Fig. 1.
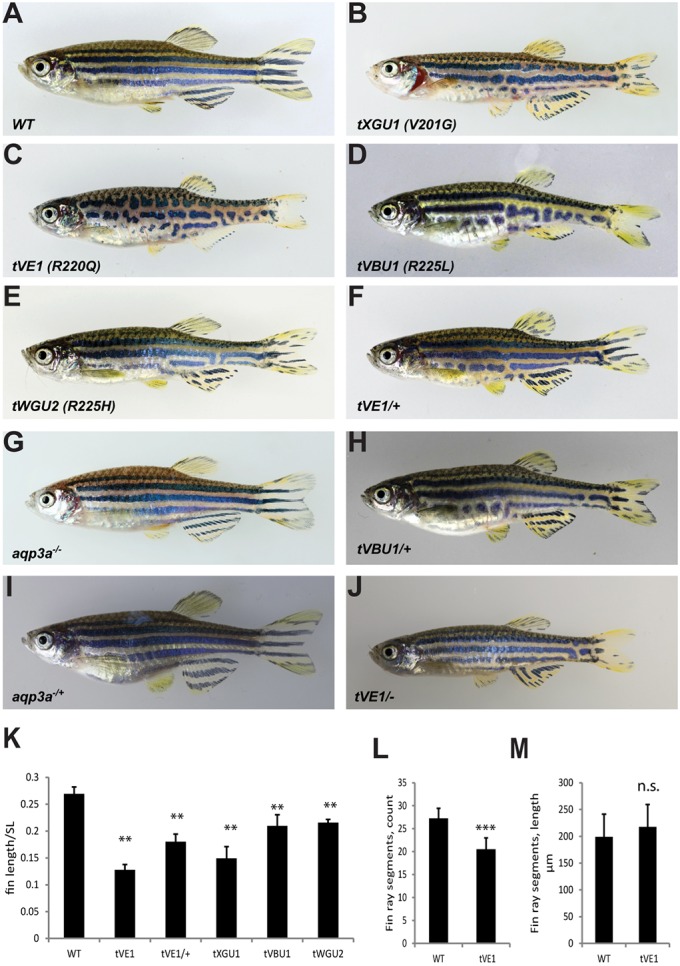
Mutations in aqp3a lead to undulating, broken stripes and short fins. (A-E) Comparison of wild type with mau mutants carrying the dominant alleles tVE1, tXGU1, tVBU1 and tWGU2. (F,H) The dominant mau phenotype is attenuated in heterozygous fish. (G,I) The loss-of-function mutant aqp3a−/−, generated in the background of aqp3atVE1/tVE1, has a wild-type phenotype in homozygous and heterozygous fish. (J) The aqp3atVE1/− phenotype is similar to that of aqp3atVE1/+. (K) Ratio of caudal fin length to standard body length (SL) in mau mutants. For each allele, seven to nine fish were measured. Mean±s.d. **P<0.01 for mutant versus wild type (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons test). (L) Number of fin ray segments in the third ray of the caudal fin in wild-type and aqp3atVE1/tVE1 fish. n=8. Mean±s.d. ***P<0.0001 (unpaired t-test). (M) Length of fin ray segments in the third ray of the caudal fin in wild-type and aqp3atVE1/tVE1 fish. n=8. Mean±s.d. n.s., not significant (unpaired t-test).
