Abstract
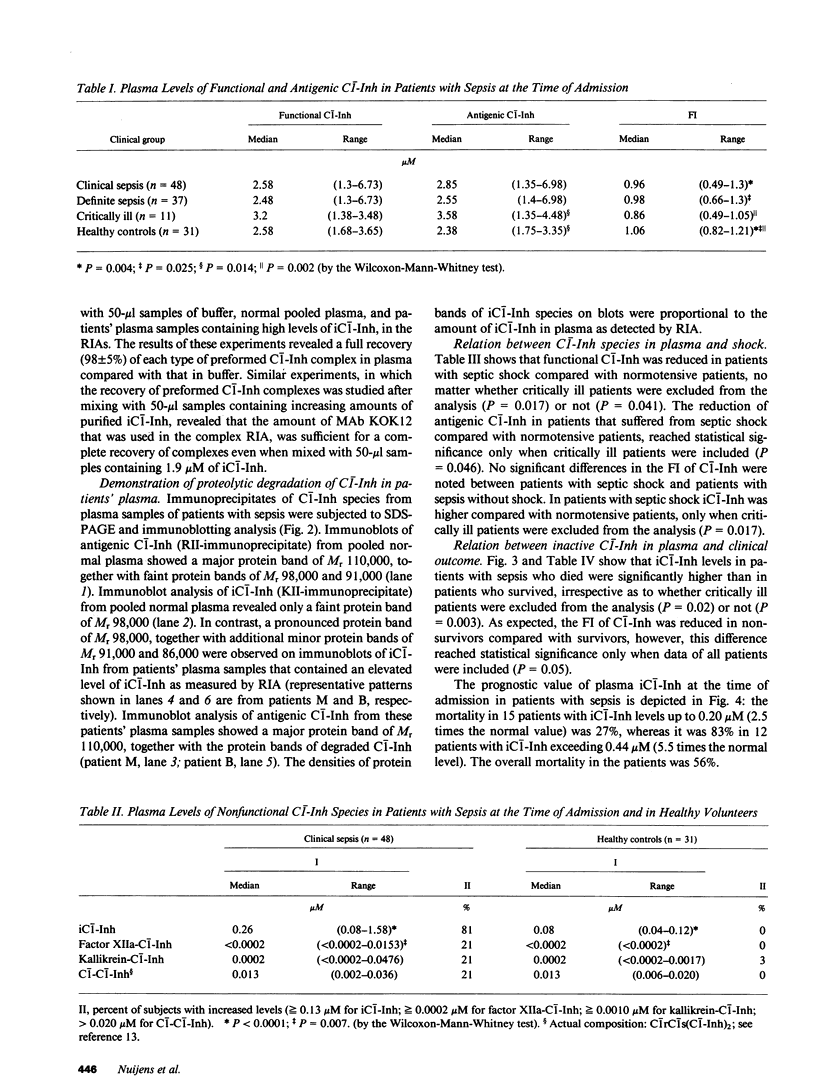
Activation of both the complement system and the contact system of intrinsic coagulation is implicated in the pathophysiology of sepsis. Because C1 inhibitor (C1-Inh) regulates the activation of both cascade systems, we studied the characteristics of plasma C1-Inh in 48 patients with severe sepsis on admission to the Intensive Care Unit at the Free University of Amsterdam. The ratio between the level of functional and antigenic C1-Inh (functional index) was significantly reduced in the patients with sepsis compared with healthy volunteers (P = 0.004). The assessment of modified (cleaved), inactive C1-Inh (iC1-Inh), and complexed forms of C1-Inh (nonfunctional C1-Inh species) revealed that the reduced functional index was mainly due to the presence of iC1-Inh. On SDS-PAGE, iC1-Inh species migrated with a lower apparent molecular weight (Mr 98,000, 91,000, and 86,000) than native C1-Inh (Mr 110,000). Elevated iC1-Inh levels (greater than or equal to 0.13 microM) were found in 81% of all patients, sometimes up to 1.6 microM. Levels of iC1-Inh on admission appeared to be of prognostic value: iC1-Inh was higher in 27 patients who died than in 21 patients who survived (P = 0.003). The mortality in 15 patients with iC1-Inh levels up to 0.2 microM was 27%, but in 12 patients with plasma iC1-Inh exceeding 0.44 microM, the mortality was 83%. The overall mortality in the patients with sepsis was 56%. We propose that the cleavage of C1-Inh in patients with sepsis reflects processes that play a major role in the development of fatal complications during sepsis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasen A. O., Erichsen N. S., Gallimore M. J., Amundsen E. Studies on components of the plasma kallikrein-kinin system in plasma samples from normal individuals and patients with septic shock. Adv Shock Res. 1980;4:1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower M. S., Harpel P. C. Proteolytic cleavage and inactivation of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor and C1 inactivator by human polymorphonuclear leukocyte elastase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9849–9854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho A. C., DeMarinis S., Scott C. F., Silver L. D., Schmaier A. H., Colman R. W. Activation of the contact system of plasma proteolysis in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Aug;112(2):270–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanese J., Kress L. F. Enzymatic inactivation of human plasma C1-inhibitor and alpha 1-antichymotrypsin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteinase and elastase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 28;789(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Beutler B. The role of cachectin/TNF in endotoxic shock and cachexia. Immunol Today. 1988 Jan;9(1):28–31. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Edelman R., Scott C. F., Gilman R. H. Plasma kallikrein activation and inhibition during typhoid fever. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):287–296. doi: 10.1172/JCI108938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R. The classical complement pathway: activation and regulation of the first complement component. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:151–216. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H. Serum inhibitor of C'1-esterase in health and disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Sep;68(3):369–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H., Wagner C. J., Tsuei B., Kindness G., Bing D. H., Harrison R. A., Rosen F. S. Interactions of plasma kallikrein and C1-s with normal and dysfunctional C1(-)-inhibitor proteins from patients with hereditary angioneurotic edema: analytic gel studies. Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1096–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duswald K. H., Jochum M., Schramm W., Fritz H. Released granulocytic elastase: an indicator of pathobiochemical alterations in septicemia after abdominal surgery. Surgery. 1985 Nov;98(5):892–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egbring R., Schmidt W., Fuchs G., Havemann K. Demonstration of granulocytic proteases in plasma of patients with acute leukemia and septicemia with coagulation defects. Blood. 1977 Feb;49(2):219–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldering E., Nuijens J. H., Hack C. E. Expression of functional human C1 inhibitor in COS cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11776–11779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Ruddy S., Schur P. H., McCabe W. R. Activation of the properdin pathway of complement in patients with gram-negative of bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 1;292(18):937–940. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505012921802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor E. R., Vitek L., Sticklin L., Creekmore S. P., Ferraro M. E., Thomas J. X., Jr, Fisher S. G., Fisher R. I. The hemodynamic effects of treatment with interleukin-2 and lymphokine-activated killer cells. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Dec 15;109(12):953–958. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-12-953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld A. B., Bronsveld W., Thijs L. G. Hemodynamic determinants of mortality in human septic shock. Surgery. 1986 Feb;99(2):140–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld A. B., Nauta J. J., Thijs L. G. Peripheral vascular resistance in septic shock: its relation to outcome. Intensive Care Med. 1988;14(2):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00257468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Hannema A. J., Eerenberg-Belmer A. J., Out T. A., Aalberse R. C. A C1-inhibitor-complex assay (INCA): a method to detect C1 activation in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1450–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Nuijens J. H., Felt-Bersma R. J., Schreuder W. O., Eerenberg-Belmer A. J., Paardekooper J., Bronsveld W., Thijs L. G. Elevated plasma levels of the anaphylatoxins C3a and C4a are associated with a fatal outcome in sepsis. Am J Med. 1989 Jan;86(1):20–26. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(89)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Cooper N. R. Studies on human plasma C1 inactivator-enzyme interactions. I. Mechanisms of interaction with C1s, plasmin, and trypsin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):593–604. doi: 10.1172/JCI107967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. A. Human C1 inhibitor: improved isolation and preliminary structural characterization. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 11;22(21):5001–5007. doi: 10.1021/bi00290a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges F., Humbel R., Dicato M., Hemmer R., Kuntziger H. Acquired C1 esterase-inhibitor deficiency: case report with emphasis on complement and kallikrein activation during two patterns of clinical manifestations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Nov;78(5 Pt 1):860–867. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekzema R., Hannema A. J., Swaak T. J., Paardekooper J., Hack C. E. Low molecular weight C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):265–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob H. S., Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D. E., Moldow C. F. Complement-induced granulocyte aggregation: an unsuspected mechanism of disease. N Engl J Med. 1980 Apr 3;302(14):789–794. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198004033021407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalter E. S., Daha M. R., ten Cate J. W., Verhoef J., Bouma B. N. Activation and inhibition of Hageman factor-dependent pathways and the complement system in uncomplicated bacteremia or bacterial shock. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1019–1027. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Silverberg M. The coagulation-kinin pathway of human plasma. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger B. E., Craven D. E., Carling P. C., McCabe W. R. Gram-negative bacteremia. III. Reassessment of etiology, epidemiology and ecology in 612 patients. Am J Med. 1980 Mar;68(3):332–343. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY L. R., LEPOW I. H. Assay and properties of serum inhibitor of C'l-esterase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:608–611. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASON D. T., MELMON K. L. EFFECTS OF BRADYKININ ON FOREARM VENOUS TONE AND VASCULAR RESISTANCE IN MAN. Circ Res. 1965 Aug;17:106–113. doi: 10.1161/01.res.17.2.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Brotóns F., Oncins J. R., Mestres J., Amargós V., Reynaldo C. Plasma kallikrein-kinin system in patients with uncomplicated sepsis and septic shock--comparison with cardiogenic shock. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Aug 4;58(2):709–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. W., Kleeberg U., Dolan P., Colman R. W. Plasma kallikrein and Hageman factor in Gram-negative bacteremia. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Oct;73(4):545–551. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-4-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R. Serum complement levels in bacteremia due to gram-negative organisms. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 4;288(1):21–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301042880105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijers J. C., Vlooswijk R. A., Bouma B. N. Inhibition of human blood coagulation factor XIa by C-1 inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 9;27(3):959–963. doi: 10.1021/bi00403a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. The effects of bacterial endotoxins on host mediation systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):526–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Barrett A. J. Human plasma kallikrein. A rapid purification method with high yield. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):187–192. doi: 10.1042/bj1930187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies A. S., Forsyth R. P., Williams H. E., Melmon K. L. Contribution of kinins to endotoxin shock in unanesthetized Rhesus monkeys. Circ Res. 1968 Feb;22(2):155–164. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Sjöholm I., Wiman B. Structural and circular-dichroism studies on the interaction between human C1-esterase inhibitor and C1s. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 1;213(3):617–624. doi: 10.1042/bj2130617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijens J. H., Huijbregts C. C., Cohen M., Navis G. O., de Vries A., Eerenberg A. J., Bakker J. C., Hack C. E. Detection of activation of the contact system of coagulation in vitro and in vivo: quantitation of activated Hageman factor-C-1-inhibitor and kallikrein-C-1-inhibitor complexes by specific radioimmunoassays. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Aug 4;58(2):778–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijens J. H., Huijbregts C. C., Eerenberg-Belmer A. J., Abbink J. J., Strack van Schijndel R. J., Felt-Bersma R. J., Thijs L. G., Hack C. E. Quantification of plasma factor XIIa-Cl(-)-inhibitor and kallikrein-Cl(-)-inhibitor complexes in sepsis. Blood. 1988 Dec;72(6):1841–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijens J. H., Huijbregts C. C., van Mierlo G. M., Hack C. E. Inactivation of C-1 inhibitor by proteases: demonstration by a monoclonal antibody of a neodeterminant on inactivated, non-complexed C-1 inhibitor. Immunology. 1987 Jul;61(3):387–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell T. F., Jr, Clowes G. H., Jr, Talamo R. C., Colman R. W. Kinin activation in the blood of patients with sepsis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1976 Oct;143(4):539–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pixley R. A., Schapira M., Colman R. W. The regulation of human factor XIIa by plasma proteinase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1723–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G. S., Catanese J. J., Kress L. F., Travis J. Primary structure of the reactive site of human C1-inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2432–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Contribution of plasma protease inhibitors to the inactivation of kallikrein in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):462–468. doi: 10.1172/JCI110470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Silver L. D., Scott C. F., Schmaier A. H., Prograis L. J., Jr, Curd J. G., Colman R. W. Prekallikrein activation and high-molecular-weight kininogen consumption in hereditary angioedema. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 5;308(18):1050–1053. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198305053081802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., de Agostini A., Schifferli J. A., Colman R. W. Biochemistry and pathophysiology of human C1 inhibitor: current issues. Complement. 1985;2(2-3):111–126. doi: 10.1159/000467851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz R., Wolf M., Egbring R., Radtke K. P., Liesenfeld A., Pittner P., Havemann K. Participation and interactions of neutrophil elastase in haemostatic disorders of patients with severe infections. Eur J Haematol. 1987 Mar;38(3):231–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1987.tb01169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Reboul A., Arlaud G. J., Villiers C. L., Colomb M. G. Interaction of 125I-labelled complement subcomponents C-1r and C-1s with protease inhibitors in plasma. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 1;97(1):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotman G. J., Burchard K. W., Williams J. J., D'Arezzo A., Yellin S. A. Interaction of prostaglandins, activated complement, and granulocytes in clinical sepsis and hypotension. Surgery. 1986 Jun;99(6):744–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergeront J. M., Stolz S. J., Crass B. A., Nelson D. B., Davis J. P., Bergdoll M. S. Prevalence of serum antibody to staphylococcal enterotoxin F among Wisconsin residents: implications for toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):692–698. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt W. Anaphylatoxins: possible roles in disease. Complement. 1986;3(3):177–188. doi: 10.1159/000467894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtfogel Y. T., Kucich U., James H. L., Scott C. F., Schapira M., Zimmerman M., Cohen A. B., Colman R. W. Human plasma kallikrein releases neutrophil elastase during blood coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1672–1677. doi: 10.1172/JCI111126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtfogel Y. T., Pixley R. A., Kucich U., Abrams W., Weinbaum G., Schapira M., Colman R. W. Purified plasma factor XIIa aggregates human neutrophils and causes degranulation. Blood. 1986 Jun;67(6):1731–1737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss V., Engel J. Heparin-stimulated modification of C1-inhibitor by subcomponent C1s of human complement. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Mar;364(3):295–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuraw B. L., Curd J. G. Demonstration of modified inactive first component of complement (C1) inhibitor in the plasmas of C1 inhibitor-deficient patients. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):567–575. doi: 10.1172/JCI112610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Agostini A., Lijnen H. R., Pixley R. A., Colman R. W., Schapira M. Inactivation of factor XII active fragment in normal plasma. Predominant role of C-1-inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;73(6):1542–1549. doi: 10.1172/JCI111360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Agostini A., Schapira M., Wachtfogel Y. T., Colman R. W., Carrel S. Human plasma kallikrein and C1 inhibitor form a complex possessing an epitope that is not detectable on the parent molecules: demonstration using a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5190–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Graaf F., Koedam J. A., Bouma B. N. Inactivation of kallikrein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):149–158. doi: 10.1172/JCI110743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Graaf F., Koedam J. A., Griffin J. H., Bouma B. N. Interaction of human plasma kallikrein and its light chain with C1 inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4860–4866. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




