Abstract
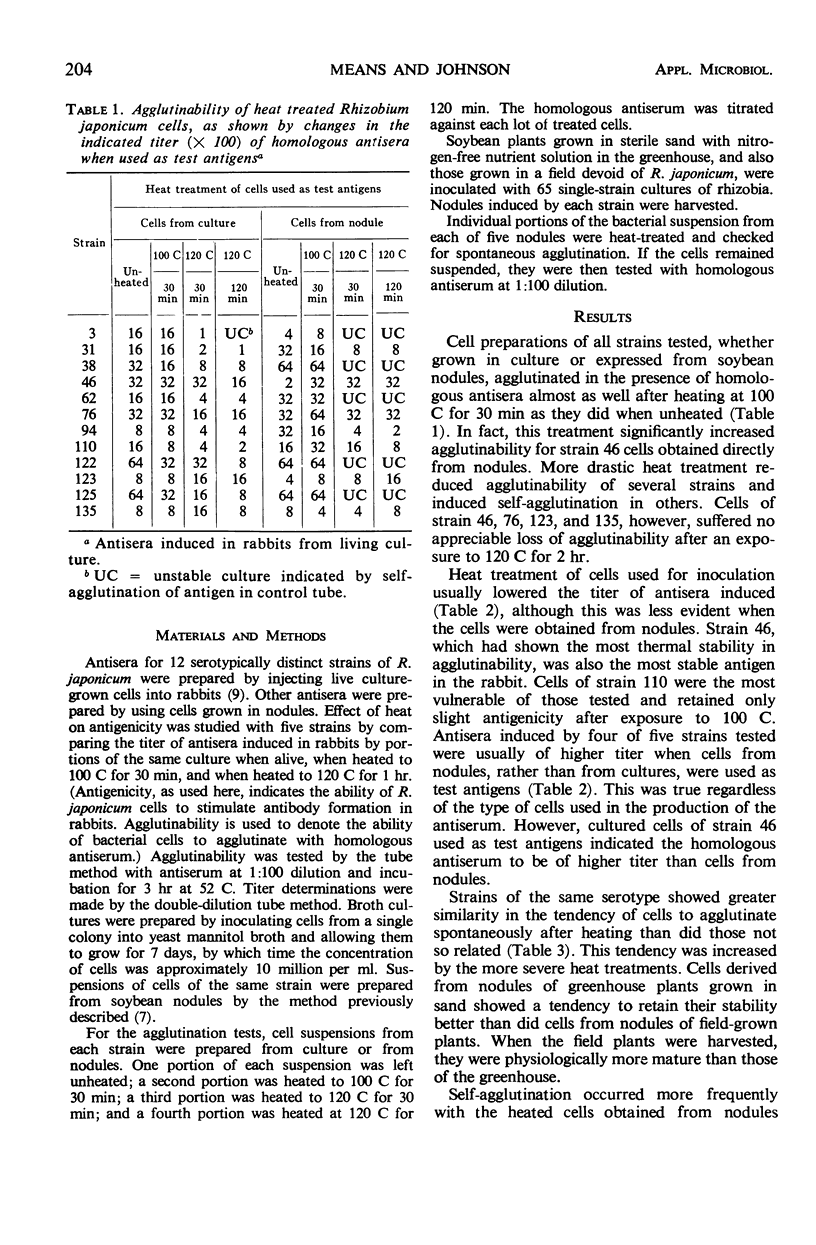
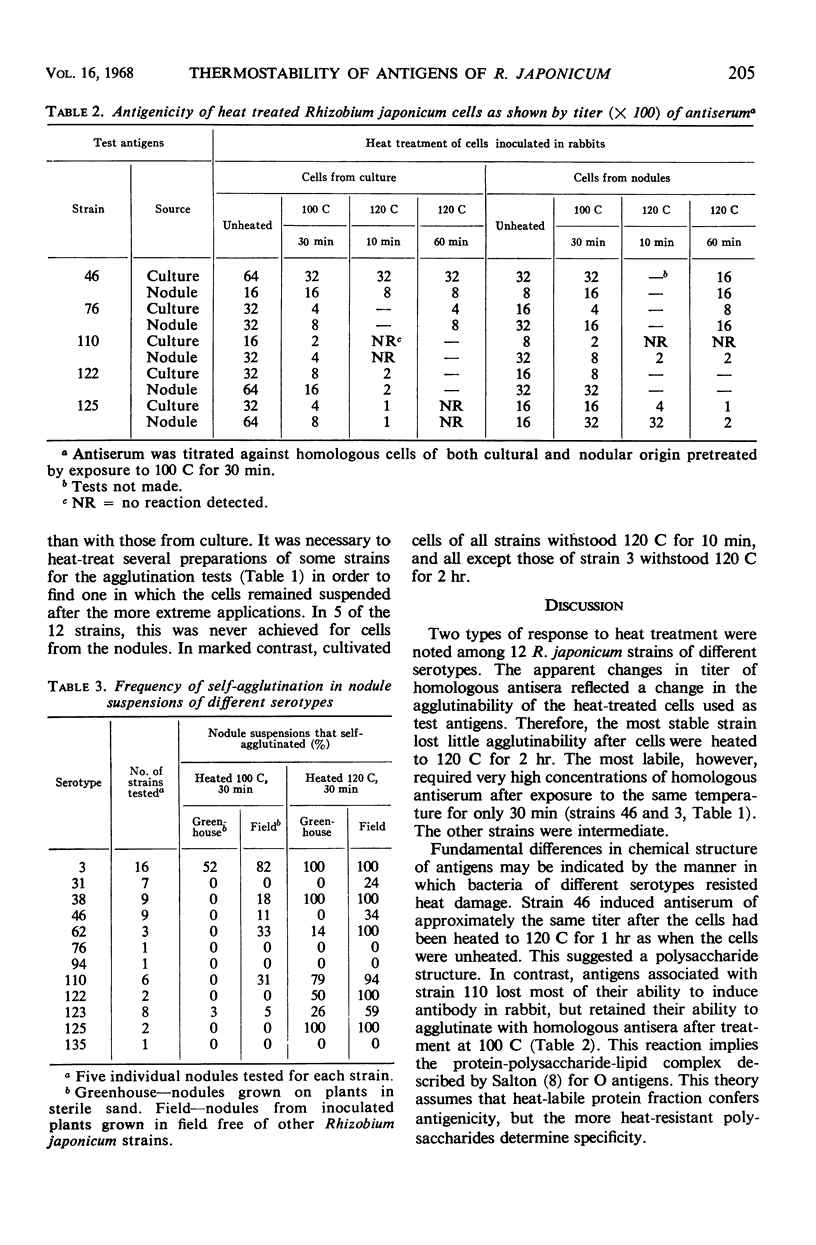
The antigens associated with serologically distinct strains of Rhizobium japonicum were found to differ in heat sensitivity. Cell preparations from 4 out of 12 strains retained agglutinability, and 1 out of 5 retained antigenicity after they were heated to 120 C. Antigenicity was reduced in most strains after heating to 100 C for 30 min, but agglutinability was not affected by this treatment. This suggests that the antigens are protein-polysaccharide-lipid complexes described for O-type antigens. Cells of strain 46, however, retained both agglutinability and antigenicity after heating to 120 C for 1 hr, and thus a protein in its structure seems improbable. Antigens associated with bacteria from soybean nodules responded to heat treatment in essentially the same manner as those from the same strain grown in nutrient broth. Certain serotypes showed a tendency to agglutinate spontaneously. A heat treatment of 100 C for 30 min, to remove nodule debris and destroy certain blocking antigens, did not interfere with the agglutination reaction. Live cells induced antiserum in rabbit to a higher titer than did heat-treated cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DATE R. A., DECKER A. M. MINIMAL ANTIGENIC CONSTITUTION OF 28 STRAINS OF RHIZOBIUM JAPONICUM. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Feb;11:1–8. doi: 10.1139/m65-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DROZANSKA D. STUDIES ON RHIZOBIUM TRIFOLII ANTIGENS. Acta Microbiol Pol. 1964;13:69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUDMAN W. F. IMMUNE DIFFUSION ANALYSIS OF THE EXTRACELLULAR SOLUBLE ANTIGENS OF TWO STRAINS OF RHIZOBIUM MELILOTI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:782–794. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.782-794.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN D. C. The bacteroids of the genus Rhizobium. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Jun;26:119–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEANS U. M., JOHNSON H. W., DATE R. A. QUICK SEROLOGICAL METHOD OF CLASSIFYING STRAINS OF RHIZOBIUM JAPONICUM IN NODULES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:547–553. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.547-553.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. Studies of the bacterial cell wall. VII. Monosaccharide constituents of the walls of gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 4;45:364–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91459-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


