Abstract
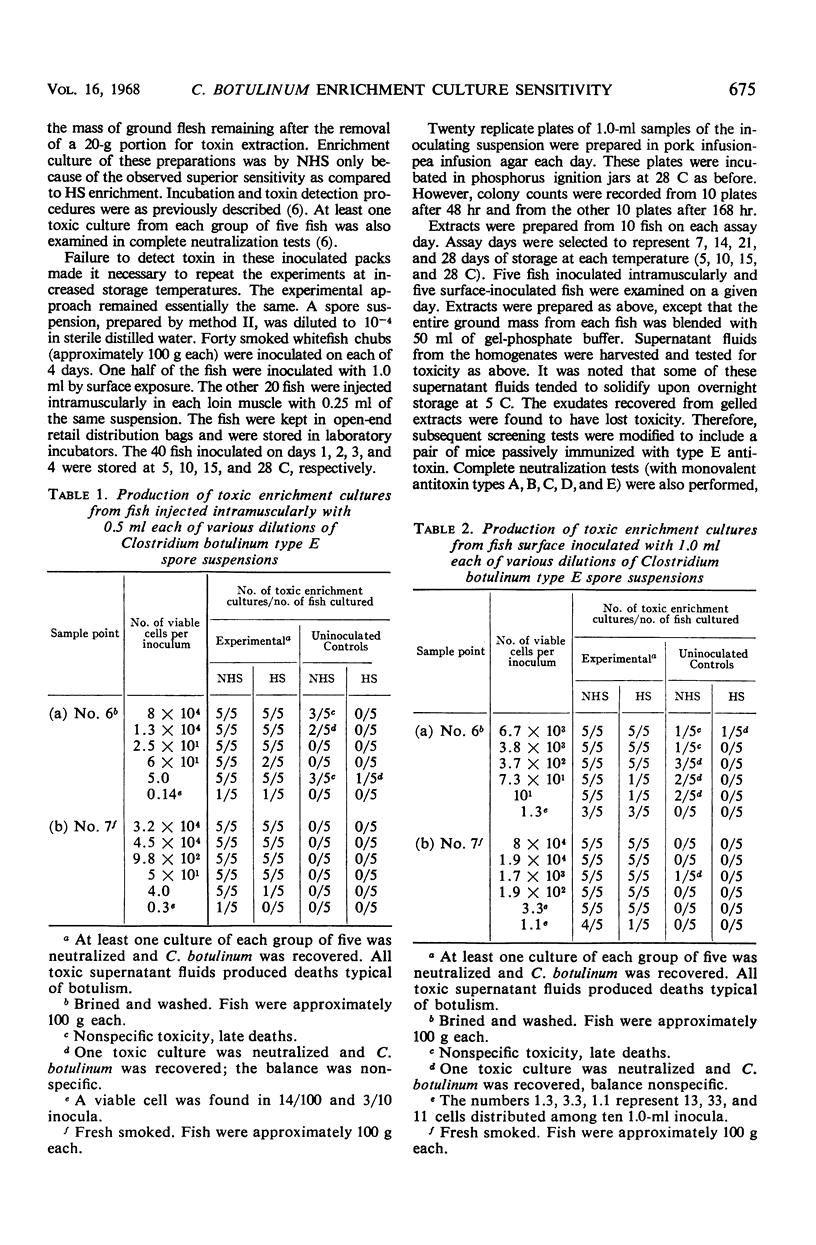
The sensitivity of an enrichment culture procedure for detecting Clostridium botulinum type E in whitefish chubs (Leucichthys sp.) was assayed. Data demonstrated that fish inoculated with 10 or more viable C. botulinum spores regularly develop specifically neutralizable enrichment cultures. Mild heat treatment (60 C, 15 min) substantially reduced the sensitivity of enrichment culturing. This effect was particularly noticeable in the culturing of fish which harbored fewer than 10 spores each. Evidence is presented which indicates that sensitivity of enrichment, without heat, approaches the level of one spore per fish. Smoked whitefish chubs, containing from one to several hundred spores each, were examined for toxin content after storage at 5, 10, 15, and 28 C for as long as 32 days. The lowest temperature at which detectable toxin was produced was 15 C. This occurred in 1 of 10 fish incubated for 14 days. C. botulinum was regularly recovered, by enrichment culture, from fish inoculated with small numbers of spores, even though toxin was not detected by direct extraction of incubated fish. Persistence of C. botulinum type E spores was observed to decline with an increase in the temperature and time at which inoculated fish were stored.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN A. A. A rapid plate method of counting spores of Clostridium botulinum. J Bacteriol. 1951 Oct;62(4):425–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.4.425-432.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUFF J. T., WRIGHT G. G., YARINSKY A. Activation of Clostridium botulinum type E toxin by trypsin. J Bacteriol. 1956 Oct;72(4):455–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.4.455-460.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace P. J., Krumbiegel E. R., Angelotti R., Wisniewski H. J. Demonstration and isolation of Clostridium botulinum types from whitefish chubs collected at fish smoking plants of the Milwaukee area. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jul;15(4):877–884. doi: 10.1128/am.15.4.877-884.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


