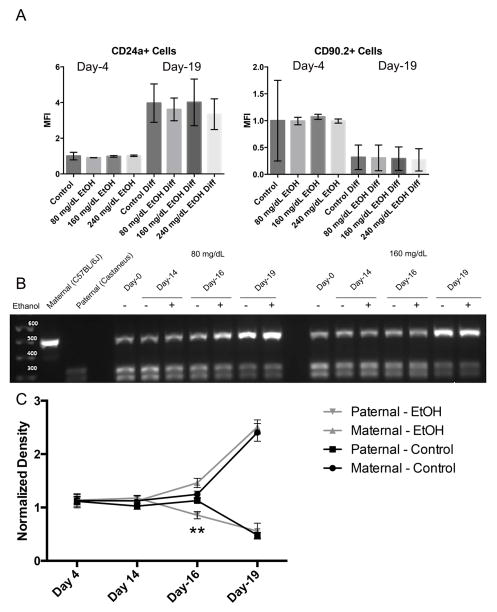
Fig. 4.
EtOH exposure does not disrupt the ability of ESCs to acquire imprinted patterns of transcription during differentiation. A) ESCs were seeded into flasks and exposed to varying concentrations of ethanol (0 mg/dL, 80 mg/dL, 160 mg/dL, or 240 mg/dL) for four days, followed by a no-ethanol recovery period for ten days. Cells were then differentiated into neuroblasts using an established 5-day protocol. At Day-4 and Day -19, cells were monitored for changes in the expression of the surface markers CD90.2 and CD24a using flow cytometry. Graphs represent three separate biological replicates (N = 3) examining half a million cells in each replicate. B) Representative graphs examining allelic patterns of Igf2R transcripts through ESC differentiation using a polymophism-based restriction digest assay. In this assay, transcripts derived from the maternal C57BL/6J strain (upper band) are refractory to Taq1 digestion, while transcripts derived from the paternal Mus musculus castaneus strain (lower doublet) are susceptible. C) Densitometry analysis of Igf2R allelic expression. Graph represents three separate biological replicates (N = 3).