Figure 5. Assessment of pulse wave velocity of the left carotid artery.
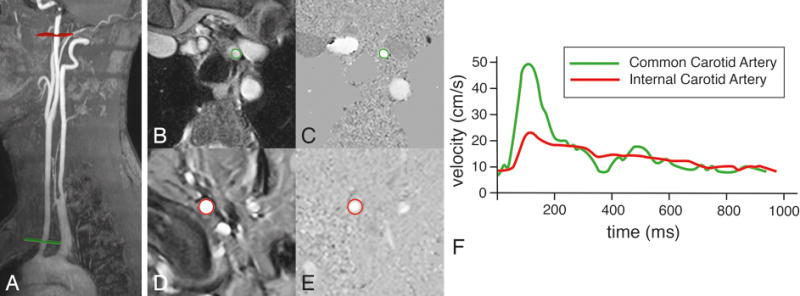
Two acquisition planes are positioned, one perpendicular to the common carotid artery just above the aortic arch (in green) and one perpendicular to the internal carotid artery just proximal to the petrous portion of the artery (in red). Velocity mapping is performed after segmentation in common carotid artery (B and C) and the internal carotid artery (D and E). Velocity-time curves are determined (F) and the pulse wave velocity is calculated from the distance Δx between both measurement sites (determined along the centerline of the vasculature) and the transit time Δt of the onset of the systolic velocity wavefront, measured at each site: PWV = Δx/Δt (in m/s). In this example of a healthy 47 year male volunteer, Δx = 19.6 cm, Δt = 25 ms, resulting in a PWV of 7.8 m/s.
