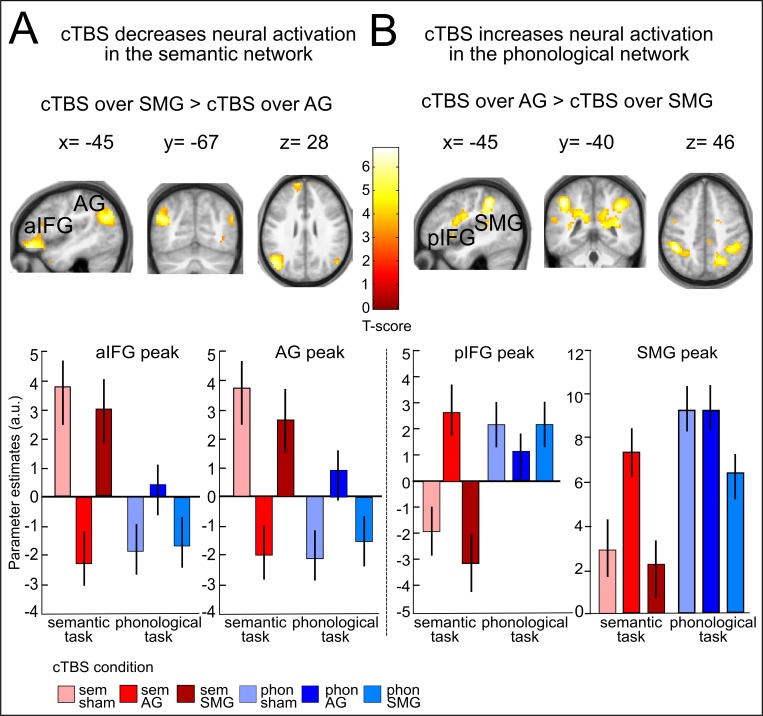
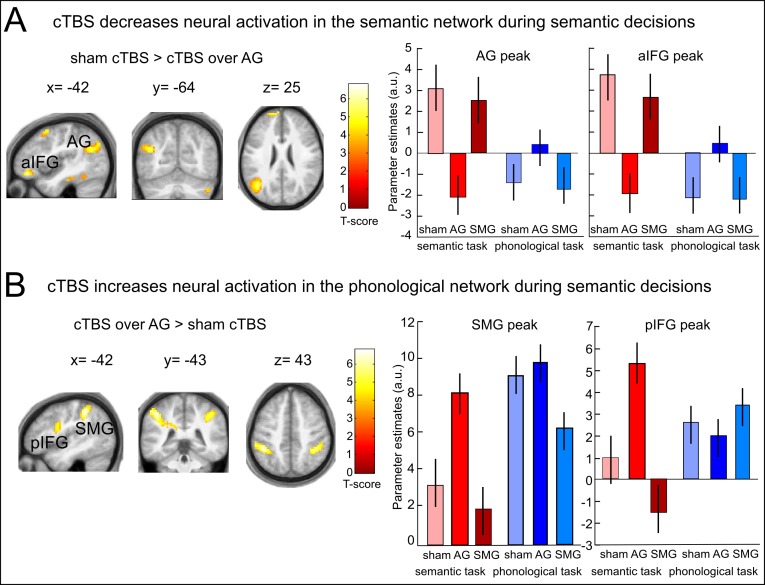
Figure 2. Effects of cTBS on semantic decisions.
(A) Relative to cTBS over SMG, cTBS of AG significantly decreased neural activity not only at the stimulated area, but in a larger network including AG and aIFG. (B) Relative to cTBS of SMG, cTBS of AG significantly increased neural activity in phonological regions, including the bilateral SMG and pIFG. Lower panels display the respective parameter estimates (arbitrary units) for the different cTBS conditions that were extracted at the respective mean peak coordinates from the effect of interest for each task condition against rest. p<0.001 for display reasons. Sem=semantic, phon=phonological task.