Abstract
Although certain strains of cellulolytic rumen bacteria cannot utilize isolated hemicelluloses or xylan as a source of energy, all strains examined can degrade or solubilize these materials from an 80% ethyl alcohol insoluble to a soluble form. Centrifugation and washing of the cellobiose-grown bacterial cells did not affect the rate or extent of utilization or degradation or both. When the level of a nonutilizing culture inoculum (either normal or washed) was doubled, a corresponding increase in the initial rate of degradation was observed. With a nitrogen-free medium, utilization of xylan was almost completely inhibited for a utilizing strain, whereas degradation by either type of organism was not markedly affected. Cellobiose medium cell-free culture filtrates from a nonutilizing strain were able to degrade or solubilize xylan. The percentage of degradation increased with the volume of cell-free filtrate, and all activity was lost when the filtrate was boiled. No utilization (loss in total pentose) was observed with cell-free filtrates from utilizing or nonutilizing strains. The release of free hexose from insoluble cellulose by culture filtrates from a nonutilizing strain was very limited. On the other hand, carboxymethylcellulose (CMC-70L) and cellulodextrins were degraded to an 80% ethyl alcohol soluble form by filtrates from both types of organisms. Similar enzyme activity was obtained in cell-free culture filtrates from four additional strains of cellulolytic rumen bacteria (one xylan utilizer and three nonutilizers). When the assays were carried out aerobically, CMC-70L solubilization was reduced to a much greater extent than xylan or cellulodextrin solubilization. The enzyme or enzymes responsible for the degradation of hemicellulose by cellololytic rumen bacteria unable to utilize the hemicellulose as an energy source appear to be constitutive in nature, and this activity may be a nonspecific action of a β-1, 4-glucosidase or -cellulase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N., BOUMA C., ROBINSON I. M. Characteristics of ruminal anaerobic celluloytic cocci and Cillobacterium cellulosolvens n. sp. J Bacteriol. 1958 Nov;76(5):529–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.5.529-537.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
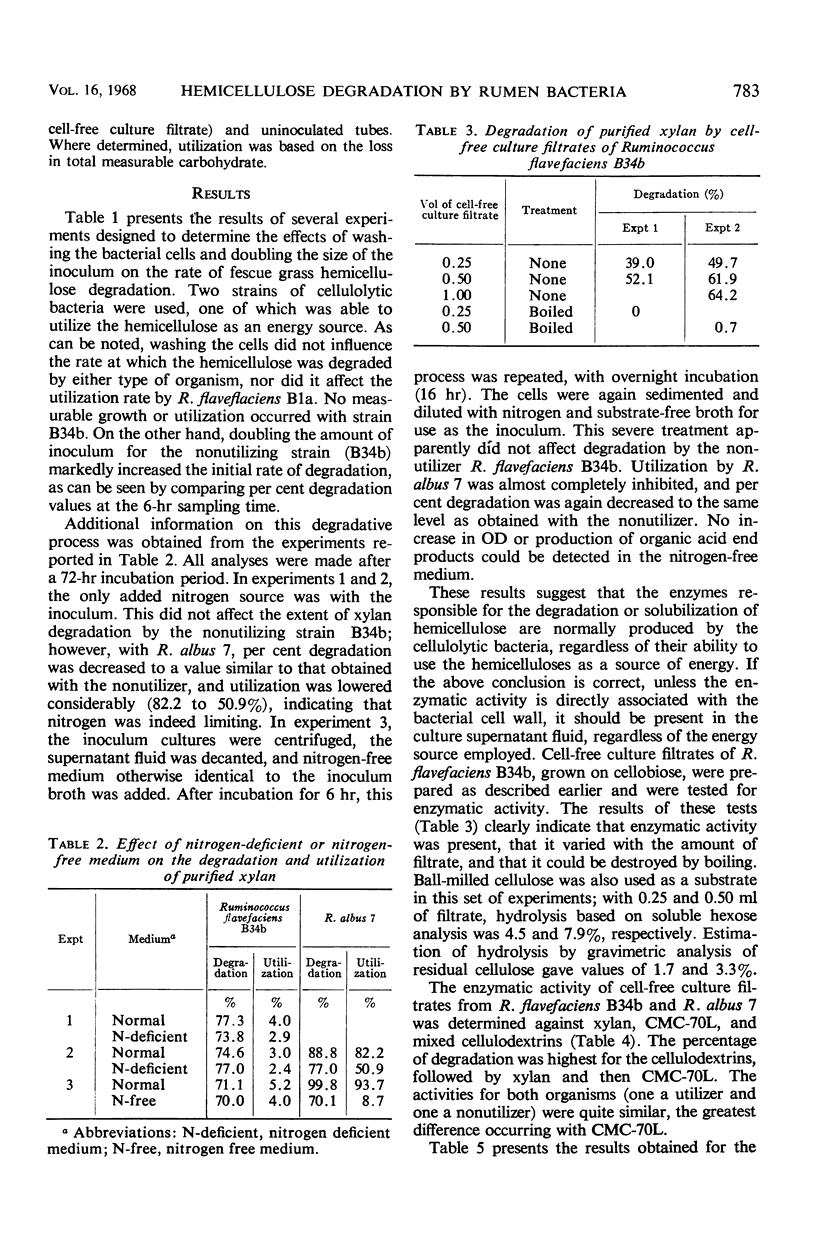
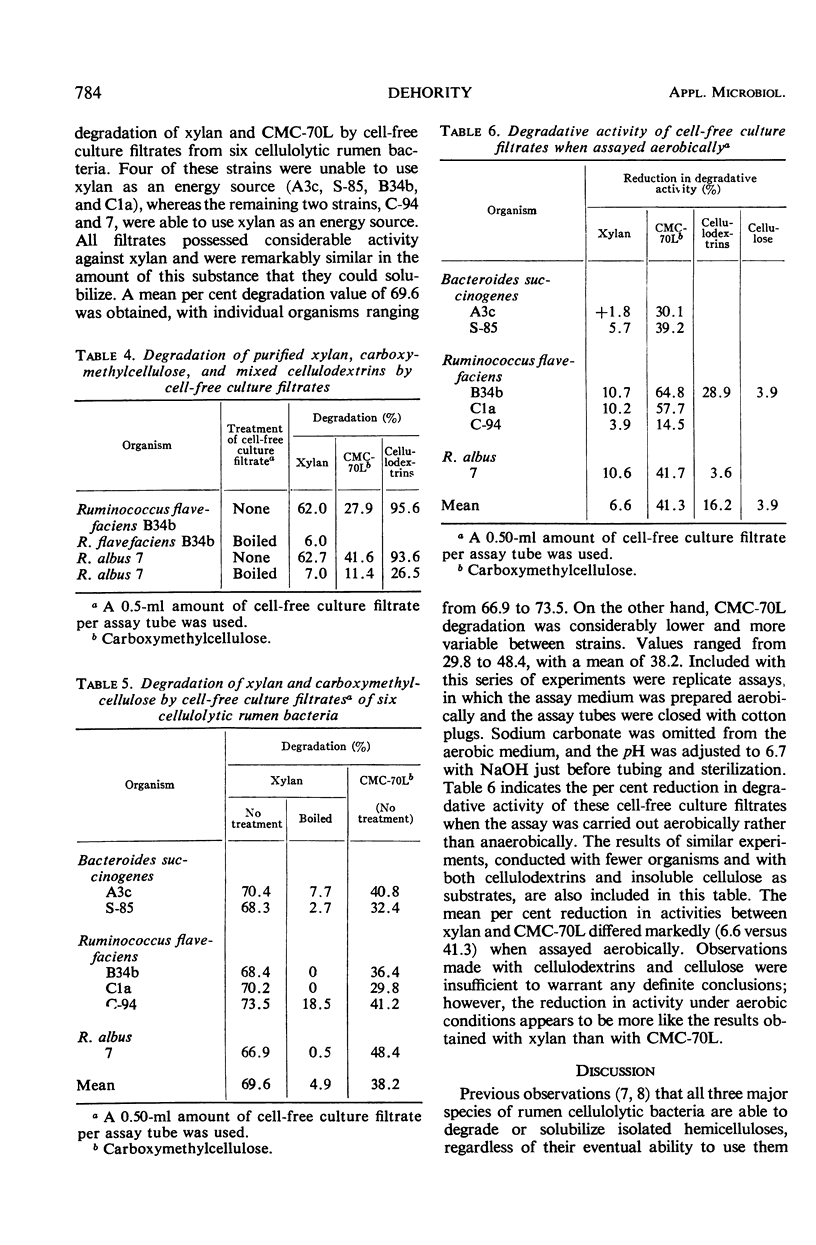
- DEHORITY B. A. DEGRADATION AND UTILIZATION OF ISOLATED HEMICELLULOSE BY PURE CULTURES OF CELLULOLYTIC RUMEN BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1515–1520. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1515-1520.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Rate of isolated hemicellulose degradation and utilization by pure cultures of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):987–993. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.987-993.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FESTENSTEIN G. N. Cellulolytic enzymes from sheep-rumen liquor micro-organisms. Biochem J. 1958 Aug;69(4):562–567. doi: 10.1042/bj0690562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G. Cellulolysis by rumen micro-organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):153–165. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G. Cellulolytic preparations from micro-organisms of the rumen and from Myrothecium verrucaria. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):166–183. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT H. W., DEHORITY B. A. VITAMIN REQUIREMENTS OF SEVERAL CELLULOLYTIC RUMEN BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1169–1175. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1169-1175.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


