Abstract
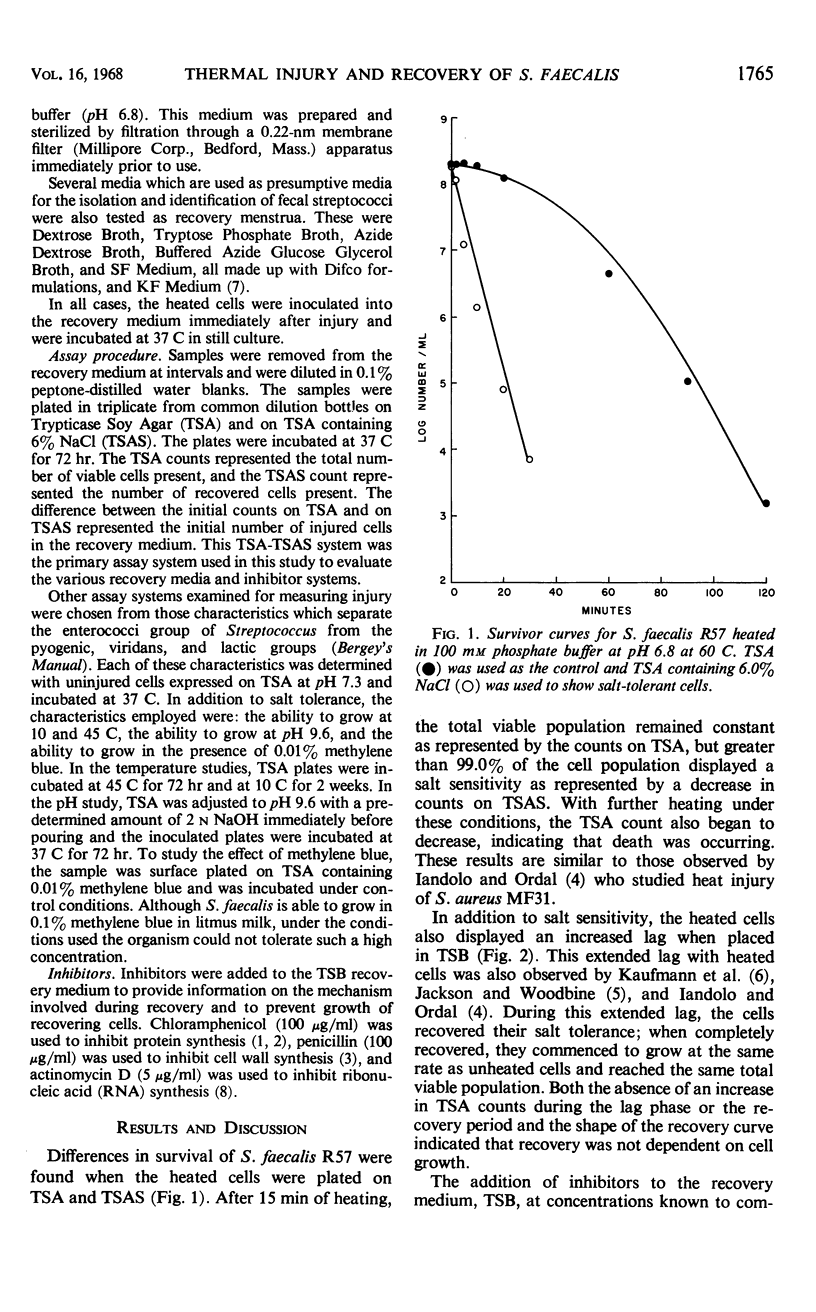
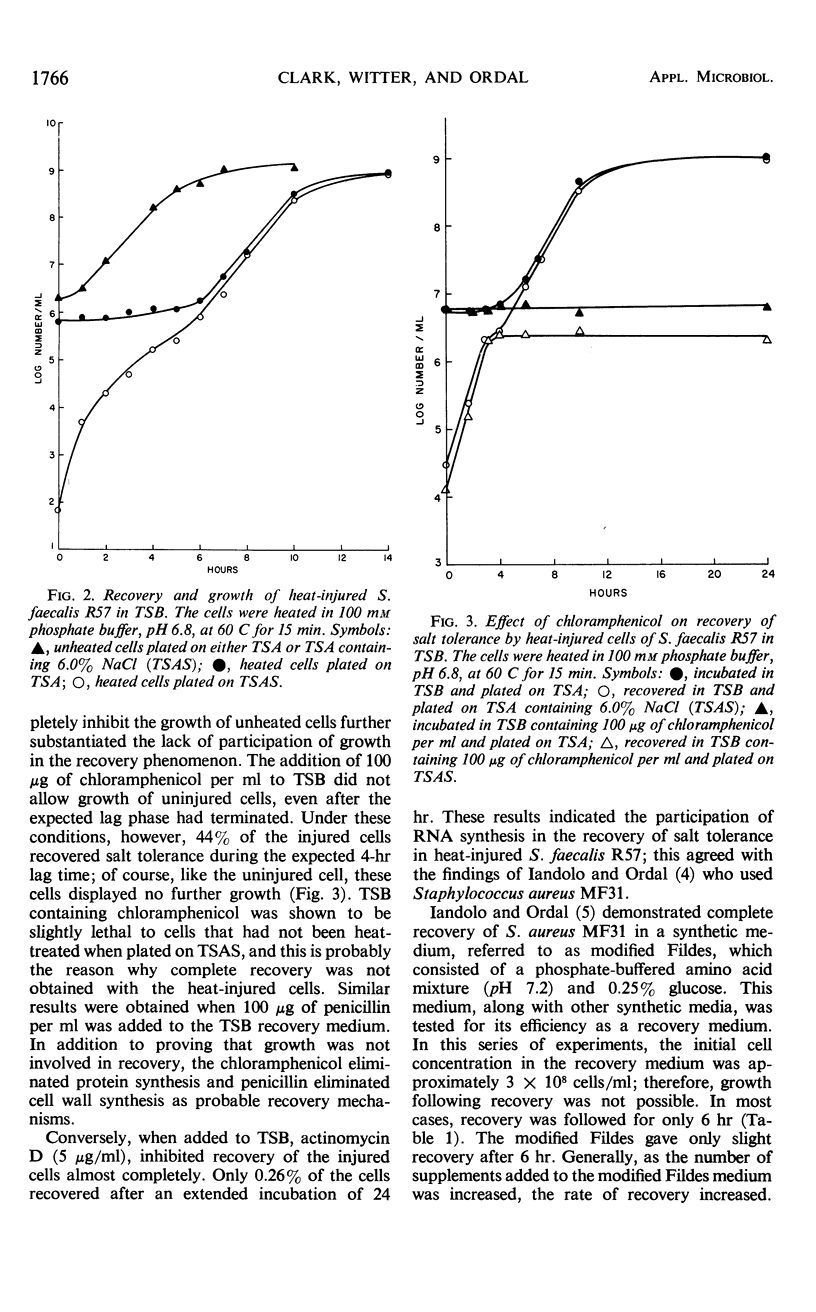
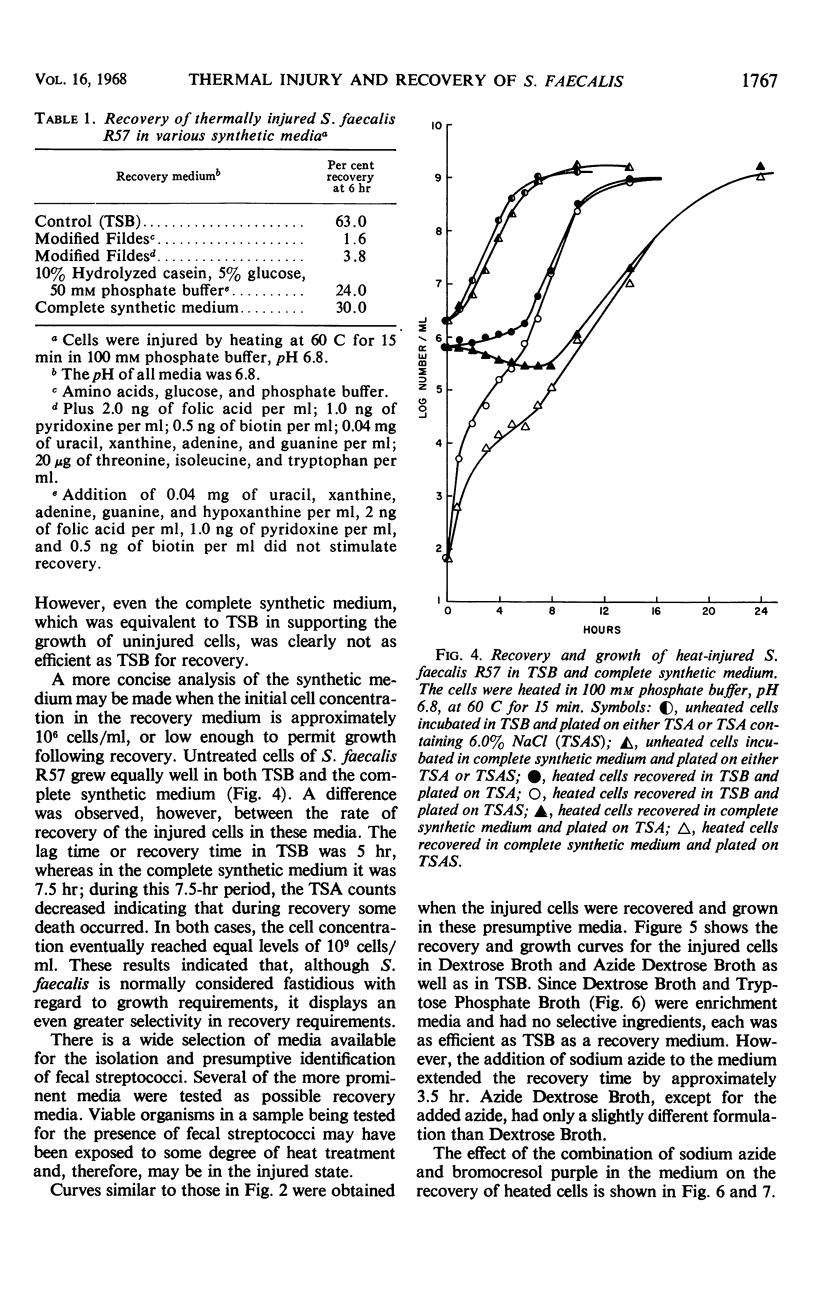
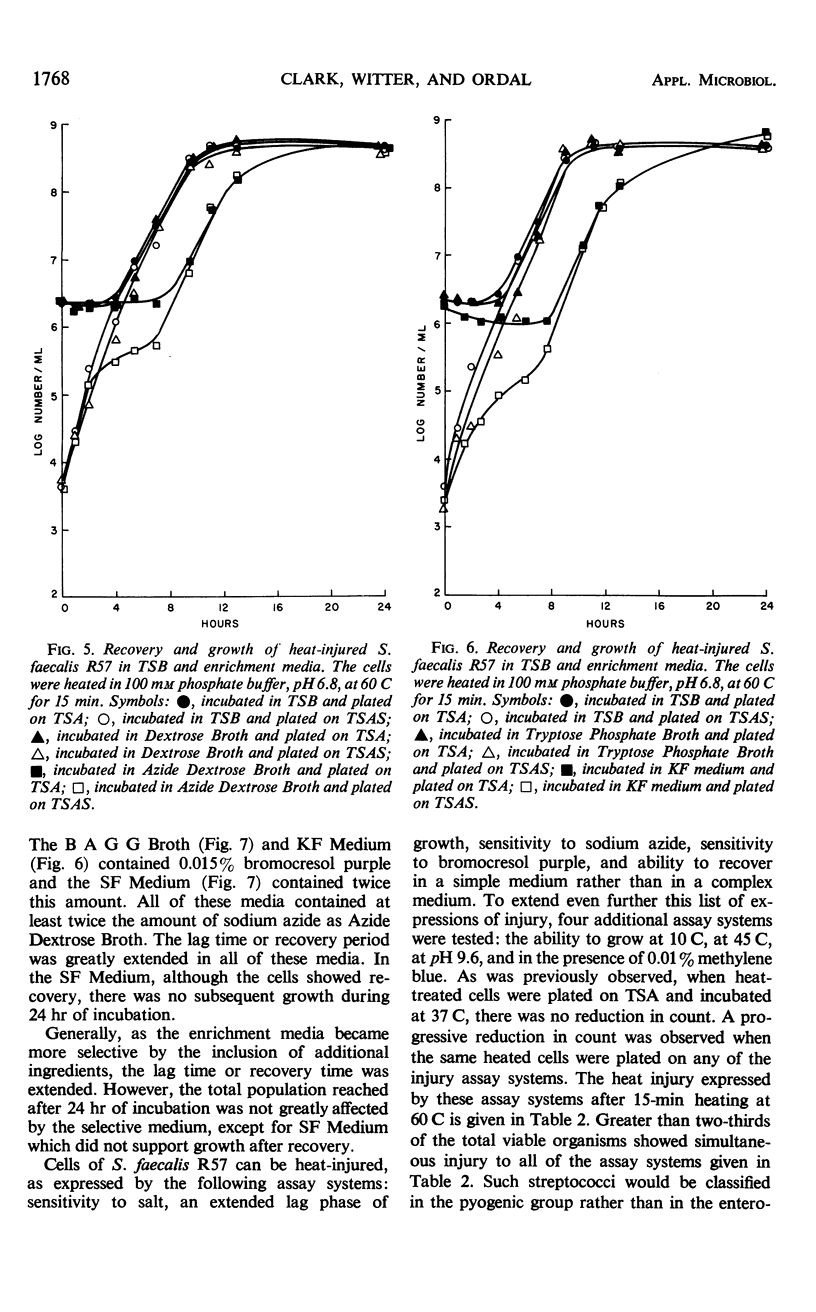
Exposure of Streptococcus faecalis R57 to sublethal heating produced a temporary change in the salt tolerance and growth of the organism. After sublethal heat treatment at 60 C for 15 min, greater than 99.0% of the viable population was unable to reproduce on media containing 6% NaCl. In addition, the heated cells displayed a sensitivity to incubation temperature, pH, and 0.01% methylene blue. When the injured cells were placed in a synthetic medium, recovery occurred at a much slower rate than in a complex medium. However, both media supported comparable growth of the uninjured organism. Various media used for the enrichment of streptococci also provided a suitable environment for the recovery of the injured cells. Generally, as more selective agents were present in the medium, the rates of recovery decreased. Metabolic inhibitor studies with chloramphenicol, penicillin, and actinomycin D substantiated the fact that the process involved was recovery and not growth, and that this recovery was linked to ribonucleic acid synthesis.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brock T. D. CHLORAMPHENICOL. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Mar;25(1):32–48. doi: 10.1128/br.25.1.32-48.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALE E. F., FOLKES J. P. The assimilation of amino-acids by bacteria. XV. Actions of antibiotics on nucleic acid and protein synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):493–498. doi: 10.1042/bj0530493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iandolo J. J., Ordal Z. J. Repair of thermal injury of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.134-142.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMANN O. W., HARMON L. G., PAIL THORP O. C., PFLUG I. J. Effect of heat treatment on the growth of surviving cells. J Bacteriol. 1959 Dec;78:834–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.6.834-838.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNER B. A., CLARK H. F., KABLER P. W. Fecal Streptococci. I. Cultivation and enumeration of Streptococci in surface waters. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Jan;9:15–20. doi: 10.1128/am.9.1.15-20.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRK J. M. The mode of action of actinomycin D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 29;42:167–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90769-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCOY T. A., WENDER S. H. Some factors affecting the nutritional requirements of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jun;65(6):660–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.6.660-665.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STILES M. E., WITTER L. D. THERMAL INACTIVATION, HEAT INJURY, AND RECOVERY OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Dairy Sci. 1965 Jun;48:677–681. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(65)88321-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin S. J., Ordal Z. J. Regeneration of ribosomes and ribosomal ribonucleic acid during repair of thermal injury to Staphylococcus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1082–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1082-1087.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- vanDEMARK P. J. The vitamin requirements for glycerol oxidation by Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):533–539. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.533-539.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



