Abstract
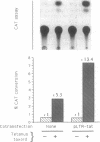
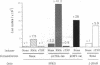
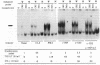
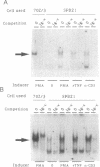
The expression of transiently transfected expression vectors under the control of the long terminal repeat (LTR) of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or its enhancer sequence and the translocation of the HIV enhancer-binding protein NF-kappa B were analyzed in two human T-cell clones stimulated through their T-cell receptor complex or by tumor necrosis factor or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. We found a dissociation of NF-kappa B translocation from transactivation of either the HIV LTR or the HIV enhancer. Interleukin 2 induced proliferation but not NF-kappa B translocation or LTR transactivation. Phorbol ester or specific antigen recognition induced HIV LTR transactivation, whereas stimulation with tumor necrosis factor or antibody to CD3 did not. The two latter signals were nevertheless able to induce NF-kappa B translocation with a pattern in the band-shift assay indistinguishable from that observed using phorbol ester. Our finding that induction of NF-kappa B by tumor necrosis factor or antibody to CD3 is not sufficient to induce HIV enhancer-dependent transcription in cloned T cells contrasts with results obtained in most lymphoblastoid T-cell lines and indicates that normal T lymphocytes differ from tumoral T cells in terms of requirements for HIV LTR activation. Furthermore, our results suggest that events linked to T-cell activation, in addition to NF-kappa B translocation per se, induce functional interactions of the NF-kappa B complex with the HIV enhancer.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Mogensen S. C., Vuillier F., Fiers W., Virelizier J. L. Autocrine secretion of tumor necrosis factor under the influence of interferon-gamma amplifies HLA-DR gene induction in human monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6087–6091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. A 65-kappaD subunit of active NF-kappaB is required for inhibition of NF-kappaB by I kappaB. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1689–1698. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Hoeffler J. P., Jameson J. L., Lin J. C., Habener J. F. Structural determinants for transcriptional activation by cAMP-responsive DNA elements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18466–18472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh E. J., Maury W. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Rabson A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Josephs S. F., Gilman M. Z., Ryan W., Clarkson B. Characterization of cellular proteins recognizing the HIV enhancer using a microscale DNA-affinity precipitation assay. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):391–395. doi: 10.1038/330391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvat R. T., Wood C. HIV promoter activity in primary antigen-specific human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2745–2751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Le Bail O., Hatat D., Piette J., Kieran M., Logeat F., Wallach D., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. TNF stimulates expression of mouse MHC class I genes by inducing an NF kappa B-like enhancer binding activity which displaces constitutive factors. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3793–3800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël N., Hazan U., Alcami J., Munier A., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Bachelerie F., Israël A., Virelizier J. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates transcription of HIV-1 in human T lymphocytes, independently and synergistically with mitogens. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3956–3960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. R. Antigen presentation, antigen-presenting cells and antigen processing. Curr Opin Immunol. 1988 Dec;1(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(88)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Kuang A., Gifford A., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B protein purification from bovine spleen: nucleotide stimulation and binding site specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8825–8829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolick J. B., Volkman D. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S. Amplification of HTLV-III/LAV infection by antigen-induced activation of T cells and direct suppression by virus of lymphocyte blastogenic responses. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1719–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElrath M. J., Pruett J. E., Cohn Z. A. Mononuclear phagocytes of blood and bone marrow: comparative roles as viral reservoirs in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):675–679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Williams T. J., Tjian R. Enhancer binding factors AP-4 and AP-1 act in concert to activate SV40 late transcription in vitro. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):557–561. doi: 10.1038/332557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Roeder R. G. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos enhancer. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90520-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheurich P., Thoma B., Ucer U., Pfizenmaier K. Immunoregulatory activity of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha: induction of TNF receptors on human T cells and TNF-alpha-mediated enhancement of T cell responses. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1786–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt C., Ballet J. J., Agrapart M., Bizzini B. Human T cell clones specific for tetanus toxoid: characterization of antigen specificity and HLA restriction. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Oct;12(10):849–854. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Psallidopoulos M. C., Lane H. C., Thompson L., Baseler M., Massari F., Fox C. H., Salzman N. P., Fauci A. S. The reservoir for HIV-1 in human peripheral blood is a T cell that maintains expression of CD4. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.2665081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz O., Virelizier J. L., Montagnier L., Hazan U. A microtransfection method using the luciferase-encoding reporter gene for the assay of human immunodeficiency virus LTR promoter activity. Gene. 1990 Apr 16;88(2):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90032-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Ijssel H., Terhorst C., de Vries J. E. Establishment of human T lymphocyte clones highly cytotoxic for an EBV-transformed B cell line in serum-free medium: isolation of clones that differ in phenotype and specificity. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):95–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Keizer G., Borst J., Terhorst C., Hekman A., de Vries J. E. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against cell surface molecules associated with cytotoxic activity of natural and activated killer cells and cloned CTL lines. Hybridoma. 1983;2(4):423–437. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1983.2.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong-Starkesen S. E., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Signaling through T lymphocyte surface proteins, TCR/CD3 and CD28, activates the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):702–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virelizier J. L. Cellular activation and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989;2(3):409–413. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(89)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Kieran M., Le Bail O., Israël A., Kourilsky P. Purification of KBF1, a common factor binding to both H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3317–3324. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02652.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yssel H., Aubry J. P., de Waal Malefijt R., de Vries J. E., Spits H. Regulation by anti-CD2 monoclonal antibody of the activation of a human T cell clone induced by anti-CD3 or anti-T cell receptor antibodies. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):2850–2855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yssel H., De Vries J. E., Koken M., Van Blitterswijk W., Spits H. Serum-free medium for generation and propagation of functional human cytotoxic and helper T cell clones. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90450-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]