Abstract
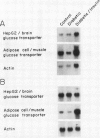
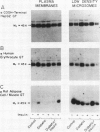
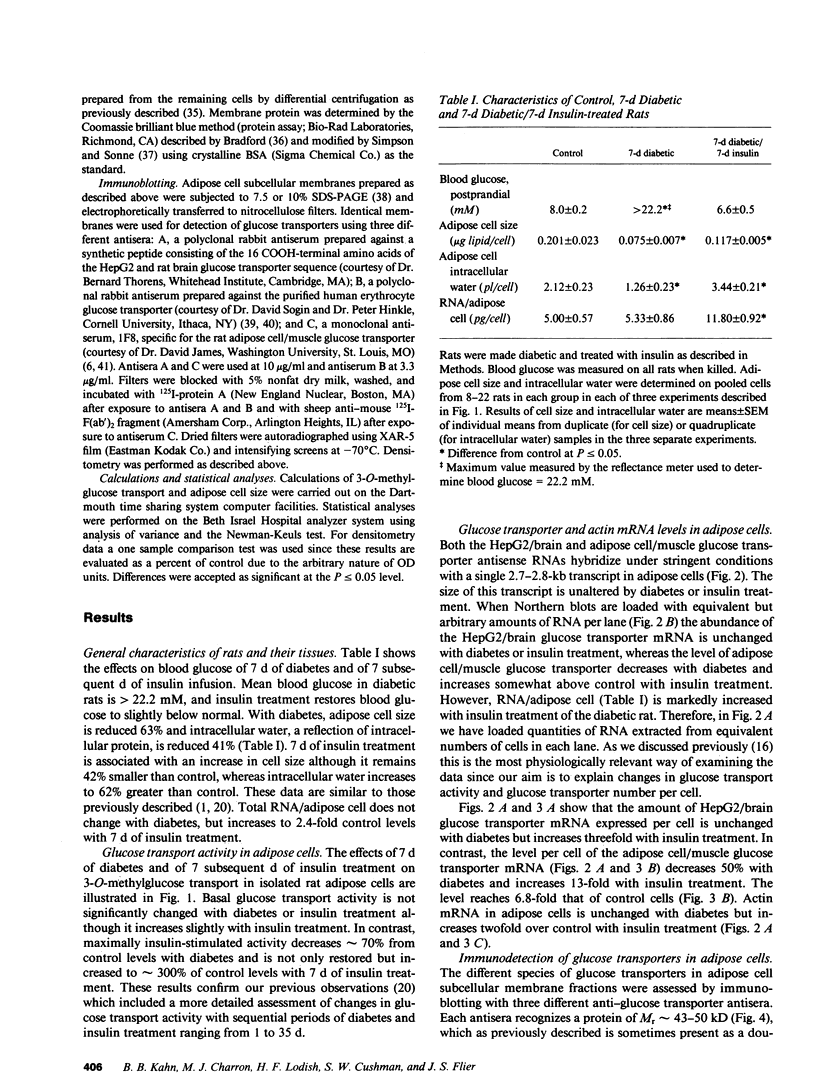
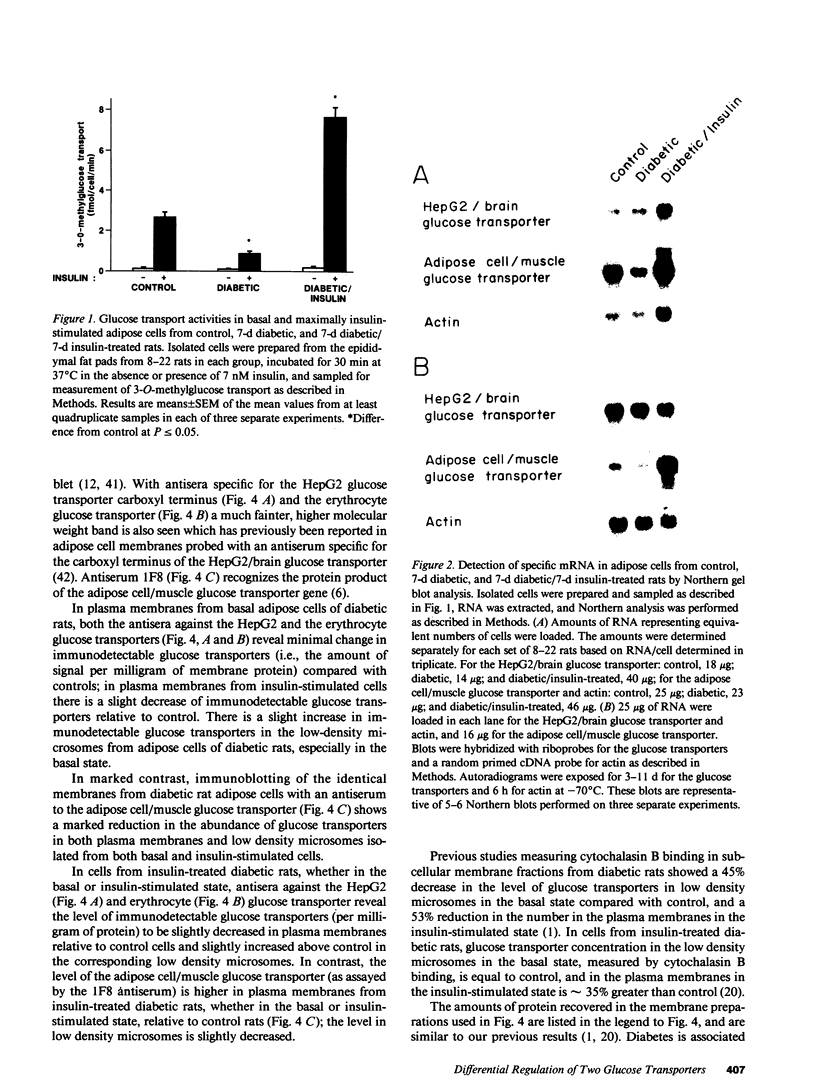
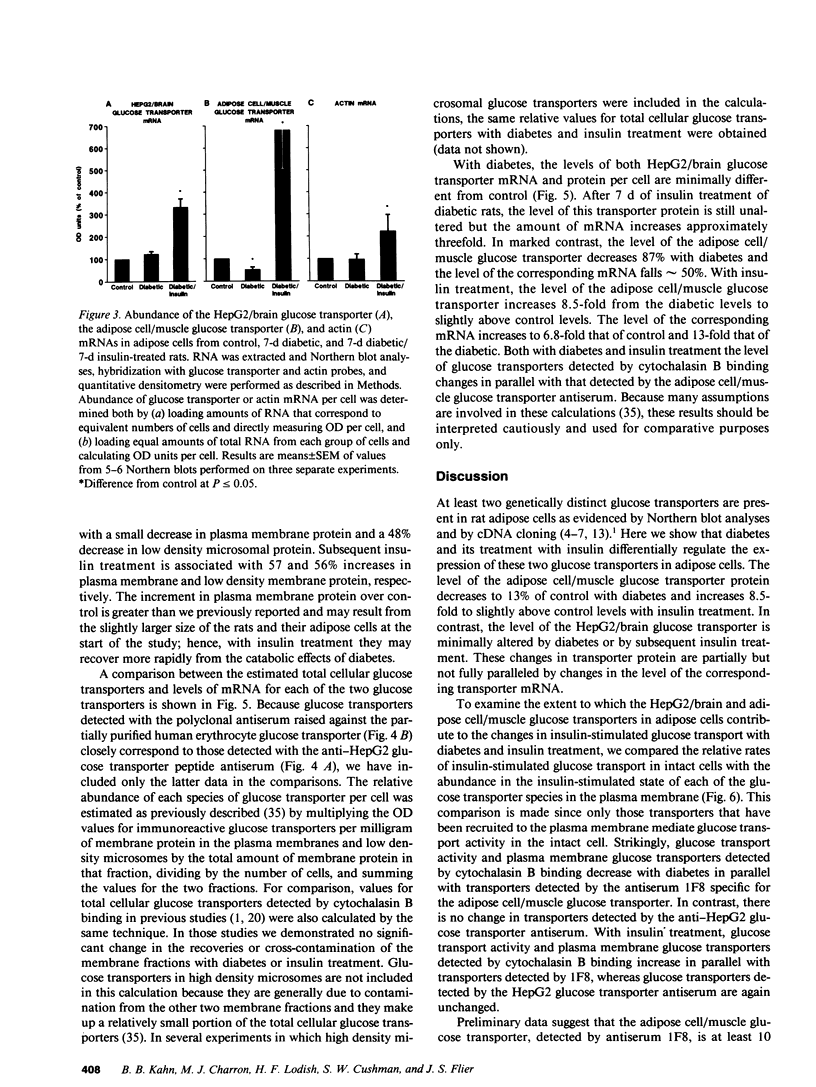
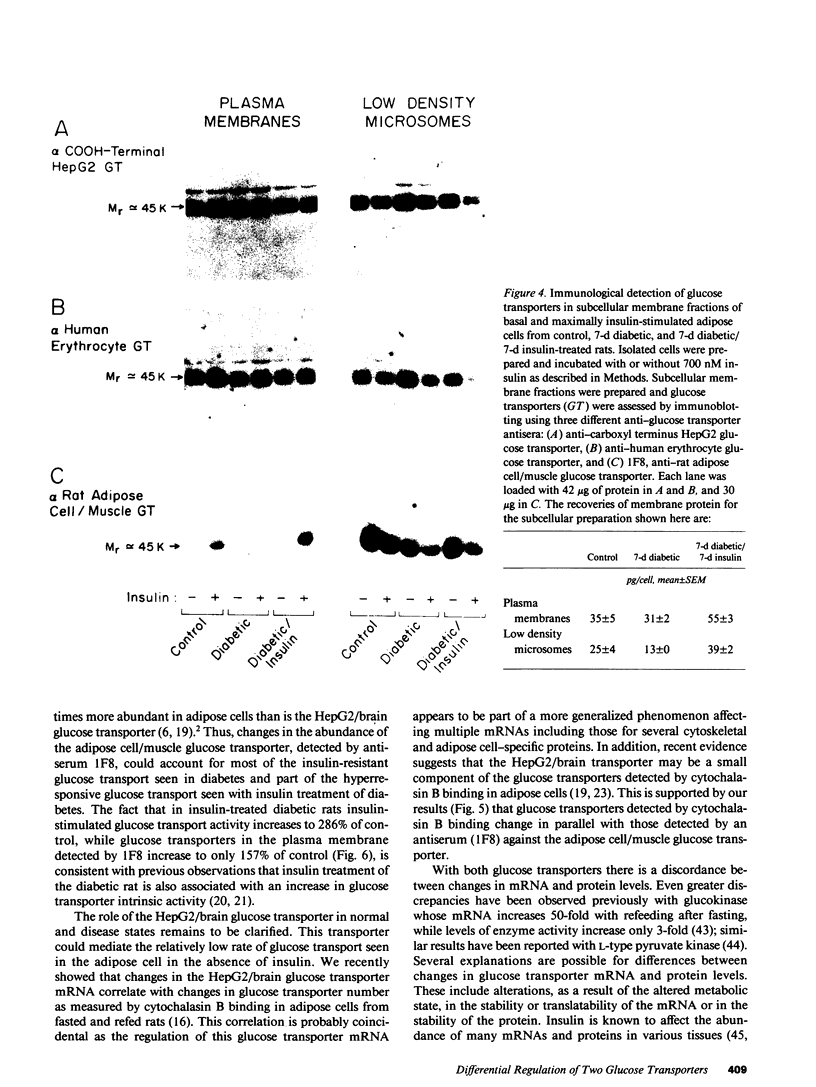
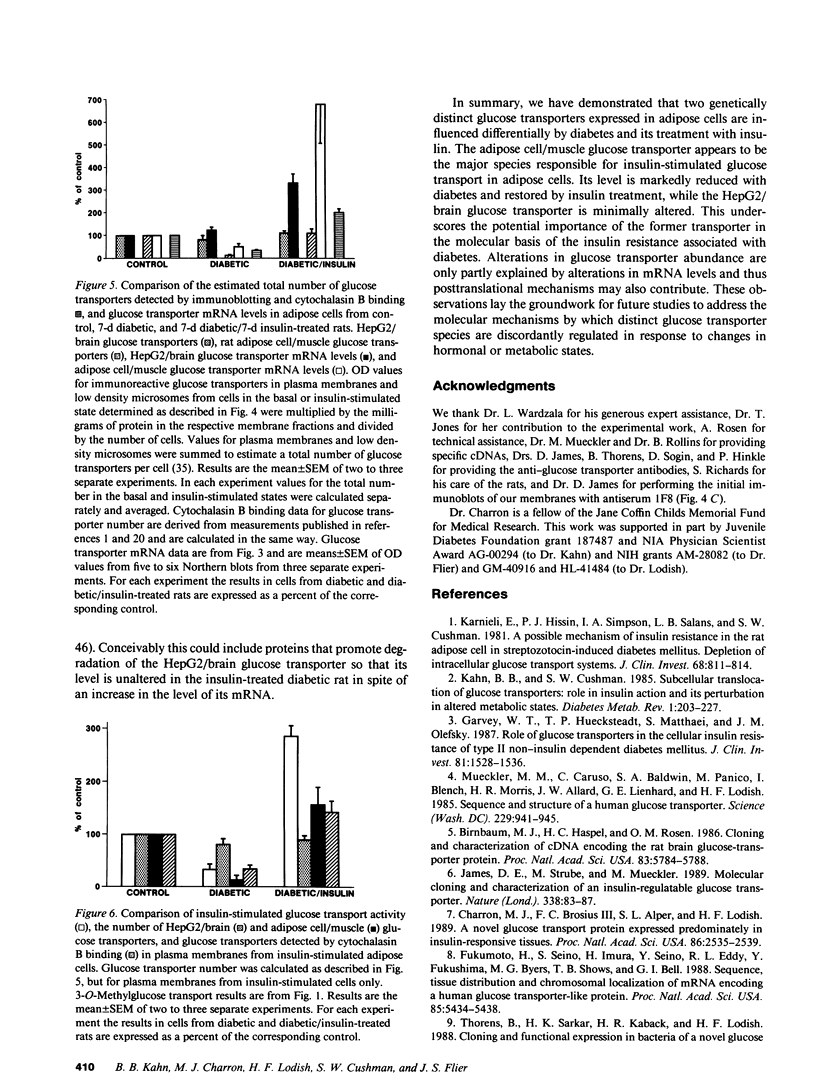
At least two genetically distinct glucose transporters (GTs) coexist in adipose cells, one cloned from human hepatoma cells and rat brain (HepG2/brain) and another from rat skeletal muscle, heart, and adipose cells (adipose cell/muscle). Here we demonstrate differential regulation of these two GTs in adipose cells of diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic rats and compare changes in the expression of each GT with marked alterations in insulin-stimulated glucose transport activity. Adipose cell/muscle GTs detected by immunoblotting with the monoclonal antiserum 1F8 (James, D. E., R. Brown, J. Navarro, and P. F. Pilch. 1988. Nature (Lond.). 333:183-185), which reacts with the protein product of the newly cloned adipose cell/muscle GT cDNA, decrease 87% with diabetes and increase to 8.5-fold diabetic levels with insulin treatment. These changes concur qualitatively with previous detection of GTs by cytochalasin B binding and with insulin-stimulated 3-O-methylglucose transport. Northern blotting reveals that the adipose/muscle GT mRNA decreases 50% with diabetes and increases to 6.8-fold control (13-fold diabetic) levels with insulin treatment. In contrast, GTs detected with antisera to the carboxyl terminus of the HepG2 GT or to the human erythrocyte GT show no significant change with diabetes or insulin treatment. The HepG2/brain GT mRNA is unchanged with diabetes and increases threefold with insulin treatment. These results suggest that (a) altered expression of the adipose cell/muscle GT forms the molecular basis for the dysregulated glucose transport response to insulin characteristic of diabetes, (b) the expression of two types of GTs in rat adipose cells is regulated independently, and (c) alterations in mRNA levels are only part of the mechanism for in vivo regulation of the expression of either GT species.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M., Curtis G., Avruch J., Goodman H. M. Insulin regulation of protein biosynthesis in differentiated 3T3 adipocytes. Regulation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11978–11985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Shibasaki Y., Ohno S., Taira H., Lin J. L., Kasuga M., Kanazawa Y., Akanuma Y., Takaku F., Oka Y. Rabbit brain glucose transporter responds to insulin when expressed in insulin-sensitive Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3416–3420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the rat brain glucose-transporter protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Transformation of rat fibroblasts by FSV rapidly increases glucose transporter gene transcription. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1495–1498. doi: 10.1126/science.3029870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M. J., Brosius F. C., 3rd, Alper S. L., Lodish H. F. A glucose transport protein expressed predominately in insulin-responsive tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2535–2539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Salans L. B. Determinations of adipose cell size and number in suspensions of isolated rat and human adipose cells. J Lipid Res. 1978 Feb;19(2):269–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W. Structure-function relationships in the adipose cell. I. Ultrastructure of the isolated adipose cell. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):326–341. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Mueckler M. M., Usher P., Lodish H. F. Elevated levels of glucose transport and transporter messenger RNA are induced by ras or src oncogenes. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1492–1495. doi: 10.1126/science.3103217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Mueckler M., McCall A. L., Lodish H. F. Distribution of glucose transporter messenger RNA transcripts in tissues of rat and man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):657–661. doi: 10.1172/JCI112864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Seino S., Imura H., Seino Y., Eddy R. L., Fukushima Y., Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Bell G. I. Sequence, tissue distribution, and chromosomal localization of mRNA encoding a human glucose transporter-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Huecksteadt T. P., Matthaei S., Olefsky J. M. Role of glucose transporters in the cellular insulin resistance of type II non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1528–1536. doi: 10.1172/JCI113485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Derechin V., James D. E., Tordjman K., Ahern S., Gibbs E. M., Lienhard G. E., Mueckler M. Insulin-stimulated translocation of the HepG2/erythrocyte-type glucose transporter expressed in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2180–2184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D. K., Andreone T. L. Insulin modulation of gene expression. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1985;1(1-2):139–170. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel H. C., Rosenfeld M. G., Rosen O. M. Characterization of antisera to a synthetic carboxyl-terminal peptide of the glucose transporter protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):398–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J., Gallian E. Methods for the determination of adipose cell size in man and animals. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Matthaei S., Olefsky J. M., Baly D. L., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Biochemical and functional heterogeneity of rat adipocyte glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1823–1828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Brown R., Navarro J., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):183–185. doi: 10.1038/333183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Cushman S. W., Flier J. S. Regulation of glucose transporter-specific mRNA levels in rat adipose cells with fasting and refeeding. Implications for in vivo control of glucose transporter number. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):199–204. doi: 10.1172/JCI113859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Cushman S. W. Mechanism for markedly hyperresponsive insulin-stimulated glucose transport activity in adipose cells from insulin-treated streptozotocin diabetic rats. Evidence for increased glucose transporter intrinsic activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5118–5124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Cushman S. W. Subcellular translocation of glucose transporters: role in insulin action and its perturbation in altered metabolic states. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1985;1(3):203–227. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610010301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Armoni M., Cohen P., Kanter Y., Rafaeloff R. Reversal of insulin resistance in diabetic rat adipocytes by insulin therapy. Restoration of pool of glucose transporters and enhancement of glucose-transport activity. Diabetes. 1987 Aug;36(8):925–931. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.8.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. A possible mechanism of insulin resistance in the rat adipose cell in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Depletion of intracellular glucose transport systems. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):811–814. doi: 10.1172/JCI110318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Zarnowski M. J., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transport systems in the isolated rat adipose cell. Time course, reversal, insulin concentration dependency, and relationship to glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4772–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayano T., Fukumoto H., Eddy R. L., Fan Y. S., Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Bell G. I. Evidence for a family of human glucose transporter-like proteins. Sequence and gene localization of a protein expressed in fetal skeletal muscle and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15245–15248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E., Kim H. H., Ransome K. J., Gorga J. C. Immunological identification of an insulin-responsive glucose transporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):1150–1156. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Asano T., Shibasaki Y., Kasuga M., Kanazawa Y., Takaku F. Studies with antipeptide antibody suggest the presence of at least two types of glucose transporter in rat brain and adipocyte. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13432–13439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Sonne O. A simple, rapid, and sensitive method for measuring protein concentration in subcellular membrane fractions prepared by sucrose density ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):424–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90608-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Yver D. R., Hissin P. J., Wardzala L. J., Karnieli E., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters in the isolated rat adipose cells: characterization of subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman B. M., Farmer S. R. Decreases in tubulin and actin gene expression prior to morphological differentiation of 3T3 adipocytes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Munnich A., Decaux J. F., Kahn A. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of L-type pyruvate kinase gene expression in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7621–7625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. The D-glucose transporter is tissue-specific. Skeletal muscle and adipose tissue have a unique form of glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15689–15695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Cushman S. W., Salans L. B. Mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Enhancement of the number of functional transport systems. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8002–8005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. J., Simpson I. A., Sogin D. C., Hinkle P. C., Cushman S. W. Detection of the rat adipose cell glucose transporter with antibody against the human red cell glucose transporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 15;105(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]