Figure 3.
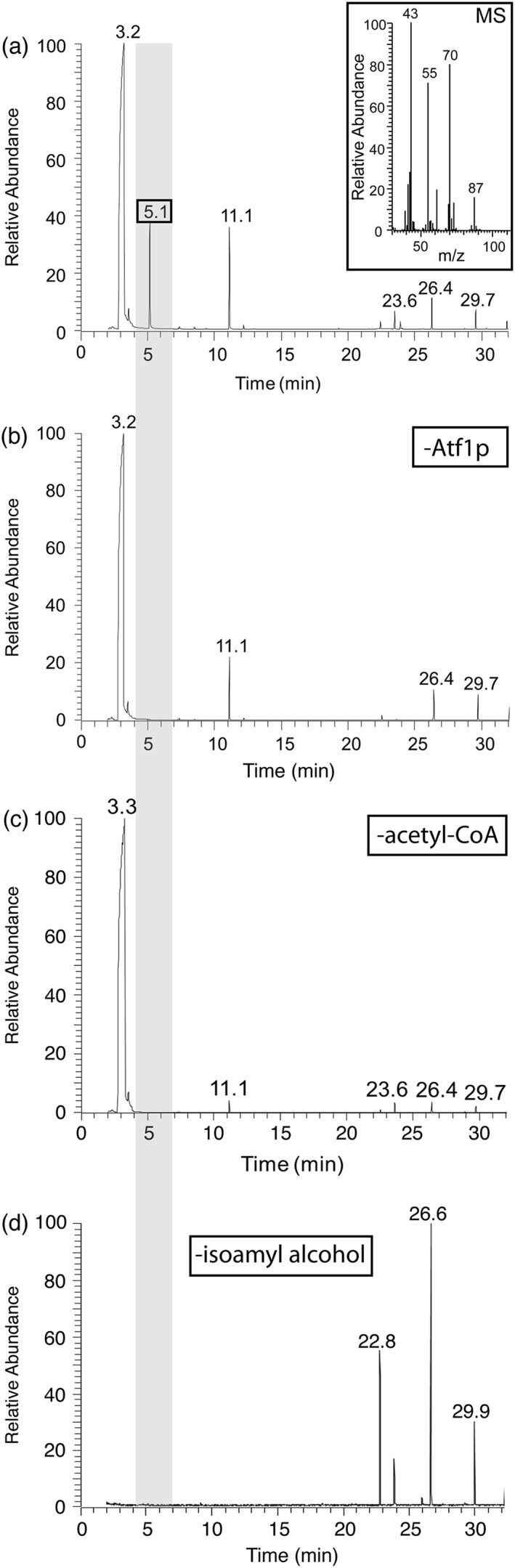
Production of a volatile ester by Atf1p. (a) Incubating purified recombinant Atf1p, isoamyl alcohol and acetyl‐CoA generates a GC peak at 5.1 min (boxed) that is confirmed as isoamyl acetate by coupled MS (inset). As expected, the molecular ion, which would have m/z = 130, is not observed. Instead, the characteristic fragmentation peaks are: m/z = 43, CH3C=O+, acetyl cation; m/z = 87, C2H4OC(=O)CH3 +, loss of alkyl free radical from molecular ion; m/z = 70, [(CH3)2CHCH=CH2]•+, elimination of neutral acetic acid from molecular ion; m/z = 55, CH3C(=CH2)CH2 +, cleavage of the preceding alkyl radical cation; the minor unlabelled peak at m/z = 61 is protonated acetic acid from the ‘McLafferty +1’ or ‘2H’ rearrangement (Sharkey et al., 1959; McGoran et al., 1996; McLafferty and Tureček, 1993). (b–d) The isoamyl acetate product is not formed spontaneously in controls lacking one of either enzyme (−Atf1p), acetyl‐CoA (−acetyl‐CoA) or alcohol (−isoamyl alcohol)
