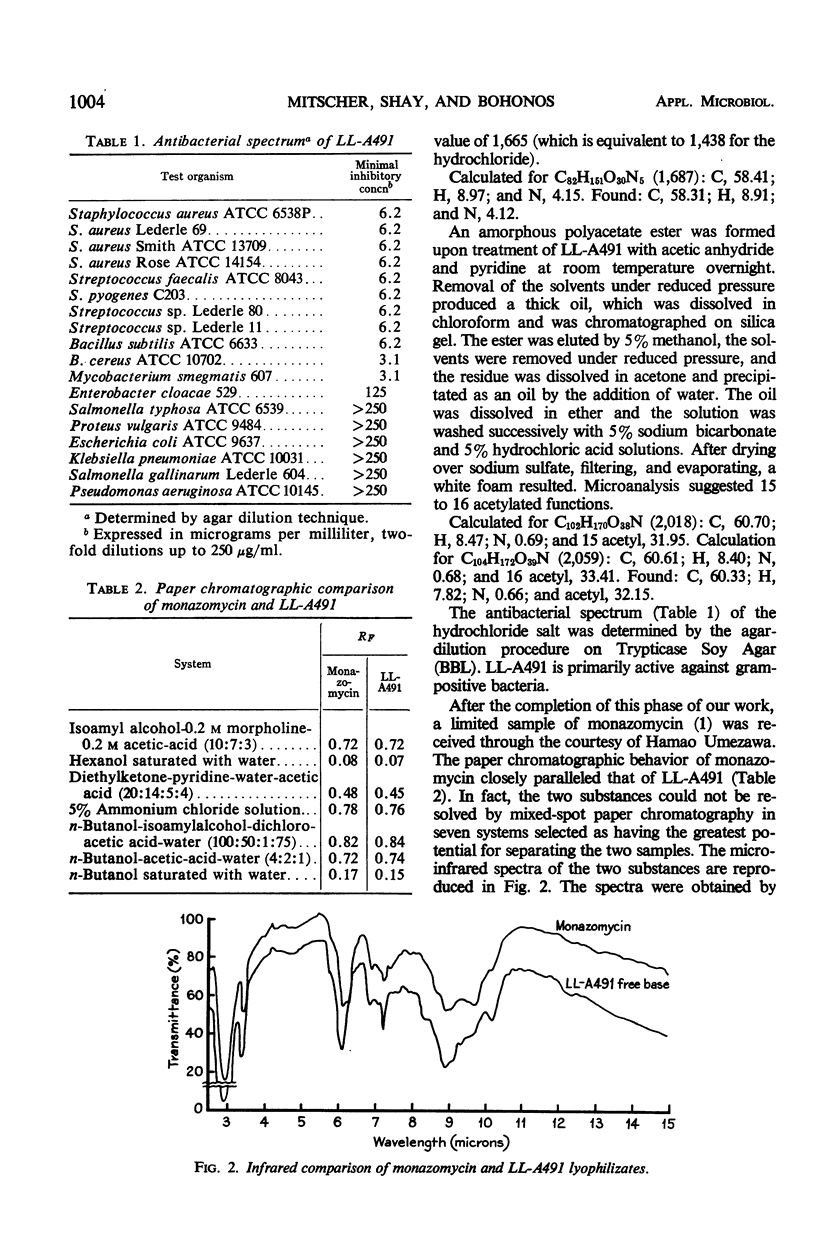
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blau K. Chromatographic methods for the study of amines from biological material. Biochem J. 1961 Jul;80(1):193–200. doi: 10.1042/bj0800193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


