Figure 4.
VR3/Lysin Complex Formation Depends on Both Hydrophobic and H-Bonding Interactions
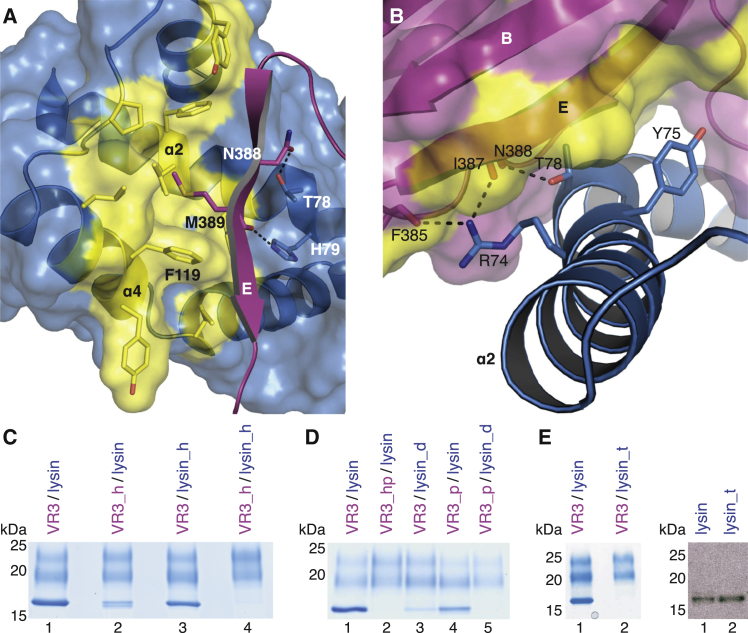
(A) Close up of the VR3/lysin interface, oriented as in the right panel of Figure 3B. Functionally important residues and surrounding hydrophobic amino acids are in stick representation. Only β strand E of VR3 is shown for clarity. Dashed black lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
(B) Lysin α2 interface residues mutated in construct lysin_t (R74A, Y75A, T78A).
(C–E) Functional analysis of VR3 and lysin interface mutants by His-pull-down. VR3_h, M389K; VR3_p, N388A; VR3_hp, N388A, M389K; lysin_h, F119S; lysin_d, T78A, H79A. Right panel of (E), anti-lysin immunoblot shows that individually expressed lysin_t is secreted as efficiently as wild-type lysin.
See also Figures S4 and S5 and Tables S4 and S5.