Abstract
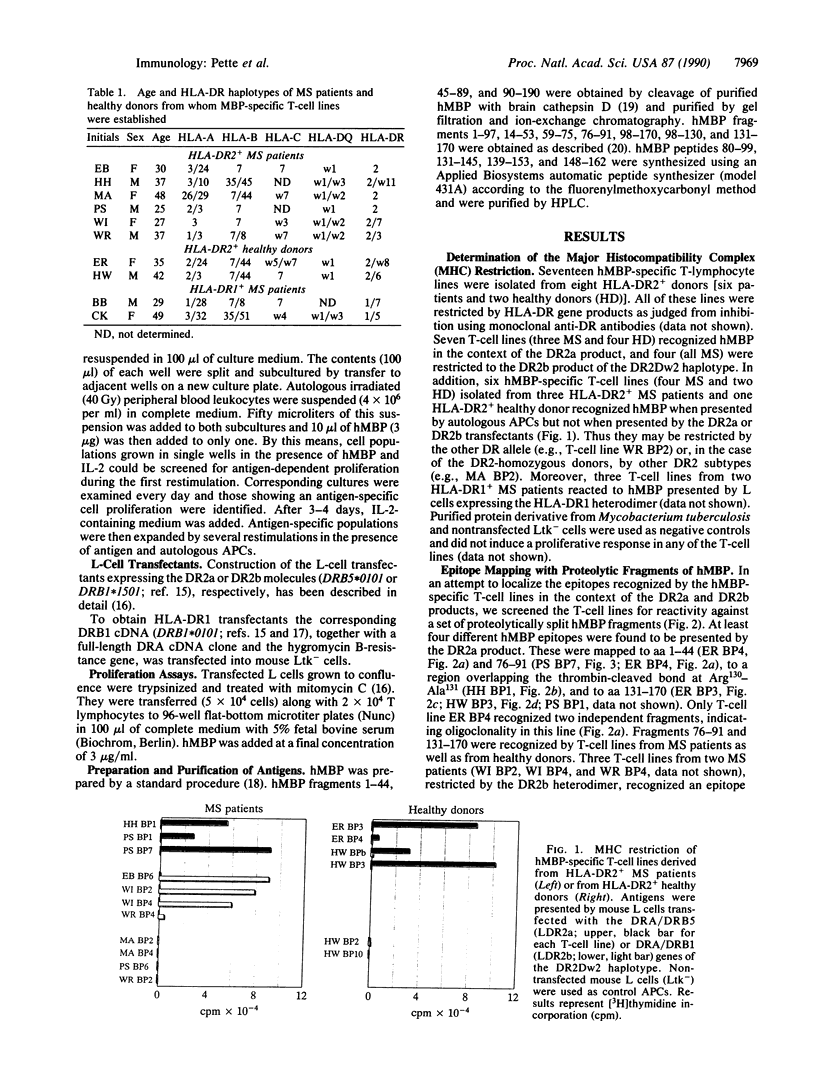
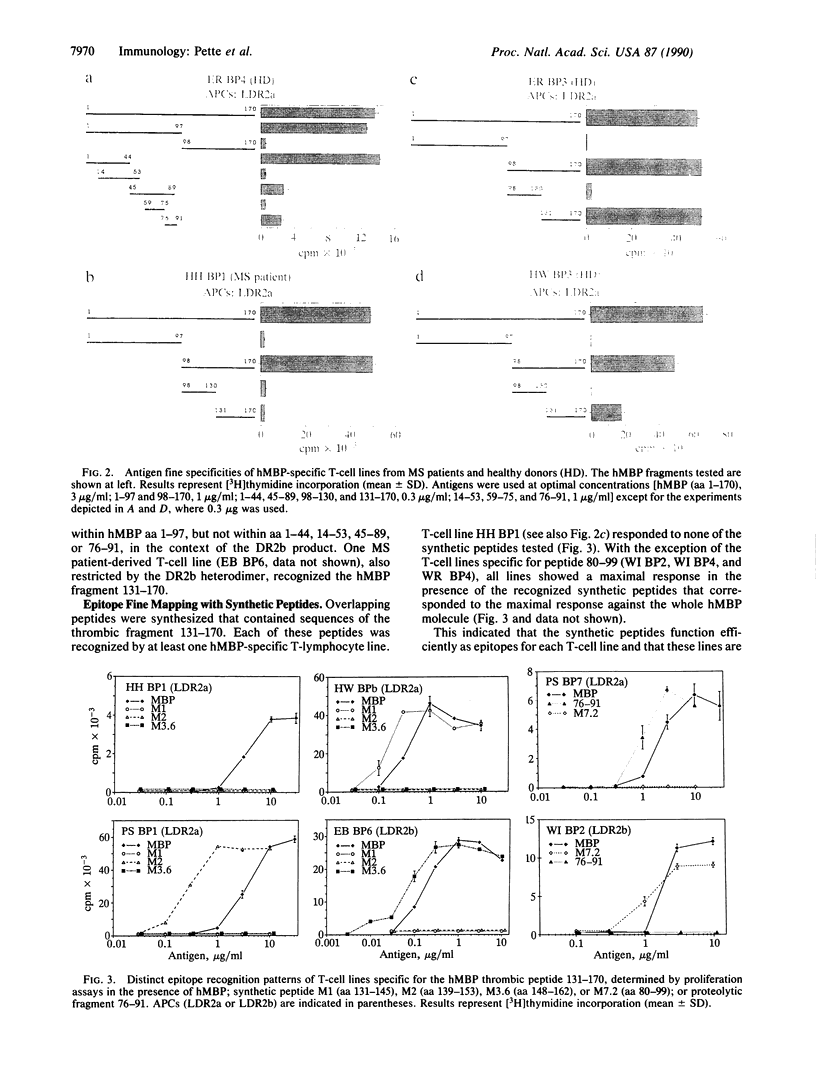
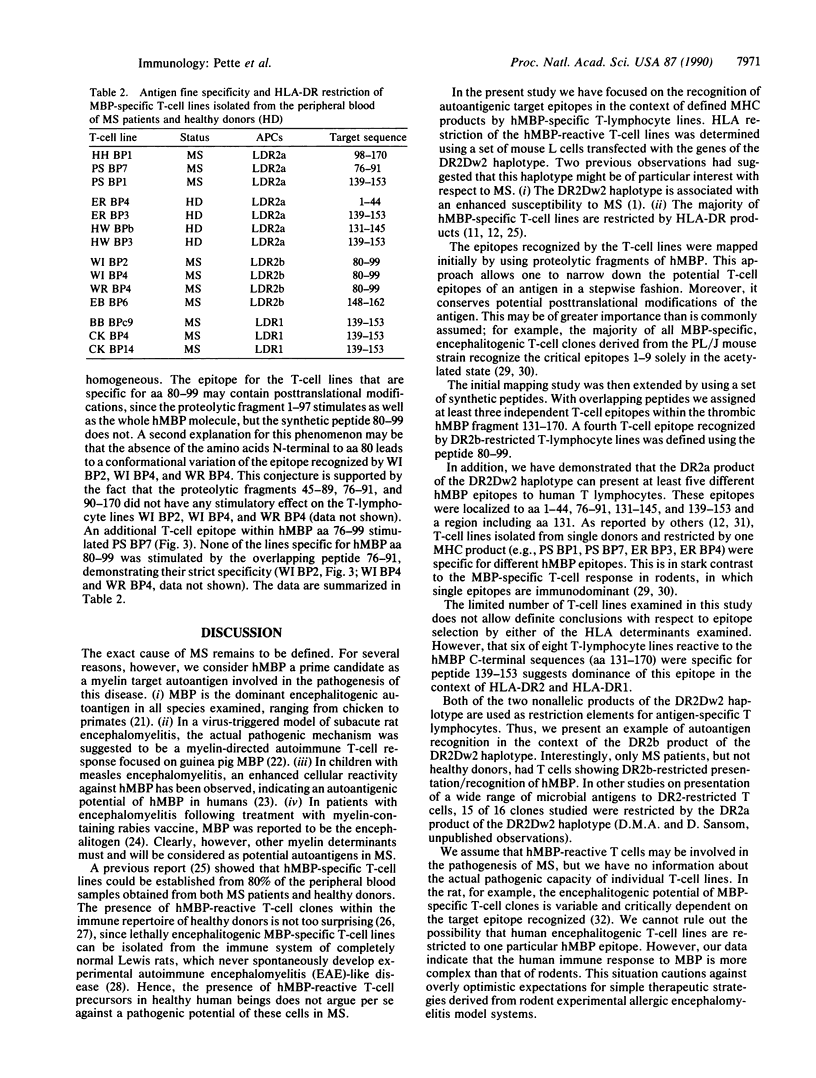
A panel of 20 human myelin basic protein (hMBP)-specific T-lymphocyte lines was generated from the peripheral blood of eight multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and two healthy donors, most of them expressing the HLA-DR2 haplotype, which is associated with an increased susceptibility to MS. Using HLA-DR gene-transfected mouse L-cell lines as antigen-presenting cells, we established that of the 20 hMBP-specific T-lymphocyte lines, 7 were restricted by the DR2a gene products of the DR2Dw2 haplotype. Four T-cell lines recognized hMBP in the context of the DR2b products of the DR2Dw2 haplotype. DR2b-restricted T-cell responses were demonstrable only in T-cell lines derived from MS patients. The hMBP epitopes presented by the DR2a heterodimer were mapped to peptides covering amino acid residues 1-44, 76-91, 131-145, or 139-153 and to a region spanning the thrombin-cleaved bond at Arg130-Ala131. DR2b-restricted T-cell lines recognized epitopes within amino acids 80-99 and 148-162. Peptide 139-153 was also presented in the context of HLA-DR1 molecules. Our data show that (i) in MS patients both the DR2a and DR2b products of the DR2Dw2 haplotype function as restriction elements for the myelin autoantigen hMBP, (ii) the DR2a molecule presents at least five different epitopes to hMBP-specific T lymphocytes, and (iii) anti-hMBP T-cell lines derived from individual donors can differ in their antigen fine specificity as well as in their HLA restriction.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. T cell receptors in murine autoimmune diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:371–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. I., Denney D., Jr, Foster L., Belt T., Todd J. A., McDevitt H. O. Allelic variation in the DR subregion of the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6234–6238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer J. G., Marsh S. G., Albert E. Nomenclature for factors of the HLA system, 1989. Immunol Today. 1990 Jan;11(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90003-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J., Rosenzweig A., Zweiman B., Lisak R. P. Isolation of myelin basic protein-reactive T-cell lines from normal human blood. Cell Immunol. 1983 Oct 15;81(2):435–440. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. K., Vainiene M., Whitham R., Bourdette D., Chou C. H., Hashim G., Offner H., Vandenbark A. A. Response of human T lymphocyte lines to myelin basic protein: association of dominant epitopes with HLA class II restriction molecules. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Jun;23(2):207–216. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490230211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H., Kniskern P. J., Jackson J. J. Myelin basic proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:323–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giegerich G., Pette M., Fujita K., Wekerle H., Epplen J. T., Hinkkanen A. Rapid method based on reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography for purification of human myelin basic protein and its thrombic and endoproteinase Lys-C peptides. J Chromatogr. 1990 Jun 8;528(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)82364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemachudha T., Griffin D. E., Giffels J. J., Johnson R. T., Moser A. B., Phanuphak P. Myelin basic protein as an encephalitogen in encephalomyelitis and polyneuritis following rabies vaccination. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):369–374. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell M. D., Winters S. T., Olee T., Powell H. C., Carlo D. J., Brostoff S. W. Vaccination against experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with T cell receptor peptides. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):668–670. doi: 10.1126/science.2814489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Griffin D. E., Hirsch R. L., Wolinsky J. S., Roedenbeck S., Lindo de Soriano I., Vaisberg A. Measles encephalomyelitis--clinical and immunologic studies. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):137–141. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Kono D. H., Urban J. L., Hood L. The T-cell receptor repertoire and autoimmune diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:657–682. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Jaraquemada D., Flerlage M., Richert J., Whitaker J., Long E. O., McFarlin D. E., McFarland H. F. Fine specificity and HLA restriction of myelin basic protein-specific cytotoxic T cell lines from multiple sclerosis patients and healthy individuals. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):540–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota K., Matsui M., Milford E. L., Mackin G. A., Weiner H. L., Hafler D. A. T-cell recognition of an immunodominant myelin basic protein epitope in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):183–187. doi: 10.1038/346183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richert J. R., Robinson E. D., Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E., Dragovic L. J., Kies M. W. Evidence for multiple human T cell recognition sites on myelin basic protein. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Jun;23(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUMACHER G. A., BEEBE G., KIBLER R. F., KURLAND L. T., KURTZKE J. F., MCDOWELL F., NAGLER B., SIBLEY W. A., TOURTELLOTTE W. W., WILLMON T. L. PROBLEMS OF EXPERIMENTAL TRIALS OF THERAPY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS: REPORT BY THE PANEL ON THE EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTAL TRIALS OF THERAPY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:552–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent C. A., Dunham I., Trowsdale J., Campbell R. D. Human major histocompatibility complex contains genes for the major heat shock protein HSP70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1968–1972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluesener H. J., Wekerle H. Autoaggressive T lymphocyte lines recognizing the encephalitogenic region of myelin basic protein: in vitro selection from unprimed rat T lymphocyte populations. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3128–3133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Blanck G., Bresnahan M., Sands J., Strominger J. L. A new cluster of genes within the human major histocompatibility complex. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):214–217. doi: 10.1126/science.2911734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D., Wekerle H. Ia-restricted encephalitogenic T lymphocytes mediating EAE lyse autoantigen-presenting astrocytes. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):70–72. doi: 10.1038/320070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnelle C., DeMars R., Long E. O. DO beta: a new beta chain gene in HLA-D with a distinct regulation of expression. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2839–2847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tournier-Lasserve E., Hashim G. A., Bach M. A. Human T-cell response to myelin basic protein in multiple sclerosis patients and healthy subjects. J Neurosci Res. 1988;19(1):149–156. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490190120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Horvath S. J., Hood L. Autoimmune T cells: immune recognition of normal and variant peptide epitopes and peptide-based therapy. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90288-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Kumar V., Kono D. H., Gomez C., Horvath S. J., Clayton J., Ando D. G., Sercarz E. E., Hood L. Restricted use of T cell receptor V genes in murine autoimmune encephalomyelitis raises possibilities for antibody therapy. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):577–592. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbark A. A., Hashim G., Offner H. Immunization with a synthetic T-cell receptor V-region peptide protects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):541–544. doi: 10.1038/341541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe R., Wege H., ter Meulen V. Adoptive transfer of EAE-like lesions from rats with coronavirus-induced demyelinating encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):150–153. doi: 10.1038/305150a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W. E., Vandermeeren M. M., Raus J. C., Buurman W. A. Human myelin basic protein-specific cytolytic T lymphocyte clones are functionally restricted by HLA class II gene products. Cell Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;120(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N., Seyer J. M. The sequential limited degradation of bovine myelin basic protein by bovine brain cathepsin D. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6956–6963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D., de Vries R. R., Madrigal J. A., Lock C. B., Morgenstern J. P., Trowsdale J., Altmann D. M. Analysis of HLA-DR glycoproteins by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Definition of DR2 beta gene products and antigen presentation to T cell clones from leprosy patients. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1442–1458. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L., Acha-Orbea H. T cell recognition as the target for immune intervention in autoimmune disease. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90786-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., Smilek D. E., Mitchell D. J., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. Antigen recognition in autoimmune encephalomyelitis and the potential for peptide-mediated immunotherapy. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







