Abstract
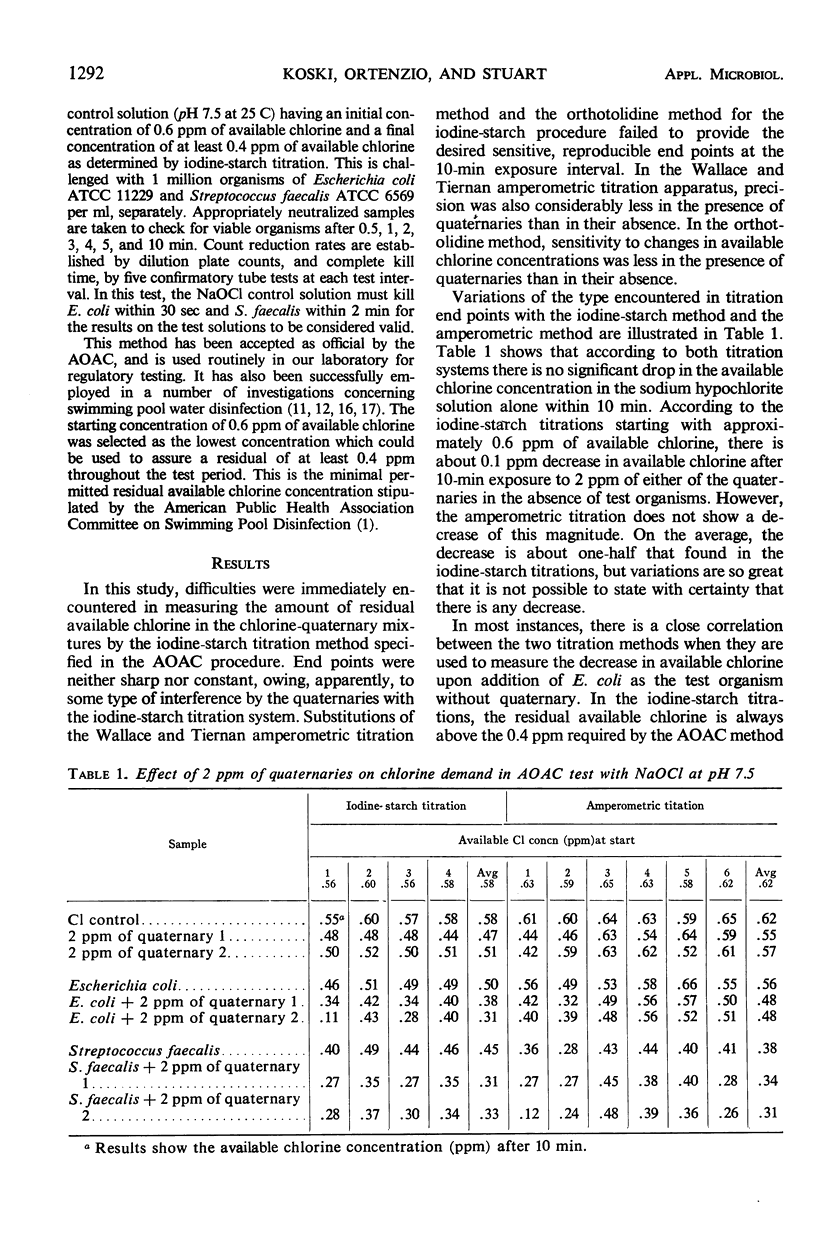
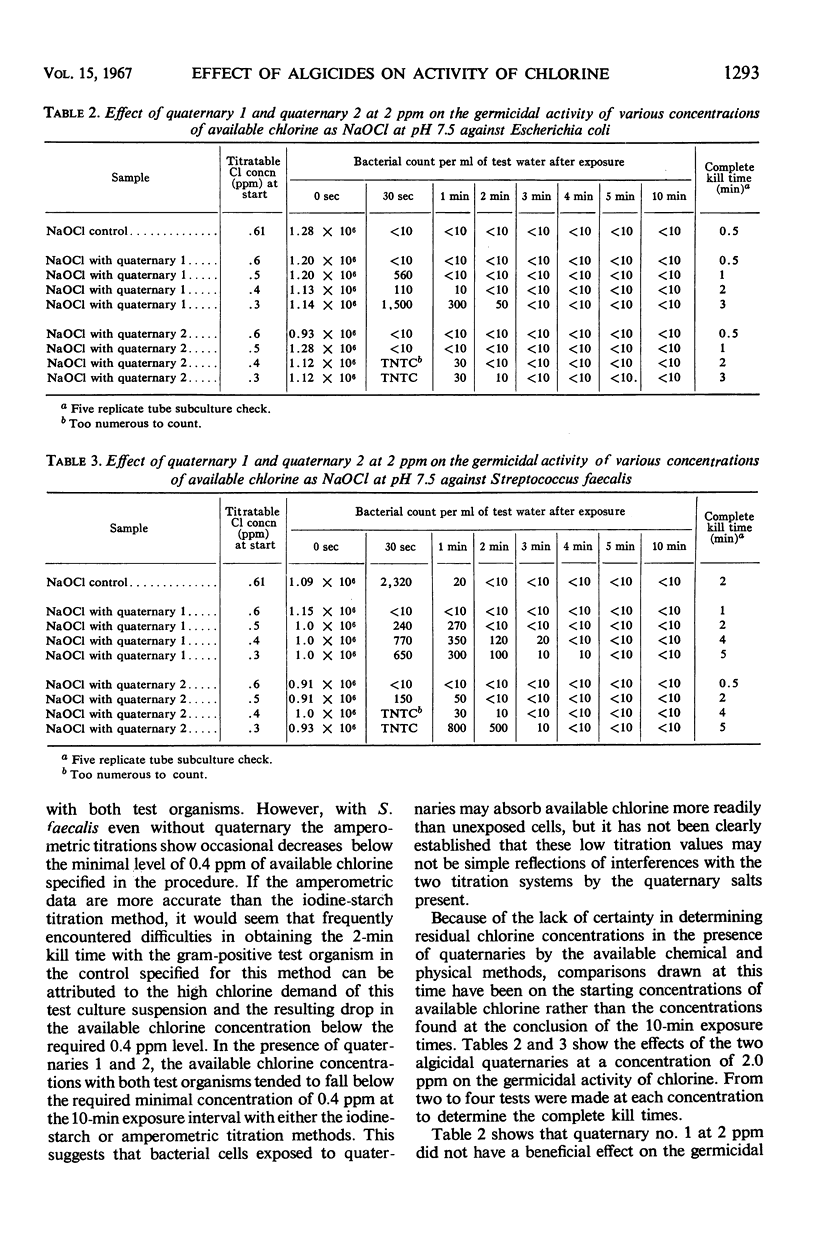
The Swimming Pool Water Disinfectant Test Method of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists was used to determine the effect of the accepted level of 2 ppm of some commercial quaternary ammonium algicides on the germicidal activity of chlorine. Accurate determinations on the amounts of residual available chlorine in chlorine-quaternary mixtures could not be made by the usual chemical methods. This made it necessary to base all comparisons on the starting concentrations of available chlorine rather than the final concentration as specified in the method employed. No evidence was obtained to support the use of lower concentrations of residual available chlorine for disinfection in the presence of algicidal quaternaries than those commonly recognized as effective by the American Public Health Association. The rate of kill against the gram-positive test organism Streptococcus faecalis was faster in quaternary-chlorine mixtures than in the sodium hypochlorite control solutions. The practical significance of this result in the bench method identified cannot be ascertained in the absence of more sensitive and precise chemical procedures for determining concentrations of residual available chlorine in the presence of quaternaries or in actual swimming pool tests.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTONIDES H. J., CHACHARONIS P. Toxicologic studies on Armazide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1962 Jan;4:44–54. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(62)90075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANTONIDES H. J., TANNER W. S. Algicidal and sanitizing properties of Armazide. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Nov;9:572–580. doi: 10.1128/am.9.6.572-580.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD G. P. Bactericidal and algicidal properties of some algicides for swimming pools. Appl Microbiol. 1959 Jul;7(4):205–211. doi: 10.1128/am.7.4.205-211.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD G. P. FACTORS IN THE TESTING AND APPLICATION OF ALGICIDES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 May;12:247–253. doi: 10.1128/am.12.3.247-253.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD G. P. Loss of algicidal chemicals in swimming pools. Appl Microbiol. 1960 Sep;8:269–274. doi: 10.1128/am.8.5.269-274.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski T. A., Stuart L. S., Ortenzio L. F. Comparison of chlorine, bromine, iodine as disinfectants for swimming pool water. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):276–279. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.276-279.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


