Abstract
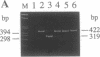
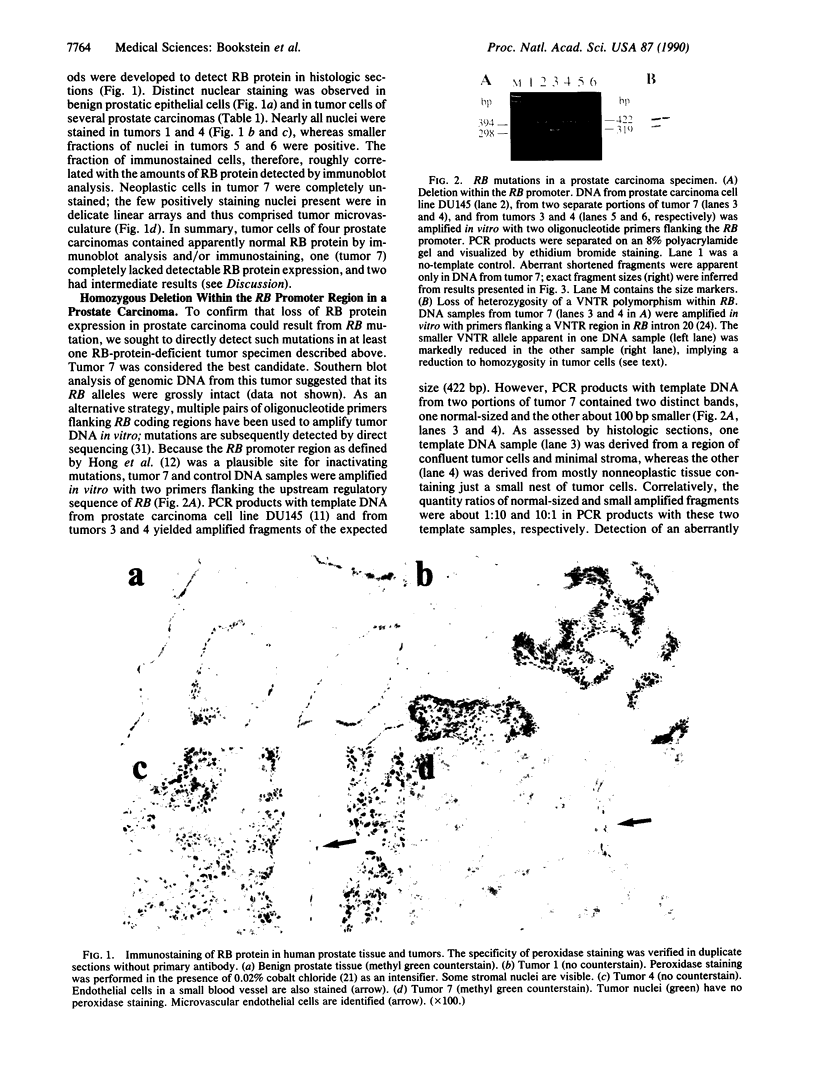
Mutational inactivation of the retinoblastoma gene (RB) is found in all retinoblastomas and in a subset of other human neoplasms, including sarcomas of bone or soft tissue and carcinomas of lung or breast. Exogenous copies of wild-type RB have been shown to suppress the tumorigenicity of several types of tumor cells with endogenous RB mutations, including a previously described human prostatic carcinoma cell line. To further support a role for RB inactivation in the genesis of prostate cancer, seven primary or metastatic prostate carcinoma specimens were examined for evidence of RB mutation. By the use of immunoblot analysis and immunostaining of histologic sections, RB-encoded protein was readily detected in tumor cells of five specimens, was equivocally detected in one specimen, and was apparently absent from tumor cells of one specimen. RB mutations in the latter case were precisely characterized as (i) a deletion of 103 nucleotides containing transcriptional start sites and (ii) loss of the second RB allele. The 103-base-pair deletion was sufficient to abolish the promoter activity of upstream DNA sequences in a heterologous expression system. These results (i) demonstrate that RB can be inactivated in vivo by mutation of its promoter, (ii) confirm the existence of RB mutations in some human prostate carcinomas, and (iii) suggest the use of immunohistochemical methods to screen for RB mutations in clinical samples of common adult neoplasms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkin N. B., Baker M. C. Chromosome study of five cancers of the prostate. Hum Genet. 1985;70(4):359–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00295378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., Shackleford G. M., Schackleford G. M., Gerber M. R., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Schartl M., Bogenmann E., Rapaport J. M., McGee T. Structure and expression of the murine retinoblastoma gene and characterization of its encoded protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6474–6478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. The molecular genetics of cancer. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):305–311. doi: 10.1126/science.3541204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R., Lai C. C., To H., Lee W. H. PCR-based detection of a polymorphic BamHI site in intron 1 of the human retinoblastoma (RB) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1666–1666. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Scully P., Lee W. H. Suppression of tumorigenicity of human prostate carcinoma cells by replacing a mutated RB gene. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):712–715. doi: 10.1126/science.2300823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Scully P., Shew J. Y., Wang J. Y., Lee W. H. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product is modulated during the cell cycle and cellular differentiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin P. T., Kan Y. W. The molecular genetics of hemoglobin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;565:1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming W. H., Hamel A., MacDonald R., Ramsey E., Pettigrew N. M., Johnston B., Dodd J. G., Matusik R. J. Expression of the c-myc protooncogene in human prostatic carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1535–1538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong F. D., Huang H. J., To H., Young L. J., Oro A., Bookstein R., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. Structure of the human retinoblastoma gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5502–5506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. M., Park S. H., Bogenmann E., Cheng J. C., Yandell D. W., Kaye F. J., Minna J. D., Dryja T. P., Weinberg R. A. Frequent inactivation of the retinoblastoma anti-oncogene is restricted to a subset of human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2775–2779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. J., Yee J. K., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Bookstein R., Friedmann T., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. Suppression of the neoplastic phenotype by replacement of the RB gene in human cancer cells. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.3201247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Wang N. P., Tseng B. Y., Lee W. H., Lee E. H. Two distinct and frequently mutated regions of retinoblastoma protein are required for binding to SV40 T antigen. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1815–1822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipreos E. T., Wang J. Y. Differential phosphorylation of c-Abl in cell cycle determined by cdc2 kinase and phosphatase activity. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):217–220. doi: 10.1126/science.2183353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G., Jr Mutation and cancer: statistical study of retinoblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):820–823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bookstein R., Hong F., Young L. J., Shew J. Y., Lee E. Y. Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: cloning, identification, and sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1394–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.3823889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Shew J. Y., Hong F. D., Sery T. W., Donoso L. A., Young L. J., Bookstein R., Lee E. Y. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein associated with DNA binding activity. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):642–645. doi: 10.1038/329642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Wheatley W., Benedict W. F., Huang C. M., Lee E. Y. Purification, biochemical characterization, and biological function of human esterase D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6790–6794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peehl D. M., Wehner N., Stamey T. A. Activated Ki-ras oncogene in human prostatic adenocarcinoma. Prostate. 1987;10(4):281–289. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990100402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Bookstein R., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. Deletion of a splice donor site ablates expression of the following exon and produces an unphosphorylated RB protein unable to bind SV40 T antigen. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Jan;1(1):17–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shew J. Y., Lin B. T., Chen P. L., Tseng B. Y., Yang-Feng T. L., Lee W. H. C-terminal truncation of the retinoblastoma gene product leads to functional inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shew J. Y., Ling N., Yang X. M., Fodstad O., Lee W. H. Antibodies detecting abnormalities of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product (pp110RB) in osteosarcomas and synovial sarcomas. Oncogene Res. 1989;4(3):205–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg E., Boring C. C., Squires T. S. Cancer statistics, 1990. CA Cancer J Clin. 1990 Jan-Feb;40(1):9–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. L., Ryschkewitsch C. F., Walker D. L., Webster H. D. JC papovavirus large tumor (T)-antigen expression in brain tissue of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and non-AIDS patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2271–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson T. C., Southgate J., Kitchener G., Land H. Multistage carcinogenesis induced by ras and myc oncogenes in a reconstituted organ. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):917–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90625-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turbat-Herrera E. A., Herrera G. A., Gore I., Lott R. L., Grizzle W. E., Bonnin J. M. Neuroendocrine differentiation in prostatic carcinomas. A retrospective autopsy study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Nov;112(11):1100–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley J. M., Armour J., Swallow J. E., Jeffreys A. J., Ponder B. A., T'Ang A., Fung Y. K., Brammar W. J., Walker R. A. The retinoblastoma gene is frequently altered leading to loss of expression in primary breast tumours. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):725–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viola M. V., Fromowitz F., Oravez S., Deb S., Finkel G., Lundy J., Hand P., Thor A., Schlom J. Expression of ras oncogene p21 in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 16;314(3):133–137. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601163140301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yandell D. W., Campbell T. A., Dayton S. H., Petersen R., Walton D., Little J. B., McConkie-Rosell A., Buckley E. G., Dryja T. P. Oncogenic point mutations in the human retinoblastoma gene: their application to genetic counseling. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 21;321(25):1689–1695. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912213212501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yandell D. W., Dryja T. P. Detection of DNA sequence polymorphisms by enzymatic amplification and direct genomic sequencing. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):547–555. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]