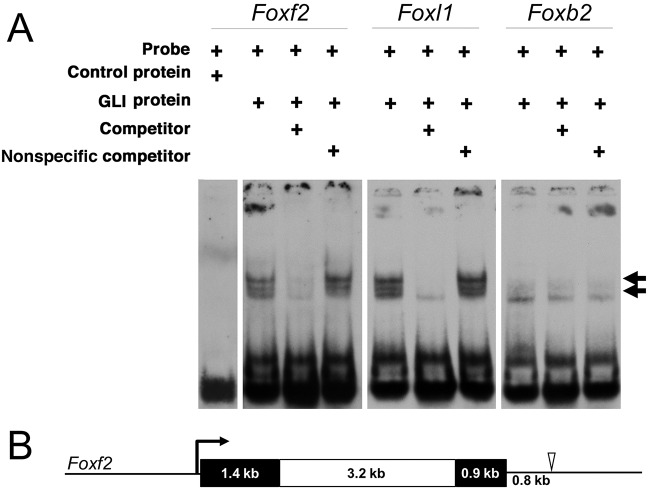
Fig. 6.
A novel GLI-binding site at the Foxf2 locus. (A) EMSAs were used to assess putative GLI-binding sites identified in silico. EMSAs of control and three unique putative GLI-binding sites near Foxf2, Foxl1 and Foxb2. Arrows indicate shifted bands marking DIG-labeled oligonucleotide probes bound by recombinant GLI1 protein. Lowest band (no arrow) marks free, unbound probe. An oligonucleotide probe containing a putative GLI-binding site 0.8 kb downstream of Foxf2 was bound by GLI1, causing a band shift. As a positive control, a probe was designed containing a known GLI-binding site near Foxl1, which was also bound by GLI1, causing a band shift. A probe containing a putative GLI-binding site near Foxb2 was not bound by GLI1. Consolidated gel images are shown. (B) A scale-drawn schematic of the mouse Foxf2 locus. Black boxes denote exons and a white box denotes the intron. The open arrowhead indicates the location of the novel GLI1 binding site 0.8 kb downstream of the Foxf2 coding sequence.