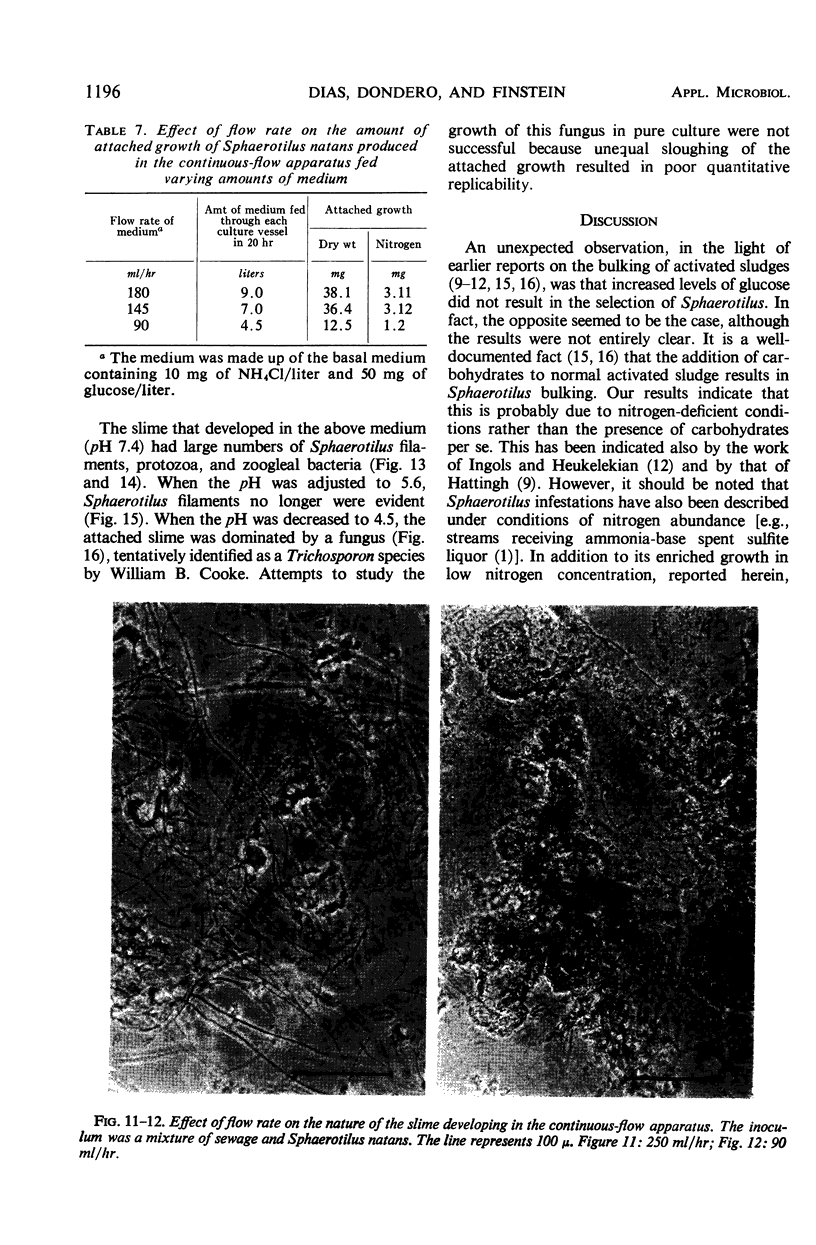
Abstract
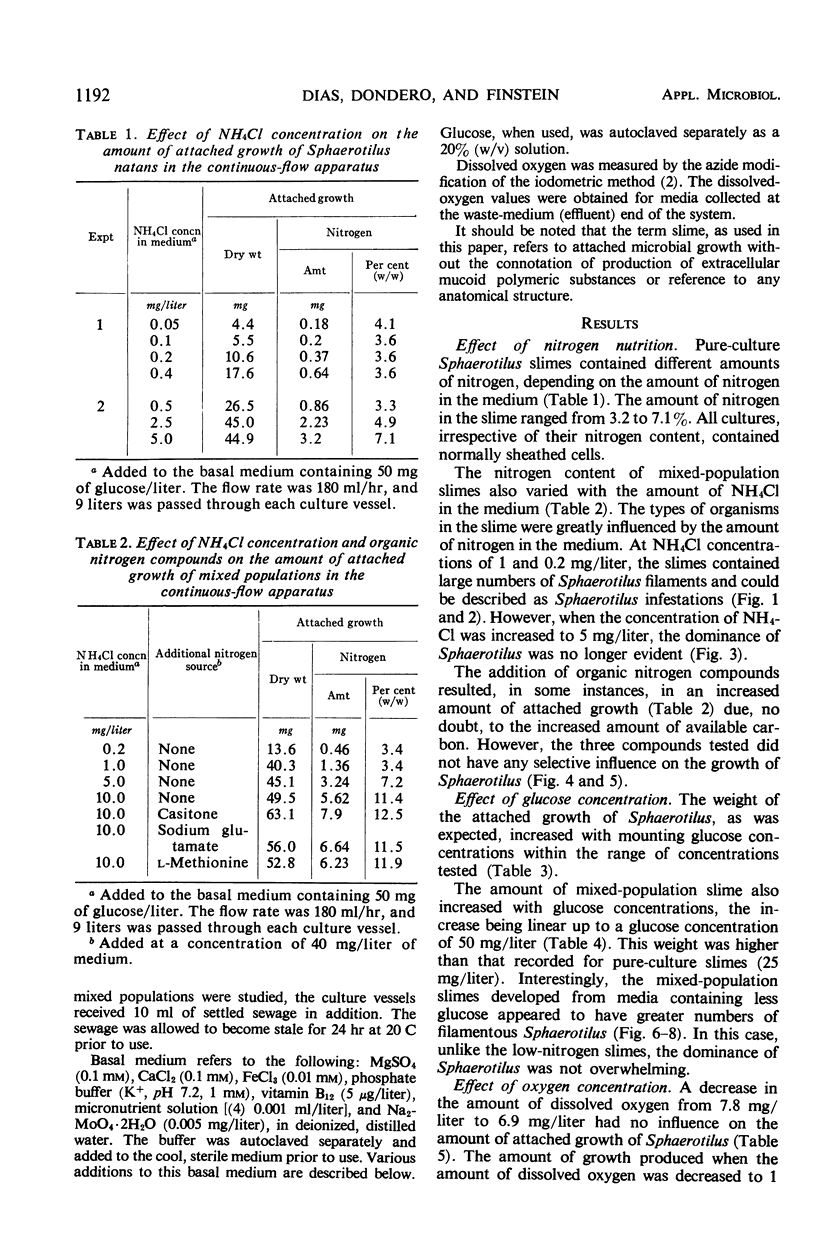
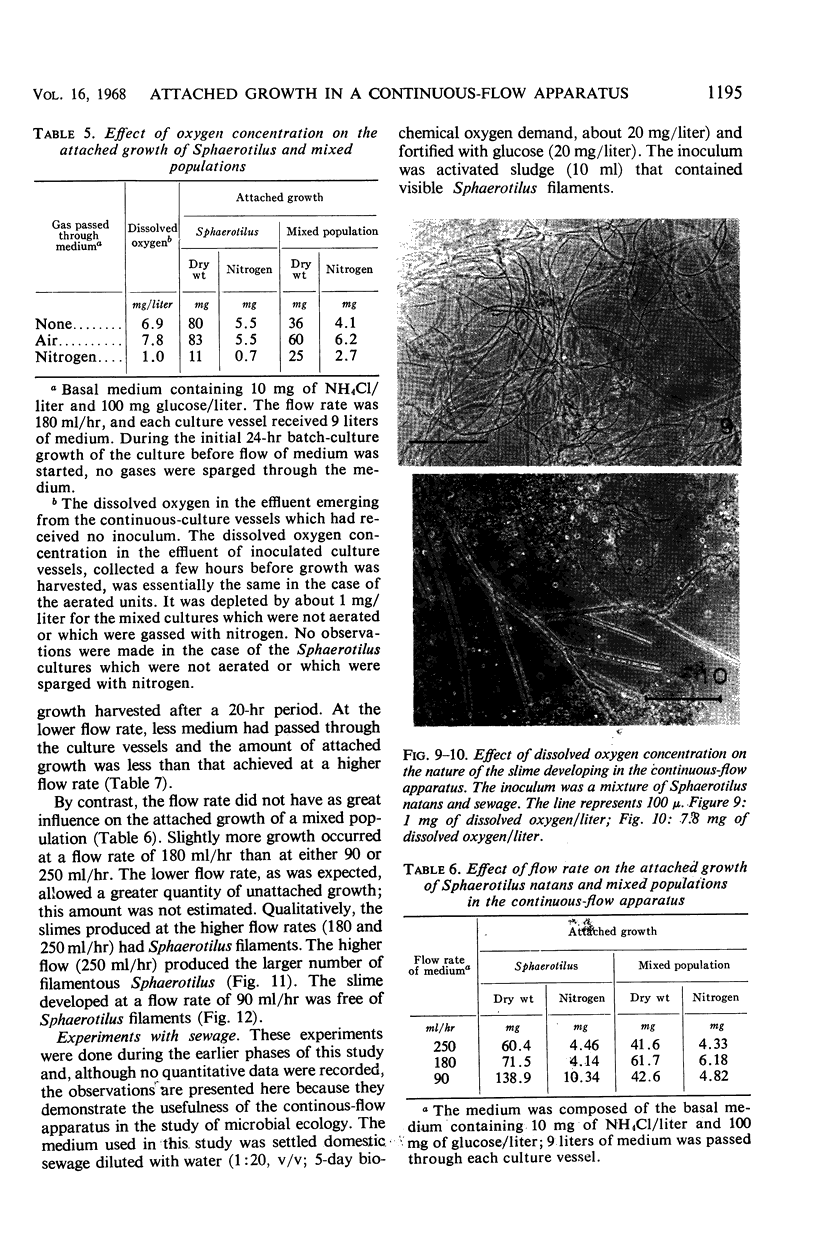
The effects of NH4Cl concentration, organic nitrogen compounds, glucose concentration, dissolved oxygen concentration, and flow rate on the attached growth of pure cultures of Sphaerotilus natans and of a mixed population in a continuous-flow apparatus are described. Low concentrations of NH4Cl and oxygen, and high flow rates resulted in attached populations that were dominated by Sphaerotilus. The conditions that allowed maximal attached growth in pure culture did not correspond to the conditions that promoted attached growth of Sphaerotilus in a mixed population.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DONDERO N. C., PHILLIPS R. A., HEUKELEKIAN H. Isolation and preservation of cultures of Sphaerotilus. Appl Microbiol. 1961 May;9:219–227. doi: 10.1128/am.9.3.219-227.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONDERO N. C. Sphaerotilus, its nature and economic significance. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1961;3:77–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70507-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dias F. F., Heukelekian H. Utilization of Inorganic Nitrogen Compounds by Sphaerotilus natans Growing in a Continuous-Flow Apparatus. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1083–1086. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.1083-1086.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKREND H., DONDERO N. C. REQUIREMENT OF SPHAEROTILUS FOR CYANOCOBALAMIN. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:286–292. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.286-292.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]