Abstract
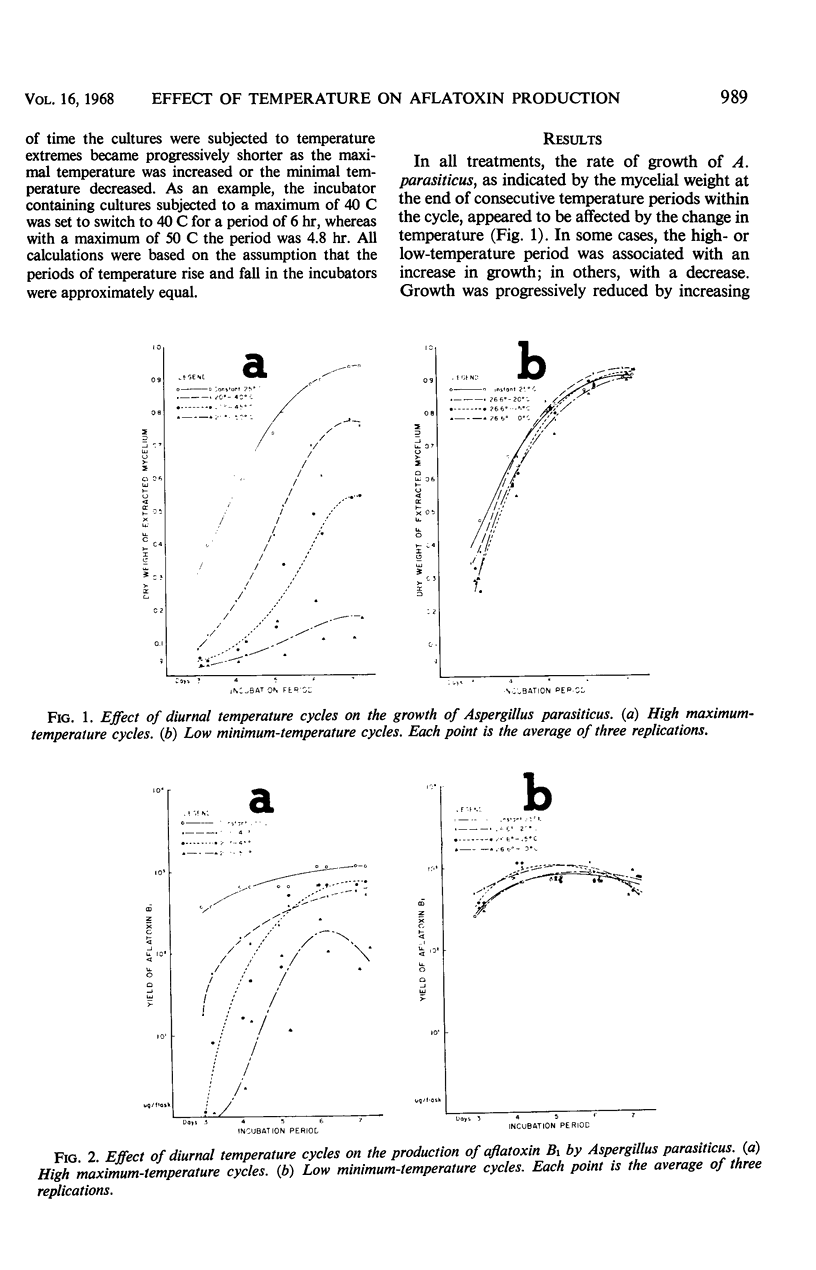
Exposures to short periods of high temperature (40 to 50 C) in each 24-hr diurnal temperature cycle (average temperature ca. 25 C) reduced growth of Aspergillus parasiticus and production and accumulation of the aflatoxins when compared with cultures held continuously at 25 C. In contrast, diurnal cycles with an average temperature of ca. 25 C but with minima as low as 10 C did not appreciably affect either growth or toxin production. The ratio of production of aflatoxin B to aflatoxin G increased as the maximal temperature was raised but remained essentially unchanged with decreasing minimal temperatures.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- PONS W. A., Jr, GOLDBLATT L. A. THE DETERMINATION OF AFLATOXINS IN COTTONSEED PRODUCTS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jun;42:471–475. doi: 10.1007/BF02540087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler A. F., Palmer J. G., Eisenberg W. V. Aflatoxin Production by Aspergillus flavus as Related to Various Temperatures. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1006–1009. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.1006-1009.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W. Effect of corn steep liquor on mycelial growth and aflatoxin production in Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):381–385. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.381-385.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Hein H., Jr Aflatoxins: production of the toxins in vitro in relation to temperature. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Mar;15(2):441–445. doi: 10.1128/am.15.2.441-445.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]