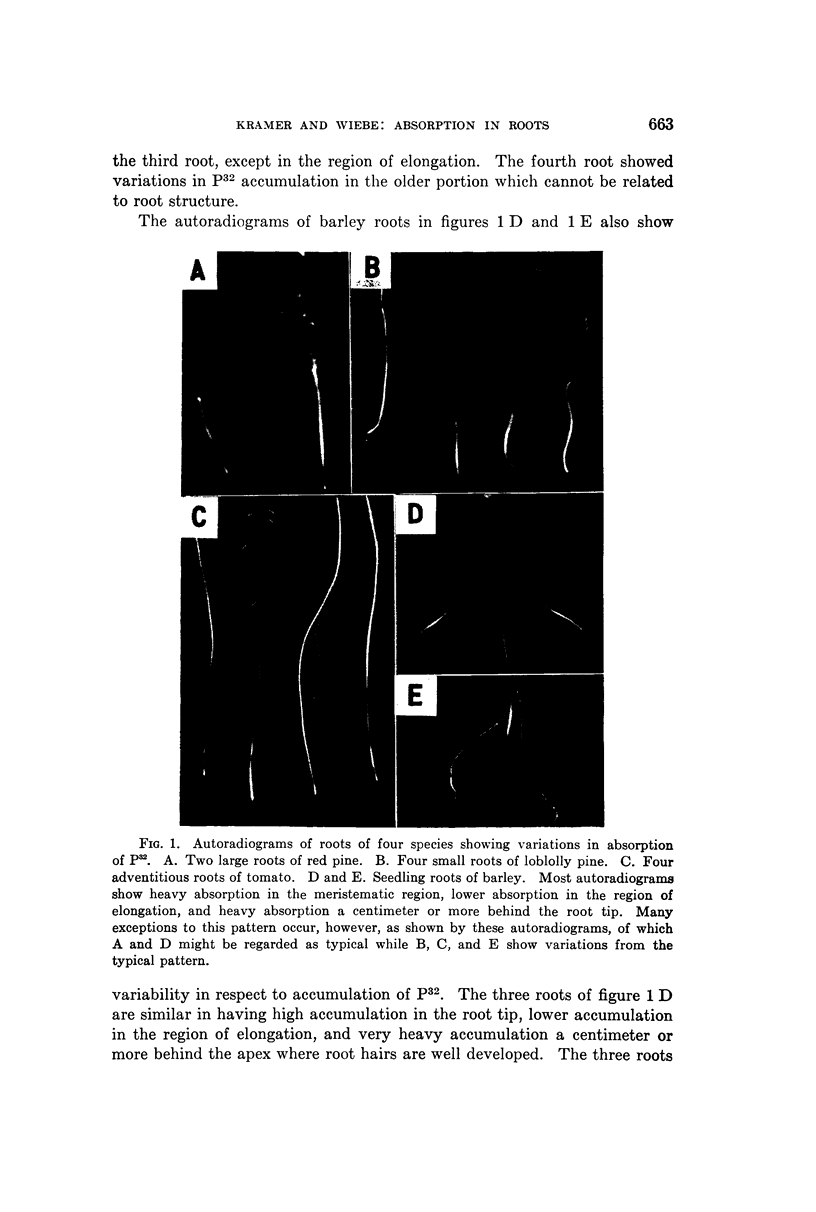
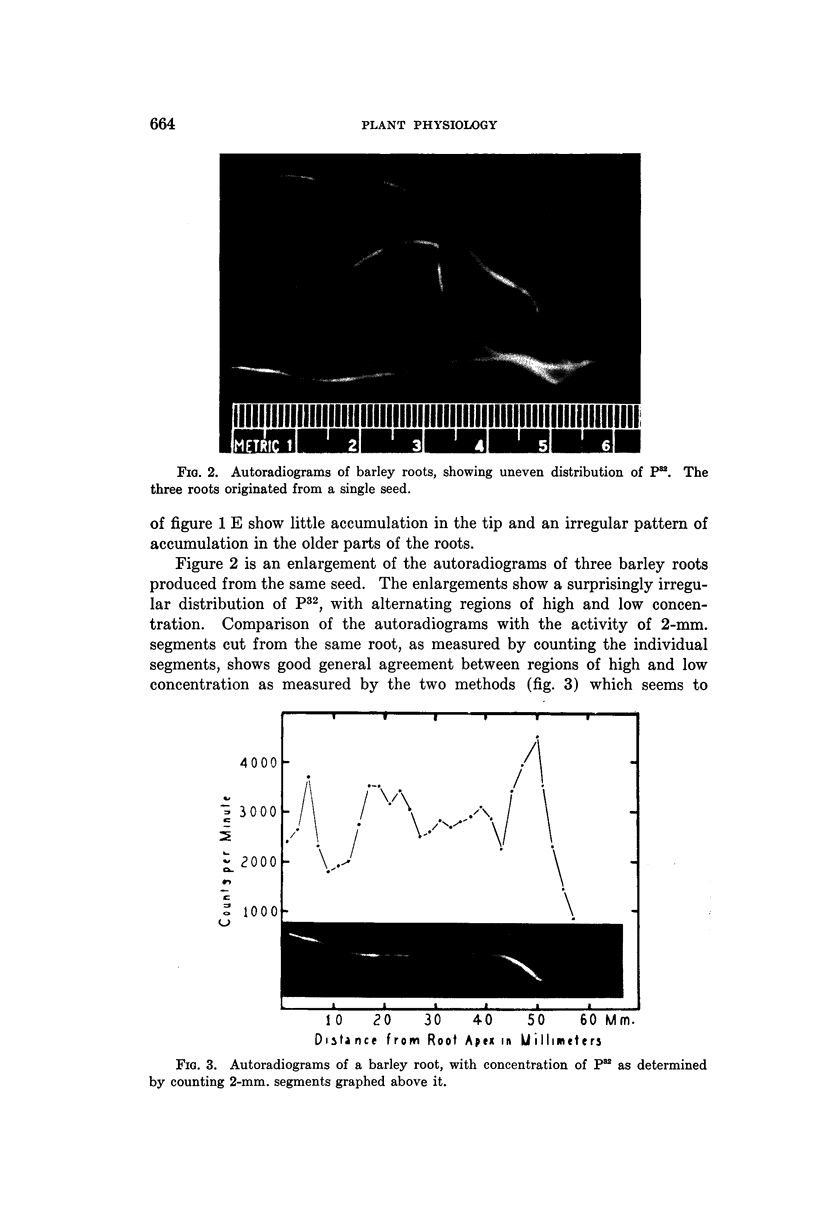
Full text
PDF

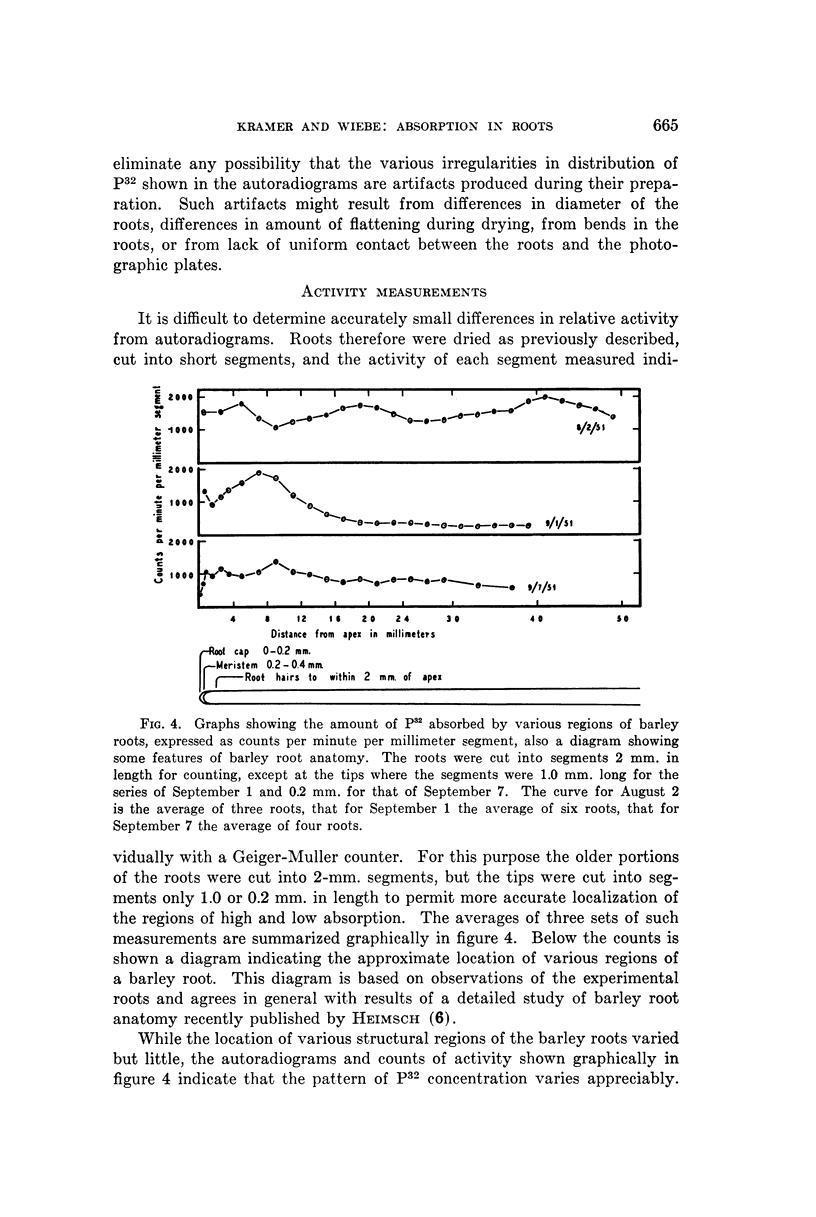

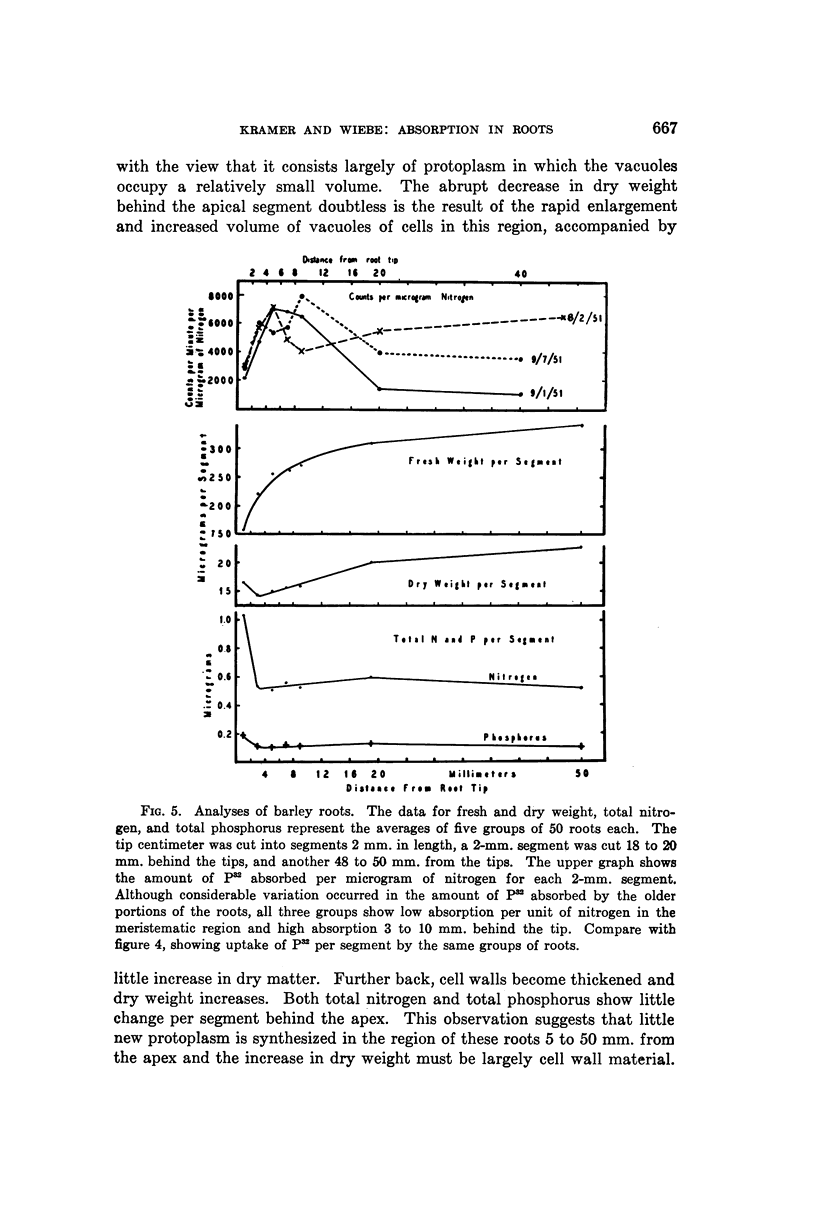

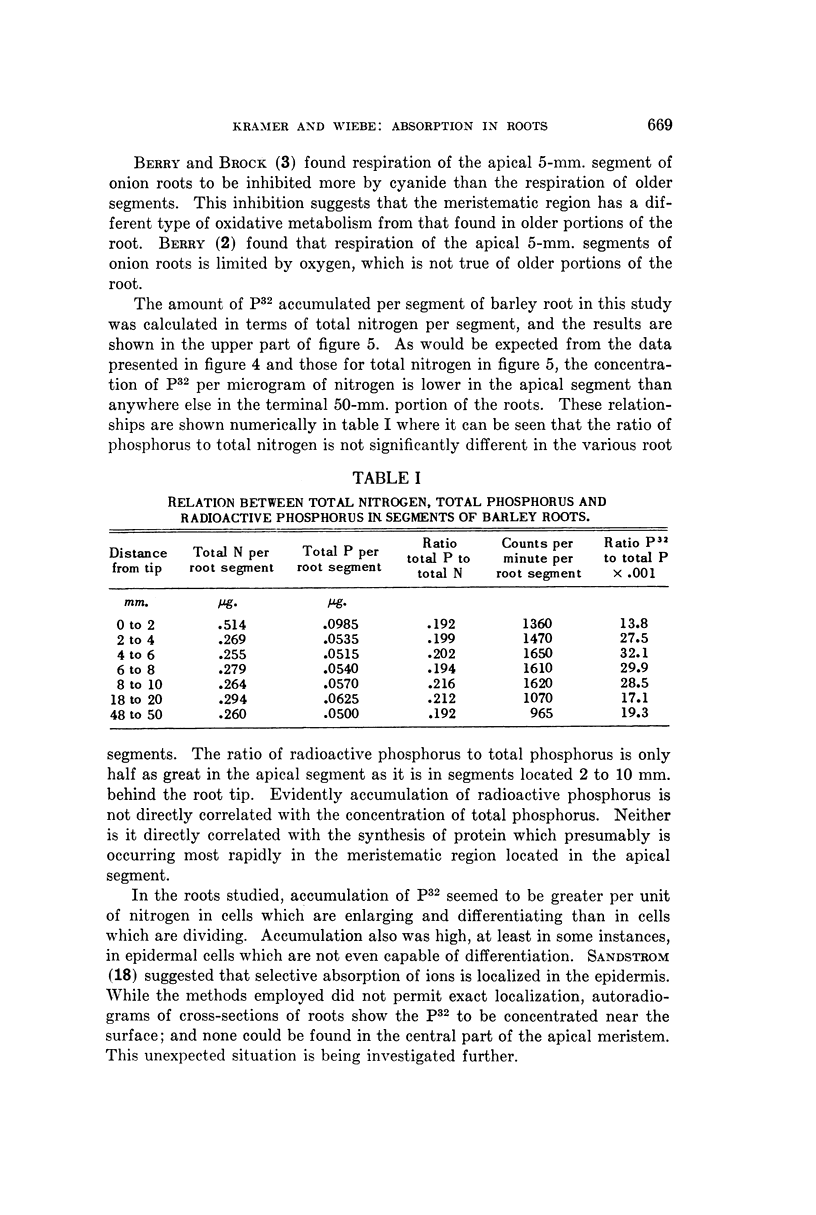





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry L. J., Brock M. J. POLAR DISTRIBUTION OF RESPIRATORY RATE IN THE ONION ROOT TIP. Plant Physiol. 1946 Oct;21(4):542–549. doi: 10.1104/pp.21.4.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. J. EFFECTS OF RESPIRATION INHIBITORS ON ACCUMULATION OF RADIOACTIVE PHOSPHORUS BY ROOTS OF LOBLOLLY PINE. Plant Physiol. 1951 Jan;26(1):30–36. doi: 10.1104/pp.26.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. J., Wilbur K. M. Absorption of Radioactive Phosphorus by Mycorrhizal Roots of Pine. Science. 1949 Jul 1;110(2844):8–9. doi: 10.1126/science.110.2844.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner R. C. RAPID ANALYTICAL METHODS FOR SOME OF THE MORE COMMON INORGANIC CONSTITUENTS OF PLANT TISSUES. Plant Physiol. 1944 Jan;19(1):76–89. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevot P., Steward F. C. SALIENT FEATURES OF THE ROOT SYSTEM RELATIVE TO THE PROBLEM OF SALT ABSORPTION. Plant Physiol. 1936 Jul;11(3):509–534. doi: 10.1104/pp.11.3.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward F. C., Prevot P., Harrison J. A. ABSORPTION AND ACCUMULATION OF RUBIDIUM BROMIDE BY BARLEY PLANTS. LOCALIZATION IN THE ROOT OF CATION ACCUMULATION AND OF TRANSFER TO THE SHOOT. Plant Physiol. 1942 Jul;17(3):411–421. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]