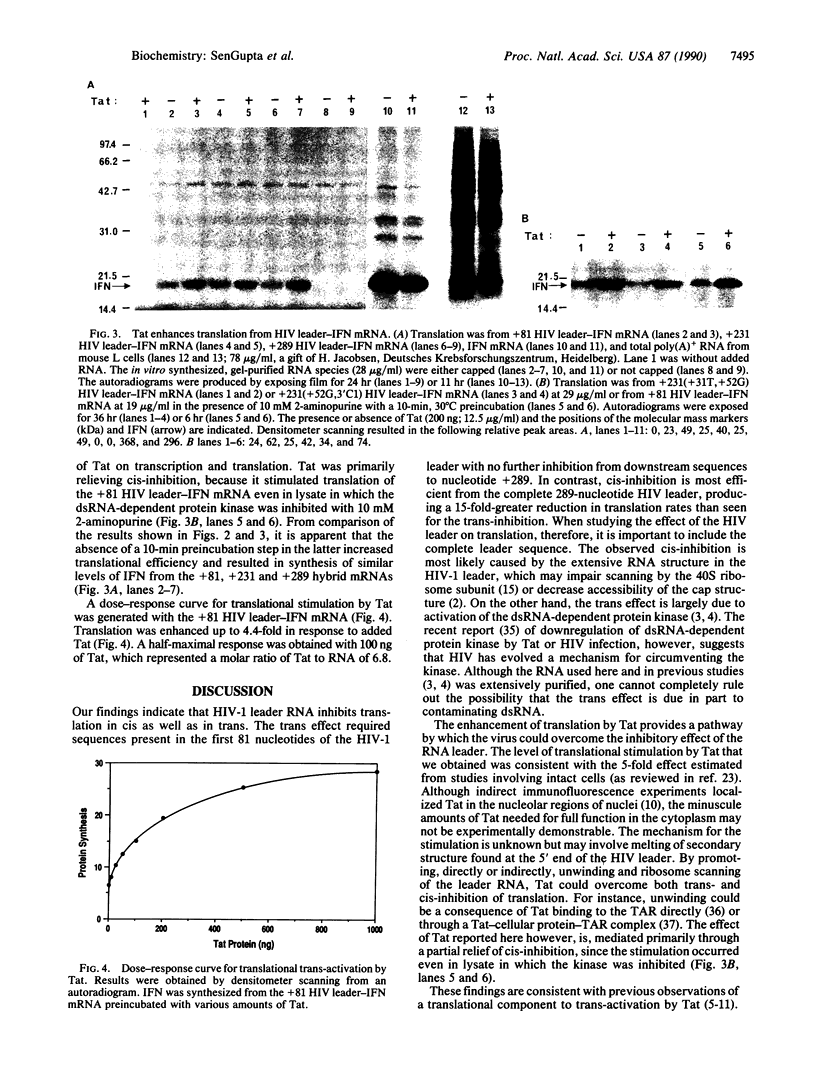
Abstract
Translational effects of the RNA leader and Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) were investigated in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Hybrid RNA species with natural or mutated HIV-1 leader fused to human interferon- gamma mRNA were produced in vitro from recombinant plasmids. HIV-1 leader RNA was found to inhibit translation through two mechanisms. A 3-fold trans-inhibition of translation was demonstrated by mixing hybrid HIV-1 leader RNA with indicator interferon mRNA. By comparison, HIV-1 leader caused a 50-fold cis-inhibition in lysate in which two trans-inhibitory factors, double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase and (2'-5')oligoadenylate synthetase, were suppressed. In contrast, purified HIV-1 Tat protein produced in Escherichia coli enhanced by 4-fold translation from HIV-1 leader-interferon mRNA but not from interferon mRNA lacking HIV sequences or from total poly(A)+ RNA. Translation of mRNA containing either a single base substitution in the loop of the "trans-acting responsive" sequence (TAR) or an alternative stem-loop in TAR was nevertheless stimulated by Tat. The enhancement of translation by Tat was largely due to relief of cis-inhibition, since the effect was found even in lysate in which double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase was inhibited with 2-aminopurine. These results suggest that translation is an important level of control in the replication cycle of HIV-1.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Guo C., Josephs S. F., Wong-Staal F. Trans-activator gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III). Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):69–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2990040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. trans activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is sequence specific for both the single-stranded bulge and loop of the trans-acting-responsive hairpin: a quantitative analysis. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5501–5504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5501-5504.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Silverman R. H., Jeang K. T. Tat trans-activates the human immunodeficiency virus through a nascent RNA target. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braddock M., Chambers A., Wilson W., Esnouf M. P., Adams S. E., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. HIV-1 TAT "activates" presynthesized RNA in the nucleus. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90841-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Regulatory pathways governing HIV-1 replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. The trans-activator gene of the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III is required for replication. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Cheroutre H., Taya Y., Degrave W., Van Heuverswyn H., Fiers W. Molecular cloning of human immune interferon cDNA and its expression in eukaryotic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2487–2501. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A., Valerio R. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 tat protein binds trans-activation-responsive region (TAR) RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Petryshyn R., Sonenberg N. Activation of double-stranded RNA-dependent kinase (dsl) by the TAR region of HIV-1 mRNA: a novel translational control mechanism. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90904-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Jarrett R. F., Aldovini A., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. HTLV-III expression and production involve complex regulation at the levels of splicing and translation of viral RNA. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):807–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Feinberg M. B., Josephs S. F., Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Reyes G., Gonda M. A., Aldovini A., Debouk C., Gallo R. C. The trans-activator gene of HTLV-III is essential for virus replication. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):367–371. doi: 10.1038/320367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatignol A., Kumar A., Rabson A., Jeang K. T. Identification of cellular proteins that bind to the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 trans-activation-responsive TAR element RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7828–7832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Bioassay for trans-activation using purified human immunodeficiency virus tat-encoded protein: trans-activation requires mRNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):821–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh W. C., Rosen C., Sodroski J., Ho D. D., Haseltine W. A. Identification of a protein encoded by the trans activator gene tatIII of human T-cell lymphotropic retrovirus type III. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):181–184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.181-184.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Mutational analysis of the trans-activation-responsive region of the human immunodeficiency virus type I long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):673–679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.673-679.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Perkins A., Heimer E. P., Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression is mediated by nuclear events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6364–6368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai J., Lesiak K., Torrence P. F. Respective role of each of the purine N-6 amino groups of 5'-O-triphosphoryladenylyl(2'----5')adenylyl(2----5')adenosine in binding to and activation of RNase L. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1390–1393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Shank P. R., Kumar A. Transcriptional activation of homologous viral long terminal repeats by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 or the human T-cell leukemia virus type I tat proteins occurs in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8291–8295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Cabradilla C. D., Benton C. V., Lasky L. A., Capon D. J. Nucleic acid structure and expression of the human AIDS/lymphadenopathy retrovirus. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):450–458. doi: 10.1038/313450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan-Sorden N. L., Lesiak K., Bayard B., Torrence P. F., Silverman R. H. Photochemical crosslinking in oligonucleotide-protein complexes between a bromine-substituted 2-5A analog and 2-5A-dependent RNase by ultraviolet lamp or laser. Anal Biochem. 1990 Feb 1;184(2):298–304. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90684-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin N. T., Cohen E. A., Darveau A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sonenberg N. Mutational analysis of the 5' non-coding region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: effects of secondary structure on translation. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2831–2837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Goh W. C., Dayton A. I., Lippke J., Haseltine W. A. Post-transcriptional regulation accounts for the trans-activation of the human T-lymphotropic virus type III. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):555–559. doi: 10.1038/319555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Katze M. G., Parkin N. T., Edery I., Hovanessian A. G., Sonenberg N. Control of the interferon-induced 68-kilodalton protein kinase by the HIV-1 tat gene product. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1216–1219. doi: 10.1126/science.2180064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SenGupta D. N., Silverman R. H. Activation of interferon-regulated, dsRNA-dependent enzymes by human immunodeficiency virus-1 leader RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):969–978. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Marciniak R. A. HIV TAR: an RNA enhancer? Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):229–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman R. H. Functional analysis of 2-5A-dependent RNase and 2-5a using 2',5'-oligoadenylate-cellulose. Anal Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;144(2):450–460. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Hay A. J. Nucleotide sequences at the 5' termini of influenza virus RNAs and their transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Apr;5(4):1207–1219. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Patarca R., Rosen C., Wong-Staal F., Haseltine W. Location of the trans-activating region on the genome of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):74–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2990041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R., Gilbert C. S., Kerr I. M. The respective roles of the protein kinase and pppA2' p5' A2' p5 A-activated endonuclease in the inhibition of protein synthesis by double stranded RNA in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1335–1350. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. M., Felber B. K., Paskalis H., Pavlakis G. N. Expression and characterization of the trans-activator of HTLV-III/LAV virus. Science. 1986 Nov 21;234(4779):988–992. doi: 10.1126/science.3490693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









