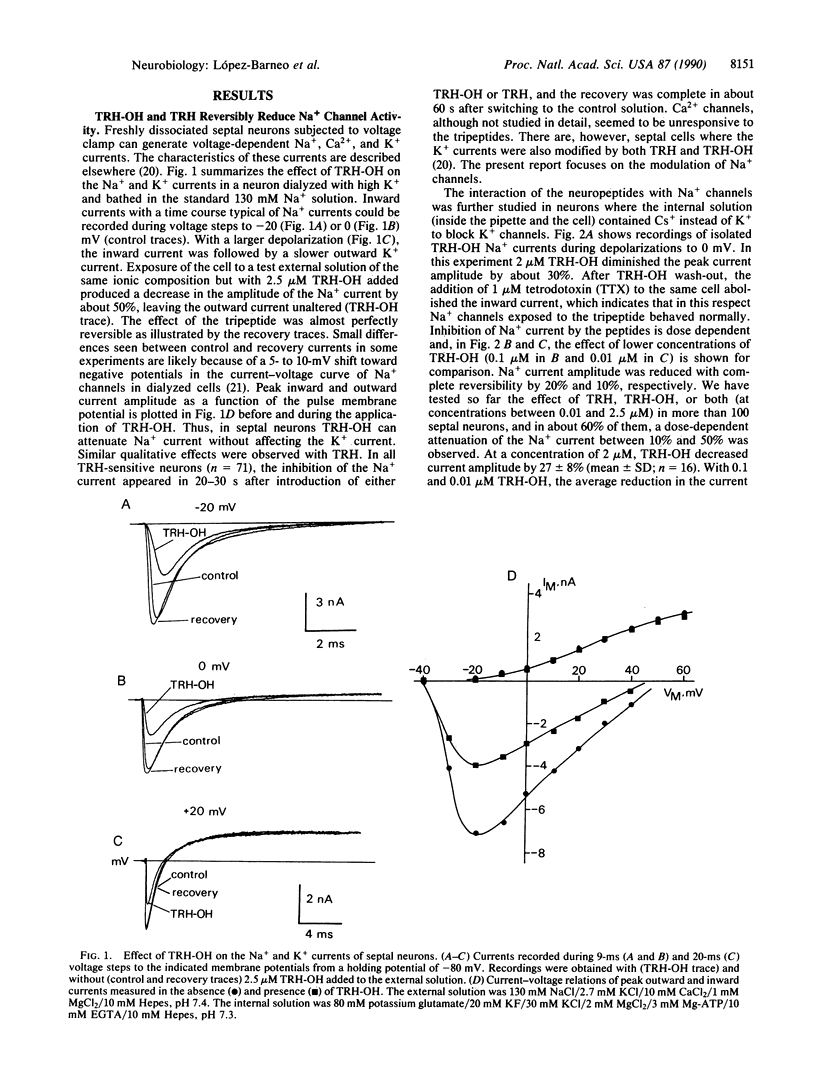
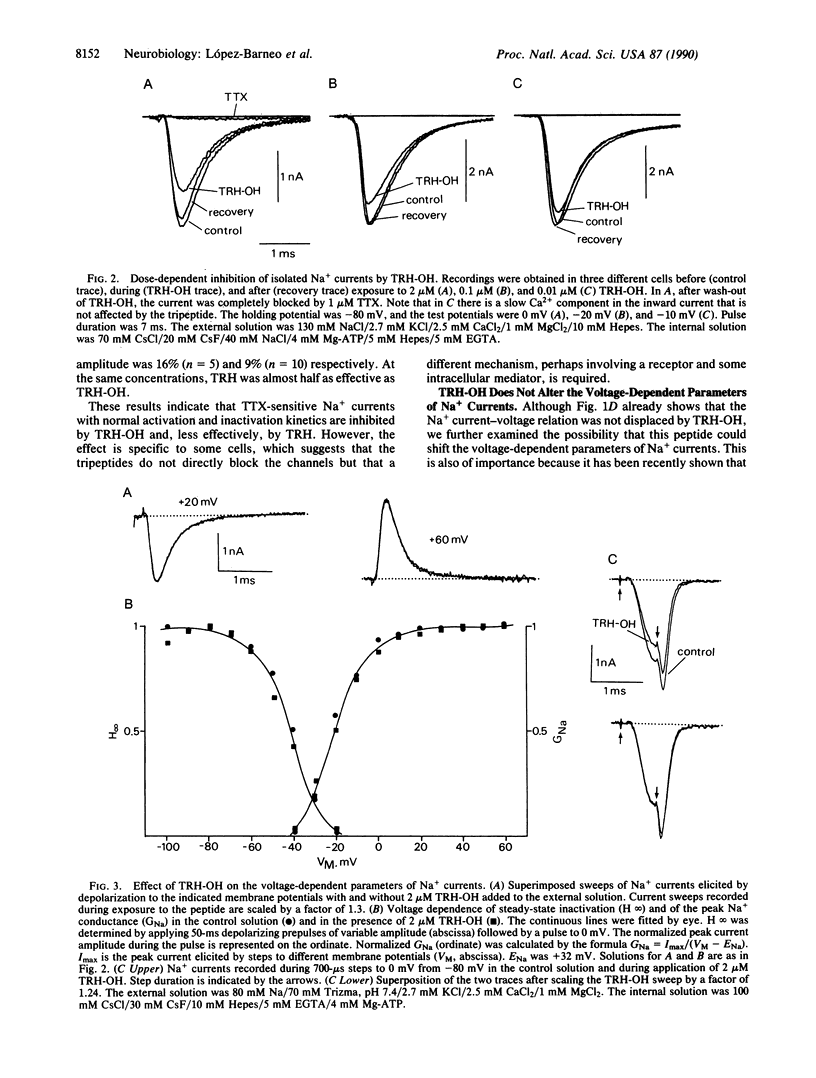
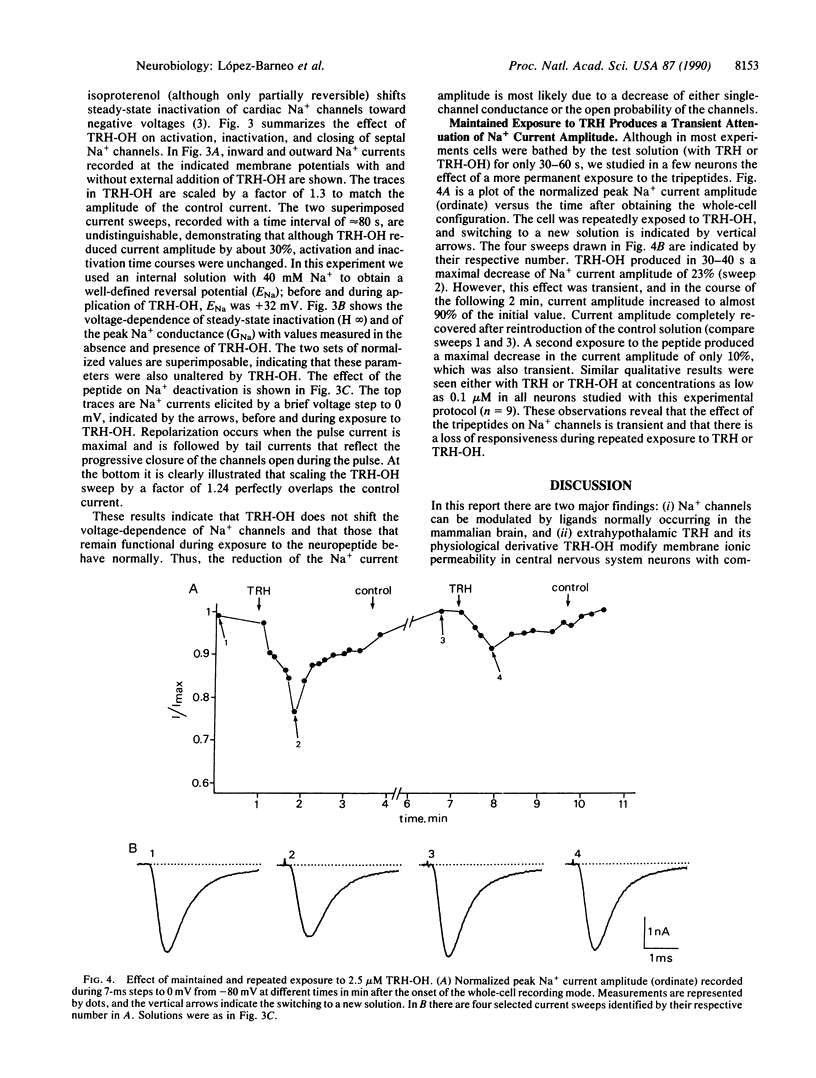
Abstract
The interaction of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and its physiological metabolite TRH-OH with Na+ channels was studied in enzymatically dissociated guinea pig septal neurons by using the whole-cell variant of the patch-clamp technique. In about 60% of the cells tested, the neuropeptides at concentrations between 0.01 and 2.5 microM produced a dose-dependent reversible attenuation of Na+ currents. With 2 microM TRH-OH, peak Na+ current amplitude was reduced by 20-50% (27 +/- 8%, mean +/- SD; n = 16), whereas at the same concentration TRH was approximately half as effective as TRH-OH. In the presence of the tripeptides, the voltage-dependent parameter of the Na+ current were unaltered. TRH-induced reduction of Na+ current amplitude was transient and recovered almost completely during maintained exposure to the peptides. In addition, the response to either TRH-OH or TRH decreased with repeated treatment. Our results demonstrate that neuronal Na+ channels can be modulated by naturally occurring neuropeptides.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez de Toledo G., López-Barneo J. Ionic basis of the differential neuronal activity of guinea-pig septal nucleus studied in vitro. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:399–415. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D. Voltage-gated and agonist-mediated rises in intracellular Ca2+ in rat clonal pituitary cells (GH3) held under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:143–158. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekin M. S., Richerson G. B., Getting P. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone induces rhythmic bursting in neurons of the nucleus tractus solitarius. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.3925552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubinsky J. M., Oxford G. S. Dual modulation of K channels by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in clonal pituitary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4282–4286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. M., Fox A. P., Krasne S. Membrane patches and whole-cell membranes: a comparison of electrical properties in rat clonal pituitary (GH3) cells. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:565–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori T., Yamasaki M., Asami T., Koga H., Kiyohara T. Responses of anterior hypothalamic-preoptic thermosensitive neurons to thyrotropin releasing hormone and cyclo(His-Pro). Neuropharmacology. 1988 Sep;27(9):895–901. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamour Y., Senut M. C., Dutar P., Bassant M. H. Neuropeptides and septo-hippocampal neurons: electrophysiological effects and distributions of immunoreactivity. Peptides. 1988 Nov-Dec;9(6):1351–1359. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan I. B. Modulation of ion channels in neurons and other cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:119–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Armstrong C. M. Na and Ca channels in a transformed line of anterior pituitary cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):371–394. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley J. E. Extrahypothalamic thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) -- its distribution and its functions. Life Sci. 1979 Oct 29;25(18):1539–1550. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90435-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A. Excitatory action of TRH on spinal motoneurones. Nature. 1977 Jan 20;265(5591):242–243. doi: 10.1038/265242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin S., Saperstein R., Jackson I. M., Boyd A. E., 3rd, Patel Y. Hypothalamic hormones. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:389–424. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud L. P., Blume H. W., Pittman Q. J., Lamour Y., Tan A. T. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone selectively depresses glutamate excitation of cerebral cortical neurons. Science. 1979 Sep 21;205(4412):1275–1277. doi: 10.1126/science.224461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud L. P., Martin J. B., Brazeau P. Depressant action of TRH, LH-RH and somatostatin on activity of central neurones. Nature. 1975 May 15;255(5505):233–235. doi: 10.1038/255233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):569–574. doi: 10.1038/301569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert B., VanDongen A. M., Kirsch G. E., Brown A. M. Beta-adrenergic inhibition of cardiac sodium channels by dual G-protein pathways. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):516–519. doi: 10.1126/science.2547248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simasko S. M., Horita A. Localization of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) receptors in the septal nucleus of the rat brain. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 2;296(2):393–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ureña J., López-López J., González C., López-Barneo J. Ionic currents in dispersed chemoreceptor cells of the mammalian carotid body. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):979–999. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ureña J., Mateos J. C., López-Barneo J. Low-cost system for automated acquisition, display and analysis of transmembrane ionic currents. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1989 Jan;27(1):94–98. doi: 10.1007/BF02442178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



