Abstract
This study deals with the design and synthesis of a series of novel 4-methoxy-substituted and 5-methyl-substituted (3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactones. The newly synthesized compounds were characterized by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), 13C-NMR, mass spectrometry, and elemental analysis. All the derivatives were subjected to in vitro cytotoxicity screening against HEPG-2 (human liver carcinoma), SGC-7901 (human gastric carcinoma), and LS174T (human colon carcinoma), by using the MTT assay. The results revealed that several of the 4-methoxy-substituted compounds exhibited potent cytotoxicity. Among these, compound 12e showed the highest activity against cancer cells which 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) values were in the range of 6.1–9.2 μM with low toxicity on normal human hepatocyte. Preliminary investigation of possible mechanisms of action of compound 12e against HEPG-2 cells indicated possible induction of apoptosis, as determined by morphological observations and Annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) double staining, in addition to apparent dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), as measured by 5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethyl-imidacarbocyanine iodide (JC-1) staining in combination with the activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 by Western blot analysis. Overall, the data suggest that compound 12e may be a promising potential anti-cancer agent that could act primarily by inducing apoptosis through the mitochondria-mediated intrinsic pathway in human hepatoma cells.
Keywords: 4-methoxy-substituted and 5-methyl-substituted (3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactones; synthesis; cytotoxic activity; apoptosis
Introduction
Cancer is now a leading cause of mortality worldwide and was responsible for 8.2 million deaths in 2012.1 In addition to surgery and radiation therapy, chemotherapy remains an important and widely used treatment option for many human malignancies.2,3 Although considerable advances have been made in chemotherapy over the past several decades, there is still an urgent need for novel chemotherapeutic agents with higher efficacy and lower toxicity. It is well known that a number of clinically useful chemotherapeutic agents such as taxol, topotecan, and irinotecan have been derived from naturally occurring small organic molecules.4
Coumarins comprise a large class of natural compounds found throughout the plant kingdom. Natural and synthetic coumarin derivatives exhibit a wide range of pharmacological actions, such as antimicrobial, antiviral, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticoagulant, and central nervous system activities, and are therefore considered to be ideal lead compounds for drug development.5–7 Khellactone, a member of the coumarin family, possesses a pyrano ring fused at positions seven and eight of the coumarin molecular skeleton and is regarded as a biosynthetic pioneer found originally in plants with the angular-type pyranocoumarin. Natural khellactone coumarins have been mainly isolated from Peucedanum species.8–10 In the past 2 decades, khellactone and its derivatives have attracted great interest in medicinal chemistry owing to their wide range of biological effects including antiviral activity,11 inhibition of platelet aggregation,12 calcium antagonist activity,13 and inhibition of P-glycoprotein.14,15 In particular, attention has been focused primarily on their anti-HIV activity, and some khellactone derivatives have been found to demonstrate extremely potent inhibitory activity against HIV-1 replication.16,17 It is notable that khellactone coumarins contain two chiral carbons of C-3′ and C-4′ (Figure 1), and previous studies showed that 3′R- and 4′R-configured khellactone derivatives are critical for anti-HIV activity.18–20
Figure 1.
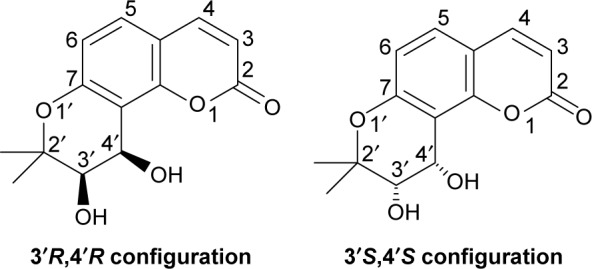
Structures of cis-khellactone with 3′R,4′R and 3′S,4′S configuration.
In previous studies, we synthesized the amount of 4-methyl-(3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone derivatives by using a chiral catalyst of (DHQD)2-PYR. Some of the synthesized derivatives exhibited considerable inhibition of human cancer cells, and this finding prompted us to further explore cis-khellactone derivatives with the 3′S,4′S configuration as new potential anticancer agents.21 This study deals with the design and synthesis of a new series of substituted (3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone. The derivatives were evaluated for their in vitro antitumor activity against three human cancer cell lines (HEPG-2, SGC-7901, and LS174T). In addition, compound 12e, which exhibited the highest activity against the HEPG-2 cancer cell line, was further investigated in an attempt to obtain insight into the primary mechanism of antitumor action of this class of agents.
Materials and methods
Materials
Melting points were measured on an XT-4 melting point apparatus without correction. NMR spectra were generated on a BRUKER AVANCE-600 spectrometer and obtained as CDCl3 or DMSO-d6 solutions (600 MHz for 1H and 150 MHZ for 13C). Chemical shifts are reported as δ values in ppm relative to TMS, and J values are expressed in Hertz. ESI mass spectra were determined in an API QTRAP 3200 LC-MS spectrometer. The elemental analyses were performed by using an Elementar Vario-III CHN analyzer and were within ±0.4% of theoretical values. Optical rotations were measured on Perkin-Elmer 241 polarimeter in a 1-dm cell. The Chiralpak AS-H chiral HPLC analysis by using Shimadzu LC-10A instrument was applied to detect the ee values of the compounds. TLC analysis of reaction mixtures was carried out on silica gel GF-254 (Qingdao Ocean Chemical Factory, Qingdao, China), and the identification was performed under ultraviolet (UV) light. Silica gel (200–300 mesh) used in column chromatography was provided by Tsingtao Marine Chemistry Co. Ltd (Qingdao, China). Chiral catalyst (DHQD)2-PYR was procured from Sigma-Aldrich Co. (St Louis, MO, USA). Other commercial chemicals were purchased from Aladdin Chemicals Co. (Shanghai, China) and used without further purification. Compounds 2, 3, 4, 6, and 7 were synthesized according to previously reported procedure.18
Synthesis of compounds
General method for the preparation of substituted seselins (8, 9)
Compounds 8 and 9 were synthesized according to previous literature, and the melting points of these two compounds were reported to be 167°C–168°C and 143°C–144°C, respectively.18 To a stirred solution of substituted 7-hydroxycoumarins 4, 7 (10 mmol) and potassium carbonate (3.45 g, 25 mmol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (20 mL), potassium iodide (1.66 g, 10 mmol) was added, followed by adding excess 3-chloro-3-methyl-1-butyne (6 mL). The stirred reaction mixture was warmed at 70°C–80°C for 72 h. Then, the solution was filtered and the solvent was evaporated in vacuo. The residue was directly added in 20 mL of N,N-diethylaniline, refluxed for 15 h. The mixture cooled down was diluted by 20 mL ethyl acetate, and successively washed using 10% aqueous hydrochloric acid, water, and brine. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The crude product was further purified by silica gel column chromatography (PE/ethyl acetate: 10/1) to obtain compounds 8 and 9.
4-Methoxyseselin (8)
Light yellow solid; yield, 41%; m.p., 162°C–164°C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.44 (s, 6H, C-2′-CH3), 3.94 (s, 3H, C-4-OCH3), 5.53 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.68 (d, 1H, J =10.02 Hz, H-3′), 6.68 (d, 1H, J =8.68 Hz, H-6), 6.85 (d, 1H, J =10.02 Hz, H-4′), 7.51 (d, 1H, J =8.68 Hz, H-5). MS (ESI) m/z 280.9 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C15H14O4: C, 69.76%; H, 5.46%. Found: C, 69.71%; H, 5.40%.
5-Methylseselin (9)
White solid; yield, 21%; m.p., 145°C–146°C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.46 (s, 6H, C-2′-CH3), 2.43 (s, 3H, C-5-CH3), 5.66 (d, 1H, J =10.05 Hz, H-3′), 6.22 (d, 1H, J =9.69 Hz, H-3), 6.58 (s, 1H, H-6), 6.86 (d, 1H, J =10.05 Hz, H-4′), 7.80 (d, 1H, J =9.69 Hz, H-4). MS (ESI) m/z 265.0 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C15H14O3: C, 74.36%; H, 5.82%. Found: C, 74.40%; H, 5.89%.
General procedure for the preparation of substituted (3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone (10, 11)
Potassium carbonate (105 mg, 0.75 mmol) was added to a solution of potassium ferricyanide (246 mg, 0.75 mmol) in tert-butanol/water (1:1, v/v) (5 mL), and the mixture was stirred for 5 min. Potassium osmate (2 mg, 0.005 mmol) and (DHQD)2-PYR (4.4 mg, 0.005 mmol) were then added, and continuously stirred for 15 min. Then, the mixture was cooled to 0°C and methane sulfonamide (24 mg, 0.25 mmol) was added under stirring. When the color of solution turned from a light yellow to an orange, substituted seselin (0.25 mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred at 0°C for approximately 24 h. TLC analysis monitored the progress of reaction. After completion of the reaction as indicated on TLC, the contents such as dichloromethane (2.5 mL), sodium pyro-sulfite (1 g), and water (2.5 mL) were added. The mixture was continuously stirred for another 4 h at room temperature, and then extracted with dichloromethane (3×15 mL). The organic layer was dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate and evaporated in vacuo. The crude product was purified by column chromatography using the PE/ethyl acetate (6:1, v/v) to obtain substituted (3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone 10 and 11.
4-Methoxy-(3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone (10)
White solid; yield, 51%; m.p., 218°C–220°C; [α]D 20=−42.6 (c 0.3, CHCl3). ee =86%, Chiral Pak AS-H column eluting with hexane/isopropanol (90:10, v:v), flow rate =0.8 mL/min, wavelength =323 nm, tR (minor) =26.21 min, tR (major) =38.91 min; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6, ppm) δ 1.34 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.36 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 3.60 (br, 1H, H-4′), 3.96 (s, 3H, C-4-OCH3), 4.88 (br, 1H, H-3′), 5.19 (br, 2H, OH ×2), 5.72 (s, 1H, H-3), 6.73 (d, 1H, J =8.79 Hz, H-6), 7.57 (d, 1H, J =8.79 Hz, H-5). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 20.99, 26.87, 56.78, 60.24, 71.18, 78.77, 87.13, 107.68, 111.65, 113.44, 123.07, 153.13, 156.08, 161.96, 166.34. MS (ESI) m/z 314.8 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C15H16O6: C, 61.64%; H, 5.52%. Found: C, 61.73%; H, 5.44%.
5-Methyl-(3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone (11)
White solid; yield, 46%; m.p., 178°C–180°C; [α]D 20=−41.5 (c 0.2, CHCl3). ee =87%, Chiral Pak AS-H column eluting with hexane/isopropanol (90:10, v:v), flow rate =0.8 mL/min, wavelength =323 nm, tR (minor) =32.58 min, tR (major) = 79.50 min; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6, ppm) δ 1.33 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.35 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 2.40 (s, 3H, C-5-CH3), 3.58 (br m, 1H, H-4′), 4.86 (br m,1H, H-3′), 5.14 (br, 2H, OH ×2), 6.24 (d, 1H, J =9.67 Hz, H-3), 6.61 (s, 1H, H-6), 8.05 (d, 1H, J =9.67 Hz, H-4). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 17.80, 21.02, 26.88, 60.05, 71.28, 78.70, 109.62, 110.86, 111.04, 114.61, 137.20, 141.72, 154.49, 155.33, 160.20; MS (ESI) m/z 277.0 ([M+H]+). Anal. Calc for C15H16O5: C, 65.21%; H, 5.84%. Found: C, 65.14%; H, 5.89%.
General method for the preparation of substituted (±)-cis-khellactone (10′, 11′)
Substituted seselin (1 mmol) was added to a mixture solution of N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide monohydrate (0.129 g, 1.1 mmol) and osmium tetroxide (10 mg, 0.04 mmol) which were dissolved in tert-butanol/tetrahydrofuran/water (10/3/1, 10 mL); the mixture was stirred for 24 h at room temperature. Then, saturated sodium hydrogen sulfite solution was added (80 mL) to keep stirring for another 2 h and was diluted with dichloromethane (80 mL). The organic layer was dried by using sodium sulfate and then evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure. Purification by column chromatography (PE/acetone: 5/1) obtained the substituted (±)-cis-khellactone 10′ and 11′.
4-Methoxy-(±)-cis-khellactone (10′)
White solid; yield, 63%; m.p., 228°C–230°C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6, ppm) δ 1.34 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.36 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 3.58 (br, 1H, H-4′), 3.97 (s, 3H, C-4-OCH3), 4.89 (br, 1H, H-3′), 5.20 (br, 2H, OH ×2), 5.72 (s, 1H, H-3), 6.74 (d, 1H, J =8.79 Hz, H-6), 7.58 (d, 1H, J =8.79 Hz, H-5). MS (ESI) m/z 314.6 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C15H16O6: C, 61.64%; H, 5.52%. Found: C, 61.71%; H, 5.58%.
5-Methyl-(±)-cis-khellactone (11′)
White solid; yield, 58%; m.p., 185°C–187°C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6, ppm) δ 1.33 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.35 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 2.40 (s, 3H, C-5-CH3), 3.57 (br m, 1H, H-4′), 4.85 (br m,1H, H-3′), 5.12 (br, 2H, OH ×2), 6.22 (d, 1H, J =9.67 Hz, H-3), 6.60 (s, 1H, H-6), 8.03 (d, 1H, J =9.67 Hz, H-4). MS (ESI) m/z 277.0 ([M+H]+). Anal. Calc for C15H16O5: C, 65.21%; H, 5.84%. Found: C, 65.15%; H, 5.91%.
General procedure for the preparation of (3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone derivatives (12a–g, 13a–g)
Excess acylating agent was added to a solution of substituted (3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone (0.2 mmol) in anhydrous pyridine (1 mL) and dichloromethane (2 mL) at 0°C, and refluxed until completed by TLC monitor. The mixture was filtered, and the filtrate was evaporated in vacuo. Purification by column chromatography (PE/acetone: 10/1) obtained target compounds.
3′S,4′S-di-O-acetyl-4-methoxy-(−)-cis-khellactone (12a)
White solid; yield, 50%; m.p., 213°C–215°C; [α]D 20=+19.8 (c 0.2, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6, ppm) δ 1.40 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.44 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 2.10 (s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.12 (s, 3H, CH3CO), 3.95 (s, 3H, C-4-OCH3), 5.29 (d, 1H, J =4.87 Hz, H-3′), 5.55 (s, 1H, H-3), 6.51 (d, 1H, J =4.87 Hz, H-4′), 6.78 (d, 1H, J =8.89 Hz, H-6), 7.69 (d, 1H, J =8.89 Hz, H-5). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 20.55, 20.59, 22.52, 24.89, 56.19, 60.99, 70.25, 77.36, 87.63, 106.50, 109.01, 113.81, 124.43, 153.13, 156.95, 161.96, 166.50, 169.92. MS (ESI) m/z 398.8 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C19H20O8: C, 60.63%; H, 5.36%. Found: C, 60.61%; H, 5.32%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-methoxyacetyl-4-methoxy-(−)-cis-khellactone (12b)
White solid; yield, 43%; m.p.,116°C–118°C; [α]D 20=+6.5 (c 0.2, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.42 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.43 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 3.46 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.47 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.95 (s, 3H, C-4-OCH3), 4.05 (m, 4H, 2× CH2), 5.42 (d, 1H, J =4.85 Hz, H-3′), 5.53 (s, 1H, H-3), 6.60 (d, 1H, J =4.85 Hz, H-4′), 6.79 (d, 1H, J =8.89 Hz, H-6), 7.70 (d, 1H, J =8.89 Hz, H-5). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 22.42, 24.91, 56.25, 59.41, 59.47, 61.44, 69.32, 69.54, 70.54, 87.64, 105.89, 109.09, 113.88, 124.77, 153.06, 156.85, 161.80, 166.46, 169.56, 169.69. MS (ESI) m/z 458.8 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C21H24O10: C, 57.80%; H, 5.54%. Found: C, 57.76%; H, 5.48%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-benzoyl-4-methoxy-(−)-cis-khellactone (12c)
White solid; yield, 42%; m.p., 242°C–244°C; [α]D 20=−3.3 (c 0.1, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.51 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.64 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 3.93 (s, 3H, C-4-OCH3), 5.50 (1H, s, H-3), 5.67 (d, 1H, J =4.92 Hz, H-3′), 6.88 (d, 1H, J =8.92 Hz, H-6), 6.95 (d, 1H, J =4.92 Hz, H-4′), 7.33 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.51 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.75 (d, 1H, J =8.92 Hz, H-5), 7.87 (m, 4H, Ar-H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 22.37, 25.61, 56.18, 61.24, 71.17, 77.43, 87.85, 106.84, 109.08, 113.91, 124.75, 128.19, 128.31, 129.31, 129.78, 132.79, 133.22, 153.35, 157.09, 161.71, 165.25, 166.31. MS (ESI) m/z 522.8 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C29H24O8: C, 69.59%; H, 4.83%. Found: C, 69.62%; H, 4.77%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-(2-methoxybenzoyl)-4-methoxy-(−)-cis-khellactone (12d)
White solid; yield, 38%; m.p., 167°C–169°C; [α]D 20=−9.6 (c 0.2, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.52 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.58 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 3.70 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.76 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.91 (s, 3H, C-4-OCH3), 5.50 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.65 (d, 1H, J =4.94 Hz, H-3′), 6.81 (d, 1H, J =8.89 Hz, H-6), 6.86 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 6.92 (d, 1H, J =4.94 Hz, H-4′), 7.38 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.69 (d, 1H, J =8.89 Hz, H-5), 7.69 (m, 2H, Ar-H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 22.07, 25.67, 55.64, 55.68, 56.12, 60.93, 70.94, 77.53, 87.67, 107.22, 108.84, 111.79, 113.80, 119.35, 119.92, 119.95, 120.64, 124.43, 131.30, 132.02, 132.80, 133.57, 153.29, 157.05, 158.74, 159.37, 161.79, 164.76, 165.20, 166.30. MS (ESI) m/z 582.7 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C31H28O10: C, 66.42%; H, 5.03%. Found: C, 66.35%; H, 4.94%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-4-methoxy-(−)-cis-khellactone (12e)
White solid; yield, 48%; m.p., 221°C–222°C; [α]D 20=−33.3 (c 0.1, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.57 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.58 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 3.95 (s, 3H, C-4-OCH3), 5.54 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.71 (d, 1H, J =4.92 Hz, H-3′), 6.84 (d, 1H, J =8.96 Hz, H-6), 6.93 (d, 1H, J =4.92 Hz, H-4′), 7.20 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.36 (m, 5H, Ar-H) 7.72 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.73 (d, 1H, J =8.96 Hz, H-5), 7.86 (m, 1H, Ar-H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 22.13, 25.86, 56.22, 61.99, 72.00, 77.42, 87.81, 106.61, 109.05, 113.99, 124.89, 126.49, 126.62, 129.65, 130.46, 130.83, 131.12, 132.05, 132.69, 133.01, 133.52, 153.31, 157.03, 161.75, 164.75, 165.18, 166.42. MS (ESI) m/z 592.6 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C29H22Cl2O8: C, 61.17%; H, 3.89%. Found: C, 61.15%; H, 3.81%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-(3-chlorobenzoyl)-4-methoxy-(−)-cis-khellactone (12f)
White solid; yield, 43%; m.p., 200°C–201°C; [α]D 20=−9.6 (c 0.1, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.50 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.62 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 3.94 (s, 3H, C-4-CH3O), 5.51 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.65 (d, 1H, J =4.94 Hz, H-3′), 6.89 (d, 1H, J =8.92 Hz, H-6), 6.91 (d, 1H, J =4.94 Hz, H-4′), 7.30 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.50 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.77 (d, 1H, J =8.92 Hz, H-5), 7.78 (m, 4H, Ar-H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 22.48, 25.36, 56.24, 61.67, 71.38, 77.29, 87.85, 106.23, 109.19, 113.97, 124.99, 127.89, 127.99, 129.65, 129.70, 129.77, 130.84, 131.30, 133.05, 133.44, 134.39, 134.57, 153.25, 156.99, 161.70, 164.15, 164.20, 166.33. MS (ESI) m/z 592.1 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C29H22Cl2O8: C, 61.17%; H, 3.89%. Found: C, 61.20%; H, 3.84%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-4-methoxy-(−)-cis-khellactone (12g)
White solid; yield, 46%; m.p., 273°C–275°C; [α]D 20=−22.4 (c 0.2, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.50 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.60 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 3.93 (s, 3H, C-4-OCH3), 5.50 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.64 (d, 1H, J =4.98 Hz, H-3′), 6.88 (d, 1H, J =8.99 Hz, H-6), 6.89 (d, 1H, J =4.98 Hz, H-4′), 7.32 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.75 (d, 1H, J =8.99 Hz, H-5), 7.79 (m, 4H, Ar-H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 22.53, 25.35, 56.22, 61.66, 71.27, 77.36, 87.83, 106.40, 109.18, 113.93, 124.89, 128.65, 128.78, 131.07, 139.44, 139.88, 153.29, 157.03, 161.66, 164.42, 164.49, 166.33. MS (ESI) m/z 592.3 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C29H22Cl2O8: C, 61.17%; H, 3.89%. Found: C, 61.13%; H, 3.82%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-acetyl-5-methyl-(−)-cis-khellactone (13a)
White solid; yield, 48%; m.p., 202°C–204°C; [α]D 20=8.4 (c 0.2, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.39 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.43 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 2.09 (s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.11 (s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.45 (s, 3H, C-5-CH3), 5.27 (d, 1H, J =4.74 Hz, H-3′), 6.24 (d, 1H, J =9.72 Hz, H-3), 6.49 (d, 1H, J =4.74 Hz, H-4′), 6.65 (s, 1H, H-6), 7.79 (d, 1H, J =9.72 Hz, H-4). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 18.37, 20.57, 20.61, 22.54, 24.93, 60.87, 70.33, 77.34, 104.69, 111.73, 112.45, 115.27, 137.93, 140.18, 154.44, 156.14, 159.86, 169.93. MS (ESI) m/z 382.7 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C19H20O7: C, 63.33%; H, 5.59%. Found: C, 63.30%; H, 5.53%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-methoxyacetyl-5-methyl-(−)-cis-khellactone (13b)
White solid; yield, 43%; m.p., 117°C–118°C; [α]D 20=11.4 (c 0.2, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.41 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.42 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 2.45 (s, 3H, C-5-CH3), 3.45 (3H, s, OCH3), 3.46 (3H, s, OCH3), 4.08 (4H, m, 2× CH2), 5.39 (1H, d, J =4.82 Hz, H-3′), 6.22 (1H, d, J =9.76 Hz, H-3), 6.57 (1H, d, J =4.82 Hz, H-4′), 6.65 (1H, s, H-6), 7.78 (1H, d, J =9.76 Hz, H-4). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 18.40, 22.37, 25.00, 59.40, 59.44, 61.32, 69.35, 69.55, 70.68, 104.12, 111.78, 112.55, 115.32, 138.31, 140.17, 154.41, 156.05, 159.65, 169.54, 169.71. MS (ESI) m/z 442.8 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C21H24O9: C, 59.99%; H, 5.75%. Found: C, 59.94%; H, 5.81%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-benzoyl-5-methyl-(−)-cis-khellactone (13c)
White solid; yield, 41%; m.p., 208°C–210°C; [α]D 20=−14.3 (c 0.1, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.50 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.64 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 2.49 (s, 3H, C-5-CH3), 5.65 (d, 1H, J =4.93 Hz, H-3′), 6.18 (d, 1H, J =9.76 Hz, H-3), 6.75 (s, 1H, H-6), 6.93 (d, 1H, J =4.93 Hz, H-4′), 7.33 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.50 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.78 (d, 1H, J =9.76 Hz, H-4), 7.88 (m, 4H, Ar-H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 18.50, 22.36, 25.64, 61.06, 71.22, 77.38, 104.97, 111.75, 112.69, 115.36, 128.19, 128.31, 129.25, 129.76, 129.80, 132.81, 133.24, 138.27, 139.99, 154.59, 156.22, 159.63, 165.26, 165.30. MS (ESI) m/z 507.2 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C29H24O7: C, 71.89%; H, 4.99%. Found: C, 71.86%; H, 4.90%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-(2-methoxybenzoyl)-5-methyl-(−)-cis-khellactone (13d)
White solid; yield, 39%; m.p., 196°C–198°C; [α]D 20= −49.9 (c 0.2, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.51 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.58 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 2.46 (s, 3H, C-5-CH3), 3.71 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.78 (s, 3H, OCH3), 5.64 (d, 1H, J =4.95 Hz, H-3′), 6.20 (d, 1H, J =9.76 Hz, H-3), 6.68 (s, 1H, H-6), 6.88 (d, 1H, J =4.95 Hz, H-4′), 6.88 (m, 4H, Ar-H); 7.37 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.42 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.68 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.77 (d, 1H, J =9.76 Hz, H-4), 7.79 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 18.45, 22.12, 25.75, 55.67, 55.73, 60.83, 71.04, 77.56, 105.44, 105.48, 111.61, 111.79, 111.85, 112.55, 131.29, 132.06, 132.79, 132.84, 133.55, 133.61, 137.96, 139.94, 140.00, 154.62, 156.27, 158.77, 159.40, 159.67, 159.73, 164.80, 165.28. MS (ESI) m/z 567.1 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C31H28O9: C, 68.37%; H, 5.18%. Found: C, 68.33%; H, 5.26%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methyl-(−)-cis-khellactone (13e)
White solid; yield, 46%; m.p., 188°C–190°C; [α]D 20=−45.1 (c 0.2, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.57 (s, 6H, 2× C-2′-CH3), 2.47 (s, 3H, C-5-CH3), 5.69 (d, 1H, J =4.86 Hz, H-3′), 6.23 (d, 1H, J =9.77 Hz, H-3), 6.70 (s, 1H, H-6), 6.91 (d, 1H, J =4.86 Hz, H-4′), 7.20 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.36 (m, 5H, Ar-H), 7.72 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.79 (d, 1H, J =9.77 Hz, H-4), 7.86 (m, 1H, Ar-H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 18.46, 22.13, 25.92, 61.85, 72.09, 77.38, 104.79, 111.74, 112.68, 115.41, 126.48, 126.62, 130.49, 130.83, 131.06, 132.05, 132.69, 133.02, 133.51, 138.42, 140.07, 140.12, 154.60, 156.18, 159.62, 159.67, 164.75, 165.21; MS (ESI) m/z 576.7 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C29H22Cl2O7: C, 62.94%; H, 4.01%. Found: C, 62.91%; H, 4.09%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-(3-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methyl-(−)-cis-khellactone (13f)
White solid; yield, 43%; m.p., 190°C–192°C; [α]D 20=−9.9 (c 0.2, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.49 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.61 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 2.50 (s, 3H, C-5-CH3), 5.64 (d, 1H, J =4.95 Hz, H-3′), 6.20 (d, 1H, J =9.42 Hz, H-3), 6.75 (s, 1H, H-6), 6.89 (d, 1H, J =4.95 Hz, H-4′), 7.31 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.49 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.77 (d, 1H, J =9.42 Hz, H-4), 7.78 (m, 4H, Ar-H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 18.49, 22.51, 25.40, 61.59, 71.50, 77.30, 104.46, 111.89, 112.77, 115.42, 127.89, 127.97, 128.16, 129.63, 129.76, 130.12, 131.37, 133.03, 133.29, 133.43, 134.42, 134.59, 138.51, 140.04, 154.58, 156.19, 159.58, 164.17, 164.26; MS (ESI) m/z 576.6 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C29H22Cl2O7: C, 62.94%; H, 4.01%. Found: C, 62.96%; H, 4.05%.
3′S,4′S-di-O-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methyl-(−)-cis-khellactone (13g)
White solid; yield, 54%; m.p., 208°C–209°C; [α]D 20=−37.1 (c 0.2, CH2Cl2). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ 1.49 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 1.59 (s, 3H, C-2′-CH3), 2.49 (s, 3H, C-5-CH3), 5.62 (d, 1H, J =4.91 Hz, H-3′), 6.19 (d, 1H, J =9.92 Hz, H-3), 6.75 (s, 1H, H-6), 6.87 (d, 1H, J =4.91 Hz, H-4′), 7.32 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.78 (d, 1H, J =9.92 Hz, H-4), 7.79 (m, 4H, Ar-H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 18.48, 22.54, 25.39, 61.52, 71.35, 77.34, 104.60, 111.84, 112.75, 115.37, 127.68, 128.16, 128.27, 128.65, 128.78, 131.07, 131.41, 138.41, 139.44, 139.88, 139.99, 154.60, 156.19, 159.51, 164.43, 164.53; MS (ESI) m/z 576.7 ([M+Na]+). Anal. Calc for C29H22Cl2O7: C, 62.94%; H, 4.01%. Found: C, 62.91%; H, 4.03%.
Cell culture
HEPG-2 (human liver carcinoma), SGC-7901 (human gastric carcinoma), LS174T (human colon carcinoma), and HL-7702 (normal human hepatocyte) cell lines were obtained from the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, China Academy of Science. The cells were cultured in DMEM, supplemented with 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated FBS, 100 units/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin at 37°C in a humidified incubator containing 5% carbon dioxide. Cells in logarithmic growth phase were employed for further experiments.
In vitro cytotoxic activity
The potential cytotoxic activity of all the target compounds in vitro was assessed using the MTT assay. Briefly, cells were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 2×104 cells/well. After overnight incubation, the cells were exposed to different concentrations of compounds for 48 h at 37°C in the atmosphere of 5% CO2. Following 48 h of treatment, the cells of each well were stained with 25 μL of MTT (5 mg/mL) and were incubated for a further 4 h at 37°C. Then, the media were removed and shaken for 10 min by adding 150 μL DMSO to all the wells. The absorbance values at 570 nm were measured using a microplate reader (Model 680; Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). The IC50 values were calculated according to the equation for Boltzmann sigmoidal concentration response curve using the nonlinear regression fitting models (Prism Version 5; GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA).
Morphological analysis by AO/EB double staining
Morphological changes induced by compound 12e were observed by fluorescence microscopy using AO/EB. In brief, HEPG-2 cells were seeded at a density of 1×105 cells/well in six-well plates. After attachment, the cells were treated with compound 12e at 6.0, 12.0, and 24.0 μM for another 24 h; then, the mixture solution containing 100 mg/mL AO and EB was added for 10 min. The stained cells were washed twice in PBS and observed immediately under fluorescence microscopy (IX-51; Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
Annexin V-FITC/PI assay
HEPG-2 cells were seeded at a density of 1×105 cells/well in six-well plates and grown in 5% CO2 at 37°C for 24 h. Then, cells were exposed to 6.0, 12.0, and 24.0 μM of compound 12e for 48 h. After incubation, cells were collected and washed twice using cold PBS and resuspended in 200 μL of binding buffer at 1×106 cells/mL. Subsequently, the samples were incubated with 5 μL of Annexin V-FITC and PI in the dark for 15 min at room temperature and then analyzed by flow cytometry within 1 h on an FACS Calibur (BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Each sample had at least 10,000 cells. The experiment was performed three times.
Measurement of MMP
Changes in the MMP were measured using JC-1 dye. Briefly, at the end of the treatment with compound 12e (6.0, 12.0, and 24.0 μM) for 48 h, HEPG-2 cells were collected, washed in ice-cold PBS, and incubated with 10 μg/mL JC-1 for 30 min at 37°C in the dark. After incubation, the stained cells were transferred to a falcon tube and characterized by flow cytometry. The red/green fluorescence ratio of JC-1 was measured using fluorescent plate reader at 529 nm emission (green)/590 nm emission (red). The relative red/green fluorescence ratio in treated HEPG-2 cells was shown graphically as a percentage of red/green fluorescence ratio value of the control group (cells without treatment), which were considered to have 100% MMP.
Western blot analysis
HEPG-2 cells were treated with different concentrations of compound 12e for 48 h, then collected and washed twice with ice-cold PBS. Whole-cell extracts were prepared using RIPA lysis buffer, and protein concentrations were measured by BCA Protein Assay kit. Proteins (40 μg) were resolved on 10% SDS-PAGE gels along with the equal amount of protein molecular weight standards, followed by transferring onto nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were blocked in TBS-T with 5% nonfat milk for 1.5 h and incubated overnight with specific primary antibodies (for caspase-9, cleaved caspase-3, and β-actin) at 4°C, then incubated with secondary HRP-linked anti-rabbit antibody. Immunodetection was carried out using ECL detection kit. The relative levels of each signaling event to control β-actin were determined by densimetric scanning.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were repeated at least three times. The results are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. We used Graph Pad software prism 5.1 for one-way analysis, followed by the Dunnett’s test. A value of P<0.05 denoted statistical significance.
Results and discussion
Chemistry
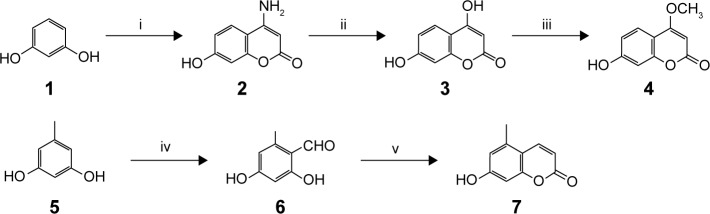
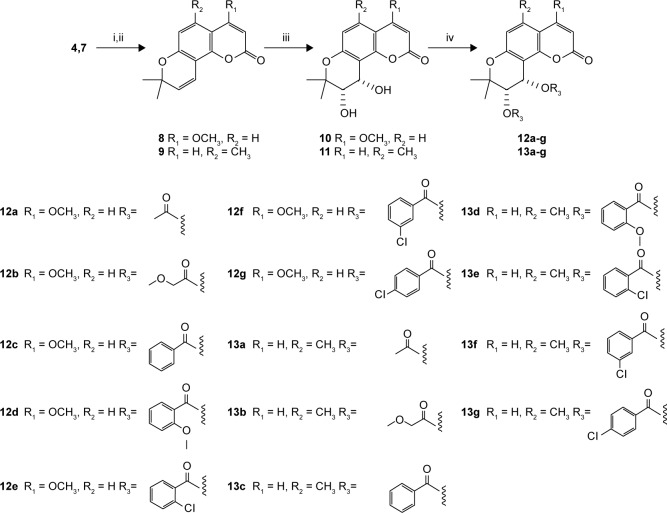
The title compounds derived in this study were obtained by applying the synthetic strategy described in Schemes 1 and 2. The condensation of 1,3-dihydroxybenzene (1) which is available by purchasing in the market with cyanoacetic acid in the presence of zinc chloride/hydrogen chloride produces 4-amino-7-hydroxycoumarin (2). Subsequent hydrolysis of 2 in 50% sulfuric acid produced 4,7-dihydroxycoumarin (3). Then, the 4-hydroxyl group of 3 was selectively methylated to produce 7-hydroxy-4-methoxycoumarin (4). To obtain 7-hydroxy-5-methylcoumarin (7), Wittig reaction and intramolecular cyclization, which consisted of the reaction of 3,5-dihydroxytoluene (5) with phosphorus oxychloride in excess N,N-dimethylformamide, were used to derive the coumarin nucleus from 2,4-dihydroxy-6-methylbenzaldehyde (6). Compound 6 was further reacted with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide (Ph3P = CHCOOEt) in dichloromethane at room temperature and refluxed by heating in xylene without purification to produce 7. In the presence of anhydrous potassium carbonate and potassium iodide, the substituted 7-hydroxycoumarins 4 and 7 were continuously reacted with 3-chloro-3-methyl-1-butyne in N,N-dimethylformamide and then thermal rearrangement occurred in boiling diethylaniline to form substituted seselins (8, 9) according to the procedures published previously.18 Similar to the process used in the previous asymmetric preparation of 4-methyl-(3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone, the substituted (−)-cis-khellactones 10, 11 with the 3′S,4′S configuration were successfully prepared by the reaction of osmium-catalyzed asymmetric dihydroxylation of the seselins 8 and 9 in the presence of a chiral catalyst, (DHQD)2-PYR.21 Target compounds 12a–g and 13a–g were synthesized by reacting the unpurified forms of compounds 10 and 11 with various acyl chlorides in the presence of appropriate pyridine, and dichloromethane used as solvent, adapting a previously reported procedure.18
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of substituted 7-hydroxycoumarins 4 and 7.
Notes: Reagents and conditions: (i) cyanoacetic acid, zinc chloride/hydrogen chloride; (ii) 50% sulfuric acid; (iii) methanol/sulfuric acid; (iv) N,N-diethylaniline/phosphorus oxychloride; (v) Ph3P=CHCOOEt.
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of (3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone derivatives (12–13).
Notes: Reagents and conditions: (i) 3-chloro-3-methyl-1-butyne, potassium carbonate, potassium iodide in DMF, 70°C–80°C, 72 h; (ii) N,N-diethylaniline, reflux, 15 h; (iii) potassium ferricyanide, potassium carbonate, (DHQD)2-PYR, potassium osmate, methane-sulfonamide, in tert-butanol/water (v/v, 1:1) at 0°C, 24 h; (iv) various acyl chlorides, anhydrous dichloromethane, pyridine, 0°C.
Abbreviations: (DHQD)2-PYR, hydroquinidine-2,5-diphenyl-4,6-pyrimidinediyl diether; DMF, N,N-dimethylformamide.
For the determination of ee, racemic substituted (±)-cis-khellactones (10′ and 11′) were produced by oxidizing the substituted seselins 8 and 9 (Scheme 3).22 Chiral HPLC analysis revealed that the reactions were highly stereoselective with good ee (>86% ee). (DHQD)2-PYR resulted primarily in cis-diol with an S, S configuration.23
Scheme 3.
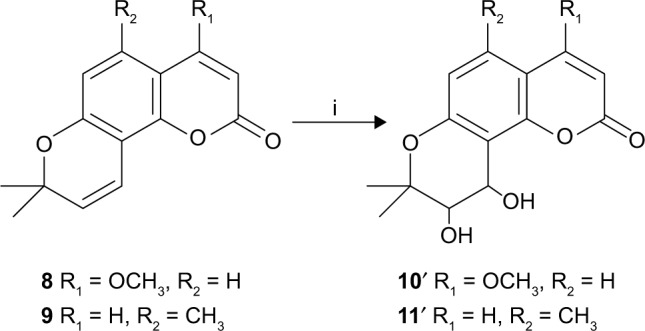
Synthesis of substituted (±)-cis-khellactone (10′, 11′).
Note: Reagents and conditions: (i) osmium tetroxide, N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide monohydrate in tert-butanol/tetrahydrofuran/water (v/v, 10:3:1) at room temperature, 24 h.
In vitro antitumor activity assays
All the synthesized target compounds (12a-g and 13a-g) are novel and were screened for their preliminary antitumor activity against three human cancer cell lines (HEPG-2, SGC-7901, and LS174T) by using the MTT assay with doxorubicin as a positive reference compound. As shown in Table 1, the substituted (3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactones 10 and 11 did not show any cytotoxicity, while some 4-methoxy-(3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone derivatives exhibited promising in vitro antitumor activity. Among the synthesized derivatives, compounds 12e, 12f, and 12g appeared to be the most potent. The IC50 values for compound 12e were 6.1, 9.2, and 8.0 μM in HEPG-2, SGC-7901, and LS174T cells, respectively, while the corresponding values for compound 12f were 13.3, 21.3, and 23.6 μM. The IC50 values of compound 12g were 8.1, 29.6, and 16.7 μM, respectively, in HEPG-2, SGC-7901, and LS174T cells. It is well known that various cancer cells have different responses to drug or compound. Interestingly, all these three compounds tended to be more sensitive in HEPG-2 cells compared to that in the other two cancer cell lines. For HEPG-2 cells, the introduction of an electron-donating methoxy group in the benzene ring at 3′ and 4′ positions (12d) led to a decrease in activity compared to that of compound 12c. Conversely, significant activity was observed with 4-methoxy-substituted derivatives having an electron-withdrawing Cl substituent on the benzoyl moiety at 3′ and 4′ positions (12e–g), and the degree of inhibition ranged as follows: 2-Cl >4-Cl >3-Cl. Furthermore, the majority of the other compounds in this group showed moderate activity. However, another group of derivatives (13a–g) synthesized with 5-methyl substitution did not show promising activity against the three cancer cell lines investigated. These results showed that the 4-methoxy-substituted derivatives possessed greater activity than the 5-methyl-substituted derivatives and that the introduction of a Cl substituent in the benzoyl moiety at 3′ and 4′ positions of 4-methoxy-(3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone plays a key role in enhancing the activity. Furthermore, compound 12e, which showed the highest activity against cancer cell lines, was chosen to investigate its cytotoxicity in HL-7702 cells, a normal human liver cell line. As shown in Figure S1, cell viability was greater than 90% after treatment with 100 μM compound 12e for 48 h. These results indicated that compound 12e is likely to be selectively toxic to liver cancer cell.
Table 1.
Cytotoxic activity of the synthesized compounds against three human cancer cell lines
| Compound | IC50 ± SD (μM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| HEPG-2 | SGC-7901 | LS174T | |
| 10 | 78.2±5.7 | 83.3±5.1 | >100 |
| 11 | >100 | >100 | 89.3±4.3 |
| 12a | 59.1±6.9 | 64.1±6.0 | >100 |
| 12b | 66.8±5.5 | >100 | >100 |
| 12c | 31.3±7.0 | 51.8±4.5 | 84.0±8.8 |
| 12d | >100 | 53.3±8.1 | 67.3±5.4 |
| 12e | 6.1±1.5 | 9.2±2.0 | 8.0±1.9 |
| 12f | 13.3±3.9 | 21.3±4.0 | 23.6±3.8 |
| 12g | 8.1±2.3 | 29.6±5.2 | 16.7±2.8 |
| 13a | 76.3±5.6 | 45.0±6.6 | 62.2±9.0 |
| 13b | 63.7±5.4 | >100 | >100 |
| 13c | 25.7±4.1 | 73.9±3.7 | 49.0±6.6 |
| 13d | 66.5±7.8 | >100 | 69.5±9.3 |
| 13e | 57.0±4.5 | 68.9±5.3 | >100 |
| 13f | 82.4±7.1 | >100 | 51.0±4.2 |
| 13g | 56.8±9.2 | 53.8±6.8 | >100 |
| Doxorubicin | 1.4±0.3 | 2.1±0.2 | 1.2±0.3 |
Note: Data represented the mean of three experiments in triplicate and are expressed as mean ± SD.
Abbreviation: IC50, 50% inhibitory concentration.
Morphological changes of HEPG-2 cell by using AO/EB double-staining assay
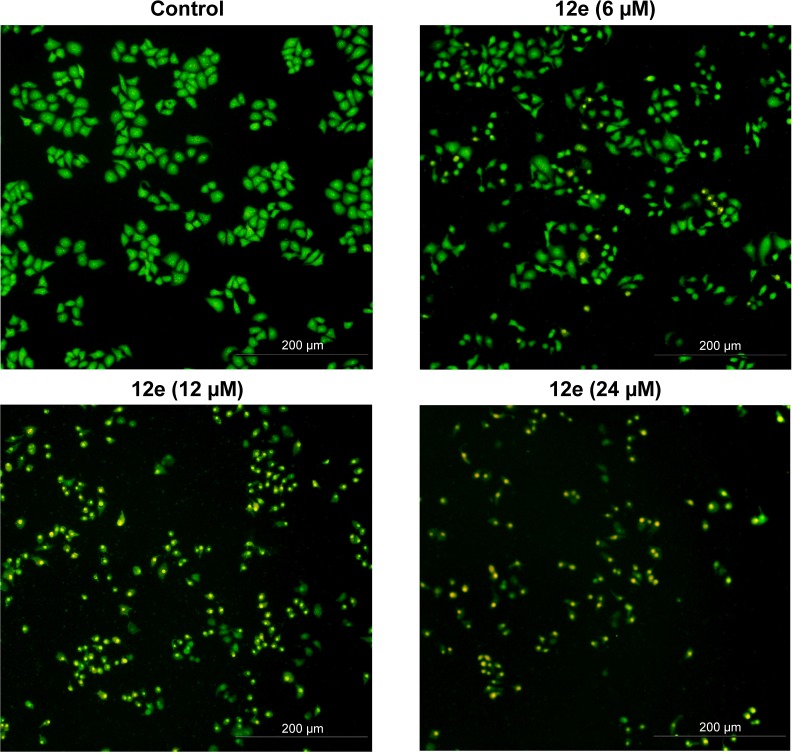
To determine whether the cytotoxicity in HEPG-2 cells caused by compound 12e was related to the induction of apoptosis, morphological observation with AO/EB staining was detected by fluorescence microscopy. As shown in Figure 2, green live cells with normal morphology were seen in the control group, while the cells exposed to compound 12e showed apoptotic morphological changes such as cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, cell nuclear fragmentation, and labeled orange color.
Figure 2.
Effects of compound 12e on the morphology of HEPG-2 cells stained by AO/EB.
Notes: After being treated with compound 12e for 24 h, HEPG-2 cells were stained by AO/EB and morphologies were immediately observed using fluorescence microscopy. Viable cells presented homogeneously stained green nuclei. Early apoptotic cells showed greenish yellow nuclei and late apoptotic cells indicated condensed orange nuclei.
Abbreviations: AO, acridine orange; EB, ethidium bromide.
Analysis of apoptosis by using the Annexin V-FITC/PI method
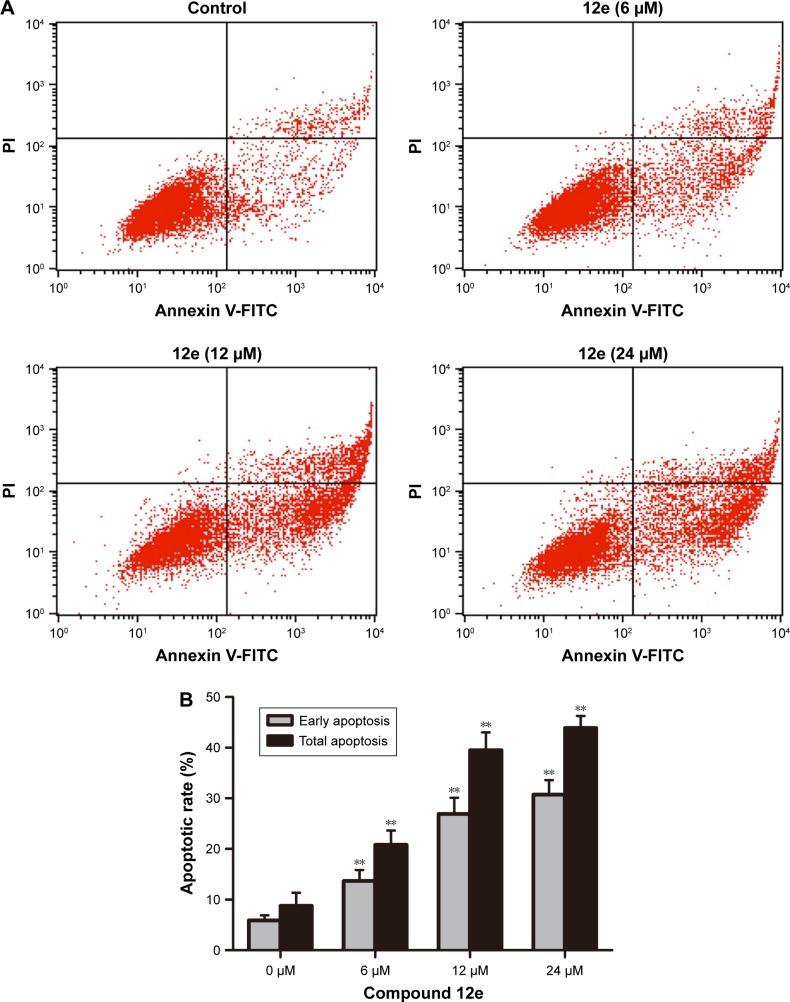
To characterize the apoptosis induced by compound 12e, the Annexin V/PI double-staining method was used to quantify the apoptotic HEPG-2 cells following treatment with 6, 12, and 24 μM of 12e. The percentage of early apoptotic cells observed at these doses were 13.68%, 26.90%, and 30.72%, respectively, and this was statistically significant compared to 5.91% observed with control cells (P<0.01). Furthermore, total apoptotic cells at the three doses tested were found to be 20.83%, 39.52%, and 43.88% respectively, while the untreated control group had 8.75% of total apoptotic cells (Figure 3). These results demonstrated that compound 12e caused a dose-dependent induction of apoptosis in HEPG-2 cells.
Figure 3.
Flow cytometric analysis of compound 12e induced apoptosis in HEPG-2 cells using Annexin V/PI double-staining assay.
Notes: Treatment with compound 12e at 0 μM, 6 μM, 12 μM, and 24 μM for 48 h followed by staining with FITC-conjugated Annexin V and PI for flow cytometric analysis. Early apoptotic cells are Annexin V positive but PI negative (low right quadrant); late apoptotic and necrotic cells are Annexin V and PI positive (upper right quadrant), and the rate of total apoptosis was the sum of early and late apoptosis. (A) Representative flow cytometric plots. (B) Flow cytometric analysis result. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n=3), and the significance was established at **P<0.01 compared with the control group.
Abbreviations: FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; PI, propidium iodide.
Loss of MMP
It is well known that altered mitochondrial function is linked to apoptosis. In particular, loss of MMP can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction and has been regarded as an important factor in controlling the induction of apoptosis.24 To assess the involvement of disruption of MMP in the apoptotic action of compound 12e, the cationic lipophilic dye, JC-1, which readily penetrates the plasma membrane into cells and accumulates in actively respiring mitochondria, was used to evaluate the disruption of MMP in HEPG-2 cells. Loss of MMP was observed in HEPG-2 cells 48 h after treatment with 6, 12, and 24 μM 12e. The values observed at these doses decreased to 82.33%, 72.67%, and 55.36%, respectively, of the value associated with untreated control cells (Figure 4). These findings suggest that apoptosis induced by compound 12e in HEPG-2 cells is associated with depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane.
Figure 4.
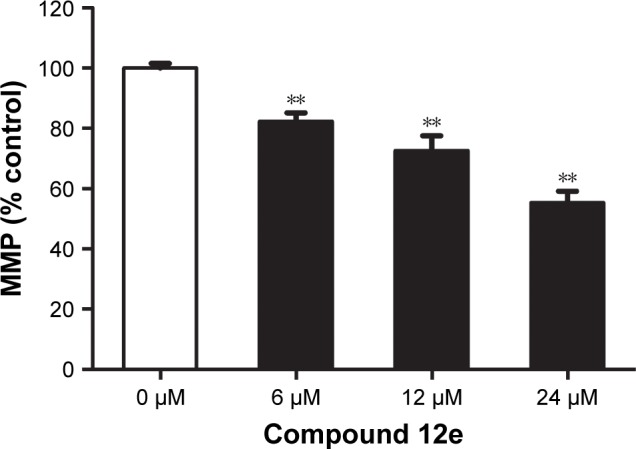
Loss of MMP induced by compound 12e in HEPG-2 cells.
Notes: Cells were treated with 0, 6, 12, and 24 μM 12e for 48 h and incubated with MMP indicator JC-1. JC-1 dye-stained cells were analyzed by flow cytometry, and the relative red/green fluorescence ratio in treated cells is expressed graphically as a percentage of red/green fluorescence ratio value of the control cells. Each value represents mean ± SD (n=3). **P<0.01 compared with the control group.
Abbreviations: JC-1, 5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethyl-imidacarbocyanine iodide; MMP, mitochondrial membrane potential.
Caspase activation induced by compound 12e
During the process of apoptosis, mitochondrial disruption leads to the release of cytochrome c, forming apoptosomes with Apaf-1 and procaspase-9, and triggering caspase-9 activation, which subsequently cleaves the effector caspase-3.25 Western blotting analysis revealed that compound 12e markedly increased the levels of caspase-9 and the effector cleaved caspase-3 in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 5). These data suggest that compound 12e induces apoptosis of HEPG-2 cells via the intrinsic pathway.
Figure 5.
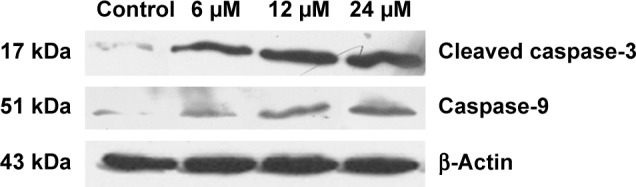
Effect of compound 12e on the protein expression of cleaved caspase-3 and caspase-9 by Western blot analysis.
Conclusion
A series of novel 4-methoxy-substituted and 5-methylsubstituted (3′S,4′S)-(−)-cis-khellactone derivatives were synthesized, characterized, and evaluated for their cytotoxic activities against three human cancer cell lines (HEPG-2, SGC-7901, and LS174T). The results revealed that 4-methoxy-substituted compounds showed potent inhibitory activity. In particular, compound 12e exhibited highest antitumor activity against the HEPG-2 cancer cell line, and the cytotoxic activity of this new agent could be attributed to its induction of apoptosis possibly via the change in MMP. Furthermore, the upregulation of caspase-9 and cleavage of caspase-3 were shown by Western blot analysis. Collectively, these data show that compound 12e induces apoptosis via a mitochondria-related caspase-dependent pathway. Hence, compound 12e could be used as a prototype for further modifications to develop new more active antitumor analogs.
Supplementary material
In vitro cytotoxicity of compound 12e on HL-7702 normal human hepatocyte.
Note: The toxicity of compound 12e to normal human liver cells was observed by MTT assay at the concentration of 25, 50, 100, and 200 μM for 48 h.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Program for the Top Young Academic Leaders of Higher Learning Institutions of Shanxi, the Collaborative Innovation Center Project of Shanxi “Astra-galus” Resource Industrialization and Industrial Internationalization (No HQXTCXZX2016-021), and Shanxi Natural Science Foundation (No 2016011112). We would also like to thank the support and help from all the teachers of School of Pharmaceutical Science, Shanxi Medical University.
Abbreviations
- AO
acridine orange
- (DHQD)2-PYR
hydroquinidine-2,5-diphenyl-4,6-pyrimidinediyl diether
- DMEM
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- DMSO
dimethyl sulfoxide
- EB
ethidium bromide
- ECL
enhanced chemiluminescence
- ee
enantiomeric excess
- ESI
electrospray ionization
- FBS
fetal bovine serum
- FITC
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- HPLC
high-performance liquid chromatography
- HRP
horseradish peroxidase
- IC50
50% inhibitory concentration
- JC-1
5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethyl-imidacarbocyanine iodide
- MMP
mitochondrial membrane potential
- NMR
nuclear magnetic resonance
- PE
petroleum ether
- PI
propidium iodide
- ppm
parts per million
- RIPA
radio-immunoprecipitation assay
- SDS-PAGE
sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- TBS-T
tris-buffered saline plus Tween-20
- TLC
thin-layer chromatography
- TMS
tetramethylsilane
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, et al. International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013. [Accessed December 18, 2013]. homepage on the Internet. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wang HJ. Lapatinib for the treatment of breast cancer in the People’s Republic of China. Onco Targets Ther. 2014;7:1367–1373. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S60586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shahbazian D, Sznol J, Kluger HM. Vertical pathway targeting in cancer therapy. Adv Pharmacol. 2012;65(2012):1–26. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-397927-8.00001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kinghorn AD, Chin YW, Swanson SM. Discovery of natural product anticancer agents from biodiverse organisms. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2009;12(2):189–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Borges F, Roleira F, Milhazes N, Santana L, Uriarte E. Simple coumarins and analogues in medicinal chemistry: occurrence, synthesis and biological activity. Curr Med Chem. 2005;12(8):887–916. doi: 10.2174/0929867053507315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fylaktakidou KC, Hadjipavlou-Litina DJ, Litinas KE, Nicolaides DN. Natural and synthetic coumarin derivatives with anti-inflammatory/antioxidant activities. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(30):3813–3833. doi: 10.2174/1381612043382710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Riveiro ME, De Kimpe NA, Moglioni A, et al. Coumarins: old compounds with novel promising therapeutic perspectives. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(13):1325–1338. doi: 10.2174/092986710790936284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Takata M, Shibata S, Okuyama T. Structures of angular pyranocoumarins of Bai-Hua-Qian-Hu, the root of Peucedanum praeruptorum. Planta Med. 1990;56(3):307–311. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-960966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen ZX, Huang BS, She QL, Zeng GF. The chemical constituents of Bai-Hua-Qian-Hu, the root of Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn. (Umbelliferae)-four new coumarins. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1979;14(8):486–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ishii H, Okada Y, Baba M, Okuyama T. Studies of coumarins from the Chinese Drug Qianhu, XXVII: structure of a new simple coumarin glycoside from Bai-Hua Qianhu, Peucedanum praeruptorum. Chem Pharm Bull. 2008;56(9):1349–1351. doi: 10.1248/cpb.56.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee T, Kashiwada Y, Huang L, Snider J, Cosentino M, Lee K. Suksdorfin: an anti-HIV principle from Lomatium suksdorfii, its structure-activity correlation with related coumarins, and synergistic effects with anti-AIDS nucleosides. Bioorg Med Chem. 1994;2(10):1051–1056. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(00)82054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.ITsai IL, Wun MF, Teng CM, Ishikawa T, Chen IS. Anti-platelet aggregation constituents from Formosan Toddalia asiatica. Phytochemistry. 1998;48(8):1377–1382. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(97)00678-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kozawa T, Sakai K, Uchida M, Okuyama T, Shibata S. Calcium antagonistic action of a coumarin isolated from “Qian-Hu”, a Chinese traditional medicine. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981;33(5):317–320. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wu JYC, Fong WF, Zhang JX, et al. Reversal of multidrug resistance in cancer cells by pyranocoumarins isolated from Radix Peucedani. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;473(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(03)01946-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shen X, Chen G, Zhu G, et al. 3′-O, 4′-O-aromatic acyl substituted 7,8-pyranocoumarins: a new class of P-glycoprotein modulators. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012;64(1):90–100. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Huang L, Kashiwada Y, Cosentino ML, et al. Anti-AIDS agents. 15. Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of dihydroseselins and related analogs. J Med Chem. 1994;37(23):3947–3955. doi: 10.1021/jm00049a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yu D, Suzuki M, Xie L, Morris-Natschke SL, Lee KH. Recent progress in the development of coumarin derivatives as potent anti-HIV agents. Med Res Rev. 2003;23(3):322–345. doi: 10.1002/med.10034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xie L, Takeuchi Y, Cosentino LM, Lee KH. Anti-AIDS agents. 37. Synthesis and structure−activity relationships of (3′R,4′R)-(+)-cis-khellactone derivatives as novel potent anti-HIV agents. J Med Chem. 1999;42(14):2662–2672. doi: 10.1021/jm9900624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Takeuchia Y, Xie L, Cosentino LM, Lee KH. Anti-AIDS agents-XXVIII.1 Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of methoxy substituted 3′,4′-Di-O-(−)-camphanoyl-(+)-cis-khellactone (DCK) analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1997;7(20):2573–2578. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(98)00367-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Xie L, Yu DL, Wild C, et al. Anti-AIDS agents. 52. Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of hydroxymethyl (3′R,4′R)-3′,4′-Di-O-(S)-camphanoyl-(+)-cis-khellactone derivatives. J Med Chem. 2004;47(3):756–760. doi: 10.1021/jm030416y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ren LH, Du X, Hu MN, Yan CQ, Liang TG, Li QS. Design, synthesis and antitumor activity of novel 4-methyl-(3′S,4′S)-cis-khellactone derivatives. Molecules. 2013;18(4):4158–4169. doi: 10.3390/molecules18044158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ternbe SB, Bhedi DN, Souza NJ, Rupp RH. Synthesis of (±)-praeruptorin A and related khellactone derivatives. Heterocycles. 1987;26(5):1239–1249. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Xie L, Crimmins MT, Lee KH. Asymmetric synthesis of 3′,4′-Di-O-(−)-camphanoyl-(+)-Cis-khellactone (DCK), a potent anti-HIV agent. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995;36(26):4529–4532. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C. Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev. 2007;87(1):99–163. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00013.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kim HE, Du F, Fang M, Wang X. Formation of apoptosome is initiated by cytochrome c-induced dATP hydrolysis and subsequent nucleotide exchange on Apaf-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(49):17545–17550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507900102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
In vitro cytotoxicity of compound 12e on HL-7702 normal human hepatocyte.
Note: The toxicity of compound 12e to normal human liver cells was observed by MTT assay at the concentration of 25, 50, 100, and 200 μM for 48 h.