Abstract
The global burden of fungal diseases has been increasing, as a result of the expanding number of susceptible individuals including people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hematopoietic stem cell or organ transplant recipients, patients with malignancies or immunological conditions receiving immunosuppressive treatment, premature neonates, and the elderly. Opportunistic fungal pathogens such as Aspergillus, Candida, Cryptococcus, Rhizopus, and Pneumocystis jiroveci are distributed worldwide and constitute the majority of invasive fungal infections (IFIs). Dimorphic fungi such as Histoplasma capsulatum, Coccidioides spp., Paracoccidioides spp., Blastomyces dermatiditis, Sporothrix schenckii, Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei, and Emmonsia spp. are geographically restricted to their respective habitats and cause endemic mycoses. Disseminated histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, and T. marneffei infection are recognized as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-defining conditions, while the rest also cause high rate of morbidities and mortalities in patients with HIV infection and other immunocompromised conditions. In the past decade, a growing number of monogenic immunodeficiency disorders causing increased susceptibility to fungal infections have been discovered. In particular, defects of the IL-12/IFN-γ pathway and T-helper 17-mediated response are associated with increased susceptibility to endemic mycoses. In this review, we put together the various forms of endemic mycoses on the map and take a journey around the world to examine how cellular and molecular defects of the immune system predispose to invasive endemic fungal infections, including primary immunodeficiencies, individuals with autoantibodies against interferon-γ, and those receiving biologic response modifiers. Though rare, these conditions provide importance insights to host defense mechanisms against endemic fungi, which can only be appreciated in unique climatic and geographical regions.
Keywords: endemic mycoses, primary immunodeficiencies, human immunodeficiency virus, histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, blastomycosis, Taloromyces marneffei
Introduction
Endemic mycoses are infections caused by a diverse group of fungi that occupy specific ecologic niche in the environment (1). The major pathogenic fungi in this group, including Blastomyces dermatiditis, Coccidioides immitis and C. posadasii, Paracoccidioides brasiliensis and P. lutzii, Histoplasma capsulatum, Sporothrix schenckii, Talaromyces marneffei (formerly known as Penicillium marneffei) and Emmonsia spp., belong to the phylum Ascomycota and are evolutionary related (2) (Table 1). They share the common characteristic of thermal dimorphism—they grow as saprophytic molds in the environment at temperatures ranging from 25 to 30°C, and undergo morphological switch to the yeast form, or spherules in Coccidioides, at body temperatures of mammalian hosts. The yeast form serves to accommodate intracellular growth within host phagocytes (3). Majority of these organisms are primary pathogens that are able to cause disease in healthy human individuals. However, they may cause severe, disseminated infections in immunocompromised hosts, such as patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, organ transplant, or hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients, and those with autoimmune disorders receiving immunosuppressants (4–7). In particular, T. marneffei and Emmonsia spp. more typically cause disease in HIV-infected individuals (5–8). The HIV pandemic and the increasing use of immunosuppressive medications, such as calcineurin and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, have resulted in a rising trend of histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycosis in endemic regions (9, 10). Exposure to the specific environmental niche, either residential, occupational, or travel precedes the development of disease.
Table 1.
Endemic regions, natural habitats and risk factors of exposure to endemic mycoses.
| Phylum | Order | Endemic regions | Animal hosts | Disease in human | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coccidioides immitis, C. posadasii | Ascomycota | Onygenales | Southwestern USA, northern Mexico, Central and South America | Non-human primates, domesticated or wide mammals, dogs, cats, horses, llamas, snakes | Coccidioidomycosis |
| Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, P. lutzii | Ascomycota | Onygenales | South America | Domesticated and wild animals (monkeys and armadillos), dogs | Paracoccidioidomycosis |
| Histoplasma capsulatum | Ascomycota | Onygenales | Worldwide; hyperendemic in Mississippi and Ohio river valleys in USA | Cattle, sheep, horses | Histoplasmosis |
| Blastomyces dermatitidis | Ascomycota | Onygenales | Worldwide (endemic in North America, autochthonous in Africa, South America, and Asia) | Dogs, cats, horses, marine mammals | Blastomycosis |
| Emmonsia spp. | Ascomycota | Onygenales | South Africa | Wild rodents | Emmonsiosis |
| Sporothrix schenckii, S. brasiliensis | Ascomycota | Ophiostomales | Worldwide | Cats, occasionally dogs, horses, cows, goats, mules, pigs, rats, armadillos, camels, dolphins, birds | Sporotrichosis |
| Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei | Ascomycota | Eurotiales | Southwest and southern China; Southeast Asia | Bamboo rats, domestic animals such as dogs and cats | Penicilliosis |
Geographical Distribution of Endemic Mycoses
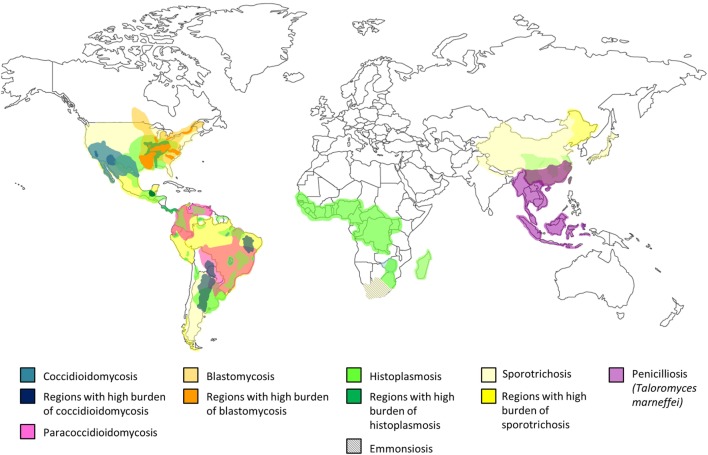
Endemic mycoses occur predominantly in specific climate zones. Coccidioidomycosis is present in semidesert areas, histoplasmosis and paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) are prevalent in tropical regions while T. marneffei is endemic in subtropical regions, and blastomycosis belongs to temperate climates (6–8). Coccidioioidomycosis (11–13) and histoplasmosis (14–18) are widely distributed in the American continent and some tropical regions, while PCM is limited to Central and South America (19–21). T. marneffei is unique to Southeast Asia (22–24), and blastomycosis is found in North America, and Central and East Africa (25–27). S. schenckii is distributed around the world, mainly reported in those tropical and temperate zones with high humidity and mild temperatures (22–27°C) (28). Recently, an emerging thermally dimorphic fungus within the genus Emmonsia that is most closely related to E. pasteuriana has been recognized to be uniquely associated with in HIV infection in South Africa (29–31). The geographical distribution of endemic mycoses is shown in Figure 1 (1, 12–14, 18–20, 27, 28, 32–39).
Figure 1.
Global distribution of endemic mycosis (1, 13, 14, 18–20, 27, 28, 32–39).
The biological niche is specific for each endemic fungus and knowledge of their natural habitat provides understanding about the risk factors for exposure to these pathogens (Table 2). C. immitis and C. posadasii are saprophytic fungi, which exist in their mycelial form in dry, alkaline soil in deserts with very low precipitation and extreme temperature variations (11–13). Coccidioidomycosis is most prevalent in Arizona and California in the United States (US) (40, 41). In contrast, H. capsulatum thrive in the tropical zones with high relative humidity, and its growth is favored by soil contaminated by bird and chicken excreta or bat guano, which creates an environment with high nitrogen content (14, 15). P. brasiliensis is also found in the tropical and very humid regions, especially in acidic soil where coffee and sugar canes are cultivated (20). PCM is prevalent in South America (Brazil, Columbia, Venezuela, Paraguay) and some regions of Central America and Mexico (19–21). B. dermatitidis exists in wet soils, and the most significant endemic epicenter is in Eastern US between the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys (25–27). T. marneffei is highly endemic in Thailand, Vietnam, Southern China, and other subtropical areas in Southeast Asia (22–24). Bamboo rats (Rhizomys spp. and Cannomys spp.) and soil from their burrows are important enzootic and environmental reservoirs of T. marneffei, respectively (39). S. schenckii is found in the soil containing decaying vegetation such as dead wood, mosses, hay, and cornstalks. Sporotrichosis is also widely prevalent in warm-blooded animals including cats, dogs, armadillos, birds, and parrots, which constitute a source of zoonotic transmission (28). To date, disseminated emmonsiosis associated with HIV infection caused by the new Emmonsia spp. has only been described in South Africa (29–31).
Table 2.
Endemic regions, natural habitats, and risk factors of exposure to endemic mycoses.
| Main endemic regions | Other areas | Natural habitat | Human activities/conditions associated with increased risk of exposure | Occupations associated with increased risk of exposure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coccidioidomycosis | Arizona and California in the US | Other parts of Southwestern US: New Mexico, Nevada, Utah and Texas Central America: Mexico, Guatemala, HondurasSouth America: Venezuela, Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay |
Alkaline soils in dry desert climates | Soil excavations Dust storms, earthquakes |
Construction site workers, farmers, military personnel, excavators, archeologists, inmates, and officers in correctional facilities |
| Histoplasmosis |
Histoplasma capsulatum var. capsulatum: Ohio and Mississippi River Valleys in the Upper Midwest and Southeastern US H. capsulatum var. duboisii (African histoplasmosis): between 20° North and 20° South of the equator, and Madagascar |
Southern Mexico Central and South America, e.g., Brazil, Uruguay, Paraguay, Argentina, Venezuela Mainland China: provinces along the Yangtze River (Yunnan, Sichuan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangsu, Zhejiang) Southeast Asia, e.g., Thailand India, especially West Bengal and Uttar Pradesh along the Gangetic plains Europe: Italy (Po River Valley), Spain, Germany |
Soil contaminated by bird and chicken excreta, or bat guano; bat caves | Walking on contaminated grounds, setting up tents Excavation, clearing foliage in a bird-roosting site |
Miners, cave explorers, guano workers, farmers, beekeepers, archeologists |
| Paracoccidioidomycosis |
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis: Brazil, Columbia, Venezuela, Paraguay P. lutzii: Center-West of Brazil |
Central America and Mexico | Acid soils in area of coffee and sugar cane plantations | Soil exposure | Farmers, outdoor workers Women are less likely to develop clinical disease as estrogens inhibit conidial transformation to yeast cells |
| Blastomycosis | US: Mississippi and Ohio River valleys, Midwestern states Canada: provinces that border the Great Lakes and the Saint Lawrence Riverway, including Manitoba and northwestern Ontario |
Middle and East Africa India |
Warm, moist soil with high organic content, e.g., animal droppings | Occupational, residential, or recreational exposures to wildlife, soil, or bodies of freshwater | Occupational, residential, or recreational exposures that occur in close proximity to bodies of freshwater |
| Talaromyces marneffei infection | Thailand, Vietnam, Southern China | Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Cambodia, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Northeastern India | Soil, particularly burrows of bamboo rats | Soil exposure during rainy season | Agricultural workers |
| Sporotrichosis | Peru, Brazil, Mexico (Jalisco and Puebla mountain ranges) | Worldwide distribution in temperate and tropical regions—US, Asia (China, India, Japan), Australia | Soil and decaying vegetation, e.g., dead wood, sphagnum moss, cornstalks, hay | Cutaneous trauma with wound contamination by plants or soil; contact with reeds after flooding, bites from mice, armadillos, squirrels, cats, and dogs | Farming, gardening, flower vending, handling hay, animal husbandry, armadillo hunting (in Uruguay), mining |
Pathogenesis and Clinical Manifestations
The acquisition of endemic fungi relates to human activities and climatic conditions that increase the risk of exposure to these organisms in susceptible individuals. Coccidioidomycosis, PCM, histoplasmosis, blastomycosis, and T. marneffei infection are acquired by the respiratory route. Occupational or recreational activities causing disturbance of the soil environment lead to aerosolization of the conidia, which could then be inhaled by exposed individuals to cause infection (1, 6–8, 14, 20, 22, 23, 27). In contrast, inhalation is not the major route by which S. schenkii is acquired. Instead, it typically occurs after traumatic inoculation or through microscopic breaks in the skin caused by pricks with plants, although the mode of transmission was not obvious in 60% of patients with sporotrichosis. Infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissues develops at the site of penetrating trauma and may spread to the muscles, fascia, cartilage, and bones (42, 43). The clinical features of these endemic mycoses are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3.
Clinical manifestations of endemic mycoses and risk factors for disseminated disease.
| Asymptomatic infections | Sites of initial infection | Distant spread/disseminated disease | Conditions predisposing to disseminated disease | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coccidioidomycosis | Asymptomatic infections in majority of immunocompetent individuals | Pneumonia, often as mild respiratory illness Rarely primary cutaneous lesions at the site of inoculation due to injury |
Fungemia, lymphadenopathy, skin lesions (in the vicinity of infected lymph nodes manifesting as abscesses, ulcers, gummata, retracting scars), osteoarticular involvement, meningitis | HIV infection PID Patients on anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibodies Chemotherapy, organ transplant and HSCT, immunosuppressants Diabetes mellitus, cardiopulmonary disease, pregnancy Higher risk of dissemination in African-American and Filipino |
| Histoplasmosis | Mostly acquired during childhood as asymptomatic infection | Most are self-limiting Acute pulmonary histoplasmosis: fever, cough, dyspnea, enlarged mediastinal, or hilar lymph nodes Chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis: cavitating lung lesions Rarely primary cutaneous lesions by injury—chancre, lymphangitis, nodular gummata |
Fungemia, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, bone marrow involvement, pancytopenia, reactive hemophagocytosis, oropharyngeal ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding, endocarditis, skin lesions (molluscum-like papules, nodular/gummatous lesions), meningeal involvement, adrenal (Addison’s disease) | HIV infection PID Patients on anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibodies Chemotherapy, organ transplant, and HSCT, immunosuppressants |
| Paracoccidioidomycosis | Asymptomatic infections in majority of immunocompetent individuals | Juvenile form: generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, lesions in the skin, oral and intestinal mucosa, bone involvement Chronic (“adult”) form: pneumonia, mucosal lesions in the oropharyngeal or nasal region, palatal ulceration extending to the gums and tongue |
Involvement of the digestive tract, pancreas and adrenal glands; hepatomegaly, splenomegaly | HIV infection PID |
| Blastomycosis | Asymptomatic infections in majority of immunocompetent individuals | Pneumonia Rarely primary skin involvement at the site of inoculation due to injury, manifesting as lymphangitis, ulcers, nodules, verruca |
Skin involvement (nodules, gummata, abscesses, ulcers) | Uncommon association with acquired immunodeficiencies; no case of PID identified in individuals with blastomycosis |
| Talaromyces marneffei infection | Asymptomatic infections in majority of immunocompetent individuals | Localized skin disease due to direct inoculation Lymphadenitis Pneumonia |
Fungemia, pneumonia, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, bone marrow involvement, osteoarticular involvement, cutaneous lesions, neurological manifestations | HIV infection PID Individuals with autoantibodies against IFN-gamma Splenectomy, diabetes mellitus, autoimmune disease Chemotherapy, organ transplant and HSCT, immunosuppressants Novel anti-cancer target therapies, e.g., anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies, kinase inhibitors |
| Sporotrichosis | Most cases are acquired through traumatic implantations, often with spontaneous resolution | Skin infections may progress into chronic cutaneous, subcutaneous, or deeper infections involving the lymphatics, fascia, muscles, cartilage and bones | Occasional cases of pulmonary or disseminated disease: multiple skin lesions at non-contiguous sites, mucosal (nasal, oral, conjunctival), osteoarticular, pulmonary and meningeal involvement | HIV infection PID Chemotherapy, organ transplant and HSCT, immunosuppressants Diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, cirrhosis, malnutrition |
HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplant; IFN, interferon; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; PID, primary immunodeficiencies.
After entry to the body, inhaled conidia converts to the yeast form, which are taken up by tissue-resident macrophages. In most individuals, the pathogenic yeasts can be eliminated by the macrophages and the infection is usually asymptomatic or mild, and self-limiting in most cases. In patients whose immunity is compromised, the yeasts continue to proliferate in the macrophages, which if uncontained, systemic dissemination may occur via the reticuloendothelial system (12, 23, 44–46). HIV infection is the most important risk factor for disseminated endemic mycoses (5). Other risk factors include malignancy and immunosuppression, as listed in Table 3 (4–7, 9, 10).
Endemic Mycoses: Insights from the HIV Epidemic
Human immunodeficiency virus infection is the most common cause for disseminated or extrapulmonary forms of histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, and T. marneffei infection, particularly in patients with profound T-cell lymphopenia (CD4+ lymphocytes <200/μL) (12, 47–50). They are considered as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-defining conditions in the World Health Organization (WHO) clinical staging of HIV/AIDS for adults and adolescents (51). The association between PCM and AIDS is relatively rare in contrast to the higher incidence of other systemic mycosis. HIV coinfection has been detected in about 5% of patients with PCM (52, 53). Although PCM and sporotrichosis are not included as AIDS-defining conditions, they are increasingly recognized as an emerging neglected opportunistic infections in HIV patients in Latin America (7, 53, 54). Systemic sporotrichosis with organ involvement or widespread cutaneous lesions may occur in these patients, causing a mortality rate of up to 30% (54, 55). Blastomycosis infrequently develops in HIV patients, but disease tends to be more severe with increased risk of central nervous system (CNS) involvement with high mortality (46, 56). The new species of Emmonsia spp. discovered in South Africa was found to cause disseminated infection almost exclusively in patients with AIDS (29–31).
The first case series of histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients was described in 1982 in the US (57). Extrapulmonary or disseminated histoplasmosis became an AIDS-defining disease in 1987 (58). The increase in morbidity and mortality from histoplasmosis has been largely contributed by the HIV pandemic. In the US, the availability of highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART) and lipid formulations of amphotericin B, the increased awareness of the disease, and the development of rapid, non-invasive diagnostic methods led to decrease in the incidence and mortality associated with histoplasmosis in patients with AIDS (16). On the other hand, extrapulmonary or disseminated histoplasmosis is becoming an important health issue in the increasing number of patients receiving chemotherapy, solid organ or HSCT, immunosuppressive treatment especially TNF-α blockade (59), as well as a rare group of patients with primary immunodeficiencies (PIDs). In contrast, in endemic areas of Latin America histoplasmosis occurs in up to 25% of HIV-infected patients and represents the first manifestation of AIDS in up to 50–75% of patients (60, 61). Due to the lack of diagnostic facilities and algorithm, histoplasmosis is undiagnosed in many HIV-infected patients and is considered as an “invisible burden” of AIDS in less resourced countries (62, 63). These phenomena illustrate how demographics of histoplasmosis could be shaped by HIV burden and socioeconomic forces in different endemic regions.
Shortly after the description of increased susceptibility to histoplasmosis in AIDS, Coccidioides infection emerged as an important form of mycosis in patients with HIV infection (64–66). A prospective study at an Arizona HIV clinic in 1988 showed a cumulative incidence of active coccidioidomycosis of 25% during 41 months of follow-up, corresponding to an average annual incidence of 7.3% (67). In contrast, in a retrospective review at the same clinic during 2003–2008, only 11.3% of HIV-infected patients (n = 257) had coccidioidomycosis, and the annual incidence was only 0.9% when compared to the previous study (47). Both studies showed that CD4 count was the only predictor for developing active coccidioidomycosis; factors such as a history of coccidioidomycosis and duration of residence in an endemic area or age, sex, race, ethnicity, plasma HIV RNA level, or receipt of HAART were not associated with increased risk for coccidioidomycosis (11, 47, 67).
While histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycosis are well recognized as human pathogens long before the HIV epidemic, the importance of T. marneffei as a human disease was not recognized until the outbreak of HIV in Asia (22, 68, 69). In 1973, the first naturally occurring human case of T. marneffei infection was reported in an American minister with Hodgkin’s disease who had been residing in Southeast Asia (70). No more than 50 cases were reported in the literature during the early 1980s (68–76). From 1988, T. marneffei infection was increasingly observed in patients with advanced HIV infection, initially in foreign visitors who have been to endemic regions, and later in local residents who were native to endemic parts of Thailand and Vietnam (22, 23, 77–79). In Northern Thailand, T. marneffei infection is the third most common opportunistic infection, accounting for 15–20% of all AIDS-related illness, after tuberculosis (TB) and cryptococcosis. T. marneffei infection is estimated to occur in 2.3% of new AIDS cases, compared with 0.39% for histoplasmosis (80). The trend of T. marneffei infection closely paralleled that of HIV, and in areas where reduction of HIV transmission and availability of HAART have improved, a decrease in the prevalence of T. marneffei infection has been observed (23, 81).
Together with Emmonsia spp., which causes disseminated infection almost exclusively in advanced HIV infection in South Africa (29–31), it is apparent that the epidemiology of coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and P. marneffei evolves with HIV epidemic. The close relationship between disease manifestation and severity with CD4+ cell count confirms the central importance of cell-mediated immunity against endemic fungi.
PIDs in Endemic Mycoses: Needles in a Haystack?
Primary immunodeficiencies are rare inborn errors of immunity. Defects of T-cell development and differentiation, phagocytic functions, and pathways involved in the innate recognition of pathogens and downstream signaling are associated with increased risk of fungal infections, the most common being candidiasis and aspergillosis. Endemic mycoses are rarely described in patients with PID, and little is known about the spectrum of PID associated with increased susceptibility to endemic fungi. On the other hand, as individuals who are apparently healthy can also develop disease caused by endemic fungi, recognition of those who may have an underlying PID could be a challenge.
Talaromyces marneffei infection is mostly seen in advanced HIV infection with CD4+ cell count <100/μL, and in fact, up to 80% or more of the cases have CD4+ count <50/μL (22, 81, 82). Only small proportion of disseminated T. marneffei infection occurs in patients with secondary immunodeficiencies (22, 23, 83, 84). It is otherwise rare in healthy persons, especially in children. The close epidemiological relationship between HIV and T. marneffei, and the fact that T. marneffei is an AIDS-defining illness (51) suggests that individuals who are HIV negative and without secondary immunodeficiencies may have underlying immune defects that are unrecognized. A systematic review by Lee et al (85) on more than 500 articles published in English and Chinese from 1970 to 2011 on penicilliosis revealed 32 patients aged 3 months to 16 years with T. marneffei infection but without known HIV infection. Twenty-four patients (75%) had disseminated disease, and 55% died of T. marneffei infection. Eight patients had PID or blood disorders, while four others had abnormal immune functions. Immune evaluations of the remaining patients were unstated. This observation highlights the knowledge gap in the immunological susceptibility to T. marneffei.
Two systematic reviews on PID in histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycoses were recently published. Lovell et al. (86) summarized all published cases of histoplasmosis in patients with PID up to August 2015 and revealed 47 patients with underlying PID, defined either molecularly or clinically. Together with the four patients described in their report, more than 50 PID patients have been documented to have Histoplasma infection. Disseminated histoplasmosis occurred in 68% of cases, and two deaths occurred because of progressive disease. Another systematic literature search on disseminated coccidioidomycosis yielded 370 case reports, and 8 cases of PID were identified (87). The frequency of PID underlying endemic mycoses is unknown. Given the rarity of PID, the proportion of PID accounting for disseminated endemic mycoses is likely to be small. However, the cellular and molecular defects of these PID can provide important mechanistic insights into host defense mechanisms against endemic fungi. More importantly, disseminated or extrapulmonary forms of endemic mycoses can be utilized as unique indicators for PIDs, which is of particular relevance to clinicians working in respective endemic areas (88).
PIDs Underlying Fungal Infections
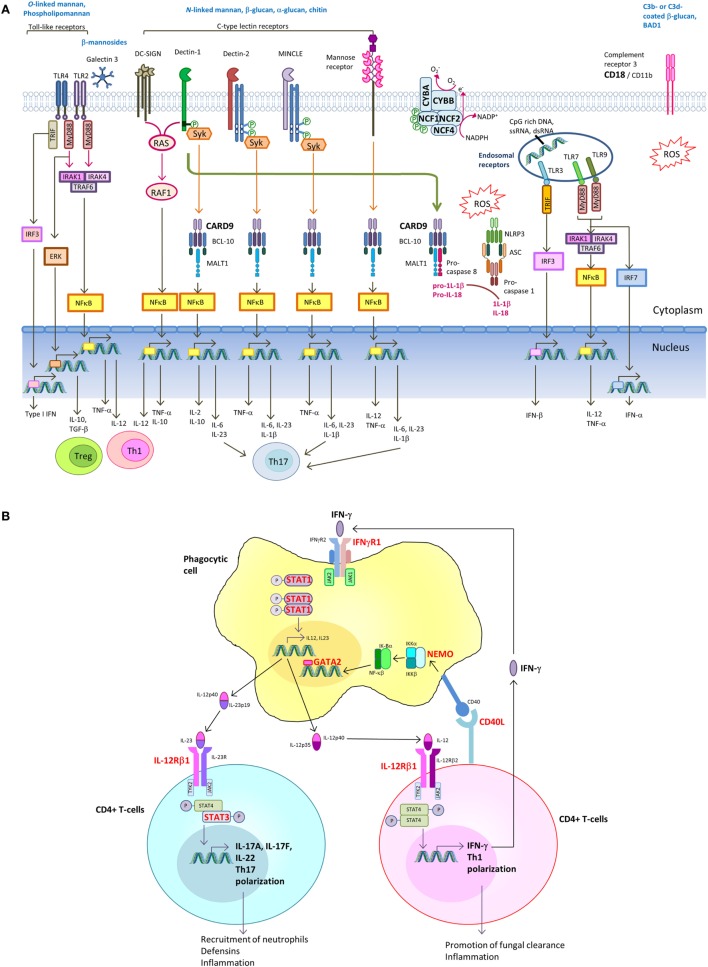
Host immune response toward fungal pathogens is initiated by the recognition of invading fungi via pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) expressed on neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells (DCs). Receptor-mediated signaling induces downstream events such as cytokine and chemokine release, phagocytosis, and respiratory burst ultimately leading to fungal killing (89–93). In addition, the cytokine responses shape the induction of Th-1 and Th-17 adaptive immune response. IL-12 drives IFN-γ production by T-helper 1 (Th1) cells, which is crucial for phagocyte activation. On the other hand, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-23 promotes Th17 differentiation (89–91). The various PRRs that recognize fungal pathogen-associated molecular patterns and the downstream signaling pathways leading to induction of Th1 and Th17 response are shown in Figure 2A.
Figure 2.
Signaling pathways in innate recognition of fungal pathogens and differentiation of CD4+ T helper cells. (A) Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) expressed by fungi are recognized by host pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), including toll-like receptors (TLRs), C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) [e.g., dendritic cell (DC)-specific ICAM3-grabbing non-integrin (DC-SIGN), Dectin-1, Dectin-2, MINCLE, and mannose receptor] and complement receptor 3 (CR3). TLRs and CLRs activate multiple intracellular signaling pathways upon binding to specific fungal PAMPs, including β-glucans, chitin, O-linked mannan and N-linked mannan, and nucleic acids. These signals activate canonical or non-canonical nuclear factor-κB and the NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. The integration of simultaneously activated PRRs occurs at the level of intracellular adaptors and transcription factors shared between overlapping pathways. The resulting cytokine responses shape the activation of adaptive immune response. Induction of IL-12 drives IFN-γ production by T-helper 1 (Th1) cells, which is crucial for phagocyte activation. Induction of IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-23 promotes Th17 differentiation. Regulatory T-cells (Treg) act as host-driven homeostatic response to keep inflammation under control. (B) Th1 and Th17 differentiation. Polarization of naive T cells into Th1 leads to IFNγ production, and its signaling is mediated through the Janus kinase (JAK)–signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) pathway, leading to transcription of IFNγ-inducible genes. IL-6 and IL-21 upregulate the expression of the retinoic acid-related orphan receptor RORγt and RORα, leading to expression of the inducible component of the IL-23 receptor (IL-23R) and further Th17 development. IL-17A and IL-17F produced by Th17 cells augments neutrophil production in the bone marrow and their recruitment to the site of infection. IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 promote production of antimicrobial peptides in epithelial cells. Molecules in which genetic defects have been identified to be associated with increased susceptibility to endemic mycoses are marked in bold red.
Defects of the dectin-1/CARD9-MALT1-BCL10 signaling pathway are associated with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMC) (94). Patients with CARD9 deficiency have defects in Th17 differentiation and impaired neutrophil killing (95), and they are susceptible to CMC (96), deep dermatophytoses (97), and invasive fungal infection, particularly Candida meningitis. Other monogenic disorders causing CMC include autosomal recessive (AR) IL-17 receptor A (IL17RA), AR IL-17RC, AR ACT1, and autosomal-dominant (AD) IL-17F deficiencies (98). These patients display deficiency of IL-17F and IL-17A/F (IL-17F mutations) or dysfunctional responses to IL-17A, IL-17A/F, and IL-17F (IL17RA, IL-17RC, and ACT1 mutations). In patients with autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy, high plasma titers of neutralizing autoantibodies against IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 can be detected, as a result of the lack of AIRE expression in the thymus causing impaired T-cell tolerance (99). However, endemic mycoses have not been reported in patients with these genetic defects.
Opportunistic fungal infections are common in patients with severe combined immunodeficiencies (SCIDs) and phagocytic disorders. Infants with classical SCID often have recurrent or persistent mucosal and/or cutaneous candidiasis involving the orodigestive tract, genital area, nails, and skin. Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP) and invasive fungal infections (IFIs) including systemic candidiasis and aspergillosis are often life-threatening (100, 101). Interestingly, endemic mycoses have not been described in SCID babies, at least in the English literature. It may be due to the fact that it is uncommon for infants to be exposed to the natural habitats containing those endemic fungi, but further epidemiological data would be required to address this. Numerical and functional defects of phagocytes such as severe congenital neutropenia, chronic granulomatous disease (CGD), and leukocyte adhesion deficiency (LAD) are major groups of PIDs predisposing to systemic candidiasis and invasive aspergillosis (102–104). Filamentous fungi other than Aspergillus causing pulmonary infections in CGD include Geosmithia argillacea and Trichosporon inkin. Osteomyelitis can also be caused by rare non-Aspergillus filamentous fungi, including Cladophialophora arxii, Inonotus tropicalis, Scedospoium apiospermum, Penicillium piceum, and P. variotii. Cerebral abscesses caused by dematiaceous molds such as Exophiala spp., Phaeoacremonium spp., and Alternaria spp. have been reported (105–107). Interestingly, endemic mycoses have not been reported in CGD and LAD.
In the following sections, we highlight the spectrum of PIDs, which are associated with increased susceptibility to disseminated endemic mycoses. The genetic defects are summarized in Figure 2B.
Combined Immunodeficiencies: CD40 Ligand, Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) Essential Modulator (NEMO), and DOCK8 Deficiencies
Mucosal candidiasis is common in combined immunodeficiencies e.g. CD40 ligand (CD40L) deficiency, NEMO (IKBG) deficiency, IKBA gain-of-function (GOF) mutation and DOCK8 deficiency, in addition to a broad range of viral, bacterial, and IFI (102, 103). CD40L is expressed on activated T-cells and signals through NEMO/NF-κB to induce IL-12 production. CD40L deficiency, also known as hyper-IgM syndrome, is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. Patients are susceptible to opportunistic infections including PCP, cryptosporidiosis, and mycobacterial infections due to impaired interaction between T-cells and antigen-presenting cells (APCs). In addition, the failure of B-cell immunoglobulin (Ig) isotype switching results in markedly low serum IgG and IgA, while IgM is elevated (108, 109). Disseminated and cutaneous forms of histoplasmosis have been reported in eight patients in patients with X-linked hyper-IgM disorder (Table 4). Five cases had disseminated histoplasmosis, while two had lymphadenitis and one had cutaneous involvement only (86, 110–115). All of them responded well to antifungal therapy, and only two patients had recurrent histoplasmosis (86, 111). One case of PCM was reported in Brazil (116). It was shown that mature DCs from patients with CD40L deficiency exhibited markedly reduced IL-12 and increased IL-10 production in response to P. brasiliensis and C. albicans compared with normal controls, and T cells had significantly reduced IFN-γ production when cocultured with their DCs, whereas IL-4 and IL-5 production was increased. In contrast, T-cell proliferation and generation of TGF-β and IL-17 were comparable with normal controls. These findings suggested that the absence of CD40L during monocyte/DC differentiation leads to functional DC abnormalities, which may contribute to the susceptibility to fungal infections in patients with CD40L deficiency (117). Four cases of T. marneffei infection were reported in CD40L deficiency (118–120). One patient who had disseminated T. marneffei infection had rapid deterioration due to late diagnosis and died, and CD40L deficiency was diagnosed after he passed away (120).
Table 4.
Endemic mycoses in CD40 ligand deficiency.
| Genetic defect | Endemic fungal pathogen | Gender/age, residence | Clinical manifestations | Other infections and comorbidities | Treatment and outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tu et al. (110) | Not stated | Histoplasma spp. | M/3 years, US | Disseminated histoplasmosis with esophageal ulcers and bone marrow involvement | Cyclical neutropenia and anemia | Not stated |
| Hostoffer et al. (111) | Not stated | Histoplasma capsulatum | M/19 years, US | Disseminated histoplasmosis with pulmonary infiltrates, pancytopenia and splenomegaly | Tongue and per-rectal ulcers | Treated with amphotericin B, recurrence due to poor compliance to itraconazole prophylaxis |
| Yilmaz et al. (112) | Not stated | Histoplasma spp. | M/5 years, Turkey | Facial lesions, cervical lymphadenopathy, bilateral pulmonary infiltration and bronchiectasis | Recurrent pulmonary infections | Treated with ketoconazole |
| Danielian et al. (113) | p.R11X | H. capsulatum | M/6 months, Argentina | Histoplasma lymphadenitis | PCP and parvovirus B19 infection, recurrent pneumonia, adenitis, anemia | Not stated |
| Dahl and Eggebeen (114) | Not stated | Histoplasma spp. | M/14 years, US | Disseminated histoplasmosis complicated by fungemia and macrophage activation syndrome | Recurrent sinopulmonary infections and neutropenia | Liposomal amphotericin B for 14 days followed by oral itraconazole; macrophage activation syndrome treated with steroid and anakinra with prompt improvement |
| Lovell et al. (86) | c.289-15T > A | Histoplasma spp. | M/6 years (patient 2) | Disseminated histoplasmosis with fever, hepatomegaly; Histoplasma identified from bone marrow biopsy | Recurrent otitis media, streptococcal pharyngitis | Amphotericin B, itraconazole; recurrence 2 years later with abdominal histoplasmosis |
| c.289-15T > A | Histoplasma spp. | M/4 years (patient 3) | Lymphadenitis | Recurrent otitis media, streptococcal pharyngitis, bronchitis | Amphotericin B, itraconazole | |
| Pedroza et al. (115) | c.233_234 delinsAA, p.S78* | H. capsulatum | M/2.5 years, Ecuador | Cutaneous histoplasmosis | Cryptosporidium parvum enteritis, oral candidiasis, pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans | Amphotericin B for 4 weeks followed by itraconazole prophylaxis |
| Cabral-Marques et al. (116) | c.345_402del | Paracoccidioides brasiliensis | M/11 years, Sao Paulo, Brazil | Prolonged fever and cough, mediastinal lymphadenopathy, bone marrow hypoplasia and tuberculoid granuloma | PCP, recurrent otitis media, and sinopulmonary infections | Treated with 8 months of itraconazole and recovered |
| Kamchaisatian et al. (118) | Complex mutation in exon 5 | Talaromyces marneffei | M/14 months, Northeastern Thailand | Prolonged fever, cough, neck pain and bloody sputum; neck imaging showed prevertebral soft tissue swelling. Throat swab, sputum, blood and bone marrow cultures yielded T. marneffei | Recurrent pneumonia, oral ulcers, cyclical neutropenia | Treated with amphotericin B for 21 days, followed by itraconazole for 10–12 weeks |
| Not stated | T. marneffei | M/1 year, Northern Thailand | Fever, cough, dyspnea, lymphadenopathy and pleural effusion; lymph node biposy yielded T. marneffei | PCP | Treated with amphotericin B for 21 days, followed by itraconazole for 10–12 weeks | |
| Sripa et al. (119) | Not stated | T. marneffei | M/3 years, Thailand | Pneumonia, positive T. marneffei culture from tracheal aspirate | PCP, cyclical neutropenia | Treated with itraconazole with good response |
| Liu et al. (120) | g.IVS1-3T > G | T. marneffei | M/2 years, China | Disseminated T. marneffei infection with airway granuloma, hepatosplenomegaly and fungemia | BCG-itis, pneumonia | Died of multi-organ failure |
Location of residence is indicated wherever information is available.
PCP, Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia.
One patient with NEMO deficiency was reported to have persistent nodal histoplamosis at the age of 52 years. Symptoms including worsening dyspnea and intermittent night sweats that lasted for 1 year, and imaging studies revealed perihilar mass and mediastinal lymphadenopathy. Positive culture of H. capsulatum was obtained from paratracheal lymph node biopsy. He responded well to posaconazole (86). A patient with DOCK8 deficiency had miliary pneumonia caused by H. capsulatum. She also had numerous infectious caused by viruses (molluscum contagiosum, recurrent herpes zoster, cutaneous human papilloma virus infection), and dermatitis with Staphylococcus aureus superinfection (86, 121).
GATA2 Deficiency
A syndrome of monocytopenia with susceptibility to non-tuberculous mycobacterial (NTM) infections, often termed “MonoMAC,” is caused by haploinsufficiency of the hematopoietic transcription factor GATA2 (122). Majority of the patients have monocytopenia, natural killer (NK), and B lymphocytopenia, while CD4 lymphocytopenia and neutropenia are also common but less marked. Affected individuals are susceptible to a broad range of viral (human herpes virus and human papillomavirus), disseminated NTM, bacterial, and fungal infections (123, 124). In a cohort of 57 patients with GATA2 mutations evaluated at the National Institutes of Health in the US (124), severe fungal infections were observed in 16%, including invasive aspergillosis (9%), disseminated histoplasmosis (5%), and recalcitrant mucosal candidiasis (5%). Another patient with GATA2 deficiency and disseminated histoplasmosis was reported by Lovell et al. (86). All the patients diagnosed to have GATA deficiency with disseminated histoplamosis were adults (86, 124). Apart from infections, other clinical features of GATA2 deficiency include congenital lymphedema, pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, and predisposition to myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia, but considerable clinical heterogeneity exists.
Inborn Errors of IFN-γ-Dependent Immunity
Host defense against intracellular bacterial and fungal pathogens depends on effective cell-mediated immunity, which is coordinated by APC and T-lymphocytes (89, 90, 125). Following phagocytosis, macrophages, monocytes, and DCs secrete IL-12p70, a heterodimer of IL-12p40 (IL12B) and IL-12p35 (IL-12A) that stimulates T and NK cells through its receptor IL-12R, a heterodimer of IL-12Rβ1 and IL-12Rβ2. IL-12Rβ1 is bound to tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2), and IL-12Rβ2 is bound to Janus kinase-2 (JAK2). IL-12 receptor signaling induces phosphorylation, dimerization, and nuclear translocation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-4 (STAT4) to induce IFN-γ production in T-cells and NK cells, and drives Th1 polarization of CD4+ T-cells. Binding of IFN-γ to its heterodimeric receptor consisting of IFN-γR1 and IFN-γR2 leads to signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) phosphorylation by Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) and JAK2. The phospho-STAT1 (p-STAT1) homodimer translocates to the nucleus and modifies gene expression regulated by the γ-regulated sequencing, resulting in phagocyte activation including production of bactericidal ROS by NADPH oxidase, further IL-12 production, and killing of intracellular pathogens (126, 127). IL-12 production is augmented by a T-cell dependent pathway through interaction of CD40 on the surface of APC with CD40L expressed on activated T-cells (128). The signaling pathway is shown in Figure 2B.
IL-23 shares the p40 component with IL-12p70, and IL-12Rβ1 combines with IL-23 receptor (IL-23R) to form the IL-23R complex (129). IL-23R signaling leads to STAT3/STAT4 heterodimer phosphorylation by TYK2 and JAK2, supporting the proliferation of Th17 cells, which are critical mediators of immunity at the mucosal surface (130). Activated Th17 cells produce IL-17 and IL-22, which induce antimicrobial peptide production in epithelial cells, and the recruitment and activation of inflammatory cells, especially neutrophils (131). These effector functions are critical in the control of mycobacteria, fungi, and bacterial pathogens such as salmonella (131–133).
Genetic defects of the IFN-γ-dependent immunity are collectively known as the Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease (MSMD) (126, 127). These disorders encompass defects of IFN-γ production or response to IFN-γ, caused by mutations in IL12B, IL12RB1, ISG15, NEMO, IFNGR1, IFNGR2, STAT1, NEMO, IRF8, and CYBB. Altogether, they constitute 18 genetic etiologies of MSMD based on the mode of inheritance, complete or partial defect, expression of the mutant allele, and the functional aberrations. Mycobacterial infection is the sole infectious phenotype in some of these disorders (AD IRF8 deficiency, AR ISG15 deficiency), while others have increased susceptibility to a broader range of pathogens (126, 127). Endemic fungal infections have been reported in AR IL12Rβ1, AR IFN-γR1, and AD GOF STAT1 defects.
AR IL12Rβ1 Deficiency
Autosomal recessive IL12Rβ1 deficiency is the most common form of MSMD, accounting for approximately half of the cases in which a genetic cause has been identified (126, 127, 134). Patients with IL12Rβ1 deficiency are recognized by their susceptibility to mycobacterial infections (M. bovis BCG, NTM, and M. tuberculosis) and non-typhoidal salmonellosis of unusual severity or frequency, but some patients are also susceptible to Candida, Klebsiella, Nocardia, Leishmania, Histoplasma, Coccicioides, and Paracoccidioides (134). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells of these patients do not respond to IL-12 and IL-23, resulting in impaired IFN-γ production by T and NK cells. The development of IL-17-producing T-cells is also impaired, due to defect of the IL-23R complex, which is composed of IL-12Rβ1 (135–137). This accounts for the susceptibility to develop CMC observed in 23% of patients (134–137).
The seven reported cases of coccidioidomycosis, PCM, and histoplasmosis in patients with IL12Rβ1 deficiency are summarized in Table 5 (134, 138–141). The age at which disseminated mycoses developed varied from childhood to adulthood, some with past history of mycobacterial infection and salmonellosis. Two cases had recurrence disease, but could be controlled by antifungal treatment.
Table 5.
Endemic mycoses in IL12RB1 deficiency and INFGR1 deficiency.
| Genetic defect | Endemic fungal pathogen | Gender/age, residence | Clinical manifestations | Other infections and comorbidities | Treatment and outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL12RB1 deficiency | ||||||
| Moraes-Vasconcelos et al. (138) | Homozygous p.L77F | Paracoccidioides brasiliensis | M/24 years, Brazil | 20 years: fever, hepatosplenomegaly, generalized lymphadenpathy | BCG cervical adenopathy at 7 m, relapse at 2 years 6 years; disseminated non-typhoidal salmonellosis which lasted for 7 years | Treated with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for 5 years with clinical resolution |
| de Beaucoudrey et al. (137) | Homozygous p.R521X | Histoplasma spp. | F/5 years | Disseminated histoplasmosis | Tuberculosis | Not mentioned |
| Vinh et al. (139) | Homozygous p.C186Y | Coccidioides spp. | Patient 1: F/22 years, US | Diffuse lymphadenopathy (cervical, supraclavicular, hilar, mediastinal, retroperitoneal) | Non-typhoidal salmonellosis (bacteremia and lymphadenopathy) | Fluconazole for 1.5 years without recurrence |
| Patient 2 (brother of Patient 1): M/6 years, Arizona, US | 6 years: coccidioidal pneumonia 14 years: right supraclavicular lymphadenopathy and a nasal lesion 16 years: osteomyelitis of the right proximal tibia |
Nil | Received fluconazole for 2 years, developed osteomyelitis 2 months after stopping fluconazole, treated with itraconazole with improvement | |||
| Hwangpo et al. (140) | IL12-receptor defect (by functional studies) | Histoplasma spp. | M/8 years | Disseminated histoplasmosis with miliary infiltration of the lungs, mediastinal lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly | Not mentioned | Itraconazole |
| Falcão et al. (141) | Homozygous p.R283X | Histoplasma capsulatum | M/4 years, Brazil | 4 years: fever, hepatosplenomegaly, generalized lymphadenopathy, bone marrow involvement 6 years: CNS histoplasmosis complicated by hydrocephalus | Tuberculous adenitis | Antifungal treatment and itraconazole prophylaxis |
| Brother of the proband | Disseminated histoplasmosis | Tuberculous adenitis, disseminated salmonellosis | Not mentioned | |||
| IFNGR1 defect | ||||||
| Zerbe and Holland (146) | Heterozygous c.818del4 | H. capsulatum | M/3 years, Tennessee, US | 3 years: fever, pneumonia, hepatosplenomegaly, cervical and paratracheal lymphadenopathy 4.5 years: fever, pneumonia, generalized lymphadenopathy, sinusitis; lymph node biopsy yielded H. capsulaum 4.8 years: right paranasal mass and osteomyelitis of the facial bones requiring debridement |
Coexisting MAC infection: 3 years: MAC found in gastric aspirate 7 years: cervical lymphadenopathy and osteomyelitis of rib, biopsy yielded MAC |
Repeated courses of intensive antifungal and antimycobacterial therapy, subcutaneous IFN-γ injection led to clearing of all bone lesions. Remained well on prophylactic itraconazole, azithromycin, and IFN-γ |
| Vinh et al. (147) | Heterozygous c.818del4 | Coccidioides spp. | M/11 years, Arizona, US | Lobar pneumonia, mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy; later developed osteomyelitis involving the vertebral spine and pelvic bone | Mycobacterium chelonae pulmonary infection at 11 months; M. kansasii abscess involving the cervical spine and retropharyngeal space | Refractory coccidioidomycosis with progressive skeletal lesions despite prolonged use of antifungal therapy (amphotericin B and azoles). Surgical debridement with implantation of amphotericin B-impregnated beads. Adjunctive IFN-γ injection for M. kansasii infection with good response |
| Lee and Lau (manuscript in preparation) | Homozygous c.182dupT, p.V61fs | Talaromyces marneffei | F/5 months, Chiang Mai, Thailand | Generalized papular skin lesions, hepatosplenomegaly, osteolytic lesions in the skull, fungemia | 11 months: fulminant salmonella septicemia | T. marneffei infection resolved with amphotericin B followed by oral itraconazole; died of salmonellosis and massive lower gastrointestinal bleeding |
Location of residence is indicated wherever information is available.
IFN, interferon; MAC, Mycobacterium avium complex.
AR IFNγ Receptor Deficiency
IFN-γR1 and IFN-γ2 are the ligand-binding and transducing receptor chains of the INF-γ receptor, respectively. Biallelic null mutations in the IFNGR1 gene result in AR complete IFNγR1 deficiency, which is characterized by high plasma concentration of IFN-γ and a lack of response to IFNγ in vitro (142, 143). These patients have early onset, life-threatening disseminated mycobacterial infections and the overall prognosis is poor with high rate of fatality. Other infections caused by viruses (cytomegalovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, varicellar zoster virus, human herpes virus 8) and bacteria (Listeria monocytogenes) have been described. In AR partial IFN-γR1 deficiency, the clinical phenotype is less severe (144). Apart from mycobacterial infections, bacterial, viral, and parasitic organisms have been reported (126, 127, 142, 144).
Autosomal dominant partial IFN-γR1 deficiency is caused by mono-allelic mutations affecting exon 6 and exon 7. A hotspot mutation, 818del4, accounts for over 80% of patients with AD IFN-γR1 deficiency (126, 127). In contrast with AR IFN-γR1 deficiency, these is an increase in IFN-γR1 protein expression on the cell surface, due to the accumulation of truncated IFN-γR1 receptors lacking the recycling domain. Despite the presence of receptors encoded by the wild-type IFNGR1 allele, the non-functioning IFN-γR1 protein impedes the normal function of IFN-γR1 dimers by negative dominance and impairs the response to IFN-γ in vitro (145). The clinical features are less severe than those seen in patients in AR complete IFN-γR1 deficiency. Most patients have BCG or NTM infections, and salmonella infection was reported in only 5% of cases (126, 127, 142). Disseminated histoplasmosis (146) and coccidioidomycosis (147) were reported in two patients with IFN-γR1 deficiency and both had a refractory or relapsing course (Table 5). Our group diagnosed AR IFN-γ receptor 1 deficiency in a Burmese infant suffering from disseminated T. marneffei infection, and she eventually died of salmonellosis (manuscript in preparation).
IFN-γR2 deficiency is less common than IFN-γR1 deficiency. Similarly, AR complete or partial IFN-γR2 deficiency cause increased susceptibility to mycobacterial infections (148–150); other infections are rare and include salmonellosis in one patient and cytomegalovirus disease in three patients (126), but mycosis has not been reported. AD form of partial IFN-γR2 deficiency was diagnosed in a patient with mild BCG disease, and clinical penetrance is very low (151).
AD STAT1 Defect
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) is a transcription factor involved in cellular responses mediated by type I (IFNα/β), type II (IFN-γ), and type III (IFN-λ) IFNs (152). AR complete STAT1 deficiency is characterized by the absence of STAT1 expression and abolished cellular response to IFN-γ as well as IFN-α/β and IFN-λ, resulting in severely impaired antimycobacterial and antiviral immunity (153, 154). Patients with complete STAT1 deficiency caused by null mutations have increased susceptibility to mycobacterial, viral, and bacterial infections, whereas biallelic hypomorphic mutations in AR partial STAT1 deficiency are associated with milder clinical severity (153–155). AD partial STAT1 deficiency with mono-allelic loss-of-function (LOF) STAT1 mutation predispose to mycobacterial infection (156); in contrast, AD GOF STAT1 mutation is recognized as the most common cause of CMC disease, accounting for half of the cases (157–159). Majority of the mutations affect the coiled-coil domain or DNA-binding domain of STAT1 (159). They increase STAT1 phosphorylation by impairing nuclear dephosphorylation. They are GOF for the STAT1-dependent cytokines including IFN-α, IFN-β, IFN-γ, and IL-27, which repress Th17 development, accounting for the low numbers of IL-17-producing T-cells in these patients (160).
In addition to CMC, invasive mycoses caused by a variety of yeasts (e.g., Cryptococcus), molds (Aspergillus, Fusarium), and endemic fungi (Histoplasma, Coccidioides, T. marneffei) have been reported in patients with GOF STAT1 mutations, as summarized in Table 6 (161, 162). The two patients who developed disseminated coccidioidomycosis during childhood had progressive disease, which persisted into teenage despite intensive treatment; one had spinal cord compression and one died of overwhelming coccidioidomycosis at 17 years. Of note, the latter patient did not have CMC or other unusual infections, implying that coccidioidomycosis could be the sole infection in patients with GOF STAT1 defect. Three patients had disseminated histoplasmosis and two of them had recurrent disease. All of them responded well to antifungal treatment (161).
Table 6.
Endemic mycoses in AD signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 defect.
| Genetic defect | Endemic fungal pathogen | Gender/age, residence | Clinical manifestations | Other infections and comorbidities | Treatment and outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampaio et al. (161) | Heterozygous p.E353K | Coccidioides spp. | Patient 1: F/17 years, AZ, USA | Coccidioidal pneumonia, mediastinal lymphadenopathy, and sternocleidomastoid abscess; progressive disease with osteomyelitis of the vertebral spine and lesions in the skin, liver, and spleen at 20 years | Extensive persistent tinea capitis and kerion caused by T. tonsurans | Progressive disease despite prolonged antifungal therapy including amphotericin B, azoles and caspofungin. Developed spinal cord compression at 20 years due to intramedullary lesion |
| Heterozygous p.A267V | Coccidioides immitis | Patient 2: F/9 years, AZ, USA | Coccidioidal pneumonia and intrathoracic lymphadenopathy, osteomyelitis of the vertebral spine; progressive disease with CNS involvement, lymphadenopathy, retinal mass, and multifocal osteomyelitis | Nil | Progressive disease despite prolonged antifungal therapy including amphotericin B, azoles, and caspofungin, suboptimal response to adjunctive IFN-γ therapy. Died of overwhelming coccidioidomycosis at 17 years | |
| Heterozygous p.T385M | Histoplasma capsulatum | Patient 3: M/21 years | Disseminated histoplasmosis at 12 years | CMC, M. fortuitum cervical lymphadenopathy, recurrent pneumonia and herpes zoster, bronchiecatasis Recurrent fractures, progressive bilateral upper limb muscle atrophy |
Histoplasmosis treated with itraconazole with good response | |
| Heterozygous p.R274G | H. capsulatum | Patient 4: M/31 years | 17 years: disseminated histoplasmosis presenting with fever, weight loss, lymphadenopathy with liver, and bone marrow involvement 30 years: CNS histoplasmosis |
CMC, warts, recurrent Salmonella septicemia Type 1 DM at 24 years 31 years: PML caused by JC virus |
Histoplasmosis treated with amphotericin B for 6 months followed by fluconazole with multiple relapses that responded to intensified treatment | |
| Heterozygous p.F172L | H. capsulatum | Patient 5: F/25 years | 7 years: disseminated histoplasmosis presenting with fever, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, and dyspnea; recurrence at 8 years | CMC Subclinical hypothyroidism at 14 years, ovarian failure at 24 years |
Histoplasmosis treated with itraconazole with good response | |
| Lee et al. (162) | Heterozygous p.A267V | Talaromyces marneffei | Patient 1: M/14 years, Hong Kong | Disseminated T. marneffei infection at 15 years with generalized lymphadenopathy, positive culture of T. marneffei from lymph node biopsy | CMC | Amphotericin B, itraconazole prophylaxis |
| Heterozygous p.L358F | T. marneffei | Patient 2: F/8 years, Hong Kong | Cavitating pneumonia with cystic cavities; mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy, positive culture of T. marneffei from BAL CMC |
Recurrent sinopulmonary infections Influenza A (H1N1) | Liposomal amphotericin, itraconazole prophylaxis | |
| Heterozygous p.T288I | T. marneffei | Patient 3: F/16 years, Hong Kong | Cervical lymphadenopathy, positive culture of T. marneffei and M. tuberculosis from lymph node biopsy; concomitant axillary, mesenteric, and retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy | CMC Recurrent sinopulmonary infections and herpes zoster EBV-associated HLH Disseminated aspergillosis |
T. marneffei infection responded well to itraconazole Disseminated aspergillosis and EBV-associated HLH at 16 years, died of massive gastrointestinal hemorrhage |
|
| Lee and Lau, unpublished | Heterozygous p.M390I | T. marneffei | M/40 years, Hong Kong | 10 years: cervical lymphadenopathy complicated by ulcerations; perforation of the hard palate, mediastinal lymphadenopathy causing SVC obstruction and sternal erosion, tissue culture yielded T. marneffei 17 years: osteomyelitis of the thumb, forearm, and tibia |
CMC | Relapsing and remitting disease course on prolonged treatment of amphotericin B and fluconazole till 20 years; infection cleared with residual scarring of the skin and dilated veins on the chest |
Location of residence is indicated wherever information is available.
BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; CMC, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis; CNS, central nervous system; DM, diabetes mellitus; EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; IFN, interferon; PML, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy; SVC, superior vena cava.
In Hong Kong, five pediatric patients were diagnosed to have T. marneffei infection from 1983 to 2009 in a single center (74, 85, 162, 163). One patient was lost to follow-up after complete recovery from T. marneffei infection (163), while the remaining four patients underwent thorough immunological investigations and genetic studies, and all were found to have GOF STAT1 defect (162). They all had CMC, and two had recurrent sinopulmonary infections, herpes virus infections (cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus and varicella zoster), TB, and disseminated aspergillosis (85, 162). The patient with chronic relapsing T. marneffei infection first reported by Yuen et al. in 1986 was subsequently investigated when his son was referred for CMC, and both were confirmed to have AD GOF STAT1 defect in 2015.
An increased incidence of herpes virus infections as well as TB and NTM infections (e.g., M. bovis BCG) has been observed in patients with GOF STAT1 defect, and it was thought that the enhancement of signaling downstream to IFN-α/IFN-β and IFN-γ caused by GOF STAT1 mutations could lead to exhaustion of virus-specific T-cells and refractory response to IFN-γ. Other clinical manifestations of GOF STAT1 mutations include autoimmunity (e.g., type 1 diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, autoimmune cytopenia, and hepatitis), vascular aneurysms, and malignancies, particularly squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus (159, 160, 164).
Inborn Errors of Immunity Associated with Impaired Th-17-Mediated Immunity
Autosomal-dominant hyper-IgE syndrome caused by LOF STAT3 mutation, also known as Job’s syndrome, is characterized by recurrent staphylococcal cold abscesses, pneumonia, and eczema. In addition, patients often display joint hyperextensibility, skeletal abnormalities and pathological fractures, delayed dental deciduation, coronary artery aneurysms, brain lesions, and Chiari’s malformation (165, 166). Pneumonia is typically caused by S. aureus, Haemophilus influenzae, or Streptococcus pneumoniae, and is often complicated by pneumoatocele formation. Approximately 20% of patients with AD hyper-IgE syndrome develop invasive infection caused by Aspergillus, which has angioinvasive properties with tendency to cause hematogenous dissemination (167–170). STAT3 promotes the expression of the gene encoding the retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor-γt (RORγt), and important transcription factor that drives differentiation of naïve CD4+ T-cells to Th17 cells. Dominant negative STAT3 mutation leads to impaired RORγt induction in response to IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-23, causing severe deficiency of IL-17-producing effector cells (171, 172).
Three cases of coccidioidomycosis, 10 cases of histoplasmosis and two cases of T. marneffei infection were reported in patients with hyper-IgE syndrome, as summarized in Table 7 (85, 87, 173–183). The three cases of hyper-IgE syndrome with coccidioidomycosis all had CNS involvement (87, 173, 174), while those with IL-12Rβ1 deficiency (139), IFN-γR1 deficiency (147), and GOF STAT1 defect (161) mainly had lymphadenopathy and osteomyelitis, so it appears that there is a predilection for Coccidioides to disseminate to the CNS in hyper-IgE syndrome. In contrast, disseminated histoplasmosis occurred in IL-12Rβ1 deficiency (141), IFN-γR1 deficiency (146), and GOF STAT1 defect (161), but 7 out of 10 cases of histoplasmosis in hyper-IgE syndrome involved the aerodigestive tract only (175–182). Two cases of T. marneffei infection were reported in hyper-IgE syndrome (85, 183).
Table 7.
Endemic mycoses in AD hyper-IgE syndrome (Job syndrome).
| Genetic defect | Endemic fungal pathogen | Gender/age, residence | Clinical manifestations | Other infections and comorbidities | Treatment and outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stanga and Dajud (173) | Not stated | Coccidioides immitis | F/4 years | Coccidioidal meningitis with cerebral infarct at multiple sites, gross left hemiplegia | Recurrent sinus and skin infections, eczema | Treated with amphotericin B and fluconazole, minimal residual deficits |
| Powers et al. (174) | Heterozygous p.T412S | C. immitis | F/17 years, UT, USA | Coccidioidal meningitis and cerebral abscess, altered mental status requiring temporary intubation | Staphylococcus aureus skin and soft tissue infections, recurrent sinopulmonary infections | Improved with liposomal amphotericin, followed by fluconazole prophylaxis |
| Odio et al. (87) | Heterozygous p.V713M | C. immitis | F/4 years, AZ, USA | Coccidioidal meningitis and pulmonary infection presenting with fever, headache, and seizure | Recurrent pneumonia and otitis, skin infections, eczema, thrush | Complicated by cerebral vascular accident and hydrocephalus, treated with liposomal amphotericin and fluconazole Residual left hemiparesis |
| Alberti-Flor et al. (175) | Not stated | Histoplasma capsulatum | M/16 years | Histoplasmosis with ileocecal involvement | Not stated | Resection of terminal ileum and right colon, treated with ketoconazole with good response |
| Cappell et al. (176) | Not stated | H. capsulatum | F/27 years | Disseminated histoplasmosis with cecum, colon, and bone marrow involvement | Not stated | Treated with amphotericin B and ketoconazole |
| Desai et al. (177) | Not stated | H. capsulatum | M/33 years | Histoplasmosis with pulmonary and tongue involvement | Eczema, recurrent sinopulmonary infections, thrush and onychomycosis, Staphylococcal septic arthritis, Cryptococcus meningitis at 37 years | Histoplasmosis treated with amphotericin B and ketoconazole; lobectomy for bronchiectasis |
| Steiner et al. (178) | Not stated | H. capsulatum | F/14 years | Histoplasmosis with ileocecal involvement | Staphylococcal pneumonitis complicated by cystic changes and bronchopleural fistula | Treated with 12 months of itraconzole with good response |
| Robinson et al. (179) | Heterozygous p.K591M | H. capsulatum | M/33 months | Disseminated histoplasmosis with pneumonia and hepatosplenomegaly | Pneumonia, otitis, thrush, eczema, folliculitis, gastroenteritis, multiple fractures, pneumatocele, multiple allergy, developmental delay | Not stated |
| Rana et al. (180) | Not stated | H. capsulatum | F/4 years, India | Histoplasmosis with rectal involvement | Recurrent subcutaneous abscess, giardiasis, Entamoeba infection, molluscum contagiosum, milk allergy | Good response to treatment |
| Jiao et al. (181) | Not stated | H. capsulatum | M/21 years | Terminal ileal perforation, histopathology showed H. capsulatum within histiocytes | Not stated | Partial small bowel resection Liposomal amphotericin, itraconazole |
| Odio et al. (182) | Heterozygous p.V432M | H. capsulatum | M/10 years, US | Disseminated histoplasmosis with pulmonary, liver, and spleen involvement | Not stated | Treated with liposomal amphotericin, itraconzaole, and posaconazole |
| Heterozygous p.F621V | H. capsulatum | F/15 years, US | Histoplasmosis with gastrointestinal involvement, complicated by duodenal stricture | Not stated | Treated with liposomal amphotericin and itraconazole | |
| Heterozygous p.W479C | H. capsulatum | F/22 years, US | Histoplasmosis with laryngeal involvement requiring reconstructive largyngoplasty | Not stated | Treated with ketoconazole | |
| Ma et al. (183) | Not stated | Talaromyces marneffei | M/30 years, Hong Kong | Lung abscess, massive hemoptysis | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia lung abscess, recurrent pneumonia, skin infections | Treated with amphotericin B, died of respiratory failure due to rapid disease progression |
| Lee et al. (85) | Heterozygous p.D374G | T. marneffei | F/12 months, Guangzhou, China | Disseminated T. marneffei infection with pancytopenia and hepatosplenomegaly, positive culture of T. marneffei from bone marrow | Pulmonary aspergillosis, Staphylococcus septicemia, pneumatocele, and pneumothorax | T. marneffei infection treated with itraconazole with good response |
Location of residence and mutation of STAT3 gene are provided wherever information is available.
To summarize, the susceptibility to endemic mycoses in CD40L deficiency, IL12Rβ1 deficiency, and IFN-γR1 deficiency highlights the critical role of the IL-12/IFN-γ crosstalk in macrophage activation and killing of these endemic fungi, while the deficiency of Th17 cells in patients with GOF STAT1 defect and AD hyper-IgE syndrome puts them at risk for both CMC and IFIs, and they frequently have CMC due to impaired mucosal immunity against C. albicans. Defective oxidative burst alone, as in CGD, is not sufficient to cause increased risk to endemic mycoses, suggestive that other mechanisms of phagosomal killing may compensate for the lack of NADPH oxidase activity to control these endemic fungi, distinguishing them from many other invasive fungi to which CGD patients are susceptible.
Protective Immunity Against Endemic Mycoses Conferred by Cytokines: Insights from Biologics and Anti-IFN-γ Autoantibodies
The development of biologic response modifiers (BRMs), such as monoclonal antibodies and receptor antagonists that target pro-inflammatory cytokines and their receptors has led to major advances in the treatment of autoimmune and malignant disorders. However, they have the potential to suppress host immune response and increase the risk of infections. The use of biologics is associated with a small but important risk of IFI. Histoplasmosis is the most common IFI associated with TNF-α inhibitors (10, 59, 184, 185). In a survey of infectious disease specialists, histoplasmosis was second only to S. aureus as the cause of serious infection complicating anti-TNF and other BRM (184). In most cases, patients reside in areas where the fungus is endemic and have received other immunosuppressants concurrently. Up to 2% of patients receiving BRMs will develop coccidioidomycosis if they reside in an endemic region (186). The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Committee on Infectious Diseases recommends that patients on BRM should be enquired about epidemiologic risk factors and possible exposures to histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycosis, which have symptoms and signs that significantly overlap with TB. If there is suspicion of signs or symptoms compatible with acute histoplasmosis or coccidioidomycosis, BRM should be discontinued immediately and patients will require evaluation with a combination of chest radiography and serologic, antigen detection, and culture tests, which are best conducted in consultation with an infectious diseases expert (186, 187).
Other targeted therapies have also been implicated as risk factors for endemic mycoses. In Hong Kong, four cases of disseminated T. marneffei infection were diagnosed in adult hematology patients receiving anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies (rituximab and obinutuzumab) and kinase inhibitors (84, 188, 189). The observation is revealing, as the importance of B-lymphocytes and humoral immune response against fungus is not well defined, and T. marneffei infection has so far not been reported in patients with congenital agammaglobulinemia. Depletion of B-lymphocytes may lead to profound deficiency in the production of neutralizing antibodies against key virulence factors of T. marneffei. Kinase inhibitors such as ruxolitinib and sorafenib are increasingly used in treating hematological malignancies, solid tumors, psoriasis, and alopecia areata. Ruxolitinib is a selective JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor that interferes with the IFN-γ and its downstream JAK-STAT signaling. Sorafenib is a multi-kinase inhibitor that exhibits immunomodulatory effect by impairing T-lymphocyte proliferation, production of IFN-γ and other pro-inflammatory cytokines, NK cell, and DC functions. The suppression of IFN-γ signaling pathway poses risk to develop T. marneffei infection (84). It would be important for clinicians to have a high index of suspicion on T. marneffei infection in patients receiving these targeted therapies to avoid delay in diagnosis and treatment.
Autoantibody against IFN-γ has been reported to be associated with adult-onset immunodeficiency in patients from Asian countries (190–195). Disseminated NTM is the most common clinical presentation. In a cross-sectional, case-control study conducted in Chiang Mai, Thailand showed that patients with opportunistic infections including disseminated NTM, disseminated T. marneffei infection, melioidosis and non-typhoidal Salmonellosis had anti-IFN-γ autoantibody level above 99th percentile of cut-off for healthy individuals, and the level of autoantibody in patients who had active opportunistic infection was relatively higher than those without active infection (193). Similar observations were also reported in Hong Kong and Taiwan (190, 192, 194, 195). HLA class II molecules HLA-DRB1*15:02–HLA-DQB1*05:01 and HLA-DRB1*16:02–HLA-DQB1*05:02 are specifically associated with anti-IFN-γ autoantibodies and NTM (196, 197). The high frequency of such alleles in Southeast Asia might account for the relatively high prevalence this condition in the Asian population. The study by Lin et al. showed that anti-IFN-γ autoantibody from patients recognizes an epitope at the C terminus of IFN-γ, and binding of the autoantibody neutralizes IFNγ-induced signaling. This epitope displays a high degree of sequence homology to the Aspergillus Noc2 protein. It was postulated that in the warm and humid environment of Southeast Asia where exposure to Aspergillus species is common in everyday life, some individuals might develop anti-IFN-γ autoantibodies due to molecular mimicry (198). The co-evolution of anti-IFN-γ autoantibody production as the susceptibility trait amongst Southeast Asians, and the high prevalence of T. marneffei, NTM, and mellioidosis in this region is a unique combination not observed in the rest of the world, and it is so interesting that exposure to a common environmental fungal agent could indirectly induce susceptibility to other pathogens.
Future Perspectives
The understanding about inborn errors of immunity predisposing to endemic mycoses is limited. First, exposure to these environmental fungal pathogens is often a chance event that depends on the natural habitat and climate, as well as the circumstances and activities in which the individual is engaged. Thus, the number of cases of endemic mycoses associating with PID is likely to be low. The proportion of patients with PID amongst those with disseminated endemic mycoses is unknown, due to the lack of information about the population incidence (i.e., the “denominator”). Second, some forms of endemic mycoses, particularly T. marneffei are prevalent in less resourced countries where well-developed clinical service for PID is lacking, and diagnosis is often delayed or missed. Third, the global health impact of these geographically restricted endemic fungi is probably less than those opportunistic fungal pathogens of worldwide distribution causing high disease burden in immunocompromised patients (e.g., Candida, Aspergillus, P. jiroveci, Cryptococcus, and Rhizopus), and they probably generate less attractions and interests in the global public and scientific community (7, 199, 200). Regional and global effort in establishing registries on disseminated endemic mycoses is crucial, in order to collect patient demographic data and determine their true population incidence.
While endemic mycoses are geographically restricted to certain regions, clinicians looking after patients with PID or acquired immunodeficiencies should gain knowledge about these rare fungal infections so that appropriate advice can be given to their patients when planning for travels, and to have heightened awareness of such diagnostic possibility when they return from endemic areas. Climate, environment, and exposure (behavior) are the “triad” that determine the risk of endemic fungal infection in susceptible hosts. High-risk activities that increase the chance of exposure to fungal conidia should be avoided, otherwise, precautionary measures should be taken.
The discovery of PID predisposing to endemic mycoses is a fascinating journey, as it illuminates the key molecules and signaling pathways that are crucial in host defense against this group of dimorphic fungi, which are closely related in phylogeny. As disseminated coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, PCM, and T. marneffei infection are recognized as AIDS-defining illness, they should also be regarded as indicator diseases for PID in individuals who are HIV-negative, and without known risk factors and secondary immunosuppression, particularly in children. There is a need to design an algorithm to evaluate such patients, with stepwise immunological investigations. A detailed history on previous infections, CMC, autoimmune manifestations, and family history should be taken. We recommend a basic panel of immunological evaluations including Ig pattern (IgG, IgA, IgM, and IgE), lymphocyte subset, and nitroblue tetrazolium, or dihydrorhodamine tests to assess oxidative burst activity. These patients should be assessed by immunologists. Abnormal results obtained during acute illness should be repeated upon full recovery. A systematic approach will facilitate clinicians to identify patients who warrant candidate gene studies or functional delineation of the pathways involved in immune recognition, T-cell activation and differentiation, cytokine signaling, and phagocytic killing. The presence of anti-IFN-γ autoantibody should be excluded. Functional evaluation of the IL-12/IFN-γ axis, STAT1 phosphorylation studies, and Th17 enumeration will be particularly relevant in this context. The utilization of next-generation sequencing techniques may lead to discoveries of novel monogenic disorders causing unique susceptibility to endemic mycoses.
Author Contributions
PL wrote the article. Y-LL provided the conceptual framework and reviewed the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer, PR-J, and handling editor declared their shared affiliation and the handling editor states that the process nevertheless met the standards of a fair and objective review.
Footnotes
Funding. The authors would like to thank the Hong Kong Society for the Relief of Disabled Children for funding the molecular testing of primary immunodeficiency disorders for patients in Hong Kong and others referred to the Asian Primary Immunodeficiency Network.
References
- 1.Hsu LY, Ng ES, Koh LP. Common and emerging fungal pulmonary infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am (2010) 24:557–77. 10.1016/j.idc.2010.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sil A, Andrianopoulos A. Thermally dimorphic human fungal pathogens – polyphyletic pathogens with a convergent pathogenicity trait. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med (2014) 5:a019794. 10.1101/cshperspect.a019794 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boyce KJ, Andrianopoulos A. Fungal dimorphism: the switch from hyphae to yeast is a specialized morphogenetic adaptation allowing colonization of a host. FEMS Microbiol Rev (2015) 39:797–811. 10.1093/femsre/fuv035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kauffman CA, Freifeld AG, Andes DR, Baddley JW, Herwaldt L, Walker RC, et al. Endemic fungal infections in solid organ and hematopoietic cell transplant recipients enrolled in the transplant-associated infection surveillance network (TRANSNET). Transpl Infect Dis (2014) 16:213–24. 10.1111/tid.12186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ramos-e-Silva M, Lima CM, Schechtman RC, Trope BM, Carneiro S. Systemic mycoses in immunodepressed patients (AIDS). Clin Dermatol (2012) 30:616–27. 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2012.01.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bonifaz A, Vázquez-González D, Perusquía-Ortiz AM. Endemic systemic mycoses: coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, paracoccidioidomycosis and blastomycosis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges (2011) 9:705–14. 10.1111/j.1610-0387.2011.07731.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Seyedmousavi S, Guillot J, Tolooe A, Verweij PE, de Hoog GS. Neglected fungal zoonoses: hidden threats to man and animals. Clin Microbiol Infect (2015) 21:416–25. 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.02.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chakrabarti A, Slavin MA. Endemic fungal infections in the Asia-Pacific region. Med Mycol (2011) 49:337–44. 10.3109/13693786.2010.551426 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bryant PA, Baddley JW. Opportunistic infections in biological therapy, risk and prevention. Rheum Dis Clin North Am (2017) 43:27–41. 10.1016/j.rdc.2016.09.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vallabhaneni S, Chiller TM. Fungal infections and new biologic therapies. Curr Rheumatol Rep (2016) 18:29. 10.1007/s11926-016-0572-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Brown J, Benedict K, Park BJ, Thompson GR, III. Coccidioidomycosis: epidemiology. Clin Epidemiol (2013) 5:185–97. 10.2147/CLEP.S34434 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nguyen C, Barker BM, Hoover S, Nix DE, Ampel NM, Frelinger JA, et al. Recent advances in our understanding of the environmental, epidemiological, immunological, and clinical dimensions of coccidioidomycosis. Clin Microbiol Rev (2013) 26:505–25. 10.1128/CMR.00005-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Malo J, Luraschi-Monjagatta C, Wolk DM, Thompson R, Hage CA, Knox KS. Update on the diagnosis of pulmonary coccidioidomycosis. Ann Am Thorac Soc (2014) 11:243–53. 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201308-286FR [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wheat LJ, Azar MM, Bahr NC, Spec A, Relich RF, Hage C. Histoplasmosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am (2016) 30:207–27. 10.1016/j.idc.2015.10.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Teixeira Mde M, Patané JS, Taylor ML, Gómez BL, Theodoro RC, de Hoog S, et al. Worldwide phylogenetic distributions and population dynamics of the genus Histoplasma. PLoS Negl Trop Dis (2016) 10:e0004732. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004732 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bahr NC, Antinori S, Wheat LJ, Sarosi GA. Histoplasmosis infections worldwide: thinking outside of the Ohio River valley. Curr Trop Med Rep (2015) 2:70–80. 10.1007/s40475-015-0044-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Benedict K, Mody RK. Epidemiology of histoplasmosis outbreaks, United States, 1938–2013. Emerg Infect Dis (2016) 22:370–8. 10.3201/eid2203.151117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pan B, Chen M, Pan W, Liao W. Histoplasmosis: a new endemic fungal infection in China? Review and analysis of cases. Mycoses (2013) 56:212–21. 10.1111/myc.12029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Theodoro RC, Teixeira Mde M, Felipe MS, Paduan Kdos S, Ribolla PM, San-Blas G, et al. Genus Paracoccidioides: species recognition and biogeographic aspects. PLoS One (2012) 7:e37694. 10.1371/journal.pone.0037694 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Martinez R. New trends in paracoccidioidomycosis epidemiology. J Fungi (2017) 3:1. 10.3390/jof3010001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Arantes TD, Theodoro RC, Teixeira Mde M, Bosco Sde M, Bagagli E. Environmental mapping of Paracoccidioides spp. in Brazil reveals new clues into genetic diversity, biogeography and wild host association. PLoS Negl Trop Dis (2016) 10:e0004606. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004606 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Supparatpinyo K, Khamwan C, Baosoung V, Nelson KE, Sirisanthana T. Disseminated Penicillium marneffei infection in southeast Asia. Lancet (1994) 344:110–3. 10.1016/S0140-6736(94)91287-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Vanittanakom N, Cooper CR, Jr, Fisher MC, Sirisanthana T. Penicillium marneffei infection and recent advances in the epidemiology and molecular biology aspects. Clin Microbiol Rev (2006) 19:95–110. 10.1128/CMR.19.1.95-110.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hu Y, Zhang J, Li X, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Ma J, et al. Penicillium marneffei infection: an emerging disease in mainland China. Mycopathologia (2013) 175:57–67. 10.1007/s11046-012-9577-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Seitz AE, Adjemian J, Steiner CA, Prevots DR. Spatial epidemiology of blastomycosis hospitalizations: detecting clusters and identifying environmental risk factors. Med Mycol (2015) 53:447–54. 10.1093/mmy/myv014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bradsher RW, Jr. The endemic mimic: blastomycosis an illness often misdiagnosed. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc (2014) 125:188–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Castillo CG, Kauffman CA, Miceli MH. Blastomycosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am (2016) 30:247–64. 10.1016/j.idc.2015.10.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chakrabarti A, Bonifaz A, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, Mochizuki T, Li S. Global epidemiology of sporotrichosis. Med Mycol (2015) 53:3–14. 10.1093/mmy/myu062 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kenyon C, Bonorchis K, Corcoran C, Meintjes G, Locketz M, Lehloenya R, et al. A dimorphic fungus causing disseminated infection in South Africa. N Engl J Med (2013) 369:1416–24. 10.1056/NEJMoa1215460 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.van Hougenhouck-Tulleken WG, Papavarnavas NS, Nel JS, Blackburn LY, Govender NP, Spencer DC, et al. HIV-associated disseminated emmonsiosis, Johannesburg, South Africa. Emerg Infect Dis (2014) 20:2164–6. 10.3201/eid2012.140902 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schwartz IS, Govender NP, Corcoran C, Dlamini S, Prozesky H, Burton R, et al. Clinical characteristics, diagnosis, management, and outcomes of disseminated emmonsiosis: a retrospective case series. Clin Infect Dis (2015) 61:1004–12. 10.1093/cid/civ439 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Environmental Fungal Diseases in the United States. (2016). Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/features/fungalinfections/
- 33.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Areas Endemic for Coccidioidomycosis. (2016). Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/coccidioidomycosis/causes.html
- 34.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Areas Endemic for Histoplasmosis. (2016). Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/histoplasmosis/causes.html
- 35.Leading International Fungal Education (LIFE). Paracoccidioidomycosis. (2016). Available from: http://www.life-worldwide.org/fungal-diseases/paracoccidioidomycosis
- 36.Leading International Fungal Education (LIFE). Blastomycosis. (2016). Available from: http://www.life-worldwide.org/fungal-diseases/blastomyces
- 37.Leading International Fungal Education (LIFE). Histoplasmosis. (2016). Available from: http://www.life-worldwide.org/fungal-diseases/histoplasmosis-chronic-cavitary-pulmonary
- 38.Leading International Fungal Education (LIFE). Talaromyces marneffei Infectiton. (2016). Available from: http://www.life-worldwide.org/fungal-diseases/talaromyces-marneffei-infection
- 39.Cao C, Liang L, Wang W, Luo H, Huang S, Liu D, et al. Common reservoirs for Penicillium marneffei infection in humans and rodents, China. Emerg Infect Dis (2011) 17:209–14. 10.3201/eid1702.100718 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Increase in reported coccidioidomycosis – United States, 1998–2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep (2013) 62:217–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hector RF, Rutherford GW, Tsang CA, Erhart LM, McCotter O, Anderson SM, et al. The public health impact of coccidioidomycosis in Arizona and California. Int J Environ Res Public Health (2011) 8:1150–73. 10.3390/ijerph8041150 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Téllez MD, Batista-Duharte A, Portuondo D, Quinello C, Bonne-Hernández R, Carlos IZ. Sporothrix schenckii complex biology: environment and fungal pathogenicity. Microbiology (2014) 160:2352–65. 10.1099/mic.0.081794-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mahajan VK. Sporotrichosis: an overview and therapeutic options. Dermatol Res Pract (2014) 2014:272376. 10.1155/2014/272376 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kauffman CA. Histoplasmosis: a clinical and laboratory update. Clin Microbiol Rev (2007) 20:115–32. 10.1128/CMR.00027-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.de Oliveira HC, Assato PA, Marcos CM, Scorzoni L, de Paula E Silva AC, Da Silva Jde F, et al. Paracoccidioides-host interaction: an overview on recent advances in the paracoccidioidomycosis. Front Microbiol (2015) 6:1319. 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01319 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Saccente M, Woods GL. Clinical and laboratory update on blastomycosis. Clin Microbiol Rev (2010) 23:367–81. 10.1128/CMR.00056-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Masannat FY, Ampel NM. Coccidioidomycosis in patients with HIV-1 infection in the era of potent antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis (2010) 50:1–7. 10.1086/648719 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Adenis A, Nacher M, Hanf M, Vantilcke V, Boukhari R, Blachet D, et al. HIV-associated histoplasmosis early mortality and incidence trends: from neglect to priority. PLoS Negl Trop Dis (2014) 8:e3100. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zheng J, Gui X, Cao Q, Yang R, Yan Y, Deng L, et al. A clinical study of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome associated Penicillium marneffei infection from a non-endemic area in China. PLoS One (2015) 10:e0130376. 10.1371/journal.pone.0130376 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kawila R, Chaiwarith R, Supparatpinyo K. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of penicilliosis marneffei among patients with and without HIV infection in Northern Thailand: a retrospective study. BMC Infect Dis (2013) 13:464. 10.1186/1471-2334-13-464 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Case Definitions of HIV for Surveillance and Revised Clinical Staging and Immunological Classification of HIV-Related Disease in Adults and Children. Geneva: WHO; (2007). [Google Scholar]
- 52.Morejón KM, Machado AA, Martinez R. Paracoccidioidomycosis in patients infected with and not infected with human immunodeficiency virus: a case-control study. Am J Trop Med Hyg (2009) 80:359–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sarti EC, de Oliveira SM, dos Santos LF, de Camargo ZP, Paniago AM. Paracoccidioidal infection in HIV patients at an endemic area of paracoccidioidomycosis in Brazil. Mycopathologia (2012) 173:145–9. 10.1007/s11046-011-9495-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Freitas DF, Valle AC, da Silva MB, Campos DP, Lyra MR, de Souza RV, et al. Sporotrichosis: an emerging neglected opportunistic infection in HIV-infected patients in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. PLoS Negl Trop Dis (2014) 8:e3110. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Moreira JA, Freitas DF, Lamas CC. The impact of sporotrichosis in HIV-infected patients: a systematic review. Infection (2015) 43:267–76. 10.1007/s15010-015-0746-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Witzig RS, Hoadley DJ, Greer DL, Abriola KP, Hernandez RL. Blastomycosis and human immunodeficiency virus: three new cases and review. South Med J (1994) 87:715–9. 10.1097/00007611-199407000-00008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jones PG, Cohen RL, Batts DH, Silva J, Jr. Disseminated histoplasmosis, invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, and other opportunistic infections in a homosexual patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Sex Transm Dis (1983) 10:202–4. 10.1097/00007435-198311000-00010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Revision of the CDC surveillance case definition for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists; AIDS program, Center for Infectious diseases. MMWR Suppl (1987) 36(Suppl 1):1S–15S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Luckett K, Dummer JS, Miller G, Hester S, Thomas L. Histoplasmosis in patients with cell-mediated immunodeficiency: human immunodeficiency virus infection, organ transplantation, and tumor necrosis factor-α inhibition. Open Forum Infect Dis (2015) 2:ofu116. 10.1093/ofid/ofu116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wheat J. Endemic mycoses in AIDS: a clinical review. Clin Microbiol Rev (1995) 8:146–59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Adenis AA, Aznar C, Couppié P. Histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients: a review of new developments and remaining gaps. Curr Trop Med Rep (2014) 1:119–28. 10.1007/s40475-014-0017-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Nacher M, Adenis A, Mc Donald S, Do Socorro Mendonca Gomes M, Singh S, Lopes Lima I, et al. Disseminated histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients in South America: a neglected killer continues on its rampage. PLoS Negl Trop Dis (2013) 7:e2319. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002319 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.The Neglected Histoplasmosis in Latin America Group. Disseminated histoplasmosis in Central and South America, the invisible elephant: the lethal blind spot of international health organizations. AIDS (2016) 30:167–70. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000961 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Abrams DI, Robia M, Blumenfeld W, Simonson J, Cohen MB, Hadley WK. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis in AIDS. N Engl J Med (1984) 310:986–7. 10.1056/NEJM198404123101511 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Roberts CJ. Coccidioidomycosis in acquired immune deficiency syndrome: depressed humoral as well as cellular immunity. Am J Med (1984) 76:734–6. 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90304-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Bronnimann DA, Adam RD, Galgiani JN, Habib MP, Petersen EA, Porter B, et al. Coccidioidomycosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med (1987) 106:372–9. 10.7326/0003-4819-106-3-372 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ampel NM, Dols CL, Galgiani JN. Coccidioidomycosis during human immunodeficiency virus infection: results of a prospective study in a coccidioidal endemic area. Am J Med (1993) 94:235–40. 10.1016/0002-9343(93)90054-S [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Li PC, Yeoh EK. Current epidemiological trends of HIV infection in Asia. AIDS Clin Rev (1992):1–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kaldor JM, Sittitrai W, John TJ, Kitamura T. The emerging epidemic of HIV infection and AIDS in Asia and the Pacific. AIDS (1994) 8:S1–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.DiSalvo AF, Fickling AM, Ajello L. Infection caused by Penicillium marneffei: description of first natural infection in man. Am J Clin Pathol (1973) 60:259–63. 10.1093/ajcp/60.2.259 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pautler KB, Padhye AA, Ajello L. Imported penicilliosis marneffei in the United States: report of a second human infection. Sabouraudia (1984) 22:433–8. 10.1080/00362178485380691 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Jayanetra P, Nitiyanant P, Ajello L, Padhye AA, Lolekha S, Atichartakarn V, et al. Penicilliosis marneffei in Thailand: report of five human cases. Am J Trop Med Hyg (1984) 33:637–44. 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.637 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Deng ZL, Connor DH. Progressive disseminated penicilliosis caused by Penicillium marneffei. Report of eight cases and differentiation of the causative organism from Histoplasma capsulatum. Am J Clin Pathol (1985) 84:323–7. 10.1093/ajcp/84.3.323 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Yuen WC, Chan YF, Loke SL, Seto WH, Poon GP, Wong KK. Chronic lymphadenopathy caused by Penicillium marneffei: a condition mimicking tuberculous lymphadenopathy. Br J Surg (1986) 73:1007–8. 10.1002/bjs.1800731224 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Deng ZL. [Penicilliosis marneffei]. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi (1987) 16(306–8):46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Deng Z, Ribas JL, Gibson DW, Connor DH. Infections caused by Penicillium marneffei in China and Southeast Asia: review of eighteen published cases and report of four more Chinese cases. Rev Infect Dis (1988) 10:640–52. 10.1093/clinids/10.3.640 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Peto TE, Bull R, Millard PR, Mackenzie DW, Campbell CK, Haines ME, et al. Systemic mycosis due to Penicillium marneffei in a patient with antibody to human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect (1988) 16:285–90. 10.1016/S0163-4453(88)97700-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Chierakul W, Rajanuwong A, Wuthiekanun V, Teerawattanasook N, Gasiprong M, Simpson A, et al. The changing pattern of bloodstream infections associated with the rise in HIV prevalence in northeastern Thailand. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg (2004) 98:678–86. 10.1016/j.trstmh.2004.01.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Nga TV, Parry CM, Le T, Lan NP, Diep TS, Campbell JI, et al. The decline of typhoid and the rise of non-typhoid salmonellae and fungal infections in a changing HIV landscape: bloodstream infection trends over 15 years in southern Vietnam. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg (2012) 106:26–34. 10.1016/j.trstmh.2011.10.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Chayakulkeeree M, Denning DW. Serious fungal infections in Thailand. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2017) 36:931–35. 10.1007/s10096-017-2927-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Le T, Wolbers M, Chi NH, Quang VM, Chinh NT, Lan NP, et al. Epidemiology, seasonality, and predictors of outcome of AIDS-associated Penicillium marneffei infection in Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam. Clin Infect Dis (2011) 52:945–52. 10.1093/cid/cir028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Wu TC, Chan JW, Ng CK, Tsang DN, Lee MP, Li PC. Clinical presentations and outcomes of Penicillium marneffei infections: a series from 1994 to 2004. Hong Kong Med J (2008) 14:103–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wong SS, Wong KH, Hui WT, Lee SS, Lo JY, Cao L, et al. Differences in clinical and laboratory diagnostic characteristics of penicilliosis marneffei in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)- and non-HIV-infected patients. J Clin Microbiol (2001) 39:4535–40. 10.1128/JCM.39.12.4535-4540.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Chan JF, Lau SK, Yuen KY, Woo PC. Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei infection in non-HIV-infected patients. Emerg Microbes Infect (2016) 5:e19. 10.1038/emi.2016.18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Lee PP, Chan KW, Lee TL, Ho MH, Chen XY, Li CH, et al. Penicilliosis in children without HIV infection – are they immunodeficient? Clin Infect Dis (2012) 54:e8–19. 10.1093/cid/cir754 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Lovell JP, Foruraghi L, Freeman AF, Uzel G, Zerbe CS, Su H, et al. Persistent nodal histoplasmosis in nuclear factor kappa B essential modulator deficiency: report of a case and review of infection in primary immunodeficiencies. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2016) 138:903–5. 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.02.040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Odio CD, Marciano BE, Galgiani JN, Holland SM. Risk factors for disseminated coccidioidomycosis, United States. Emerg Infect Dis (2017) 23:308–11. 10.3201/eid2302.160505 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Lee PP, Lau YL. Endemic infections in Southeast Asia provide new insights to the phenotypic spectrum of primary immunodeficiency disorders. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol (2013) 31:217–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Romani L. Immunity to fungal infections. Nat Rev Immunol (2011) 11:275–88. 10.1038/nri2939 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Drummond RA, Gaffen SL, Hise AG, Brown GD. Innate defense against fungal pathogens. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med (2014) 5:a019620. 10.1101/cshperspect.a019620 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Plato A, Hardison SE, Brown GD. Pattern recognition receptors in antifungal immunity. Semin Immunopathol (2015) 37:97–106. 10.1007/s00281-014-0462-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Sukhithasri V, Nisha N, Biswas L, Anil Kumar V, Biswas R. Innate immune recognition of microbial cell wall components and microbial strategies to evade such recognitions. Microbiol Res (2013) 168:396–406. 10.1016/j.micres.2013.02.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Barreto-Bergter E, Figueiredo RT. Fungal glycans and the innate immune recognition. Front Cell Infect Microbiol (2014) 4:145. 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Turvey SE, Durandy A, Fischer A, Fung SY, Geha RS, Gewies A, et al. The CARD11-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) signalosome complex: stepping into the limelight of human primary immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2014) 134:276–84. 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.06.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Drewniak A, Gazendam RP, Tool AT, van Houdt M, Jansen MH, van Hamme JL, et al. Invasive fungal infection and impaired neutrophil killing in human CARD9 deficiency. Blood (2013) 121:2385–92. 10.1182/blood-2012-08-450551 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Glocker EO, Hennigs A, Nabavi M, Schäffer AA, Woellner C, Salzer U, et al. A homozygous CARD9 mutation in a family with susceptibility to fungal infections. N Engl J Med (2009) 361:1727–35. 10.1056/NEJMoa0810719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Lanternier F, Pathan S, Vincent QB, Liu L, Cypowyj S, Prando C, et al. Deep dermatophytosis and inherited CARD9 deficiency. N Engl J Med (2013) 369:1704–14. 10.1056/NEJMoa1208487 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Okada S, Puel A, Casanova JL, Kobayashi M. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis disease associated with inborn errors of IL-17 immunity. Clin Transl Immunol (2016) 5:e114. 10.1038/cti.2016.71 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Puel A, Döffinger R, Natividad A, Chrabieh M, Barcenas-Morales G, Picard C, et al. Autoantibodies against IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 in patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis and autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I. J Exp Med (2010) 207:291–7. 10.1084/jem.20091983 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Chinn IK, Shearer WT. Severe combined immunodeficiency disorders. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am (2015) 35:671–94. 10.1016/j.iac.2015.07.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Cirillo E, Giardino G, Gallo V, D’Assante R, Grasso F, Romano R, et al. Severe combined immunodeficiency – an update. Ann N Y Acad Sci (2015) 1356:90–106. 10.1111/nyas.12849 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Vinh DC. Insights into human antifungal immunity from primary immunodeficiencies. Lancet Infect Dis (2011) 11:780–92. 10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70217-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Lanternier F, Cypowyj S, Picard C, Bustamante J, Lortholary O, Casanova JL, et al. Primary immunodeficiencies underlying fungal infections. Curr Opin Pediatr (2013) 25:736–47. 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Dinauer MC. Primary immune deficiencies with defects in neutrophil function. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program (2016) 2016:43–50. 10.1182/asheducation-2016.1.43 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Falcone EL, Holland SM. Invasive fungal infection in chronic granulomatous disease: insights into pathogenesis and management. Curr Opin Infect Dis (2012) 25:658–69. 10.1097/QCO.0b013e328358b0a4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Henriet S, Verweij PE, Holland SM, Warris A. Invasive fungal infections in patients with chronic granulomatous disease. Adv Exp Med Biol (2013) 764:27–55. 10.1007/978-1-4614-4726-9_3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Haidar G, Zerbe CS, Cheng M, Zelazny AM, Holland SM, Sheridan KR. Phellinus species: an emerging cause of refractory fungal infections in patients with X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Mycoses (2017) 60:155–60. 10.1111/myc.12573 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Davies EG, Thrasher AJ. Update on the hyper immunoglobulin M syndromes. Br J Haematol (2010) 149:167–80. 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08077.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.de la Morena MT. Clinical phenotypes of hyper-IgM syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract (2016) 4:1023–36. 10.1016/j.jaip.2016.09.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Tu RK, Peters ME, Gourley GR, Hong R. Esophageal histoplasmosis in a child with immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM. AJR Am J Roentgenol (1991) 157:381–2. 10.2214/ajr.157.2.1853826 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Hostoffer RW, Berger M, Clark HT, Schreiber JR. Disseminated Histoplasma capsulatum in a patient with hyper IgM immunodeficiency. Pediatrics (1994) 94:234–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Yilmaz GG, Yilmaz E, Coşkun M, Karpuzoğlu G, Gelen T, Yeğin O. Cutaneous histoplasmosis in a child with hyper-IgM. Pediatr Dermatol (1995) 12:235–8. 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1995.tb00166.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Danielian S, Oleastro M, Eva Rivas M, Cantisano C, Zelazko M. Clinical follow-up of 11 Argentinian CD40L-deficient patients with 7 unique mutations including the so-called “milder” mutants. J Clin Immunol (2007) 27:455–9. 10.1007/s10875-007-9089-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Dahl K, Eggebeen A. Hyper IgM, histoplasmosis and MAS. J Clin Immunol (2012) 32:355. [Google Scholar]
- 115.Pedroza LA, Guerrero N, Stray-Pedersen A, Tafur C, Macias R, Muñoz G, et al. First case of CD40LG deficiency in Ecuador, diagnosed after whole exome sequencing in a patient with severe cutaneous histoplasmosis. Front Pediatr (2017) 5:17. 10.3389/fped.2017.00017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Cabral-Marques O, Schimke LF, Pereira PV, Falcai A, de Oliveira JB, Hackett MJ, et al. Expanding the clinical and genetic spectrum of human CD40L deficiency: the occurrence of paracoccidioidomycosis and other unusual infections in Brazilian patients. J Clin Immunol (2012) 32:212–20. 10.1007/s10875-011-9623-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Cabral-Marques O, Arslanian C, Ramos RN, Morato M, Schimke L, Soeiro Pereira PV, et al. Dendritic cells from X-linked hyper-IgM patients present impaired responses to Candida albicans and Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2012) 129:778–86. 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.10.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Kamchaisatian W, Kosalaraksa P, Benjaponpitak S, Hongeng S, Direkwattanachai C, Lumbiganon P, et al. Penicilliois in patients with X-linked hyperimmunoglobulin M syndrome (XHIGM), case reports from Thailand. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2006) 117:S282. 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.12.1166 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Sripa C, Mitchai J, Thongsri W, Sripa B. Diagnostic cytology and morphometry of Penicillium marneffei in the sputum of a hypogammaglobulinemia with hyper-IgM patient. J Med Assoc Thai (2010) 93:S69–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Liu D, Zhong LL, Li Y, Chen M. Recurrent fever, hepatosplenomegaly and eosinophilia in a boy [article in Chinese]. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi (2016) 18:1145–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Chu EY, Freeman AF, Jing H, Cowen EW, Davis J, Su HC, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of DOCK8 deficiency syndrome. Arch Dermatol (2012) 148:79–84. 10.1001/archdermatol.2011.262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Hsu AP, McReynolds LJ, Holland SM. GATA2 deficiency. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol (2015) 15:104–9. 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000126 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Collin M, Dickinson R, Bigley V. Haematopoietic and immune defects associated with GATA2 mutation. Br J Haematol (2015) 169:173–87. 10.1111/bjh.13317 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Spinner MA, Sanchez LA, Hsu AP, Shaw PA, Zerbe CS, Calvo KR, et al. GATA2 deficiency: a protean disorder of hematopoiesis, lymphatics, and immunity. Blood (2014) 123:809–21. 10.1182/blood-2013-07-515528 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Erwig LP, Gow NA. Interactions of fungal pathogens with phagocytes. Nat Rev Microbiol (2016) 14:163–76. 10.1038/nrmicro.2015.21 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Bustamante J, Boisson-Dupuis S, Abel L, Casanova JL. Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease: genetic, immunological, and clinical features of inborn errors of IFN-γ immunity. Semin Immunol (2014) 26:454–70. 10.1016/j.smim.2014.09.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Boisson-Dupuis S, Bustamante J, El-Baghdadi J, Camcioglu Y, Parvaneh N, El Azbaoui S, et al. Inherited and acquired immunodeficiencies underlying tuberculosis in childhood. Immunol Rev (2015) 264:103–20. 10.1111/imr.12272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol (2003) 3:133–46. 10.1038/nri1001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Floss DM, Schröder J, Franke M, Scheller J. Insights into IL-23 biology: from structure to function. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev (2015) 26:569–78. 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.07.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Boniface K, Blom B, Liu YJ, de Waal Malefyt R. From interleukin-23 to T-helper 17 cells: human T-helper cell differentiation revisited. Immunol Rev (2008) 226:132–46. 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00714.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Gaffen SL, Jain R, Garg AV, Cua DJ. The IL-23-IL-17 immune axis: from mechanisms to therapeutic testing. Nat Rev Immunol (2014) 14:585–600. 10.1038/nri3707 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Espinosa V, Rivera A. Cytokines and the regulation of fungus-specific CD4 T cell differentiation. Cytokine (2012) 58:100–6. 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.11.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Jin W, Chen D. IL-17 cytokines in immunity and inflammation. Emerg Microbes Infect (2013) 2:e60. 10.1038/emi.2013.58 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.de Beaucoudrey L, Samarina A, Bustamante J, Cobat A, Boisson-Dupuis S, Feinberg J, et al. Revisiting human IL-12Rβ1 deficiency: a survey of 141 patients from 30 countries. Medicine (Baltimore) (2010) 89:381–402. 10.1097/MD.0b013e3181fdd832 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Ouederni M, Sanal O, Ikinciogullari A, Tezcan I, Dogu F, Sologuren I, et al. Clinical features of candidiasis in patients with inherited interleukin 12 receptor β1 deficiency. Clin Infect Dis (2014) 58:204–13. 10.1093/cid/cit722 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Fieschi C, Bosticardo M, de Beaucoudrey L, Boisson-Dupuis S, Feinberg J, Santos OF, et al. A novel form of complete IL-12/IL-23 receptor {beta}1 deficiency with cell surface-expressed nonfunctional receptors. Blood (2004) 104:2095–101. 10.1182/blood-2004-02-0584 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.de Beaucoudrey L, Puel A, Filipe-Santos O, Cobat A, Ghandil P, Chrabieh M, et al. Mutations in STAT3 and IL12RB1 impair the development of human IL-17-producing T cells. J Exp Med (2008) 205:1543–50. 10.1084/jem.20080321 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Moraes-Vasconcelos DD, Grumach AS, Yamaguti A, Andrade ME, Fieschi C, de Beaucoudrey L, et al. Paracoccidioides brasiliensis disseminated disease in a patient with inherited deficiency in the beta1 subunit of the interleukin (IL)-12/IL-23 receptor. Clin Infect Dis (2005) 41:e31–7. 10.1086/432119 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Vinh DC. Coccidioidal meningitis: disseminated disease in patients without HIV/AIDS. Medicine (Baltimore) (2011) 90:87. 10.1097/MD.0b013e3182073ae3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Hwangpo TA, Harriw WT, Atkinson P, Cassady K, Kankirawatana S. IL-12 receptor defect predisposes to histoplasmosis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol (2012) 109:A80. [Google Scholar]
- 141.Falcão ACAM, Marques PTL, Santos AR, Oliveira JB. Disseminated histoplasmosis caused by IL12RB1 gene mutations in two Brazilian siblings. J Clin Immunol (2012) 32:405. [Google Scholar]
- 142.Dorman SE, Picard C, Lammas D, Heyne K, van Dissel JT, Baretto R, et al. Clinical features of dominant and recessive interferon gamma receptor 1 deficiencies. Lancet (2004) 364:2113–21. 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17552-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Fieschi C, Dupuis S, Picard C, Smith CI, Holland SM, Casanova JL. High levels of interferon gamma in the plasma of children with complete interferon gamma receptor deficiency. Pediatrics (2001) 107:E48. 10.1542/peds.107.4.e48 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Sologuren I, Boisson-Dupuis S, Pestano J, Vincent QB, Fernández-Pérez L, Chapgier A, et al. Partial recessive IFN-γR1 deficiency: genetic, immunological and clinical features of 14 patients from 11 kindreds. Hum Mol Genet (2011) 20:1509–23. 10.1093/hmg/ddr029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Jouanguy E, Lamhamedi-Cherradi S, Lammas D, Dorman SE, Fondanèche MC, Dupuis S, et al. A human IFNGR1 small deletion hotspot associated with dominant susceptibility to mycobacterial infection. Nat Genet (1999) 21:370–8. 10.1038/7701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Zerbe CS, Holland SM. Disseminated histoplasmosis in persons with interferon-gamma receptor 1 deficiency. Clin Infect Dis (2005) 41:e38–41. 10.1086/432120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Vinh DC, Masannat F, Dzioba RB, Galgiani JN, Holland SM. Refractory disseminated coccidioidomycosis and mycobacteriosis in interferon-gamma receptor 1 deficiency. Clin Infect Dis (2009) 49:e62–5. 10.1086/605532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Dorman SE, Holland SM. Mutation in the signal-transducing chain of the interferon-gamma receptor and susceptibility to mycobacterial infection. J Clin Invest (1998) 101:2364–9. 10.1172/JCI2901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Döffinger R, Jouanguy E, Dupuis S, Fondanèche MC, Stephan JL, Emile JF, et al. Partial interferon-gamma receptor signaling chain deficiency in a patient with bacille Calmette-Guérin and Mycobacterium abscessus infection. J Infect Dis (2000) 181:379–84. 10.1086/315197 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Moncada-Vélez M, Martinez-Barricarte R, Bogunovic D, Kong XF, Blancas-Galicia L, Tirpan C, et al. Partial IFN-γR2 deficiency is due to protein misfolding and can be rescued by inhibitors of glycosylation. Blood (2013) 122:2390–401. 10.1182/blood-2013-01-480814 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Kong XF, Vogt G, Itan Y, Macura-Biegun A, Szaflarska A, Kowalczyk D, et al. Haploinsufficiency at the human IFNGR2 locus contributes to mycobacterial disease. Hum Mol Genet (2013) 22:769–81. 10.1093/hmg/dds484 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Schneider WM, Chevillotte MD, Rice CM. Interferon-stimulated genes: a complex web of host defenses. Annu Rev Immunol (2014) 32:513–45. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120231 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Dupuis S, Jouanguy E, Al-Hajjar S, Fieschi C, Al-Mohsen IZ, Al-Jumaah S, et al. Impaired response to interferon-alpha/beta and lethal viral disease in human STAT1 deficiency. Nat Genet (2003) 33:388–91. 10.1038/ng1097 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Chapgier A, Wynn RF, Jouanguy E, Filipe-Santos O, Zhang S, Feinberg J, et al. Human complete Stat-1 deficiency is associated with defective type I and II IFN responses in vitro but immunity to some low virulence viruses in vivo. J Immunol (2006) 176:5078–83. 10.4049/jimmunol.176.8.5078 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Chapgier A, Kong XF, Boisson-Dupuis S, Jouanguy E, Averbuch D, Feinberg J, et al. A partial form of recessive STAT1 deficiency in humans. J Clin Invest (2009) 119:1502–14. 10.1172/JCI37083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Dupuis S, Dargemont C, Fieschi C, Thomassin N, Rosenzweig S, Harris J, et al. Impairment of mycobacterial but not viral immunity by a germline human STAT1 mutation. Science (2001) 293:300–3. 10.1126/science.1061154 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Smeekens SP, Plantinga TS, van de Veerdonk FL, Heinhuis B, Hoischen A, Joosten LA, et al. T1 hyperphosphorylation and defective IL12R/IL23R signaling underlie defective immunity in autosomal dominant chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. PLoS One (2011) 6:e29248. 10.1371/journal.pone.0029248 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.van de Veerdonk FL, Plantinga TS, Hoischen A, Smeekens SP, Joosten LA, Gilissen C, et al. STAT1 mutations in autosomal dominant chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. N Engl J Med (2011) 365:54–61. 10.1056/NEJMoa1100102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Toubiana J, Okada S, Hiller J, Oleastro M, Lagos Gomez M, Aldave Becerra JC, et al. Heterozygous STAT1 gain-of-function mutations underlie an unexpectedly broad clinical phenotype. Blood (2016) 127:3154–64. 10.1182/blood-2015-11-679902 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Liu L, Okada S, Kong XF, Kreins AY, Cypowyj S, Abhyankar A, et al. Gain-of-function human STAT1 mutations impair IL-17 immunity and underlie chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. J Exp Med (2011) 208:1635–48. 10.1084/jem.20110958 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Sampaio EP, Hsu AP, Pechacek J, Bax HI, Dias DL, Paulson ML, et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) gain-of-function mutations and disseminated coccidioidomycosis and histoplasmosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2013) 131:1624–34. 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.01.052 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Lee PP, Mao H, Yang W, Chan KW, Ho MH, Lee TL, et al. Penicillium marneffei infection and impaired IFN-γ immunity in humans with autosomal-dominant gain-of-phosphorylation STAT1 mutations. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2014) 133:894–6.e5. 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.08.051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Kwan EY, Lau YL, Yuen KY, Jones BM, Low LC. Penicillium marneffei infection in a non-HIV infected child. J Paediatr Child Health (1997) 33:267–71. 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1997.tb01596.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Uzel G, Sampaio EP, Lawrence MG, Hsu AP, Hackett M, Dorsey MJ, et al. Dominant gain-of-function STAT1 mutations in FOXP3 wild-type immune dysregulation-polyendocrinopathy-enteropathy-X-linked-like syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2013) 131:1611–23. 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.11.054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Farmand S, Sundin M. Hyper-IgE syndromes: recent advances in pathogenesis, diagnostics and clinical care. Curr Opin Hematol (2015) 22:12–22. 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Woellner C, Gertz EM, Schäffer AA, Lagos M, Perro M, Glocker EO, et al. Mutations in STAT3 and diagnostic guidelines for hyper-IgE syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2010) 125:424–32.e8. 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.10.059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Freeman AF, Holland SM. The hyper-IgE syndromes. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am (2008) 28:277–91, viii. 10.1016/j.iac.2008.01.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Vinh DC, Sugui JA, Hsu AP, Freeman AF, Holland SM. Invasive fungal disease in autosomal-dominant hyper-IgE syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2010) 125:1389–90. 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.01.047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Chandesris MO, Melki I, Natividad A, Puel A, Fieschi C, Yun L, et al. Autosomal dominant STAT3 deficiency and hyper-IgE syndrome: molecular, cellular, and clinical features from a French national survey. Medicine (Baltimore) (2012) 91:e1–19. 10.1097/MD.0b013e31825f95b9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Roxo P, Menezes UP, Tucci S, Jr, Andrade MF, Silva GE, Melo JM. Renal abscess in hyper-IgE syndrome. Urology (2013) 81:414–6. 10.1016/j.urology.2012.10.035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Milner JD, Brenchley JM, Laurence A, Freeman AF, Hill BJ, Elias KM, et al. Impaired T(H)17 cell differentiation in subjects with autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome. Nature (2008) 452:773–6. 10.1038/nature06764 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Al Khatib S, Keles S, Garcia-Lloret M, Karakoc-Aydiner E, Reisli I, Artac H, et al. Defects along the T(H)17 differentiation pathway underlie genetically distinct forms of the hyper IgE syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2009) 124:342–8, 348.e1–5. 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Stanga SD, Dajud MV. Visual changes in a 4-year-old. Clin Pediatr (Phila) (2008) 47:959–61. 10.1177/0009922808319788 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Powers AE, Bender JM, Kumánovics A, Ampofo K, Augustine N, Pavia AT, et al. Coccidioides immitis meningitis in a patient with hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome due to a novel mutation in signal transducer and activator of transcription. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2009) 28:664–6. 10.1097/INF.0b013e31819866ec [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Alberti-Flor JJ, Granda A. Ileocecal histoplasmosis mimicking Crohn’s disease in a patient with Job’s syndrome. Digestion (1986) 33:176–80. 10.1159/000199290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Cappell MS, Manzione NC. Recurrent colonic histoplasmosis after standard therapy with amphotericin B in a patient with Job’s syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol (1991) 86:119–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Desai K, Huston DP, Harriman GR. Previously undiagnosed hyper-IgE syndrome in an adult with multiple systemic fungal infections. J Allergy Clin Immunol (1996) 98:1123–4. 10.1016/S0091-6749(96)80202-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Steiner SJ, Kleiman MB, Corkins MR, Christenson JC, Wheat LJ. Ileocecal histoplasmosis simulating Crohn disease in a patient with hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2009) 28:744–6. 10.1097/INF.0b013e31819b65e0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Robinson WS, Arnold SR, Michael CF, Vickery JD, Schoumacher RA, Pivnick EK, et al. Case report of a young child with disseminated histoplasmosis and review of hyper immunoglobulin e syndrome (HIES). Clin Mol Allergy (2011) 9:14. 10.1186/1476-7961-9-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Rana C, Krishnani N, Kumari N, Shastri C, Poddar U. Rectal histoplasmosis in Job’s syndrome. Indian J Gastroenterol (2013) 32:64–5. 10.1007/s12664-012-0275-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Jiao J, Horner CC, Kau AL. Terminal ileum perforation in a patient with hyper-IgE syndrome. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol (2014) 113:S61. [Google Scholar]
- 182.Odio CD, Milligan KL, McGowan K, Rudman Spergel AK, Bishop R, Boris L, et al. Endemic mycoses in patients with STAT3-mutated hyper-IgE (Job) syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2015) 136:1411–3.e1–2. 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.07.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Ma BH, Ng CS, Lam R, Wan S, Wan IY, Lee TW, et al. Recurrent hemoptysis with Penicillium marneffei and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in Job’s syndrome. Can Respir J (2009) 16:e50–2. 10.1155/2009/586919 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Salvana EM, Salata RA. Infectious complications associated with monoclonal antibodies and related small molecules. Clin Microbiol Rev (2009) 22:274–90. 10.1128/CMR.00040-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Ordonez ME, Farraye FA, Di Palma JA. Endemic fungal infections in inflammatory bowel disease associated with anti-TNF antibody therapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis (2013) 19:2490–500. 10.1097/MIB.0b013e31828f1fba [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Davies HD, Committee on Infectious Diseases . Infectious complications with the use of biologic response modifiers in infants and children. Pediatrics (2016) 138:e20161209. 10.1542/peds.2016-1209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Galgiani JN, Ampel NM, Blair JE, Catanzaro A, Geertsma F, Hoover SE, et al. Executive summary: 2016 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) clinical practice guideline for the treatment of coccidioidomycosis. Clin Infect Dis (2016) 63:717–22. 10.1093/cid/ciw538 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Chan JF, Chan TS, Gill H, Lam FY, Trendell-Smith NJ, Sridhar S, et al. Disseminated infections with Talaromyces marneffei in non-AIDS patients given monoclonal antibodies against CD20 and kinase inhibitors. Emerg Infect Dis (2015) 21:1101–6. 10.3201/eid2107.150138 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Tse E, Leung RY, Kwong YL. Invasive fungal infections after obinutuzumab monotherapy for refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Ann Hematol (2015) 94:165–7. 10.1007/s00277-014-2120-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Tang BS, Chan JF, Chen M, Tsang OT, Mok MY, Lai RW, et al. Disseminated penicilliosis, recurrent bacteremic nontyphoidal salmonellosis, and burkholderiosis associated with acquired immunodeficiency due to autoantibody against gamma interferon. Clin Vaccine Immunol (2010) 17:1132–8. 10.1128/CVI.00053-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Kampitak T, Suwanpimolkul G, Browne S, Suankratay C. Anti-interferon-γ autoantibody and opportunistic infections: case series and review of the literature. Infection (2011) 39:65–71. 10.1007/s15010-010-0067-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Browne SK, Burbelo PD, Chetchotisakd P, Suputtamongkol Y, Kiertiburanakul S, Shaw PA, et al. Adult-onset immunodeficiency in Thailand and Taiwan. N Engl J Med (2012) 367:725–34. 10.1056/NEJMoa1111160 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Wongkulab P, Wipasa J, Chaiwarith R, Supparatpinyo K. Autoantibody to interferon-gamma associated with adult-onset immunodeficiency in non-HIV individuals in Northern Thailand. PLoS One (2013) 8:e76371. 10.1371/journal.pone.0076371 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Chan JF, Trendell-Smith NJ, Chan JC, Hung IF, Tang BS, Cheng VC, et al. Reactive and infective dermatoses associated with adult-onset immunodeficiency due to anti-interferon-gamma autoantibody: Sweet’s syndrome and beyond. Dermatology (2013) 226:157–66. 10.1159/000347112 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Chi CY, Lin CH, Ho MW, Ding JY, Huang WC, Shih HP, et al. Clinical manifestations, course, and outcome of patients with neutralizing anti-interferon-γ autoantibodies and disseminated nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Medicine (Baltimore) (2016) 95:e3927. 10.1097/MD.0000000000003927 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Chi CY, Chu CC, Liu JP, Lin CH, Ho MW, Lo WJ, et al. Anti-IFN-γ autoantibodies in adults with disseminated nontuberculous mycobacterial infections are associated with HLA-DRB1*16:02 and HLA-DQB1*05:02 and the reactivation of latent varicella-zoster virus infection. Blood (2013) 121:1357–66. 10.1182/blood-2012-08-452482 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Ku CL, Lin CH, Chang SW, Chu CC, Chan JF, Kong XF, et al. Anti-IFN-γ autoantibodies are strongly associated with HLA-DR*15:02/16:02 and HLA-DQ*05:01/05:02 across Southeast Asia. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2016) 137:945–8.e8. 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.09.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Lin CH, Chi CY, Shih HP, Ding JY, Lo CC, Wang SY, et al. Identification of a major epitope by anti-interferon-γ autoantibodies in patients with mycobacterial disease. Nat Med (2016) 22:994–1001. 10.1038/nm.4158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Dujardin JC, Herrera S, do Rosario V, Arevalo J, Boelaert M, Carrasco HJ, et al. Research priorities for neglected infectious diseases in Latin America and the Caribbean region. PLoS Negl Trop Dis (2010) 4:e780. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000780 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Brown GD, Denning DW, Gow NA, Levitz SM, Netea MG, White TC. Hidden killers: human fungal infections. Sci Transl Med (2012) 4:165rv13. 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]