Abstract
The plate-dilution frequency technique described facilitates simultaneous enumeration of a wide range of physiologically different microorganisms in complex systems with a precision comparable to dilution tube (most probable number) methods. Replicate microsamples are inoculated from each member of a dilution series onto areas delineated on plates of prepoured solid media; the plates are incubated, and the occurrence of growth or specific biochemical transformation is recorded for each inoculated area. Microbial enumeration is accomplished by reference to appropriate tables. Details of the experimental procedures are described, and tables are presented from which microbial numbers with 95% confidence limits can be obtained and compared for significant difference directly for 10-fold and 4-fold dilution series. Results of experiments in which microbial populations were estimated simultaneously by the plate-dilution frequency and conventional plate count methods are compared. The potential of the technique for broad-spectrum microbial assay is also discussed.
Full text
PDF


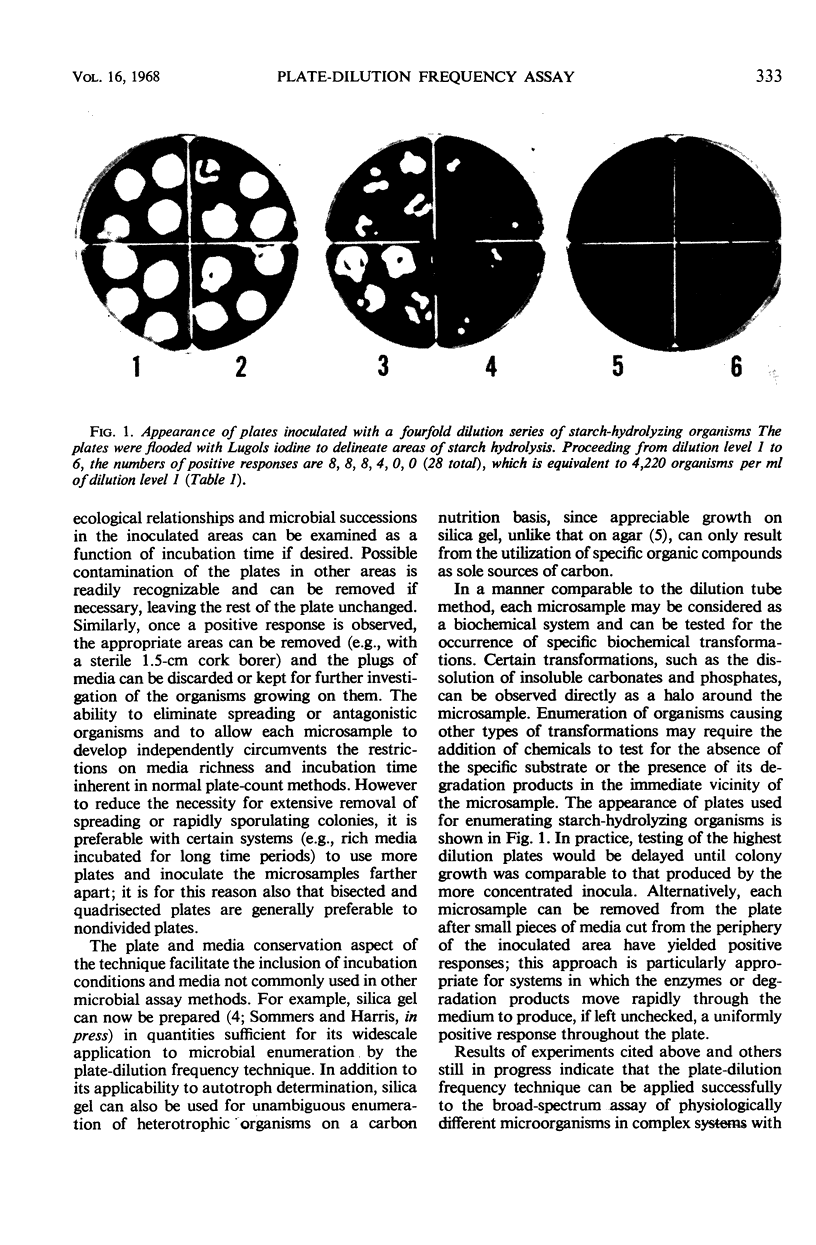

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COCHRAN W. G. Estimation of bacterial densities by means of the "most probable number". Biometrics. 1950 Jun;6(2):105–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUNK H. B., KRULWICH T. A. PREPARATION OF CLEAR SILICA GELS THAT CAN BE STREAKED. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1200–1201. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1200-1201.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



