Abstract
Background
It has been argued that postoperative pain treatment should be “procedure-specific”, since different analgesics may have specific effects dependent on the surgical procedure. The aim of the present subgroup analysis was to compare the beneficial and harmful effects of perioperative gabapentin treatment in different surgical procedures.
Methods
Relevant databases were searched for randomized clinical trials (RCTs) comparing gabapentin versus placebo. Two authors independently screened titles and abstracts, extracted data and assessed risk of bias. The primary outcomes were differences in 24-h morphine consumption, and serious adverse events (SAE) between surgical procedures. These subgroup analyses were predefined in a PRISMA compliant systematic review registered at PROSPERO (ID: CRD42013006538). It was predefined that conclusions should primarily be based on trials classified as overall low risk of bias.
Results
Seventy-four RCTs with 5645 patients were included, assessing benefit and harm in cholecystectomy, hysterectomy, mastectomy, and arthroplasty surgery, spinal surgery, and thoracic surgery.
Only eight of 74 trials were classified as overall low risk of bias limiting our ability to conclude on the estimates in most meta-analyses. The differences between surgical procedures in these trials were not statistically significant when tested for subgroup differences. Fifteen trials with 1377 patients reported a total of 59 SAEs, most of which were observed in the thoracic surgery group.
Conclusion
Both beneficial and harmful effects in these subgroup analyses were influenced by bias and insufficient data, limiting conclusions. With these limitations, we could not adequately test for differences in beneficial or harmful outcomes between six surgical subgroups undergoing perioperative gabapentin treatment.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12871-017-0373-8) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Gabapentin, Gamma-Aminobutyric acid, Analgesics, Therapeutic use, Pain, Drug therapy, Procedure-specific pain management, Postoperative pain management, Systematic review, Subgroup analyses
Background
Pain management is a crucial component in postoperative care of the surgical patient. The combination of non-opioid and opioid analgesics, known as multimodal analgesia, is a cornerstone in the treatment of postoperative pain. Gabapentin has recently become a part of a wide array of postoperative multimodal analgesic regimens [1–3].
It has been argued that postoperative pain treatment should be “procedure-specific”, that is, adapted to the particular surgical procedure, since different analgesics may have specific effects dependent on the nature of the surgery [4, 5].
Gabapentin has been used in postoperative pain management since 2002. It is an anti-epileptic drug presumed to affect nociceptive processing through α2δ-subunits of voltage gated calcium channels, thereby causing decrease in excitatory neurotransmitters, e.g. glutamate, substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) [6, 7]. The anti-hyperalgesic properties have been investigated in several experimental and clinical trials [8–11].
In a recent systematic review we pooled data from all clinical trials and different surgical interventions with gabapentin [12, 13]. The conclusion from this review was, that firm evidence for use of gabapentin is lacking, as clinically relevant beneficial effects of gabapentin may be absent and harm is imminent, especially when added to multimodal analgesic regimens [12]. In the present preplanned subgroup analyses and post hoc analyses, we aimed to compare the procedure-specific effects of peri-operative gabapentin on postoperative opioid consumption, pain intensity, and adverse- and serious adverse events in six different surgical procedures. It was our hypothesis that the reduction in 24-h morphine consumption and incidence of SAE’s would differ between surgical procedures.
Methods
These are preplanned subgroup analyses and post hoc analyses from a systematic review following the methodology recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration. The protocol was published in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) (www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO) registration no. CRD42013006538 [13].
Search strategy
The search was planned by a trial search coordinator using the Cochrane Library’s CENTRAL, PubMed, EMBASE, and Science Citation Index Expanded databases. Previous reviews, reference lists and Google Scholar were hand-searched for eligible trials. Www.clinicaltrials.gov; www.controlled-trials.com; www.centerwatch.com; www.eudraCT.com, and at the homepage of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) were searched for unpublished trials. Non-English articles were translated to English. The electronic search (Additional file 1: Appendix 1 - search strategies) was last updated April 12th, 2016.
Data extraction
After removal of duplicates, titles and abstracts were screened by two authors (MLF, AG). MLF and one other independent author (AG, MSH, PLP, LN) assessed full texts, extracted data and assessed bias. The following characteristics were extracted from the trials using a data extraction form: Year of publication, number of participants, type of surgery, follow-up period and dose regimen, consumption of opioid, and non-opioid medication, pain intensity, and any adverse events described in the trials, including serious adverse events (SAEs).
The corresponding author was contacted whenever data were insufficiently reported, and contact was repeated after 14 days. In case of no response, the involved bias domains were classified as unclear.
Risk of bias assessment
Risk of bias was assessed using The Cochrane Handbook guidelines. All trials were classified as low, unclear or high risk of bias using the following domains: Random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding, incomplete outcome data, selective outcome reporting and other bias, including funding and confirmatory bias.
Disagreements between authors on study selection, data extraction or bias assessment were solved by OM, JBD or JW.
We decided a priori to report and conclude based primarily on results from trials classified as low risk of bias.
Small trial size
All trials were evaluated in this post hoc analysis and allocated to the corresponding group according to the numbers of participants included in the analyses. Small trials were defined as trials with less than 50 patients included in each group. Trials were allocated to the remaining two groups if they included either more than 50 patients, or more than 200 patients [12].
Analyses
The present subgroup analyses of surgical procedures were predefined in the protocol investigating the effect of different surgical procedures: Cholecystectomy, hysterectomy, mastectomy, orthopedic arthroplasty surgery, spinal and thoracic surgery on the primary and secondary outcomes. Analyses of thoracic surgery and orthopedic arthroplasty surgery have been added post hoc [13]. The surgical procedures were chosen to represent a wide range of surgical interventions and patient populations. Cholecystectomy is a minor procedure, often performed as day-case surgery, whereas thoracic surgery is a major procedure, which may be associated with intensive care in the immediate postoperative period. Mastectomy and hysterectomy are procedures with moderate to severe pain postoperatively. Orthopedic arthroplasty and spinal surgery often represents patients with chronic pain preoperatively. We chose to add trials investigating thoracic surgery and orthopedic arthroplasty surgery post hoc, in order to broaden the range of surgical interventions.
The planning and interpretation of the subgroup analyses followed the direction of the Cochrane Handbook [14].
Outcomes
The primary outcomes were difference in 24-h postoperative opioid sparing effects, and reported serious adverse events (SAE) between surgical procedures. SAE’s were defined according to the International Conference of Harmonization – Good Clinical Practice (ICH-GCP) definitions: Medical events being either life threatening, resulting in death, disability or significant loss of function, or causing hospital admission or prolonged hospitalization [15].
Secondary outcomes were differences in early (6-h) and late (24-h) pain postoperatively, both at rest and during mobilization, and all other adverse events, between surgical procedures.
All opioids were converted to intravenous morphine based upon equivalency as presented in Additional file 1: Appendix 2. Various scales were used to report pain intensity in the trials. All pain intensity scales reporting pain levels between 0 and 10 were converted to the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) 0 to 100 mm.
Statistical analysis
Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program], Version 5.1.6, Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014, and Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA) software (version 0.9.5.5 Beta), Copenhagen Trial Unit, Denmark, was used for statistical analyses as predefined in the protocol.
In trials with more than one active treatment arm, including trials testing doses delivered pre- and immediate postoperatively, means and standard deviations were combined for the intervention groups.
Mean and standard deviations were estimated from median and range values according to the method described by Hozo et al. [16] Standard deviations were calculated by dividing the difference in interquartile ranges with 1.35 [14].
Longer ordinal scales were analyzed as continuous data. For dichotomous data, RR with a 95% confidence interval was calculated.
We examined the heterogeneity between trials using chi-squared test. The heterogeneity was measured by I2, which quantifies inconsistencies. If the I2 was greater than zero the results were calculated using both a fixed effect model (FEM) and random effect model (REM) and the most conservative estimation was used [14, 17]. In the case of very few and rare events, Peto’s odd ratio was used to provide the best coverage of confidence intervals [18, 19].
Estimates were pooled in meta-analyses whenever more than one trial was included for the outcome. Tests for subgroup differences were carried out for all surgical procedures on all outcomes whenever a meta-analysis was possible. Using RevMan, the method to test for subgroup differences was implemented for all types of meta-analyses [14]. Our test for subgroup differences was performed on each of the subgroups testing them for subgroup differences against the compiled, remaining subgroups using the chi-squared test.
We used Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA) in post hoc analyses to adjust the confidence intervals for sparse data and repetitive testing. Minimal clinical relevant differences were defined as in our main review [12]. In the event that the accrued information size was less than 5% of the required information size, no TSA was reported, as the TSA program is unable to calculate trial sequential monitoring boundaries in this situation.
Results
The search strategies revealed 19,137 titles. Duplicates were removed and 16,303 titles were sorted according to inclusion- and exclusion criteria. One-hundred-thirty-five randomized controlled trials and observational studies were included in the original systematic review. After excluding 61 trials investigating other surgical procedures, a total of 74 randomized controlled trials with 5645 patients were included in the present analyses (Fig. 1: PRISMA flowchart) [20–94].
Fig. 1.
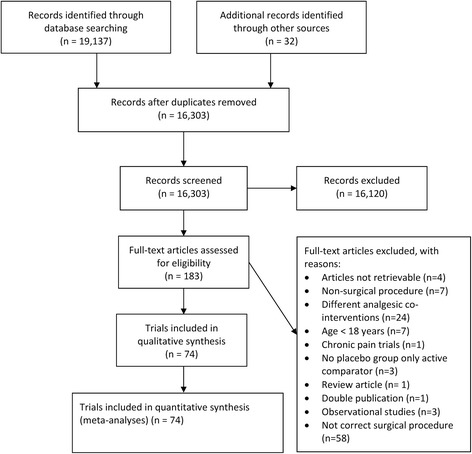
PRISMA flowchart
Characteristics of included trials
Trial characteristics are presented in Table 1. Eight trials were classified as overall low risk of bias, [39, 43, 46, 56, 59, 72, 73, 85] 18 trials were overall unclear risk of bias [21, 23, 24, 26, 28, 29, 31, 36, 38, 42, 52, 54, 55, 61, 65, 66, 68, 69, 80] and 48 trials were classified as high risk of bias, [20, 22, 25, 27, 30, 32–35, 37, 40, 41, 44, 45, 47–51, 53, 57, 58, 60, 62–64, 67, 70, 71, 74–79, 81–84, 86–94] (Fig. 2: Bias assessment). Allocation concealment, selective outcome reporting and “other bias” were the domains with most unclear or high risk of bias evaluations (Fig. 3: Risk of bias graph).
Table 1.
Trial characteristics
| Reference (Author and year) | Surgical procedure | N Gabapentin/Control | Intervention | Postoperative analgesia | Anesthetic technique | Bias assessment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose (mg) (mg/day a ) | Single/Continuous | ||||||
| Cholecystectomy trials | |||||||
| Bashir 2009 [24] | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | 50/50 | 600 mg | Single | Not described | GA | Unclear |
| Bekawi 2014 [26] | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | 30/30 | 1200 mg (400 mg) |
Continuous | NSAID Pethidine Tramadol |
GA | Unclear |
| Bhandari 2014 [27] | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | 20/20 | 600 mg (600 mg) |
Continuous | NSAID | GA | High |
| Hosseini 2015 [48] | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | 22/22 | 600 mg | Single | Morphine | GA | High |
| Khademi 2009 [51] | Open cholecystectomy | 44/43 | 600 mg | Single | Pethidine | GA | High |
| Mishra 2016 [63] | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | 30/30 | 900 mg | Single | Tramadol | GA | High |
| Neogi 2012 [64] | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | 30/30 | 900 mg | Single | Tramadol | GA | High |
| Panday 2004b [68] | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | 153/153 | 300 mg | Single | Fentanyl | GA | Unclear |
| Panday 2006 [70] | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | 125/125 | 600 mg | Single | Fentanyl | GA | High |
| Pathak 2013 [71] | Open cholecystectomy | 40/40 | 1200 mg | Single | Pethidine | GA | High |
| Saeed 2013 [79] | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | 50/50 | 600 mg | Single | Pethidine NSAID |
GA | High |
| Semira 2013 [81] | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | 30/30 | 600 mg | Single | Not described | GA | High |
| Sharma 2015 [83] | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | 20/20 | 600 mg (600 mg) |
Continuous | NSAID | GA | High |
| Srivastava 2009 [85] | Open cholecystectomy | 60/60 | 600 mg | Single | Tramadol | GA | Low |
| Syal 2010 [86] | Open cholecystectomy | 30/30 | 1200 mg | Single | Tramadol | GA | High |
| Takmaz 2009 [87] | Open cholecystectomy | 30/15 | 900/1200 mg | Single | Tramadol Meripedine |
GA | High |
| Hysterectomy trials | |||||||
| Ajori 2011 [20] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 69/69 | 600 mg | Single | Meripedine | GA | High |
| Badawy 2014 [23] | Hysterectomy | 20/20 | 800 mg | Single | Meripedine Acetaminophen | GA | Unclear |
| Behdad 2012 [25] | Hysterectomy | 30/31 | 100 mg (300 mg/d) |
Continuous | An opioid | GA | High |
| Dierking 2003 [33] | Abdominal hysterectomy (salphinooophrectomy) | 40/40 | 1200 mg (1800 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine | GA | High |
| Durmus 2006 [36] | Hysterectomy | 25/25 | 1200 mg | Single | Morphine | GA | Unclear |
| Fassoulaki 2005 [39] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 29/30 | 400 mg (1600 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine Paracetamol Codeine |
GA | Low |
| Fassoulaki 2006 [40] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 30/30 | 400 mg (1600 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine Paracetamol Codeine Local anesthetic |
GA | High |
| Frouzanfard 2013 [41] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 25/25 | 1200 mg | Single | Morphine NSAID |
GA | High |
| Ghafari 2009 [42] | Abdominal hysterectomy and salphinooophrectomy | 33/33 | 300 mg (300 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine | GA | Unclear |
| Ghai 2011 [43] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 30/30 | 900 mg | Single | Morphine NSAID |
GA | Low |
| Gilron 2004 [44] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 23/24 | 1800 mg (1800 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine | GA | High |
| Joseph 2014 [50] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 25/25 | 600 mg | Single | Morphine | GA | High |
| Khan 2013 [53] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 34/35 | 1200 mg | Single | Nalbuphine | GA | High |
| Ram 2015 [75] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 30/30 | 900 mg | Single | NSAID | Spinal anesthesia | High |
| Ray 2015 [77] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 30/30 | 300 mg | Single | NSAID | Spinal anesthesia | High |
| Rorarius 2004 [78] | Vaginal hysterectomy | 45/45 | 600 mg | Single | Fentanyl | GA | High |
| Sekhavet 2009 [80] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 49/49 | 600 mg (300 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine NSAID |
GA | Unclear |
| Sen 2009a [82] | Abdominal hysterectomy and salphinooophrectomy | 20/20 | 1200 mg | Single | Morphine Acetaminophen Codeine |
GA | High |
| Turan 2003a [88] | Abdominal hysterectomy and salphinooophrectomy | 25/25 | 1200 mg | Single | Tramadol | GA | High |
| Turan 2006 [90] | Abdominal hysterectomy and salphinooophrectomy | 25/25 | 1200 mg (1200 mg/d) |
Continuous | Acetaminophen Codeine |
GA | High |
| Verma 2008 [94] | Abdominal hysterectomy | 25/25 | 300 mg | Single | Epidural analgesia | Spinal-epidural anesthesia | High |
| Mastectomy trials | |||||||
| Amr 2009 [21] | Radical or partial mastectomy | 50/50 | 300 mg (300 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine Acetaminophen Codeine |
GA | Unclear |
| Azemati 2013 [22] | Radical mastectomy or quandrandectomy and axillary node dissection | 50/50 | 600 mg | Single | Pethidine Acetaminophen |
GA | High |
| Bharti 2012 [28] | Total mastectomy with axillary node dissection | 20/20 | 600 mg | Single | Morphine NSAID |
GA | Unclear |
| Butt 2010 [29] | Mastectomy | 50/50 | 1200 mg | Single | Morphine | GA | Unclear |
| Dirks 2002 [34] | Unilateral radical mastectomy with axillary dissection | 31/34 | 1200 mg | Single | Morphine | GA | High |
| Doha 2010 [35] | Radical mastectomy | 30/30 | 1200 mg | Single | Tramadol NSAID |
GA | High |
| Fassoulaki 2002 [38] | Radical mastectomy or lobectomy with axillary lymph node dissection | 25/25 | 400 mg (1200 mg/d) |
Continuous | Propoxyphene Acetaminophen Codeine |
GA | High |
| Gosai 2015 [45] | Radical mastectomy | 30/30 | 600 mg | Single | NSAID | GA | High |
| Grover 2009 [47] | Total mastectomy with axillary node dissection | 27/23 | 600 mg | Single | Morphine | GA | High |
| Kim 2004 [55] | Mastectomy | 21/20 | 900 mg | Single | Fentanyl | GA | Unclear |
| Metry 2008 [62] | Unilateral radical mastectomy and axillary dissection | 67/34 | 1200 mg | Single | Morphine | GA | High |
| Orthopedic arthroplasty surgery trials | |||||||
| Clarke 2009a [30] | Total knee arthroplasty | 29/7 | 600 mg (300/600/900 mg/d) |
Single/continuous | Morphine NSAID Regional anesthesia |
Spinal anesthesia and sedation | High |
| Clarke 2009b [31] | Total hip arthroplasty | 76/39 | 600 mg | Single (pre/post-operative administration) |
Morphine NSAID Acetaminophen Dexamethasone |
Spinal anesthesia | Unclear |
| Clarke 2014 [32] | Total knee arthroplasty | 95/84 | 600 mg | Single | Morphine NSAID Regional anesthesia |
Spinal anesthesia and sedation | High |
| Lunn 2015 [59] | Total knee arthroplasty | 186/99 | 900/600 mg (1300/900 mg/d) | Continuous | Sufentanil Oxycodone NSAID Acetaminophen Local infiltration analgesia |
Spinal anesthesia and sedation | Low |
| Paul 2013 [73] | Total knee arthroplasty | 52/49 | 600 mg (600 mg) |
Continuous | Morphine NSAID Acetaminophen |
Spinal anesthesia and sedation | Low |
| Paul 2015 [72] | Total hip arthroplasty | 48/54 | 600 mg (600 mg) |
Continuous | Morphine NSAID Acetaminophen |
Spinal anesthesia and sedation | Low |
| Spinal surgery trials | |||||||
| Erten 2010 [37] | Laminectomy | 39/20 | 900/1200 mg | Single | Tramadol Pethidine NSAID |
GA | High |
| Khan 2010 [52] | Laminectomy | 150/25 | 600/900/1200 mg (600/900/1200 mg) |
Continuous | Morphine | GA | Unclear |
| Khurana 2013 [54] | Discoidectomy | 30/30 | 300 mg (900 mg/d) |
Continuous | Tramadol NSAID | GA | Unclear |
| Leung 2006 [58] | Spine surgery | 9/12 | 900 mg (900 mg/d) |
Continuous | Hydromorphine | GA | Unclear |
| Özgencil 2011 [66] | Laminectomy or discoidectomy | 30/30 | 1800 mg (1200 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine | GA | Unclear |
| Panday 2004a [67] | Discoidectomy | 80/20 | 300/600/900/1200 mg | Single | Fentanyl | GA | High |
| Panday 2004c [69] | Discoidectomy | 28/28 | 300 mg | Single | Fentanyl | GA | Unclear |
| Radhakrishnan 2005 [74] | Laminectomy or Discoidectomy | 30/30 | 800 mg (800 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine | GA | High |
| Turan 2003b [89] | Discoidectomy or spinal fusion | 25/25 | 1200 mg | Single | Morphine | GA | High |
| Vahedi 2011 [92] | Laminectomy or Discoidectomy |
36/40 | 300 mg | Single | Morphine | GA | High |
| Vasigh 2015 [93] | Laminectomy | 38/38 | 600 mg (900 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine | GA | High |
| Thoracic surgery trials | |||||||
| Grosen 2014 [46] | Thoracotomy for malignancies | 52/52 | 1200 mg (increasing dose to 1200 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine NSAID Acetaminophen Epidural analgesia |
GA | Low |
| Hout 2007 [49] | Exploratory thoracotomy, pneumonectomy, lobectomy, segmentectomy, biopsy | 23/28 | 1200 mg | Single | Hydromorphine Epidural analgesia |
GA | High |
| Kinney 2011 [56] | Thoratectomy; Lobectomy; Wedge resection; Segmentectomy; Pneumonectomy; Chest wall resection | 57/68 | 600 mg | Single | Fentanyl NSAID Acetaminophen Epidural analgesia |
GA | Low |
| Kosucu 2013 [57] | Posterolateral or lateral thoracotomy | 29/31 | 1200 mg | Single | Morphine Meriphidine NSAID |
GA | High |
| Menda 2010 [61] | Coronary artery bypass graft | 30/30 | 600 mg | Single | Morphine Acetaminophen |
GA | Unclear |
| Omran 2005 [65] | Posterolateral thoracotomy for lobectomy | 25/25 | 1200 mg (1200 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine | GA | Unclear |
| Rapchuk 2009 [76] | Cardiac surgery via Sternum | 27/27 | 1200 mg (600 mg/d) |
Continuous | Fentanyl Acetaminophen |
GA | High |
| Soltanzadeh 2011 [84] | Coronary artery bypass graft | 30/30 | 800 mg (400 mg/d) |
Continuous | Morphine | GA | High |
| Ucak 2011 [91] | Coronary artery bypass graft | 20/20 | 1200 mg (1200 mg/d) |
Continuous | Tramadol Acetaminophen |
GA | High |
aThe continuous treatment is defined as more than one administration of gabapentin. The mg/day is the dose of gabapentin per day in the treatments that extends one administration
Fig. 2.
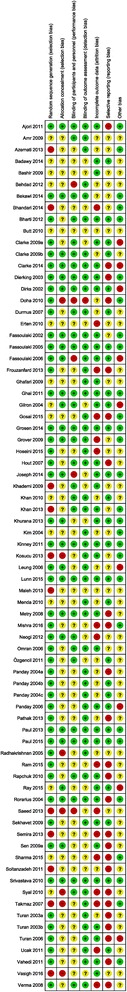
Risk of bias assessment. Risk of bias graph: The ‘Other’ bias domain is an evaluation of risk of financial bias and confirmatory bias
Fig. 3.
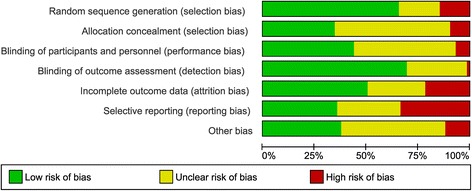
Risk of bias graph. Risk of bias summary
Sixty-six trials were classified as small trials [21–27, 29–31, 33–45, 47–55, 57, 58, 61–64, 66, 67, 69, 71–81, 83, 84, 86–94], five had more than 50 participants in each group [20, 32, 46, 56, 85], and three included more than 200 patients [59, 68, 70].
The gabapentin dose in the included trials ranged from 100 mg to 1800 mg, and was mostly administered as a single dose (46 trials). [20, 22–24, 28–32, 34–37, 41, 43, 45, 47–51, 53, 55–57, 61–64, 67–71, 75, 77–79, 81, 82, 85–90, 92, 94] In 30 trials, gabapentin was administered in combination with a basic, non-opioid/opioid analgesic regimen [20, 22, 23, 26, 28, 30–32, 37–41, 43, 46, 49, 54, 56, 57, 59, 61, 72, 73, 76, 79, 80, 82, 87, 90, 91]. In 44 trials, gabapentin was administered together with an opioid as the only analgesic [20, 25, 27, 29, 33–36, 44, 45, 47, 48, 50–53, 55, 58, 62–71, 74, 75, 77, 78, 83–86, 88, 89, 92–94]. In five trials, gabapentin was administered in combination with a NSAID [27, 45, 75, 77, 83],, and in two trials, the postoperative analgesic regimen was not described [24, 81].
Bias assessments in surgical subgroups
Eight trials were classified as overall low risk of bias. None from the mastectomy subgroup and one trial from the cholecystectomy group was overall low risk of bias [85]. In the subgroups hysterectomy, [39, 43] and thoracic surgery [46, 56] two trials were low risk of bias in each group, and three trials were classified as low risk of bias in the orthopedic arthroplasty subgroup [59, 72, 73].
Below, we present analyses from trials with low risk of bias. In addition, analyses from all trials are presented in Table 2: Primary outcomes from trials with low risk of bias and all trials estimates, and Table 3: Secondary outcomes from trials with low risk of bias and all trials estimate.
Table 2.
Primary outcomes from trials with low risk of bias and all trials estimates
| Surgical procedure | Cholecystectomy | Hysterectomy | Mastectomy | Orthopedic arthroplasty surgery | Spinal Surgery | Thoracic surgery | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcomes | Reduction (mg)/RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
Reduction (mg) /RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
Reduction (mg) /RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
Reduction (mg) /RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
Reduction (mg) /RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
Reduction (mg)/RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
| Beneficial outcomes | ||||||||||||
| 24-h morphine consumption Low risk of bias |
12.2 mg (9.8, 14.6; 1 trial) |
- | 1.6 mg (−4.8, 8.0; 2 trials) |
P = 0.21 | - | - | 4.0 mg (−0.8, 8.7; 3 trials) |
P = 0.75 | - | - | 6.7 mg (−2.0, 15.4; 1 trial) |
- |
| 24-h morphine consumption All trials |
7.3 mg (95% CI: 4.6, 9.9; p < 0.00001; 10 trials; TSA adj.CI: 3.5, 11.0; 62.4%) |
P = 0.9 | 10.5 mg (95% CI: 6.7, 14.4; p < 0.00001; 14 trials; TSA adj. CI: 3.0, 18.1; 30.2%) |
P = 0.16 | 5.2 mg (95% CI: 0.9, 9.5; p = 0.02; 6 trials; TSA adj. CI: −4.6, 15.0; 24.3%) |
P = 0.15 | 6.1 mg (95% CI: 0.2, 12.1; p = 0.04; 6 trials; TSA adj.CI: −18.1, 30.3; 5.8%) |
P = 0.47 | 10.6 mg (95% CI: 2.1, 19.0; p = 0.01; 8 trials; TSA adj.CI: −24.1, 45.2; 6.1%) |
P = 0.52 | 6.3 mg (95% CI: 2.9, 9.8; p = 0.0003; 7 trials; TSA adj.CI: −0.3, 12.3; 28.9%) |
P = 0.25 |
| Harmful outcomes | ||||||||||||
| Serious adverse events Low risk of bias |
Not estimable | - | - | - | - | - | 2.98 (0.36, 24.41; two trials) |
P = 0.49 | - | - | 1.35 (0.69, 2.63; two trials) |
P = 0.49 |
| Serious adverse events All trials |
Not estimable | - | 0.55 (95% CI: 0.05, 5.61; p 0.61; 5 trials; TSA adj. CI -; 3.3%) |
P = 0.16 | Not estimable | - | 2.98 (95% CI: 0.36, 24.41; p = 0.31; 2 trials; TSA adj. CI: -; 2.1%) |
P = 0.3 | Not estimable | - | 1.06 (95% CI: 0.57, 1.74; p = 0.81; 4 trials; TSA adj.CI: 0.5, 2.1; 55.9%) |
P = 0.72 |
Table 3.
Secondary outcomes from trials with low risk of bias and all trials
| Surgical procedure | Cholecystectomy | Hysterectomy | Mastectomy | Orthopedic arthroplasty surgery | Spinal Surgery | Thoracic surgery | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcomes | Reduction (mm)/RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
Reduction (mm)/RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
Reduction (mm)/RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
Reduction (mm)/RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
Reduction (mm)/RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
Reduction (mm)/RR Estimate (95% CI; p-value; trials) |
Test for subgroup differences P-value |
| Beneficial outcomes | ||||||||||||
| 6-h VAS at rest Low risk of bias |
26.0 mm (24.8, 27.2; 1 trial) |
- | 3.0 mm (−12.9, 18.9; 1 trial) |
- | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5.0 mm (−0.7, 10.7; 2 trials) |
P = 0.36 |
| 6-h VAS at rest All trials |
13.6 mm (95% CI: −6.2, 33.4; p = 0.18; 3 trials; TSA adj. CI: -; 4.4%) |
P = 0.87 | 16.4 mm (95% CI: 11.9, 21.0; p < 0.00001; 16 trials; TSA adj. CI: 11.9, 21.0; 104.3%) |
P = 0.05 | 7.8 mm (95% CI: 1.9, 13.7; p = 0.01; 7 trials; TSA adj. CI: −1.1, 16.7; 51.9%) |
P = 0.15 | Not estimable | - | 10.2 mm (95% CI: 2.3, 18.0; p = 0.01; 7 trials; TSA adj. CI: −5.7, 26.0; 29.6%) |
P = 0.59 | 6.6 mm (95% CI: 0.8, 12.4; p = 0.05; 6 trials; TSA adj.CI: −3.0, 12.3; 59.2%) |
P = 0.02 |
| 6-h VAS at mobilization Low risk of bias |
11.5 mm (10.3, 12.7; 1 trial) |
- | 13.0 mm (−26.0, 52.0; 1 trial) |
- | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8.9 mm (1.6, 16.1; 1 trial) |
- |
| 6-h VAS at mobilization All trials |
11.5 mm (95%CI: 10.3, 12.7; p < 0.00001; 1 trial; TSA adj. CI: -) |
P = 0.04 | 8.5 mm (95%CI: 2.8, 14.2; p = 0.004; 6 trials; TSA adj.CI: 0.2, 16.7; 56.1%) |
P = 0.97 | 5.2 mm (95%CI: −1.6, 12.0; p = 0.14; 6 trials; TSA adj.CI: −5.1, 15.7; 44.8%) |
P = 0.07 | Not estimable | - | 10.0 mm (95%CI: 1.1, 19.0; p = 0.03; 1 trial; TSA adj. CI: -) |
P = 0.73 | 10.9 mm (95%CI: 4.4, 17.4; p = 0.001; 4 trials; TSA adj.CI: 0.1, 21.7; 42.8%) |
P = 0.41 |
| 24-h VAS at rest Low risk of bias |
7.0 mm (5.8, 8.2; 1 trial) |
- | 9.0 mm (−2.8, 20.8; 1 trial) |
- | - | - | 0.9 mm (−6.3, 8.1; 1 trial) |
- | - | - | 4.2 mm (−0.2, 8.5; 2 trials) |
P = 0.06 |
| 24-h VAS at rest All trials |
3.2 mm (95% CI: −1.9, 8.4; p = 0.22; 3 trials; TSA adj.CI: −3.3, 9.8; 69.1%) |
P = 0.1 | 10.5 mm (95% CI: 6.9, 14.2; p < 0.00001; 15 trials; TSA adj.CI: 6.7, 14.4; 136.3%) |
P = 0.02 | 2.6 mm (95% CI: −3.2, 8.5; p = 0.2; 3 trials; TSA adj. CI: −3.2, 8.5; 112.9%) |
P = 0.02 | 1.0 mm (95% CI: −1.7, 3.7; p = 0.45; 3 trials; TSA adj.CI: −3.9, 6.0; 248.0%) |
P = 0.001 | 6.2 mm (95% CI: 0.9, 11.6; p = 0.02; 6 trials; TSA adj.CI: 0.9, 13.3; 64.1%) |
P = 0.61 | 9.7 mm (95% CI: 2.4, 17.1; p = 0.01; 8 trials; TSA adj.CI: −4.2, 23.7; 33.6%) |
P = 0.51 |
| 24-h VAS at mobilization Low risk of bias |
16.0 mm (15.1, 16.9; 1 trial) |
- | 0.5 mm (−36.5, 37.5; 1 trial) |
- | - | - | 0.5 mm (−11.4, 12.3; 1 trial) |
- | - | - | 0.1 mm (−8.9, 9.1; 1 trial) |
- |
| 24-h VAS at mobilization All trials |
16.0 mm (95% CI: 15.1, 16.9; p < 0.0001; 1 trial; TSA adj. CI: -) |
P < 0.00001 | 7.7 mm (95% CI: −8.2, 23.6; p = 0.34; 5 trials; TSA adj.CI: −16.3, 25.4; 22.5%) |
P = 0.91 | 3.1 mm (95% CI: −13.6, 19.8; p = 0.72; 3 trials; −65.1, 71.3; 6.5%) |
P = 0.87 | Increase 6.5 mm (95% CI: 3.0, 9.9; p = 0.0002; 2 trials; TSA adj.CI: +2.5, +10.5; 150.7%) |
P = 0.0008 | Not estimable | - | 3.0 mm (95% CI: −4.5, 10.4; p = 0.43; 6 trials; TSA adj.CI: −11.2, 17.1; 33.1%) |
P = 0.86 |
| Harmful outcomes | ||||||||||||
| Nausea Low risk of bias |
- | - | - | - | - | - | 0.8 (0.6,1.0; 2 trials) |
P = 0.5 | - | - | 0.7 (0.5, 0.9; 1 trial) |
- |
| Nausea All trials |
0.5 (95% CI: 0.25, 0.99; p = 0.05; 1 trial; TSA adj. CI: -) |
P = 0.16 | 0.77 (95% CI: 0.63, 0.95; p = 0.01; 11 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.6, 1.1; 49.4%) |
P = 0.73 | 1.38 (95% CI: 0.85, 2.23; p = 0.19; 3 trials; TSA adj. CI: -; 2.69%) |
P = 0.33 | 0.83 (95% CI: 0.66, 1.03; p = 0.08; 4 trials; TSA adj. CI: -; 79.7%) |
P = 0.91 | 1.07 (95% CI: 0.68, 1.68; p = 0.78; 8 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.4, 3.2; 22.8%) |
P = 0.29 | 0.66 (95% CI: 0.5, 0.88; p = 0.005; 5 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.4, 1.0; 49.9%) |
P = 0.1 |
| Vomiting Low risk of bias |
- | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.1 (0.7, 1.6; 1 trial) |
- |
| Vomiting All trials |
0.5 (95%CI: 0.21, 1.16; p = 0.11; 1 trial; TSA adj. CI: -) |
P = 0.28 | 0.71 (95% CI: 0.57, 0.9; p = 0.005; 9 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.5, 1.0; 71.7%) |
P = 0.61 | 0.81 (95% CI: 0.48, 1.37; p = 0.44; 5 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.1, 6.9; 16.5%) |
P = 0.92 | 0.64 (95% CI: 0.26, 1.59; p = 0.34; 1 trial; TSA adj. CI: -) |
P = 0.66 | 0.61 (95% CI: 0.33, 1.12; p = 0.11; 7 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.2, 2.3; 18.6%) |
P = 0.51 | 1.01 (95% CI: 0.69, 1.49; p = 0.96; 5 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.2, 4.9; 8.0%) |
P = 0.32 |
| Sedation Low risk of bias |
1.8 (0.8, 3.9; 1 trial) |
- | 0.8 (0.4, 1.6; 1 trial) |
- | - | - | 0.9 (0.7, 1.2; 1 trial) |
- | - | - | 1.2 (0.7, 2.3; 2 trials) |
P = 0.55 |
| Sedation All trials |
3.28 (95% CI: 1.55, 6.94; p = 0.002; 5 trials; TSA adj. CI: -; 3.9%) |
P = 0.009 | 1.08 (95% CI: 0.81, 1.45; p = 0.61; 7 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.5, 2.2; 23.2%) |
P = 0.06 | 1.04 (95% CI: 0.75, 1.44; p = 0.83; 2 trials; TSA adj. CI: -; 4.8%) |
P = 0.06 | 0.97 (95% CI: 0.76, 1.24; p = 0.82; 2 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.7, 1.6; 44.3%) |
P = 0.01 | 2.65 (95% CI: 0.94, 7.52; p = 0.07; 7 trials; TSA adj. CI: -; 2.3%) |
P = 0.19 | 1.34 (95% CI: 0.78, 2.32; p = 0.29; 5 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.1, 12.5; 10.8%) |
P = 0.68 |
| Dizziness Low risk of bias |
1.0 (0.7, 1.4; 1 trial) |
- | 6.2 (1.1, 34.0; 1 trial) |
- | - | - | 0.7 (0.2, 2.1; 1 trial) |
- | - | - | 1.0 (0.8, 1.3; 2 trials) |
P = 0.64 |
| Dizziness All trials |
0.7 (95% CI: 0.52, 0.94; p = 0.02; 6 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.2, 2.6; 27.1%) |
P = 0.01 | 1.34 (95% CI: 0.95, 1.89; p = 0.1; 11 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.3, 5.6; 16.8%) |
P = 0.2 | 1.03 (95% CI: 0.74, 1.43; p = 0.88; 5 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.6, 2.1; 31.4%) |
P = 0.84 | 0.72 (95% CI: 0.32, 1.66; p = 0.45; 3 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.0, 18.1; 5.6%) |
P = 0.44 | 1.49 (95% CI: 0.77, 2.86; p = 0.24; 6 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.6, 3.1; 31.4%) |
P = 0.22 | 1.04 (95% CI: 0.85, 1.26; p = 0.7; 4 trials; TSA adj. CI: 0.7, 1.5; 36.4%) |
P = 0.66 |
Primary outcomes
24-h morphine consumption
24-h morphine consumption was reported in 51 trials with 4193 patients. [21, 23, 26, 28, 30–33, 35–44, 46, 48–53, 55, 57, 59–63, 65–70, 72, 73, 80, 82, 84–89, 91–93] Of these 51 trials, 7 were classified as overall low risk of bias [39, 43, 46, 59, 72, 73, 85].
In cholecystectomy, one trial reported a reduction of 12.2 mg [9.8, 14.6] in 24-h morphine consumption in the gabapentin treatment group compared to controls [85], two trials in hysterectomy found a reduction of 1.6 mg [−4.8, 8.0] [39, 43], and three trials in orthopedic arthroplasty demonstrated a reduction of 4.0 mg [−0.8, 8.7] [58, 71, 72]. Finally, one trial in thoracic surgery reported a reduction of 6.7 mg [−2.0, 15.4] [46]. We found no difference between the surgical procedures when tested for subgroup differences.
(Table 2: The intervention effect estimated from trials with low risk of bias, and from all trials despite risk of bias; Fig. 4: Forest plot of 24-h morphine consumption from trials with low risk of bias).
Fig. 4.
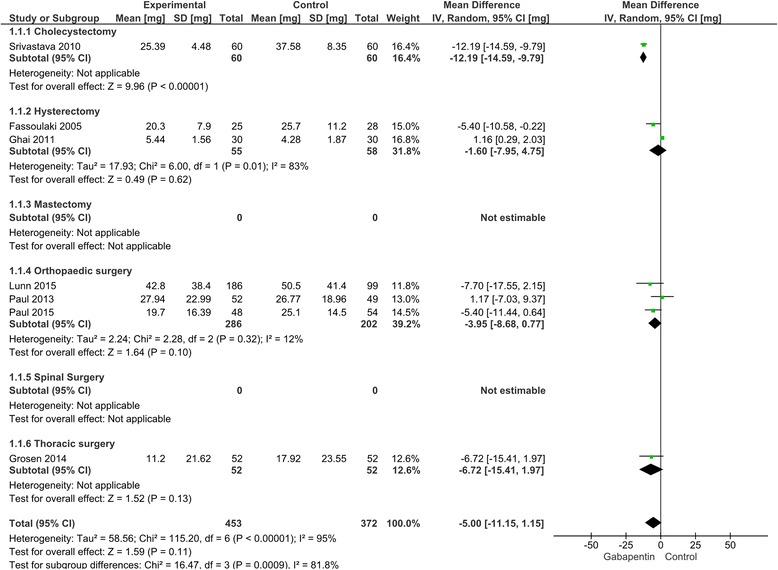
Forest plot of 24-h morphine consumption. Forest plot of 24-h morphine consumption of trials with overall low risk of bias
(Additional file 1: Appendix 3 - Forest plot of 24-h morphine consumption from all trials, Additional file 1: Appendix 4–9 - TSA of estimates from all trials and cholecystectomy, hysterectomy, mastectomy, orthopedic arthroplasty, spinal and thoracic surgery groups).
Serious adverse events
Fifteen trials with 1377 patients reported SAEs [20, 33, 34, 38, 39, 44, 46, 49, 53, 56, 59, 72, 85, 91, 92]. Of the 15 trials, 5 were classified as overall low risk of bias [46, 56, 59, 72, 85]. The reported SAEs were: Death, urticarial rash, re-operation, prolonged admission, re-admission to hospital, pneumonia, and atrial fibrillation.
One cholecystectomy trial, two orthopedic arthroplasty trials, and two thoracic surgery trials were classified as overall low risk of bias. [46, 56, 59, 72, 85] In the trials with low risk of bias, the risk of SAE’s were 2.98 [0.36, 24.41] in the orthopedic arthroplasty subgroup [59, 72] and 1.35 [0.69, 2.63] in the thoracic subgroup [46, 56]. A comparison of pooled-estimates in test for subgroup differences from trials with low risk of bias indicated no difference between groups, p = 0.49.
(Table 2: SAEs estimated from trials with low risk of bias, and from all trials despite risk of bias; Fig. 5: Forest plot of SAEs from trials with low risk of bias.
Fig. 5.
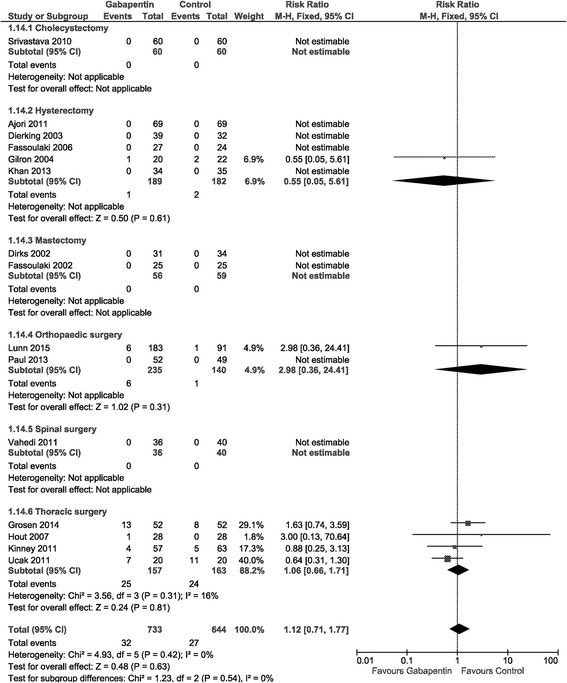
Forest plot of serious adverse events. Forest plot of Serious Adverse Events of trials with overall low risk of bias
(Additional file 1: Appendix 10 - Forest plot of SAEs in all trials, Appendix 11 - TSA of SAEs in the thoracic surgery subgroup).
Secondary outcomes
Pain intensity
In general, only few data were available from trials with low risk of bias, rendering tests for subgroup differences impossible and/or unreliable.
(Table 3: The intervention effect estimated from trials with low risk of bias, and from all trials despite risk of bias).
(Additional file 1: Appendix 12–15 - Forest plots of VAS 6 h postoperative at rest and mobilization, 24 h postoperative at rest and mobilization, all trials estimates).
Adverse events
No subgroup differences were demonstrated in any adverse event in trials with low risk of bias.
(Table 3: Adverse events estimated from trials with low risk of bias, and from all trials despite risk of bias).
(Additional file 1: Appendix 16–19 - Forest plots of nausea, vomiting, sedation and dizziness, all trials).
Discussion
It has been argued that postoperative pain treatment should be “procedure-specific”, since different analgesics may have specific effects dependent on the surgical procedure [4, 5]. In the present, preplanned subgroup analyses, we aimed to compare the effects of perioperative gabapentin on postoperative opioid consumption, pain intensity, and adverse- and serious adverse events in six different surgical procedures. Our primary outcomes were 24-h morphine consumption and the risk of SAEs.
Our results are limited by the fact that overall, only eight trials were classified as overall low risk of bias, limiting our ability to test for subgroup differences, and to pool estimates in meta-analyses of these eight trials. When interpreting the results from the all trials analyses, it should be noted that about two-thirds of these trials had overall high risk of bias, which is a severe limitation to any conclusion on the outcomes.
In trials with low risk of bias, 24-h morphine consumption varied, and only the cholecystectomy subgroup indicated a difference between groups. With only one trial in this subgroup, the result has not been reproduced, and is difficult to interpret.
For the analysis of all trials, the difference in 24-h morphine consumption between surgical procedures was not statistically significant, when tested for subgroup differences. A reduction in 24-h morphine consumption was demonstrated for all surgical procedures compared with controls. However, the TSA did not reach required information size in any subgroup. Consequently, the effects observed in the individual procedures may be due to both random and systematic error, as indicated in the main systematic review [12].
SAEs were primarily reported in the thoracic surgery trials but overall, since SAEs were very poorly reported and data was sparse, it is not possible to conclude on this outcome.
For pain intensity outcomes, very few data were available from trials with low risk of bias. In the analyses of data from all trials, the results were divergent across surgical subgroups, and it is difficult to interpret the direction and authenticity in the test for subgroup differences.
No subgroup difference was demonstrated for any adverse event in trials with low risk of bias, and results from data including all trials were divergent across surgical subgroups, with no consistent differences in adverse events between surgical procedures. This indicates a similar adverse event profile of gabapentin for postoperative pain management irrespective of surgical procedure. Much like the previous outcomes, there is far too few data to firmly conclude based on these results. Poor reporting and high risk of bias limits any interpretation.
Strengths and limitations of the subgroup analyses
These subgroup analyses have some strength. The analyses were planned in a PROSPERO published protocol, and were derived from a PRISMA compliant systematic review adhering to Cochrane standards in methodology and bias assessment. The trials have been critically assessed using the Cochrane bias assessment tools, and conclusions are based on trials with low risk of bias, which is unlike most of the previous systematic reviews. The TSA has been added to adjust for sparse data and repetitive resting, which is a risk when the vast majority of included trials are small, that is <50 patients in each group [95–98].
The limitations of this analysis mirror those of the included trials, and the limitations of the general methodology in subgroup analyses. Subgroup comparisons are to be perceived as observational because we compare pre-existing non-randomized groups, and must be interpreted as such [14].
The critical assessment of the trial methodology shows a very small number of trials with overall low risk of bias. Eighty-nine percent of the included trials have unclear or high risk of bias in one of the bias domains or more, risking an overestimation of beneficial -, and underestimation of harmful outcomes.
Despite the larger number of included trials in each subgroup compared with previous published systematic reviews, there is still a risk of spurious results due to lack of sufficient data. The lack of statistically significant p-values in the present subgroup analyses may be due to a small effect size, or poor power to detect a large effect.
According to Oxman and Guyatt [99], Xin Sun et al [100] and their criteria to evaluate the credibility of subgroup analyses, we have to consider further limitations such as: If the subgroup can be considered independent; no a-priori direction of the subgroup effect has been published; the subgroup effects found in our analyses does not seem to consequently manifest in closely related outcomes.
Relation to the previously published systematic reviews
A number of systematic reviews investigating individual surgical procedures, or with a procedure specific approach, have been published [95–98, 101–103]. Overall, there are some general methodological differences that separates the present work from previously published systematic reviews, such as: The emphasis on trials with low risk of bias, subgroup analyses with test for subgroup differences, and the use of trial sequential analyses. The emphasis on trials with low risk of bias prevents any direct comparison with estimates from other systematic reviews. Several reviews have evaluated bias in the included trials, and report different overall bias evaluations and number of trials with overall low risk of bias, compared to the present review [97, 98, 104]. This may be explained by the fact that that we contacted every author whenever a bias domain was deemed unclear risk of bias, to give them a chance to describe their methods in greater detail. To our knowledge, this was not done in the previously published systematic reviews.
In a recent review, the effect of trials with high risk of bias were tested using sensitivity analyses, and no impact was demonstrated on the outcomes [104]. This is in contrast to the present analyses, and to the findings of our recently published systematic review [12, 104]. The different approach to author contact, and a different statistical approach, may explain some of the differences in the findings. Further, the systematic review by Doleman et al. [104] reports that the type of surgery was not independently associated with the effect of gabapentin, which may provide some confirmation of the results from the present analyses. However, the results are obtained with different statistical approaches and the number and types of surgeries are not stated in the findings from Doleman et al. Consequently, the confirmation must be interpreted with caution [104]. In another review, Mathiesen et al. demonstrated a greater beneficial effect (reduction in 24-h opioid consumption) in their hysterectomy and spinal surgery groups [95], which seems similar to the results from the all trials estimates in Table 2 in the present review. Mathiesen et al., however, did not test for subgroup differences [95], and we found no differences between subgroups in the all trials estimates of the present review.
Most previous systematic reviews report favorable results for gabapentin treatment, similar to the findings from the all trials estimates in the subgroup analyses of the present review. In comparison with the systematic reviews of gabapentin for hysterectomy, cholecystectomy and thoracic surgeries [95, 96, 101], more trials have been included in our subgroups. Due to different inclusion criteria and subgroup analyses in the different published systematic reviews, it is not possible to conduct a full comparison of estimates.
However, none of the systematic reviews above have investigated the risk of SAEs, limiting the ability to weigh the benefit and harm of gabapentin in perioperative pain management [95–98, 101].
Impact of the analyses
We observed no systematic differences in postoperative opioid consumption, pain intensity, or adverse- or serious adverse events between six different surgical procedures treated with peri-operative gabapentin.
SAEs were very poorly reported, and only half the subgroups reported this outcome. More than 80% of the SAEs were reported in the thoracic surgery trials, making it impossible to rely on the risk and subgroup differences between the surgical procedures. In the original review, excess SAEs were reported in the gabapentin versus control groups, and approximately twice as many SAEs were found in trials with low risk of bias, compared with all trials [13]. Most trials have a short follow-up period and only report on SAEs and adverse effects for a short period postoperatively, which seems insufficient for a full evaluation. The inconsequent and diverse reporting of SAEs and adverse events complicates any reliable evaluation of these outcomes.
Conclusion
Both beneficial and harmful effects in the present subgroup analyses are influenced by bias and insufficient data, limiting any conclusion. The very poorly reported incidence of SAEs limits any conclusion based on this outcome. Because of these limitations, we could not properly test for any major differences in beneficial or adverse outcomes between various surgical subgroups with gabapentin for postoperative pain. Consequently, our analyses cannot confirm or reject the concept of a procedure specific effect of gabapentin on postoperative pain.
Additional files
Appendix 1. Search strategies. Appendix 2. Opioid conversion table. Appendix 3. Forest plot of 24-h morphine consumption from all trials estimates. Appendix 4. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the cholecystectomy subgroup, all trials. Appendix 5. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the hysterectomy subgroup, all trials. Appendix 6. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the mastectomy subgroup, all trials. Appendix 7. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the orthopedic arthroplasty subgroup, all trials. Appendix 8. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the spinal subgroup, all trials. Appendix 9. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the thoracic surgery subgroup, all trials. Appendix 10. Forest plot of SAEs, all trials. Appendix 11. TSA of SAEs in the thoracic surgery subgroup, all trials. Appendix 12. Forest plot of VAS 6 h at rest, all trials. Appendix 13. Forest plot of VAS 6 h at mobilization, all trials. Appendix 14. Forest plot of VAS 24 h at rest, all trials. Appendix 15. Forest plot of VAS 24 h at mobilization, all trials. Appendix 16. Forest plot nausea, all trials. Appendix 17. Forest plot vomiting, all trials. Appendix 18. Forest plot sedation, all trials. Appendix 19. Forest plot dizziness, all trials. (PDF 736 kb)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Sarah Louise Klingenberg, Trial Search Coordinator at Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group for the extensive literature searches; Morten Sejer Hansen, MD, Dep. of Anaesthesiology, Centre of Head and Orthopaedics, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital, Denmark; and Lone Nikolajsen, DMSci, Associate Professor, Dep. of Anaesthesiology, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark, for their help in data extraction.
Funding
No grants were received for this work.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on request.
These are preplanned, protocolled subgroup analyses from a systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses: Fabritius ML, Geisler A, Hansen MS, Nikolajsen L, Hamunen K, Kontinen V, Wetterslev J, Dahl JB, Mathiesen O. Gabapentin for post-operative pain management - a systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2016; 60: 1188–208.
The protocolled subgroup analyses are a few of the planned analyses from the original systematic review which have been published in PROSPERO. Some of the subgroups have been published in the original review while a few are to be published in separate subgroup analyses, others have too few trials included to convey any usable information and have thus been excluded and not published.
Authors’ contributions
All authors have made substantive intellectual contributions to this systematic review adhering to the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) guidelines. OM, JW and JBD have all made substantial contributions to the original idea and design, analyses and interpretation of data as well as revising the manuscript and all have given final approval to the submitted version of the manuscript. AG and PLP made substantial contribution to acquisition of data, revising the manuscript critically and have given final approval to the submitted version of the manuscript. MLF made substantial contributions to design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting the manuscript and given final approval of the submitted manuscript. All authors have agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Competing interests
All authors declare no financial competing interests. JW reports that he is a member of the task force at Copenhagen Trial Unit to develop the software and manual for doing Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA). AG, PLP, JBD, OM and MLF have no competing interests to declare.
Consent for publication
Not relevant.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not relevant.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- CI
Confidence interval
- D
Day
- GA
General anesthesia
- ICH-GCP
International committee of harmonization – good clinical practice
- ICMJE
International committee of medical journal editors
- NSAID
None-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs
- PRISMA
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
- RCT
Randomized, clinical trial
- SAE
Serious adverse events
- TSA
Trial sequential analysis
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12871-017-0373-8) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
Maria Louise Fabritius, Phone: 004560179531, Email: malou_fabritius@dadlnet.dk.
Anja Geisler, Email: agei@regionsjaelland.dk.
Pernille Lykke Petersen, Email: pernille.lykke@outlook.com.
Jørn Wetterslev, Email: wetterslev@ctu.dk.
Ole Mathiesen, Email: omat@regionsjaelland.dk.
Jørgen Berg Dahl, Email: joergen.berg.dahl@regionh.dk.
References
- 1.Kehlet H, Dahl JB. Anaesthesia, surgery, and challenges in postoperative recovery. Lancet. 2003;362:1921–1928. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14966-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dahl JB, Mathiesen O, Kehlet H. An expert opinion on postoperative pain management, with special reference to new developments. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010;11:2459–2470. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2010.499124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McDaid C, Maund E, Rice S, Wright K, Jenkins B, Woolacott N. Paracetamol and selective and non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for the reduction of morphine-related side effects after major surgery: a systematic review. Health Technol Assess. 2010;14:1–153. doi: 10.3310/hta14170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kehlet H, Wilkinson RC, Fischer HB, Camu F, Prospect WG. PROSPECT: evidence-based, procedure-specific postoperative pain management. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2007;21:149–159. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2006.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gerbershagen HJ, Aduckathil S, van Wijck AJ, Peelen LM, Kalkman CJ, Meissner W. Pain intensity on the first day after surgery: a prospective cohort study comparing 179 surgical procedures. Anesthesiology. 2013;118:934–944. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31828866b3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sills GJ. The mechanisms of action of gabapentin and pregabalin. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006;6:108–113. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2005.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yaksh TL. Calcium channels as therapeutic targets in neuropathic pain. J Pain. 2006;7:S13–S30. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2005.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dirks J, Petersen KL, Rowbotham MC, Dahl JB. Gabapentin suppresses cutaneous hyperalgesia following heat-capsaicin sensitization. Anesthesiology. 2002;97:102–107. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200207000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mathiesen O, Imbimbo BP, Hilsted KL, Fabbri L, Dahl JB. CHF3381, a N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist and monoamine oxidase-a inhibitor, attenuates secondary hyperalgesia in a human pain model. J Pain. 2006;7:565–574. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2006.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gottrup H, Juhl G, Kristensen AD, et al. Chronic oral gabapentin reduces elements of central sensitization in human experimental hyperalgesia. Anesthesiology. 2004;101:1400–1408. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200412000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Penprase B, Brunetto E, Dahmani E, Forthoffer JJ, Kapoor S. The efficacy of preemptive analgesia for postoperative pain control: a systematic review of the literature. AORN J. 2015;101:94–105. doi: 10.1016/j.aorn.2014.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fabritius ML, Geisler A, Petersen PL, et al. Gabapentin for post-operative pain management - a systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2016;60:1188–1208. doi: 10.1111/aas.12766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fabritius ML, Geisler A, Hansen MS, et al. Benefit and harm of perioperative gabapentin treatment: a systematic review of randomised clinical trials with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses. PROSPERO 2013. https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.asp?ID=CRD42013006538.
- 14.Deeks JJ, JPT H, Altman DG. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: JPT H, Green S, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Chichester: Wiley; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 15.ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline . Clinical safety data management: definitions and standards for expedited reporting E2A. 1994. pp. 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005;5:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Thorlund K, Imberger G, Walsh M, et al. The number of patients and events required to limit the risk of overestimation of intervention effects in meta-analysis--a simulation study. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16: special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration. 2011. Available from wwwhandbookcochraneorg. Accessed 4 Jan 2017.
- 19.Sweeting MJ, Sutton AJ, Lambert PC. What to add to nothing? Use and avoidance of continuity corrections in meta-analysis of sparse data. Stat Med. 2004;23:1351–1375. doi: 10.1002/sim.1761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ajori L, Nazari L, Mazloomfard MM, Amiri Z. Effects of gabapentin on postoperative pain, nausea and vomiting after abdominal hysterectomy: a double blind randomized clinical trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2012;285:677–682. doi: 10.1007/s00404-011-2023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Amr YM, Yousef AA. Evaluation of efficacy of the perioperative administration of Venlafaxine or gabapentin on acute and chronic postmastectomy pain. Clin J Pain. 2010;26:381–385. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181cb406e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Azemati S, Dokouhaki AG, Talei A, Khademi S, Moin-Vaziri N. Evaluation of the effect of a preoperative single dose of Gabapentin on emergence agitation in patients undergoing breast cancer surgery. Middle East J Cancer. 2013;4:145–151. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Badawy AA, Sakka AE. Preoperative gabapentin alone or in combination with dexamethasone on postoperative pain relief after abdominal hysterectomies. A randomized controlled trial. Eg J Anaesth. 2015;31:107–113. doi: 10.1016/j.egja.2014.12.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bashir FM, Qazi S, Hashia AM. A randomized, double blind, placebo controlled study evaluating preventive role of gabapentin for PONV in patients undergoing laparascopic cholecystectomy. JK Sci. 2009;11:190–193. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Behdad S, Ayatollahi V, Bafghi AT, Tezerjani MD, Abrishamkar M. Effect of gabapentin on postoperative pain and operation complications: a randomized placebo controlled trial. West Indian Med J. 2012;61:128–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bekawi MS, El Wakeel LM, Al Taher WM, Mageed WM. Clinical study evaluating pregabalin efficacy and tolerability for pain management in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Clin J Pain. 2014;30:944–952. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bhandari V, Dhasmana D, Sharma J, Sachan P, Chaturvedi A, Dureja S. Gabapentin for post-operative nausea and vomiting: a pilot study. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol. 2014;3:627. doi: 10.5455/2319-2003.ijbcp20140812. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bharti N, Bala I, Narayan V, Singh G. Effect of gabapentin pretreatment on propofol consumption, hemodynamic variables, and postoperative pain relief in breast cancer surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwanica. 2013;51:10–13. doi: 10.1016/j.aat.2013.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Butt A, Mohammad K, M Ommid, M Ahmad, N Jehan, S Qazi. A randomized double blind placebo controlled study of prophylactic gabapentin for prevention of postoperative pain and morphine consumption in patients undergoing mastectomy. The Int J Anesth. 2010;30:1-7.
- 30.Clarke H, Pereira S, Kennedy D, et al. Gabapentin decreases morphine consumption and improves functional recovery following total knee arthroplasty. Pain Res Manag. 2009;14:217–222. doi: 10.1155/2009/930609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Clarke H, Pereira S, Kennedy D, et al. Adding gabapentin to a multimodal regimen does not reduce acute pain, opioid consumption or chronic pain after total hip arthroplasty. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2009;53:1073–1083. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2009.02039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Clarke HA, Katz J, McCartney CJ, et al. Perioperative gabapentin reduces 24 h opioid consumption and improves in-hospital rehabilitation but not post-discharge outcomes after total knee arthroplasty with peripheral nerve block. Br J Anaesth. 2014;113:855–864. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dierking G, Duedahl TH, Rasmussen ML, et al. Effects of gabapentin on postoperative morphine consumption and pain after abdominal hysterectomy: a randomized, double-blind trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2004;48:322–327. doi: 10.1111/j.0001-5172.2004.0329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dirks J, Fredensborg BB, Christensen D, Fomsgaard JS, Flyger H, Dahl JB. A randomized study of the effects of single-dose gabapentin versus placebo on postoperative pain and morphine consumption after mastectomy. Anesthesiology. 2002;97:560–564. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200209000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Doha NM, Rady A, El Azab SR. Preoperative use of gabapentin decreases the anesthetic and analgesic requirements in patients undergoing radical mastectomy. Eg J Anaesth. 2010;26:287–291. doi: 10.1016/j.egja.2010.05.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Durmus M, Kadir But A, Saricicek V, Ilksen Toprak H, Ozcan EM. The post-operative analgesic effects of a combination of gabapentin and paracetamol in patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy: a randomized clinical trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007;51:299–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2006.01237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Erten E, Bilgin F, Çekmen N, Özhan MÖ, Orhan ME, Kurt E. The analgesic effect of different doses of preemptive gabapentin preoperatively on patients undergoing elective laminectomy during postoperative period [Elektif laminektomi operasyonu gecirecek hastalarda preoperatif verilen gabapentinin farkli dozlarinin postoperatif analjeziye etkisi] Anestzi Dergisi. 2010;18:99–105. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fassoulaki A, Patris K, Sarantopoulos C, Hogan Q. The analgesic effect of gabapentin and mexiletine after breast surgery for cancer. Anesth Analg. 2002;95(4):985–991. doi: 10.1097/00000539-200210000-00036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fassoulaki A, Stamatakis E, Petropoulos G, Siafaka I, Hassiakos D, Sarantopoulos C. Gabapentin attenuates late but not acute pain after abdominal hysterectomy. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2006;23:136–141. doi: 10.1017/S0265021505002048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fassoulaki A, Melemeni A, Stamatakis E, Petropoulos G, Sarantopoulos C. A combination of gabapentin and local anaesthetics attenuates acute and late pain after abdominal hysterectomy. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2007;24:521–528. doi: 10.1017/S0265021506002134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Frouzanfard F, Fazel MR, Abolhasani A, Fakharian E, Mousavi G, Moravveji A. Effects of gabapentin on pain and opioid consumption after abdominal hysterectomy. Pain Res Manag. 2013;18:94–96. doi: 10.1155/2013/787401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ghafari MH, Akrami M, Nouralishahi B, Sadegh A. Preoperative Gabapentin or Clonidine decreases postoperative pain and morphine consumption after abdominal hysterectomy. Res J Biol Sci. 2009;4:458–463. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ghai A, Gupta M, Hooda S, Singla D, Wadhera R. A randomized controlled trial to compare pregabalin with gabapentin for postoperative pain in abdominal hysterectomy. Saudi J Anaesth. 2011;5:252–257. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.84097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gilron I, Orr E, Tu D, O’Neill JP, Zamora JE, Bell AC. A placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial of perioperative administration of gabapentin, rofecoxib and their combination for spontaneous and movement-evoked pain after abdominal hysterectomy. Pain. 2005;113:191–200. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2004.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gosai N, Patel L, Patel D, Umarania R, Patel B. Comparative evaluation of Gabapentin and Clonidine for premedication on postoperative analgesia in patient undergoing modified radical mastectomy under general anesthesia. Asian Pac J Health Sci. 2015;2:59–63. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Grosen K, Drewes AM, Hojsgaard A, Pfeiffer-Jensen M, Hjortdal VE, Pilegaard HK. Perioperative gabapentin for the prevention of persistent pain after thoracotomy: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014;46:76–85. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezu032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Grover VK, Mathew PJ, Yaddanapudi S, Sehgal S. A single dose of preoperative gabapentin for pain reduction and requirement of morphine after total mastectomy and axillary dissection: randomized placebo-controlled double-blind trial. J Postgrad Med. 2009;55:257–260. doi: 10.4103/0022-3859.58928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hosseini VS, Yekta R, Marashi S, Marashi SM. The efficacy of melatonin, Clonidine and Gabapentin in reducing preoperative anxiety and postoperative pain in patients undergoing laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: a randomized clinical trial. Archives Anesthesiol Crit Care. 2015;1:120–125. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Huot MP, Chouinard P, Girard F, Ruel M, Lafontaine ER, Ferraro P. Gabapentin does not reduces post-thoracotomy shoulder pain: a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study [La gabapentine ne réduit pas la douleur à l’épaule post-thoracotomie: une étude randomisée, à double insu et contrôlée par placebo] Can J Anesth. 2008;55:337–343. doi: 10.1007/BF03021488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Joseph TT, Krishna HM, Kamath S. Premedication with gabapentin, alprazolam or a placebo for abdominal hysterectomy: effect on pre-operative anxiety, post-operative pain and morphine consumption. Indian J Anaesth. 2014;58:693–699. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.147134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Khademi S, Ghaffarpasand F, Heiran HR, Asefi A. Effects of preoperative gabapentin on postoperative nausea and vomiting after open cholecystectomy: a prospective randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Med Princ Pract. 2010;19:57–60. doi: 10.1159/000252836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Khan ZH, Rahimi M, Makarem J, Khan RH. Optimal dose of pre-incision/post-incision gabapentin for pain relief following lumbar laminectomy: a randomized study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011;55:306–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2010.02377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Khan MA, Siddiqi KJ, Aqeel M. Effect of gabapentin on opioid requirements in patients undergoing total abdominal hysterectomy. Anaeshesia Pain Intensive Care. 2013;17:131–135. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Khurana G, Jindal P, Sharma JP, Bansal KK. Postoperative pain and long-term functional outcome after administration of gabapentin and pregabalin in patients undergoing spinal surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014;39:E363–E368. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kim SI, Park DY, Ok SY, Kim SC. Effect of pre-emptive Gabapentin on Postoerative pain after mastectomy. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2004;47:527–531. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2004.47.4.527. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kinney MA, Mantilla CB, Carns PE, et al. Preoperative gabapentin for acute post-thoracotomy analgesia: a randomized, double-blinded, active placebo-controlled study. Pain Pract. 2012;12:175–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2011.00480.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Koşucu M, Tugcugil E, Ertürk E, Topbaş M, Eroğlu A, Ulusoy H, et al. The effects of the pre-emptive oral gabapentin on post-anesthesia recovery criteria, acute post-thoracotomy pain and development of chronicity in pain with benign thoracotomy operations. Turk Gogus Kalp Dama. 2014;22:389–396. doi: 10.5606/tgkdc.dergisi.2014.7707. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Leung JM, Sands LP, Rico M, et al. Pilot clinical trial of gabapentin to decrease postoperative delirium in older patients. Neurology. 2006;67:1251–1253. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000233831.87781.a9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lunn TH, Husted H, Laursen MB, Hansen LT, Kehlet H. Analgesic and sedative effects of perioperative gabapentin in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled dose-finding study. Pain. 2015;156:2438–2448. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Maleh PA, Alijanpour E, Nickbakhsh N, Modarress R, Naghshineh A, Esmaeili M. Effects of Gabapentin on postoperative pain following laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. J Mazand Univ Med Sci. 2013;23:28-31.
- 61.Menda F, Koner O, Sayin M, Ergenoglu M, Kucukaksu S, Aykac B. Effects of single-dose gabapentin on postoperative pain and morphine consumption after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2010;24:808–813. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2009.10.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Metry A, Ishak S, Khattab A. Does gabapentin have preemptive effects in women undergoing mastectomy? [Il gabapentin possiede un effetto pre-emptive in pazienti sottoposte a mastectomia?] Acta Anaesth Italica. 2008;59:62–76. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Mishra R, Tripathi M, Chandola HC. Comparative clinical study of gabapentin and pregabalin for postoperative analgesia in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesth Essays Res. 2016;10:201–206. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.164737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Neogi M, Basak S, Ghosh D, Mukherjee S, Dawn S, Bhattacharjee DP. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical study on the effects of gabapentin premedication on hemodynamic stability during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2012;28:456–459. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.101903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Omran A, Mohammad AE. A randomized study of the effects of gabapentin versus placebo on post-thoracotomy pain and pulmonary function. Eg J Anaesth. 2005;21:277–281. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ozgencil E, Yalcin S, Tuna H, Yorukoglu D, Kecik Y. Perioperative administration of gabapentin 1,200 mg day-1 and pregabalin 300 mg day-1 for pain following lumbar laminectomy and discectomy: a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. Singap Med J. 2011;52:883–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Pandey CK, Navkar DV, Giri PJ, et al. Evaluation of the optimal preemptive dose of gabapentin for postoperative pain relief after lumbar diskectomy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2005;17:65–68. doi: 10.1097/01.ana.0000151407.62650.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Pandey CK, Priye S, Singh S, Singh U, Singh RB, Singh PK. Preemptive use of gabapentin significantly decreases postoperative pain and rescue analgesic requirements in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Can J Anaesth. 2004;51:358–363. doi: 10.1007/BF03018240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Pandey CK, Sahay S, Gupta D, et al. Preemptive gabapentin decreases postoperative pain after lumbar discoidectomy. Can J Anaesth. 2004;51:986–989. doi: 10.1007/BF03018484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Pandey CK, Priye S, Ambesh SP, Singh S, Singh U, Singh PK. Prophylactic gabapentin for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Postgrad Med. 2006;52:97–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pathak L, Chatuvedi AS. Effect of gabapentin premedication on preoperative anxiety and postoperative pain. Health Renaissance. 2013;11:254–259. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Paul JE, Nantha-Aree M, Buckley N, et al. Gabapentin does not improve multimodal analgesia outcomes for total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Can J Anaesth. 2013;60:423–431. doi: 10.1007/s12630-013-9902-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Paul JE, Nantha-Aree M, Buckley N, et al. Randomized controlled trial of gabapentin as an adjunct to perioperative analgesia in total hip arthroplasty patients. Can J Anaesth. 2015;62:476–484. doi: 10.1007/s12630-014-0310-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Radhakrishnan M, Bithal PK, Chaturvedi A. Effect of preemptive gabapentin on postoperative pain relief and morphine consumption following lumbar laminectomy and discectomy: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2005;17:125–128. doi: 10.1097/01.ana.0000167147.90544.ab. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Ram B, Khanna R, Kumar M, Tiwary PK, Suwalka U. Pre-emptive gabapentin v/s pregabalin for acute postoperative analgesia following abdominal hysterctomy under spinal anaesthesia: a randomized double blind study. SEAJCRR. 2015;4:2031–2034. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Rapchuk IL, O’Connell L, Liessmann CD, Cornelissen HR, Fraser JF. Effect of gabapentin on pain after cardiac surgery: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2010;38:445–451. doi: 10.1177/0310057X1003800306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ray D, Bhattacharjee S. Effect of pre-oeprative gabapentin on early post operative pain, nausea, vomiting and analgesic consumption following hysterectomy in a tertiary care teaching hospital: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2015;2:113–118. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Rorarius MG, Mennander S, Suominen P, et al. Gabapentin for the prevention of postoperative pain after vaginal hysterectomy. Pain. 2004;110:175–181. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2004.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Saeed MH, Krikor AW, Yaquob ZA, Yihya MW, Khayat HS. Preopertive gabapentin in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Bas J Surg. 2013;19:24–29. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Sekhavet L, Zare F, Mojibian M. The postoperative analgesic effects of low-dose gabapentin in patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy. SAJOG. 2009;15:37–40. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Semira A, Zaffar T, Vishal R, Bashir A, Kour K. A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, trial comparing the effectiveness of gabapentin, ondansetron & dexamethasone in prevention of nausea & vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. JK Sci. 2013;15:117–121. [Google Scholar]
- 82.Sen H, Sizlan A, Yanarates O, et al. A comparison of gabapentin and ketamine in acute and chronic pain after hysterectomy. Anesth Analg. 2009;109:1645–1650. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181b65ea0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Sharma JP, Bijalwan A, Beg MA, et al. Effect of gabapentin in postoperative pain, nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Int J Med Sci Public Health. 2015;4:565–568. doi: 10.5455/ijmsph.2015.19122014116. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Soltanzadeh M, Ebad A, Pipelzadeh MR, et al. Gabapentin may relieve post-coronary artery bypass graft pain: a double blind randomized clinical trial. Iran Cardiovasc Res J. 2011;5:79–82. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Srivastava U, Kumar A, Saxena S, Mishra AR, Saraswat N, Mishra S. Effect of preoperative gabapentin on postoperative pain and tramadol consumption after minilap open cholecystectomy: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2010;27:331–335. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e328334de85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Syal K, Goma M, Dogra RK, Ohri A, Gupta AK, Goel A. “protective premedication”: a comparative study of acetaminophen, gabapentin and combination of acetaminophen with gabapentin for post-operative analgesia. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2010;26:531–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Takmaz SA, Kaymak C, Pehlivan BS, Dikmen B. Effect of preoperative 900 and 1200 mg single oral dose of gabapentin on postoperative pain relief and tramadol consumption in open cholecystectomy surgery. Agri. 2007;19:32–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Turan A, Karamanlioglu B, Memis D, Usar P, Pamukcu Z, Ture M. The analgesic effects of gabapentin after total abdominal hysterectomy. Anesth Analg. 2004;98:1370–1373. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000108964.70485.B2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Turan A, Karamanlioglu B, Memis D, et al. Analgesic effects of gabapentin after spinal surgery. Anesthesiology. 2004;100:935–938. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200404000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Turan A, White PF, Karamanlioglu B, et al. Gabapentin: an alternative to the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors for perioperative pain management. Anesth Analg. 2006;102:175–181. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000184824.43411.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ucak A, Onan B, Sen H, Selcuk I, Turan A, Yilmaz AT. The effects of gabapentin on acute and chronic postoperative pain after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2011;25:824–829. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2010.11.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Vahedi P, Shimia M, Aghamohammadi D, Mohajernexhadfard Z, Shoeibi A, Lotfinia I. Does Preemptive Gabapentin reduce morphine consumption and remaining leg pain after lumbar Discectomy? Neurosurg Q. 2011;21:114–120. doi: 10.1097/WNQ.0b013e3182059576. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Vasigh A, Jaafarpour M, Khajavikhan J, Khani A. The effect of Gabapentin plus Celecoxib on pain and associated complications after Laminectomy. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10:UC04–UC08. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/17923.7346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Verma A, Arya S, Sahu S, Lata S, Panday HD, Singh H. To evaluate the role of Gabapentin as Preemptive analgesic in patients undergoing Total abdominal hysterectomy in epidural anaesthesia. Indian J Anaesth. 2008;52:428–431. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Mathiesen O, Moiniche S, Dahl JB. Gabapentin and postoperative pain: a qualitative and quantitative systematic review, with focus on procedure. BMC Anesthesiol. 2007;7:6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2253-7-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Alayed N, Alghanaim N, Tan X, Tulandi T. Preemptive use of gabapentin in abdominal hysterectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:1221–1229. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Yu L, Ran B, Li M, Shi Z. Gabapentin and pregabalin in the management of postoperative pain after lumbar spinal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013;38:1947–1952. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182a69b90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Han C, Li XD, Jiang HQ, Ma JX, Ma XL. The use of gabapentin in the management of postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty: a PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e3883. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Oxman AD, Guyatt GH. A consumer’s guide to subgroup analyses. Ann Intern Med. 1992;116:78–84. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-1-78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Sun X, Briel M, Walter SD, Guyatt GH. Is a subgroup effect believable? Updating criteria to evaluate the credibility of subgroup analyses. BMJ. 2010;340:c117. doi: 10.1136/bmj.c117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Zakkar M, Frazer S, Hunt I. Is there a role for gabapentin in preventing or treating pain following thoracic surgery? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013;17:716–719. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivt301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Straube S, Derry S, Moore RA, Wiffen PJ, HJ MQ. Single dose oral gabapentin for established acute postoperative pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;5:CD008183. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008183.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Fischer HB, Simanski CJ, Sharp C, et al. A procedure-specific systematic review and consensus recommendations for postoperative analgesia following total knee arthroplasty. Anaesthesia. 2008;63:1105–1123. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2008.05565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Doleman B, Heinink TP, Read DJ, Faleiro RJ, Lund JN, Williams JP. A systematic review and meta-regression analysis of prophylactic gabapentin for postoperative pain. Anaesthesia. 2015;70:1186–1204. doi: 10.1111/anae.13179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Appendix 1. Search strategies. Appendix 2. Opioid conversion table. Appendix 3. Forest plot of 24-h morphine consumption from all trials estimates. Appendix 4. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the cholecystectomy subgroup, all trials. Appendix 5. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the hysterectomy subgroup, all trials. Appendix 6. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the mastectomy subgroup, all trials. Appendix 7. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the orthopedic arthroplasty subgroup, all trials. Appendix 8. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the spinal subgroup, all trials. Appendix 9. TSA of 24-h morphine consumption in the thoracic surgery subgroup, all trials. Appendix 10. Forest plot of SAEs, all trials. Appendix 11. TSA of SAEs in the thoracic surgery subgroup, all trials. Appendix 12. Forest plot of VAS 6 h at rest, all trials. Appendix 13. Forest plot of VAS 6 h at mobilization, all trials. Appendix 14. Forest plot of VAS 24 h at rest, all trials. Appendix 15. Forest plot of VAS 24 h at mobilization, all trials. Appendix 16. Forest plot nausea, all trials. Appendix 17. Forest plot vomiting, all trials. Appendix 18. Forest plot sedation, all trials. Appendix 19. Forest plot dizziness, all trials. (PDF 736 kb)
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on request.
These are preplanned, protocolled subgroup analyses from a systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses: Fabritius ML, Geisler A, Hansen MS, Nikolajsen L, Hamunen K, Kontinen V, Wetterslev J, Dahl JB, Mathiesen O. Gabapentin for post-operative pain management - a systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2016; 60: 1188–208.
The protocolled subgroup analyses are a few of the planned analyses from the original systematic review which have been published in PROSPERO. Some of the subgroups have been published in the original review while a few are to be published in separate subgroup analyses, others have too few trials included to convey any usable information and have thus been excluded and not published.


