Abstract
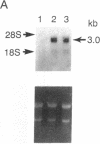
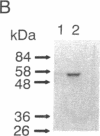
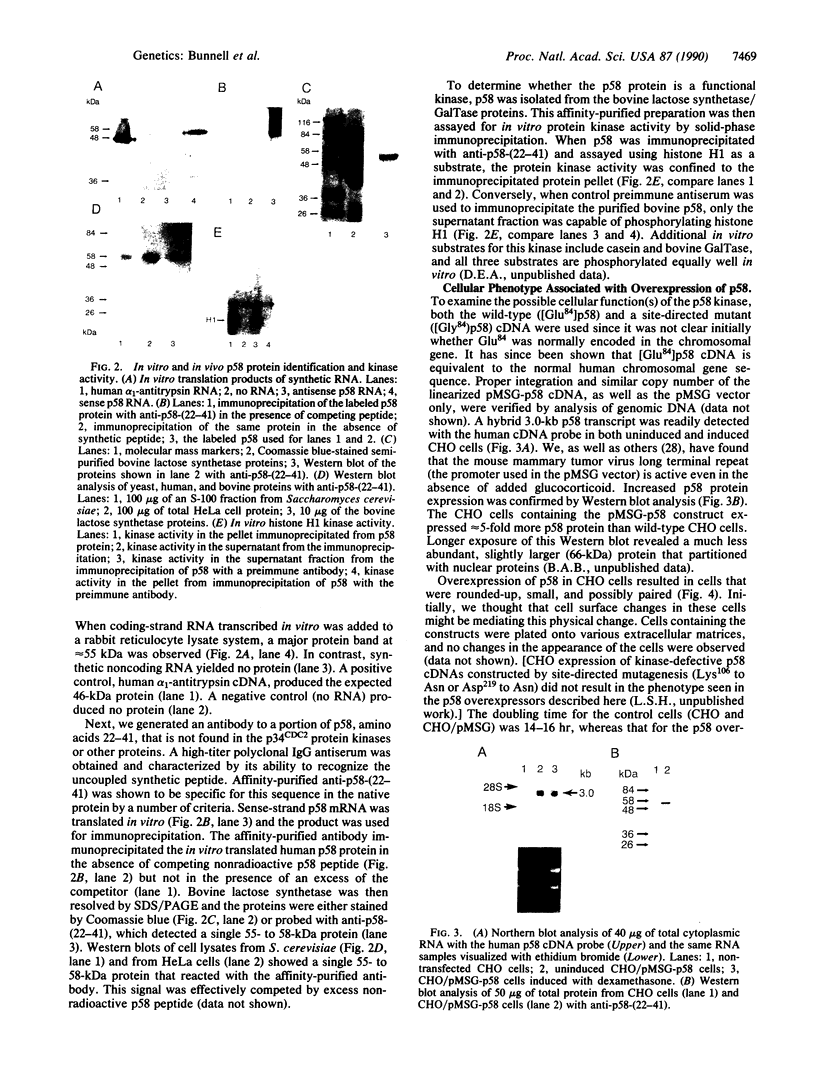
We have isolated and characterized cDNA encoding a human 58-kDa protein kinase that is homologous to the cell division control (CDC) protein kinases. This protein kinase also contains a unique N-terminal domain that may potentially regulate its function. Due to its relatedness to p34CDC2, the human p58 cDNA was overexpressed in CHO cells to determine the effect on the cell cycle. Elevated expression of p58 in these cells resulted in prolonged late telophase and early G1 phase of the cell cycle. These p58 overexpressors showed a significantly increased frequency of tubulin midbodies as well as significant increases in mitotic abnormalities. Thus, proper regulation of p58 protein kinase is essential for normal cell cycle progression in these cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brinkley B. R., Zinkowski R. P., Mollon W. L., Davis F. M., Pisegna M. A., Pershouse M., Rao P. N. Movement and segregation of kinetochores experimentally detached from mammalian chromosomes. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):251–254. doi: 10.1038/336251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunnell B. A., Fillmore H., Gregory P., Kidd V. J. A dominant negative mutation in two proteins created by ectopic expression of an AU-rich 3' untranslated region. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1990 Mar;16(2):151–162. doi: 10.1007/BF01233045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Gasdaska P., Hartwell L. Dominant effects of tubulin overexpression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1049–1059. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Sowder J. T., Lahti J. M., Cihak J., Lösch U., Cooper M. D. TCR3: a third T-cell receptor in the chicken. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2351–2355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courchesne W. E., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. A putative protein kinase overcomes pheromone-induced arrest of cell cycling in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1107–1119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90509-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Grisafi P. L., Fink G. R. FUS3 encodes a cdc2+/CDC28-related kinase required for the transition from mitosis into conjugation. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):649–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90668-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller G. M., Brinkley B. R., Boughter J. M. Immunofluorescence of mitotic spindles by using monospecific antibody against bovine brain tubulin. Science. 1975 Mar 14;187(4180):948–950. doi: 10.1126/science.1096300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Wittenberg C., Richardson H. E., de Barros Lopes M., Reed S. I. A family of cyclin homologs that control the G1 phase in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6255–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K. Homology probing: identification of cDNA clones encoding members of the protein-serine kinase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):388–392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys-Beher M. G., Bunnell B., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Kidd V. J. Molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of human 4-beta-galactosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8918–8922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., Guerriero V., Jr, Bagchi I. C., Means A. R. The calmodulin binding domain of chicken smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase contains a pseudosubstrate sequence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2542–2548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Brough D. E., Cleghon V. Introduction, stable integration, and controlled expression of a chimeric adenovirus gene whose product is toxic to the recipient human cell. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1354–1362. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long G. L., Chandra T., Woo S. L., Davie E. W., Kurachi K. Complete sequence of the cDNA for human alpha 1-antitrypsin and the gene for the S variant. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):4828–4837. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lörincz A. T., Reed S. I. Primary structure homology between the product of yeast cell division control gene CDC28 and vertebrate oncogenes. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):183–185. doi: 10.1038/307183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeks-Wagner D., Hartwell L. H. Normal stoichiometry of histone dimer sets is necessary for high fidelity of mitotic chromosome transmission. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90483-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K., Draetta G., Brizuela L., Vandre D., Beach D. The cdc2 kinase is a nuclear protein that is essential for mitosis in mammalian cells. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Sundsmo M., Roch J. M., Kimura N., Cole G., Schubert D., Oltersdorf T., Schenk D. B. Secreted form of amyloid beta protein precursor is involved in the growth regulation of fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., van Kerkhof P., Fallon R. J., Schwartz A. L. Golgi galactosyltransferase contains serine-linked phosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 1;169(2):307–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Blumenthal D. K., Edelman A. M., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G., Titani K. Amino acid sequence of an active fragment of rabbit skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6028–6037. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Wade R. D., Smith S. B., Krebs E. G., Walsh K. A., Titani K. Guanosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase, a chimeric protein homologous with two separate protein families. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4207–4218. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]