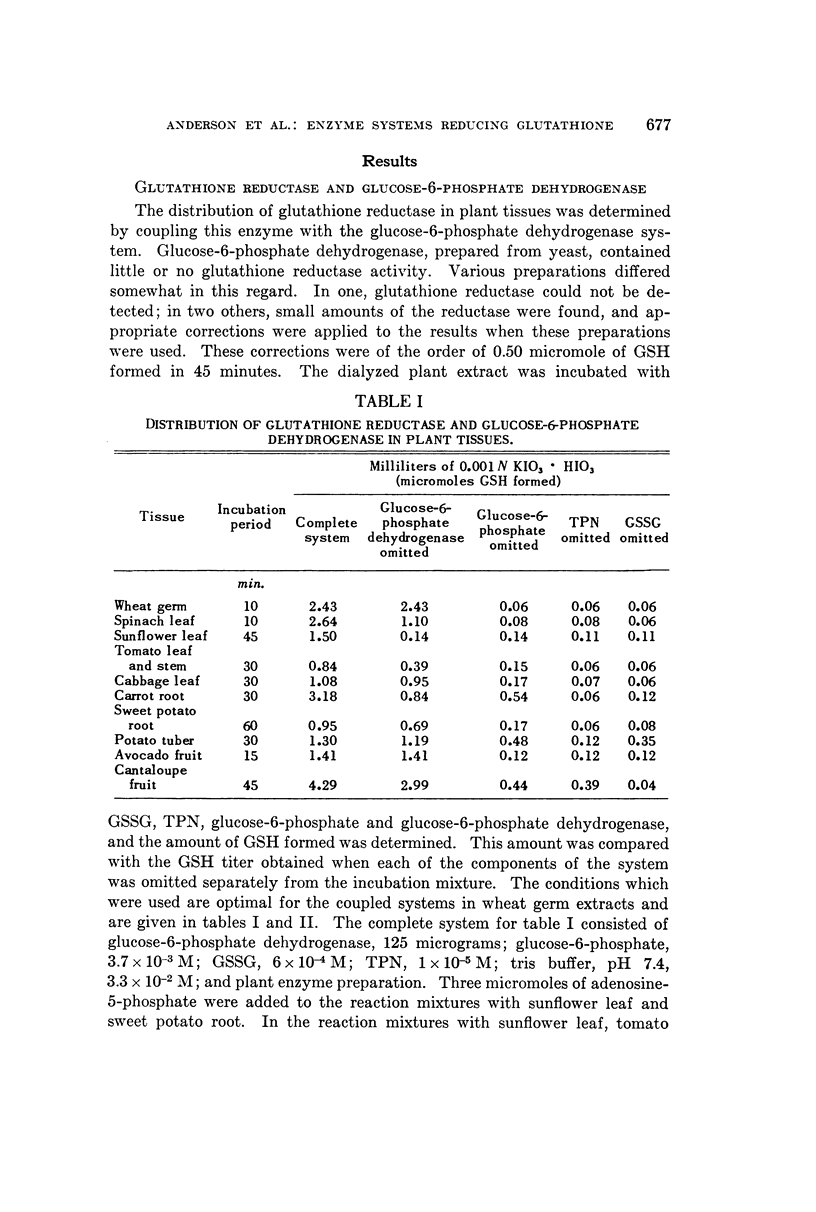
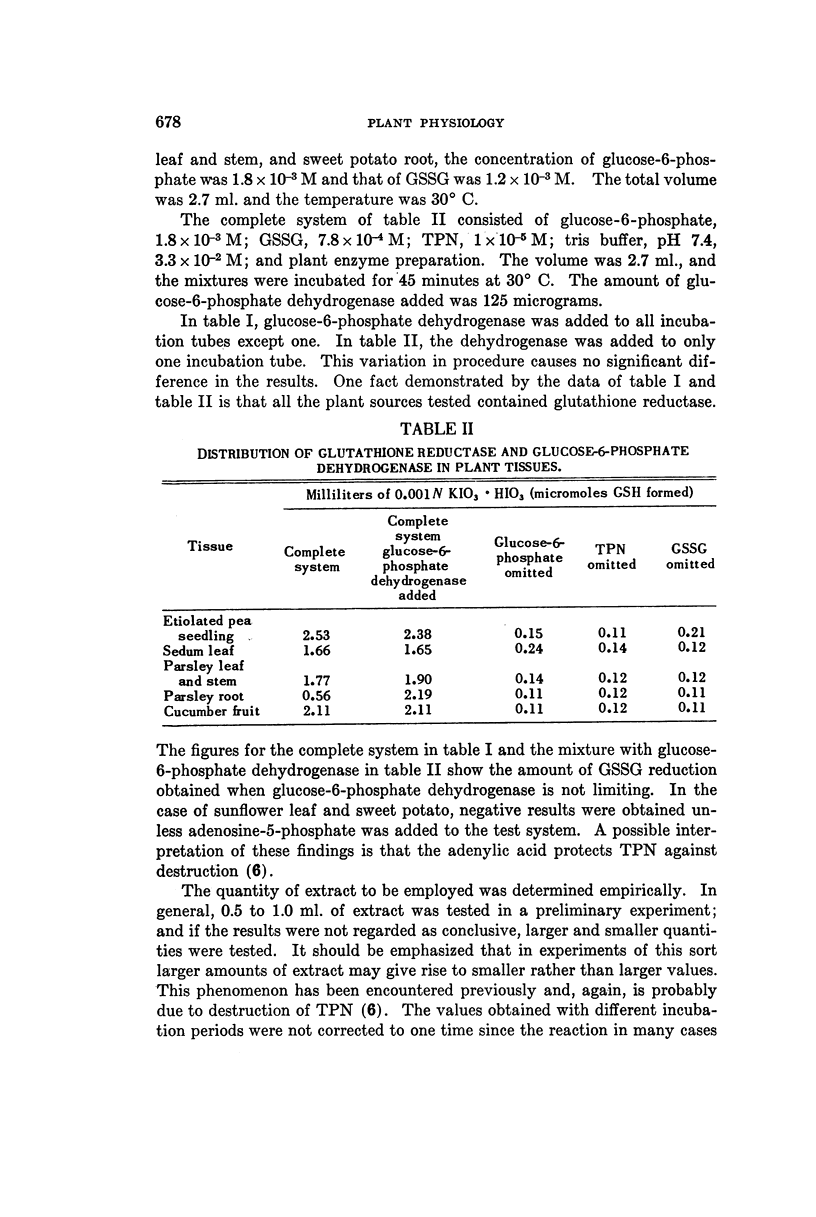
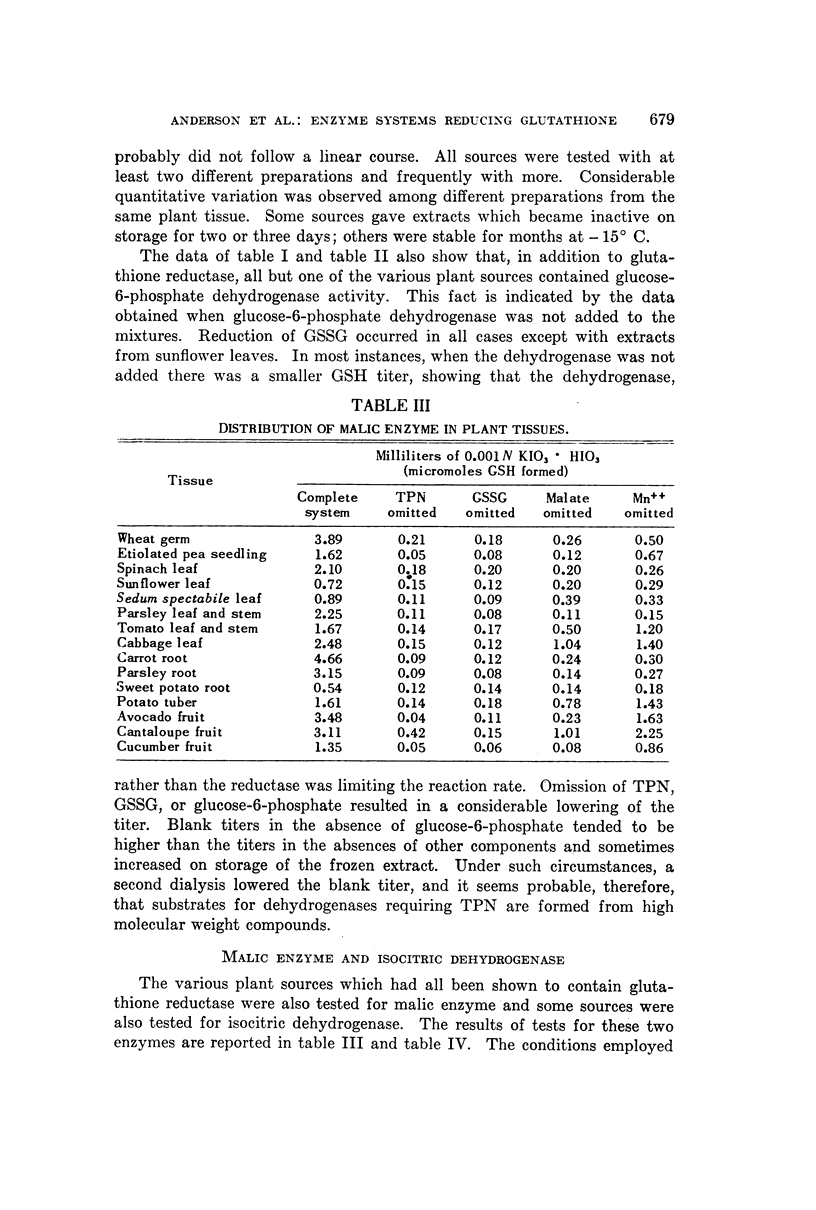
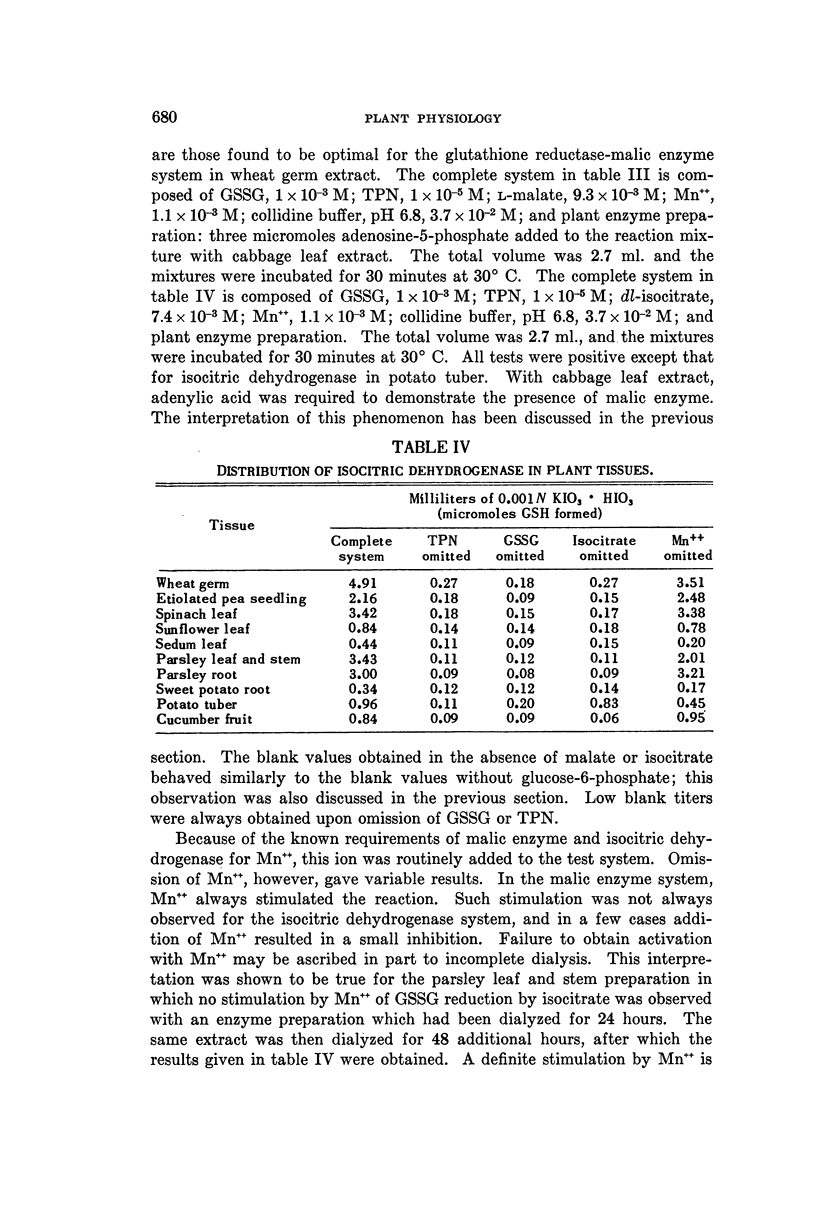
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHEN S. S. The synthesis of nucleic acid by virus-infected bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1951 Sep;15(3):131–146. doi: 10.1128/br.15.3.131-146.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONN E. E., VENNESLAND B. Glutathione reductase of wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1951 Sep;192(1):17–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKENS F., GLOCK G. E. Direct oxidation of glucose-6-phosphate, 6-phosphogluconate and pentose-5-phosphates by enzymes of animal origin. Biochem J. 1951 Nov;50(1):81–95. doi: 10.1042/bj0500081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A., Eggleston L. V. Micro-determination of isocitric and cis-aconitic acids in biological material. Biochem J. 1944;38(5):426–437. doi: 10.1042/bj0380426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAPSON L. W., GODDARD D. R. The reduction of glutathione by plant tissues. Biochem J. 1951 Oct;49(5):592–601. doi: 10.1042/bj0490592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirie N. W. The cuprous derivatives of some sulphydryl compounds. Biochem J. 1931;25(2):614–628. doi: 10.1042/bj0250614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL T. W., LEHNINGER A. L. Glutathione reductase of animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1952 Jan;194(1):119–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



