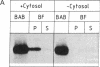
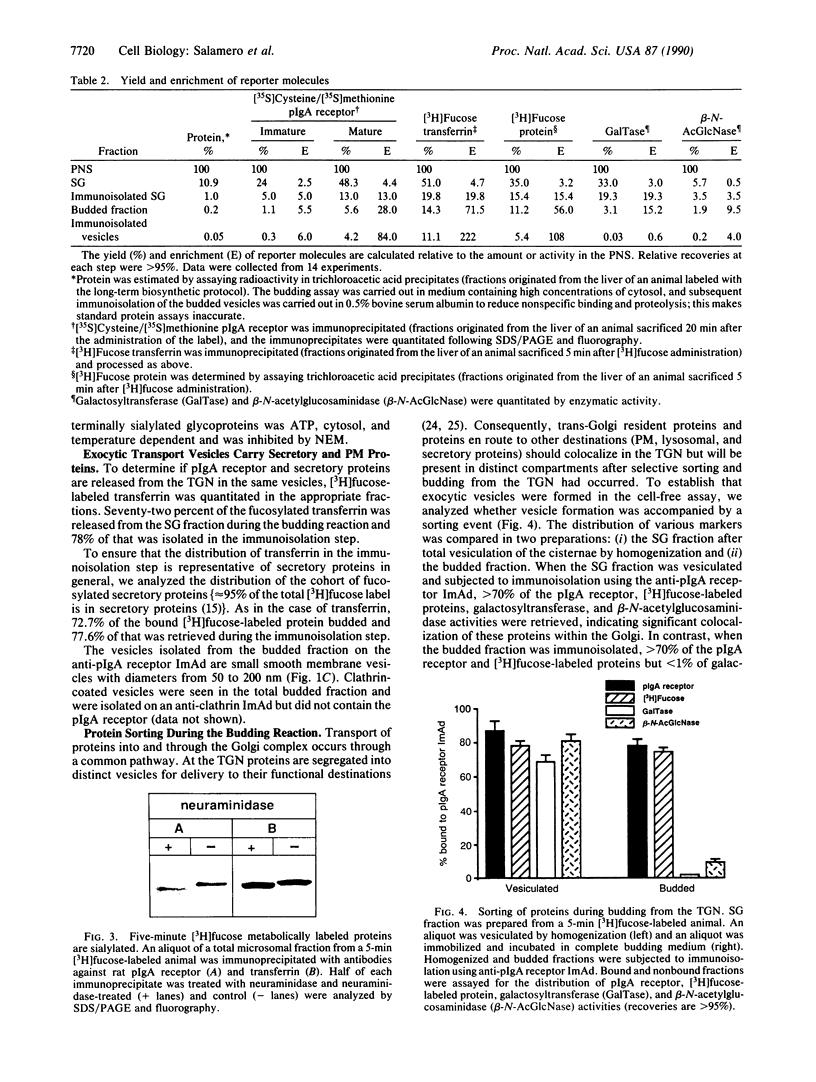
Abstract
We have developed a cell-free assay that reproduces vesicular budding during exit from the Golgi complex. The starting preparation for the in vitro system was a rat liver stacked Golgi fraction immobilized on a magnetic solid support by means of an antibody against the cytoplasmic domain of the polymeric IgA receptor. Vesicular budding was ATP, cytosol, and temperature dependent and was inhibited by 1 mM N-ethylmaleimide. Budding was maximum within 10 min and originated preferentially from the trans-Golgi. Exocytic transport vesicles immunoisolated from the total budded population were enriched in the mature forms of secretory and membrane proteins destined to the basolateral plasma membrane and were depleted in lysosomal enzymes and galactosyl-transferase activity. The finding that a major proportion (greater than 70%) of newly synthesized, siaylated secretory and transmembrane proteins is contained in a single population of post-Golgi transport vesicles implies that, in a constitutively secreting cell, basolaterally destined proteins are sorted and packaged together into the same exocytic transport vesicles.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Wagner K. R., Keller D. S. Reconstitution of transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex using a cell-free system. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):749–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartles J. R., Feracci H. M., Stieger B., Hubbard A. L. Biogenesis of the rat hepatocyte plasma membrane in vivo: comparison of the pathways taken by apical and basolateral proteins using subcellular fractionation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1241–1251. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess T. L., Kelly R. B. Constitutive and regulated secretion of proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:243–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brands R., Rothman J. E. Attachment of terminal N-acetylglucosamine to asparagine-linked oligosaccharides occurs in central cisternae of the Golgi stack. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):463–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90161-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G. Progress in unraveling pathways of Golgi traffic. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:447–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J., Howell K. E. Immuno-isolation of vesicles using antigenic sites either located on the cytoplasmic or the exoplasmic domain of an implanted viral protein. A quantitative analysis. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;38(2):312–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Ito A., Palade G. E. Endoplasmic reticulum marker enzymes in Golgi fractions--what does this mean? J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):581–589. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Schmid R., Ugelstad J., Gruenberg J. Immunoisolation using magnetic solid supports: subcellular fractionation for cell-free functional studies. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:265–292. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61615-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn L. C., Kraehenbuhl J. P. Monoclonal antibodies recognizing the secreted and membrane domains of the IgA dimer receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:751–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Brauchbar M., Bucher K., Hauri H. P. Sorting of endogenous plasma membrane proteins occurs from two sites in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90594-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Malhotra V., Amherdt M., Serafini T., Rothman J. E. Dissection of a single round of vesicular transport: sequential intermediates for intercisternal movement in the Golgi stack. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Nelson W. J. Morphogenesis of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2672330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Berger E. G. Immunocytochemical localization of galactosyltransferase in HeLa cells: codistribution with thiamine pyrophosphatase in trans-Golgi cisternae. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):223–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff J. M., Fisher M. M., Jones A. L., Underdown B. J. Human IgA as a heterovalent ligand: switching from the asialoglycoprotein receptor to secretory component during transport across the rat hepatocyte. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):920–931. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Fuller S. D. Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:243–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Willemsen R., van Kerkhof P., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Lodish H. F. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein, albumin, and transferrin are transported to the cell surface via the same Golgi vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1815–1822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suissa M. Spectrophotometric quantitation of silver grains eluted from autoradiograms. Anal Biochem. 1983 Sep;133(2):511–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztul E. S., Howell K. E., Palade G. E. Biogenesis of the polymeric IgA receptor in rat hepatocytes. II. Localization of its intracellular forms by cell fractionation studies. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1255–1261. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztul E. S., Howell K. E., Palade G. E. Intracellular and transcellular transport of secretory component and albumin in rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1582–1591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodman P. G., Edwardson J. M. A cell-free assay for the insertion of a viral glycoprotein into the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1829–1835. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Curtis I., Simons K. Isolation of exocytic carrier vesicles from BHK cells. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):719–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]