Abstract
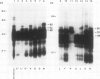
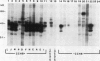
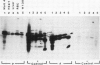
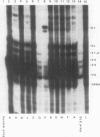
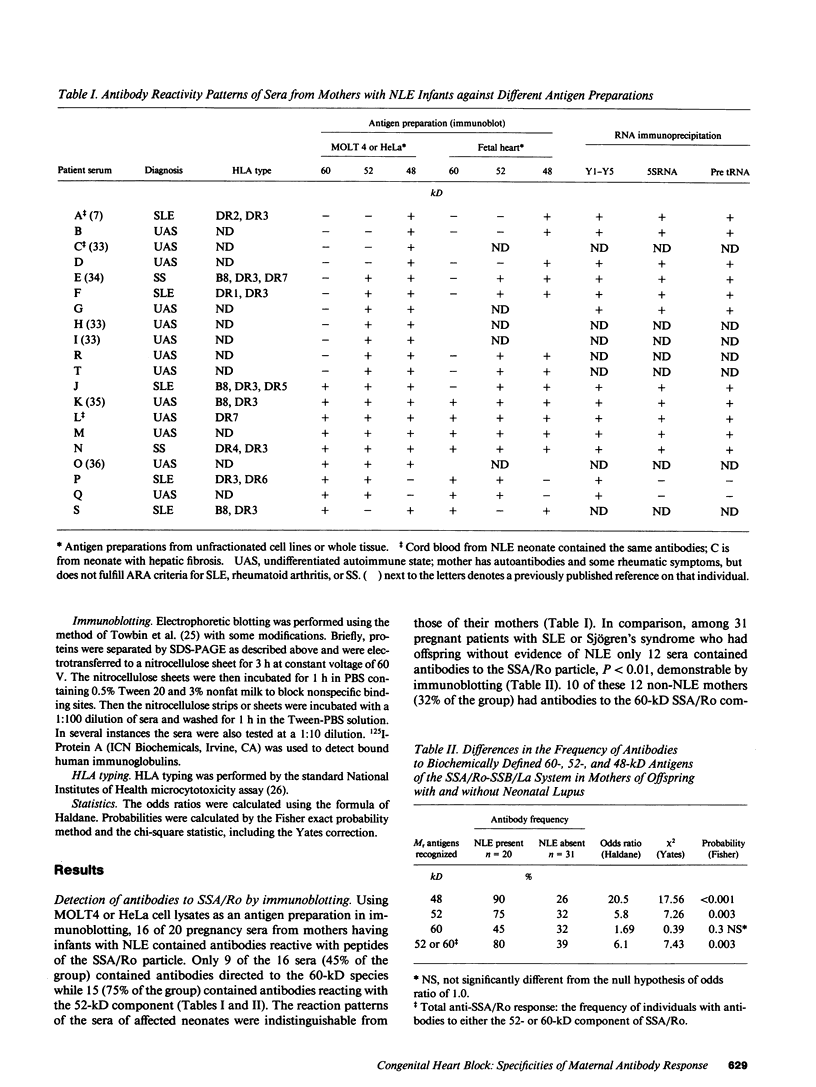
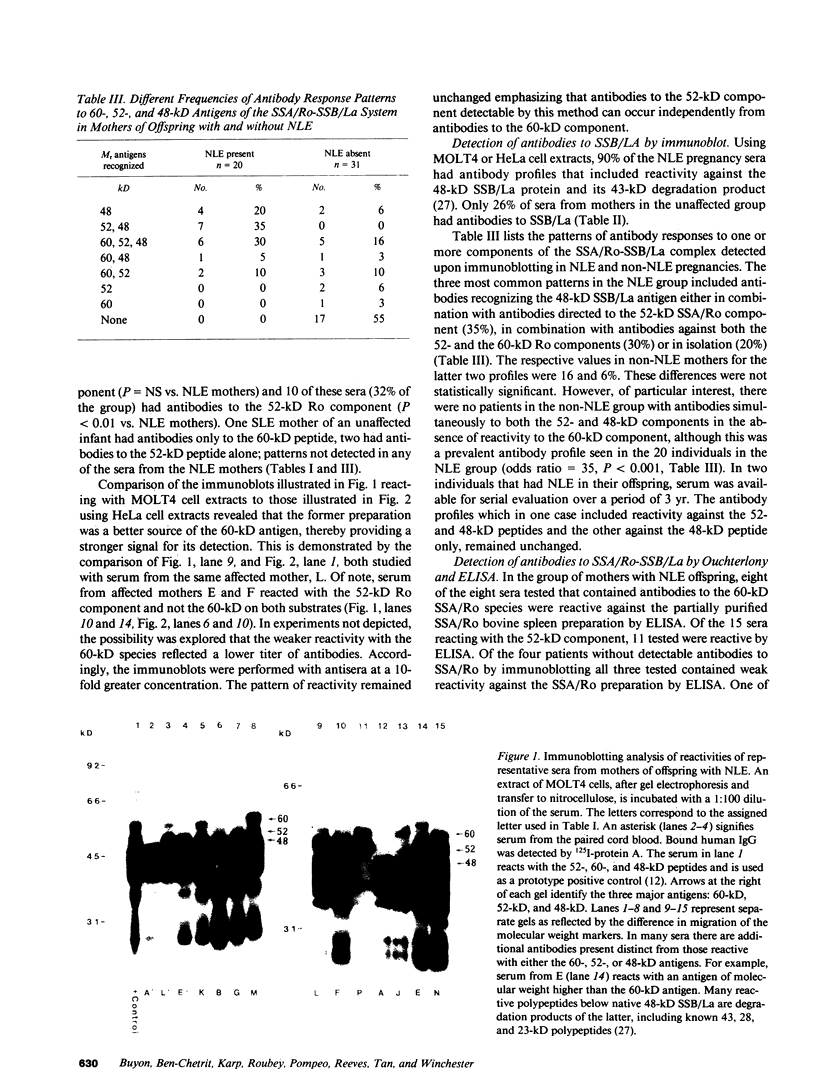
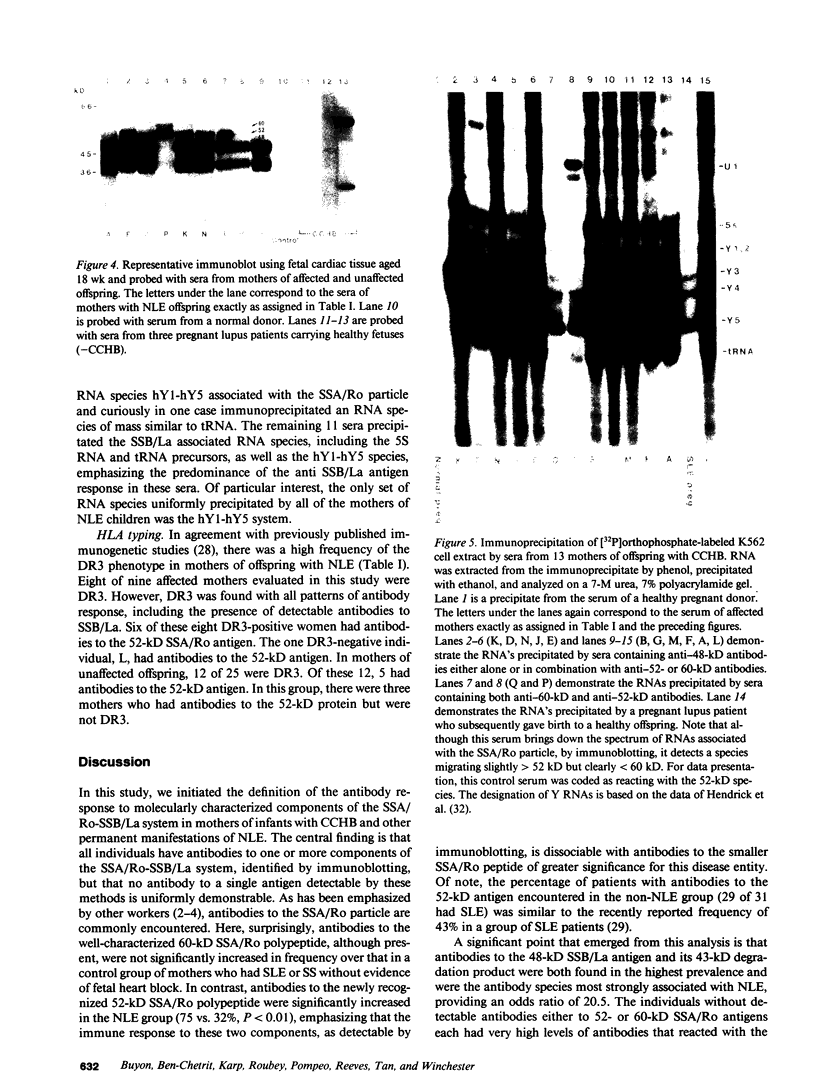
The molecular basis of autoantibody reactivity with components of the SSA/Ro-SSB/La particle exhibited by sera of mothers of infants with severe and permanent manifestations of neonatal lupus (NLE) was investigated using immunoblotting and immunoprecipitation. The characteristics of NLE that were studied included congenital complete heart block (CCHB), second degree heart block, and hepatic fibrosis. Antibodies specific for one or more components of the SSA/Ro-SSB/La particle were found in sera from all 20 mothers of permanently affected infants. However, no antibody specific for a single peptide of this particle was common to all sera. Using tissue extracts from a human cell substrate, 80% of these sera had antibodies to one or more components of the SSA/Ro particle demonstrable by immunoblotting. The predominant antibody response in the NLE group was to the newly recognized 52-kD SSA/Ro peptide component. In contrast, antibodies to the 60-kD SSA/Ro component although present, were the least represented and not significantly increased in frequency among mothers of these infants, compared with a group of 31 mothers with autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythromatosus (SLE) but who had healthy offspring. Antibodies directed to the 48-kD SSB/La antigen were demonstrated in 90% of the NLE mothers often accompanying antibodies against the 52-kD SSA/Ro component. The combination of antibodies to 48- and 52-kD structures was significantly increased in the NLE group, with an odds ratio of 35. The type of cell or tissue substrate was shown to influence detectability of antibodies. The 52-kD SSA/Ro peptide and the 48-kD SSB/La peptide were abundant in cardiac tissues from fetuses aged 18-24 wk, further supporting the possible relevance of these peptides to heart block.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Chetrit E., Chan E. K., Sullivan K. F., Tan E. M. A 52-kD protein is a novel component of the SS-A/Ro antigenic particle. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1560–1571. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierman F. Z., Baxi L., Jaffe I., Driscoll J. Fetal hydrops and congenital complete heart block: response to maternal steroid therapy. J Pediatr. 1988 Apr;112(4):646–648. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buyon J., Roubey R., Swersky S., Pompeo L., Parke A., Baxi L., Winchester R. Complete congenital heart block: risk of occurrence and therapeutic approach to prevention. J Rheumatol. 1988 Jul;15(7):1104–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buyon J., Szer I. Passively acquired autoimmunity and the maternal fetal dyad in systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1986;9(2-3):283–304. doi: 10.1007/BF02099027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. C., Keene J. D. Isolation and analysis of cDNA clones expressing human lupus La antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2115–2119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Francoeur A. M., Tan E. M. Epitopes, structural domains, and asymmetry of amino acid residues in SS-B/La nuclear protein. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3744–3749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng J. S., Bair L. W., Jr, Shen-Schwarz S., Ramsey-Goldman R., Medsger T., Jr Localization of Ro (SS-A) antigen in the cardiac conduction system. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Nov;30(11):1232–1238. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng J. S., Sontheimer R. D., Gilliam J. N. Expression of Ro/SS-A antigen in human skin and heart. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Nov;85(5):412–416. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng J. S., Sontheimer R. D., Gilliam J. N. Molecular characteristics of SS-B/La and SS-A/Ro cellular antigens. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Feb;84(2):86–90. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12274950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Robinson C. A., Curd J. G., Kozin F., Howell F. V. Sjögren's syndrome. Proposed criteria for classification. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 May;29(5):577–585. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco H. L., Weston W. L., Peebles C., Forstot S. L., Phanuphak P. Autoantibodies directed against sicca syndrome antigens in the neonatal lupus syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981 Jan;4(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(81)70011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Wolin S. L., Rinke J., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins are a subclass of La ribonucleoproteins: further characterization of the Ro and La small ribonucleoproteins from uninfected mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1138–1149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFeber W. P., Norris D. A., Ryan S. R., Huff J. C., Lee L. A., Kubo M., Boyce S. T., Kotzin B. L., Weston W. L. Ultraviolet light induces binding of antibodies to selected nuclear antigens on cultured human keratinocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1545–1551. doi: 10.1172/JCI111569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. A., Bias W. B., Arnett F. C., Jr, Huff J. C., Norris D. A., Harmon C., Provost T. T., Weston W. L. Immunogenetics of the neonatal lupus syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Nov;99(5):592–596. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-5-592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Hardin J. A., Steitz J. A. Two novel classes of small ribonucleoproteins detected by antibodies associated with lupus erythematosus. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.6164096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieu T. S., Newkirk M. M., Capra J. D., Sontheimer R. D. Molecular characterization of human Ro/SS-A antigen. Amino terminal sequence of the protein moiety of human Ro/SS-A antigen and immunological activity of a corresponding synthetic peptide. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):96–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI113607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litsey S. E., Noonan J. A., O'Connor W. N., Cottrill C. M., Mitchell B. Maternal connective tissue disease and congenital heart block. Demonstration of immunoglobulin in cardiac tissue. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 10;312(2):98–100. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501103120206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin M. D., Bonfa E., Elkon K., Druzin M. L. Neonatal lupus risk to newborns of mothers with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jun;31(6):697–701. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez-Roldan A., Szer I., Toguchi T., Cuttner J., Winchester R. Association of certain Ia allotypes with the occurrence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Recognition by a monoclonal anti-Ia reagent of a susceptibility determinant not in the DR series. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1872–1877. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rader M. D., O'Brien C., Liu Y. S., Harley J. B., Reichlin M. Heterogeneity of the Ro/SSA antigen. Different molecular forms in lymphocytes and red blood cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1293–1298. doi: 10.1172/JCI114014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H., Fisher D. E., Wisniewolski R., Gottlieb A. B., Chiorazzi N. Psoriasis and Raynaud's phenomenon associated with autoantibodies to U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 10;315(2):105–111. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607103150207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke J., Steitz J. A. Precursor molecules of both human 5S ribosomal RNA and transfer RNAs are bound by a cellular protein reactive with anti-La lupus antibodies. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosario M. O., Fox O. F., Koren E., Harley J. B. Anti-Ro (SS-A) antibodies from Ro (SS-A)-immunized mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Feb;31(2):227–237. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. S., Maddison P. J., Taylor P. V., Esscher E., Scott O., Skinner R. P. Connective-tissue disease, antibodies to ribonucleoprotein, and congenital heart block. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jul 28;309(4):209–212. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307283090403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess A. D., Peterson M. G., McNeilage L. J., Whittingham S., Coppel R. L. Characteristics and epitope mapping of a cloned human autoantigen La. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3212–3218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. M., Lane A. T., Barnett N. K., Bias W. B., Arnett F. C., Provost T. T. Neonatal lupus erythematosus. A clinical, serological and immunogenetic study with review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1984 Nov;63(6):362–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. The Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins: identification of the antigenic protein and its binding site on the Ro RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1996–2000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]