Abstract
Key points
5‐HT is a neuromodulator released from carotid body (CB) chemoreceptor (type I) cells and facilitates the sensory discharge following chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH).
In the present study, we show that, in addition to type I cells, adjacent glial‐like type II cells express functional, ketanserin‐sensitive 5‐HT2 receptors, and their stimulation increases cytoplasmic Ca2+ derived from intracellular stores.
In type II cells, 5‐HT activated a ketanserin‐sensitive inward current (I 5‐HT) that was similar to that (I UTP) activated by the P2Y2R agonist, UTP.
As previously shown for I UTP, I 5‐HT was inhibited by BAPTA‐AM and carbenoxolone (5 μm), a putative blocker of ATP‐permeable pannexin (Panx)‐1 channels; I UTP was reversibly inhibited by the specific Panx‐1 mimetic peptide channel blocker, 10Panx peptide.
Paracrine stimulation of type II cells by 5‐HT, leading to ATP release via Panx‐1 channels, may contribute to CB excitability, especially in pathophysiological conditions associated with CIH (e.g. obstructive sleep apnoea).
Abstract
Carotid body (CB) chemoreceptor (type I) cells can synthesize and release 5‐HT and increased autocrine–paracrine 5‐HT2 receptor signalling contributes to sensory long‐term facilitation during chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH). However, recent studies suggest that adjacent glial‐like type II cells can respond to CB paracrine signals by elevating intracellular calcium (Δ[Ca2+]i) and activating carbenoxolone‐sensitive, ATP‐permeable, pannexin (Panx)‐1‐like channels. In the present study, using dissociated rat CB cultures, we found that 5‐HT induced Δ[Ca2+]i responses in a subpopulation of type I cells, as well as in most (∼67%) type II cells identified by their sensitivity to the P2Y2 receptor agonist, UTP. The 5‐HT‐induced Ca2+ response in type II cells was dose‐dependent (EC50 ∼183 nm) and largely inhibited by the 5‐HT2A receptor blocker, ketanserin (1 μm), and also arose mainly from intracellular stores. 5‐HT also activated an inward current (I 5‐HT) in type II cells (EC50 ∼200 nm) that was reversibly inhibited by ketanserin (1–10 nm), the Ca2+ chelator BAPTA‐AM (5 μm), and low concentrations of carbenoxolone (5 μm), a putative Panx‐1 channel blocker. I 5‐HT reversed direction at approximately −11 mV and was indistinguishable from the UTP‐activated current (I UTP). Consistent with a role for Panx‐1 channels, I UTP was reversibly inhibited by the specific Panx‐1 mimetic peptide blocker 10Panx (100 μm), although not by its scrambled control peptide (scPanx). Because ATP is an excitatory CB neurotransmitter, it is possible that the contribution of enhanced 5‐HT signalling to the increased sensory discharge during CIH may occur, in part, by a boosting of ATP release from type II cells via Panx‐1 channels.
Keywords: 5‐HT2 receptors, ketanserin, pannexin‐1 channels
Key points
5‐HT is a neuromodulator released from carotid body (CB) chemoreceptor (type I) cells and facilitates the sensory discharge following chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH).
In the present study, we show that, in addition to type I cells, adjacent glial‐like type II cells express functional, ketanserin‐sensitive 5‐HT2 receptors, and their stimulation increases cytoplasmic Ca2+ derived from intracellular stores.
In type II cells, 5‐HT activated a ketanserin‐sensitive inward current (I 5‐HT) that was similar to that (I UTP) activated by the P2Y2R agonist, UTP.
As previously shown for I UTP, I 5‐HT was inhibited by BAPTA‐AM and carbenoxolone (5 μm), a putative blocker of ATP‐permeable pannexin (Panx)‐1 channels; I UTP was reversibly inhibited by the specific Panx‐1 mimetic peptide channel blocker, 10Panx peptide.
Paracrine stimulation of type II cells by 5‐HT, leading to ATP release via Panx‐1 channels, may contribute to CB excitability, especially in pathophysiological conditions associated with CIH (e.g. obstructive sleep apnoea).
Abbreviations
- CB
carotid body
- CIH
chronic intermittent hypoxia
- 5‐HT2AR
5‐HT2A receptor
- Panx
pannexin
Introduction
The mammalian carotid bodies (CB) are sensory organs that monitor acutely blood chemicals such as O2, CO2 and pH and maintain homeostasis in the cardiovascular and cardiorespiratory systems via the initiation of appropriate reflex responses (Gonzalez et al. 1994; Kumar & Prabhakar, 2012). Dysfunction of the CB chemoreflex occurs in several pathophysiological conditions associated with sympathetic overactivity, including hypertension, heart failure, diabetes and sleep apnoea (Kumar & Prabhakar, 2012, 2015; Schultz et al. 2015; Iturriaga et al. 2016). The mechanisms underlying these alterations in CB function are incompletely understood but have commonly been attributed to changes in chemoreceptor (type I) cell function, including expression levels of their secreted neurotransmitters and neuromodulators, as well as their cognate receptors within the CB (Iturriaga & Alcayaga, 2004; Kumar & Prabhakar, 2012; Nurse, 2014; Prabhakar et al. 2015). Thus, clarification of the roles of these neuroactive agents is critical for understanding the integrated function of the CB in both normal and pathophysiological conditions. This task has recently become even more challenging subsequent to the demonstration that, in addition to type I cells, neighbouring sustentacular type II cells may also express functional G‐protein coupled receptors for type I cell paracrine signals including ATP, ACh and angiotensin II (Xu et al. 2003; Tse et al. 2012; Zhang et al. 2012; Murali et al. 2014,2015). Stimulation of these receptors in type II cells causes a rise in intracellular calcium that is considered to be necessary for the activation of an inward current carried by non‐selective ion channels (Murali et al. 2014). In a previous study (Zhang et al. 2012), these channels appeared to be ATP‐permeable and their sensitivity to low doses of carbenoxolone (5 μm), together with immunolocalization evidence, led us to propose they were similar to pannexin (Panx)‐1 channels, which are known to act as conduits for ATP release in various cell types (Locovei et al. 2006; Huang et al. 2007; Zhang et al. 2012; Murali et al. 2014). However, there is increasing skepticism over the reliability of pharmacological agents such as carbenoxolone with respect to distinguishing Panx‐1 channels from gap junctional connexin hemichannels (Lohman & Isakson, 2014). Nevertheless, given that ATP is a major excitatory neurotransmitter in the CB (Nurse, 2014), these findings have led to the proposal that type II cells may also contribute to the CB afferent discharge via paracrine signalling pathways (Tse et al. 2012; Zhang et al. 2012; Nurse, 2014).
The monoamine 5‐HT is among the less well‐studied CB neuromodulators. However, there is abundant evidence that chemoreceptor type I cells can synthesize and store 5‐HT (Gronblad et al. 1983; Oomori et al. 1994; Zhang & Nurse, 2000; Liu et al. 2011; Yokoyama et al. 2013) and, at least in some studies, 5‐HT can be released in response to acute hypoxia (Zhang et al. 2003; Peng et al. 2009; Ramirez et al. 2012). Moreover, exogenous 5‐HT elicits complex physiological responses in the CB involving multiple receptor types located on type I cells, sensory nerve endings and/or blood vessels (Kirby & McQueen, 1984). Importantly, a critical role proposed for 5‐HT in the CB is to promote long‐term facilitation of the sensory discharge during exposure to chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH), a situation observed in pathophysiological conditions that lead to autonomic imbalances (e.g. central or obstructive sleep apnoea) (Peng et al. 2009; Prabhakar, 2011). The actions of 5‐HT result in the modulation of the CB sensory response and have been largely attributed to the presence of 5‐HT2A receptors (5‐HT2AR) localized mainly (but not exclusively) to type I cells (Kirby & McQueen, 1984; Zhang et al. 2003; Jacono et al. 2005; Yokoyama et al. 2015). However, RT‐PCR analysis suggests that, in addition to 5‐HT2AR, and controversially 5‐HT5AR, mRNAs, at least seven more 5‐HT receptor mRNAs are expressed in extracts of rat CB (Wang et al. 2000; Zhang et al. 2003; Yokoyama et al. 2015). Taken together, these studies indicate a complex role of 5‐HT and its receptors in paracrine signalling pathways in the CB.
In the present study, we tested the hypothesis that rat CB type II cells may participate in the paracrine actions of 5‐HT via expression of functional 5‐HT receptors. We found that 5‐HT, acting mainly via ketanserin‐sensitive 5‐HT2 receptors, evoked robust intracellular Ca2+ responses in a significant proportion of type II cells and, surprisingly, these responses were detected more frequently than corresponding ones in neighbouring type I cells. Previous studies have demonstrated that stimulation of Ca2+ signalling pathways in type II cells by other CB neuromodulators (e.g. ATP and angiotensin II) leads to activation of a similar inward current carried by non‐selective cation channels (Zhang et al. 2012; Murali et al. 2014) and we found that this was also the case for 5‐HT. Finally, to strengthen the evidence for a role of Panx‐1 channels in the activation of the inward current, we compared the effects of a specific mimetic peptide inhibitor of Panx‐1 channels, 10Panx peptide, with its scrambled control peptide, scPanx (Thompson et al. 2008; Lohman & Isakson, 2014).
Methods
Ethical approval
Procedures for animal handling and tissue removal followed the guidelines of the Canadian Council on Animal Care and were approved by the McMaster's Animal Research Ethics Board. Animals were housed in the McMaster Central Animal Facility under a constant 12:12 h light/dark cycle with access to food and water available ad libitum. We understand the ethical principles of the journal with respect to studies on animals and our work complies with its animal ethic checklist.
Carotid body cultures
The procedures for preparing CB cultures were similar to those described in detail previously (Zhang et al. 2000, 2012). Briefly, rat pups 9–14 days old (Wistar, Charles River, Quebec, Canada) were rendered unconscious by a blow to the back of the head and then killed immediately by decapitation. The carotid bifurcations were excised and the CBs were isolated, cleaned of surrounding tissue and then exposed to a physiological salt solution containing 0.1% trypsin (Sigma‐Aldrich, Oakville, Ontario, Canada) and 0.1% collagenase (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA). The tissue was then mechanically dissociated and the resulting cell suspension plated on modified tissue culture dishes pre‐coated with a thin layer of Matrigel (BD Biosciences, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada). The cells were cultured at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 95% air/5% CO2 for 2–7 days. The growth medium consisted of F‐12 nutrient medium supplemented with 1% penicillin‐streptomycin, 1% glutamine, 0.3% glucose, 3 μg ml−1 insulin and a series of serum additives, as described previously (Zhang et al. 2012; Murali et al. 2014). The Ca2+ imaging experiments were usually performed on cultures that were ∼48 h old, whereas patch clamp recordings were obtained from 5–7‐day‐old cultures to facilitate optimal recordings from isolated type II cells (Zhang et al. 2012).
Fura‐2 intracellular Ca2+ measurements
Fura‐2 measurements of intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) were obtained from both type I and type II cells using procedures similar to those described in detail elsewhere (Piskuric & Nurse, 2012; Zhang et al. 2012; Murali et al. 2014). Briefly, cells were loaded with 2.5 μm fura‐2 AM diluted in a physiological bicarbonate‐buffered solution for 30 min at 37°C. After washing for ∼15 min to remove free dye, cells were imaged using an Eclipse TE2000‐U inverted microscope (Nikon, Mississauga, ON, Canada) equipped with Lambda DG‐4 ultra‐high‐speed wavelength changer (Sutter Instrument CO., Novato, CA, USA), a Hamamatsu OCRCA‐ET digital CCD camera (Hamamatsu, Sewickley, PA, USA) and a Nikon S‐Fluor 40x oil‐immersion objective lens with a numerical aperture of 1.3. The perfusion (extracellular) solution was maintained at ∼35 °C and contained (mm): 24 NaHCO3, 115 NaCl, 5 glucose, 5 KCl, 2 CaCl2 and 1 MgCl2 (pH ∼7.4), as maintained by bubbling a 5% CO2/95% air mixture. Images were acquired every 2 s at 340 nm and 380 nm excitation (510 emission), with an exposure time of 100–200 ms. Pseudocolour ratiometric data were obtained using Simple PCI, version 5.3 (Hamamatsu Photonics, Shizuoka, Japan). The procedures for instrument calibration and calculation of intracellular free [Ca2+] were identical to those described previously (Piskuric & Nurse, 2012; Zhang et al. 2012). For most experiments statistical analysis was performed using repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc multiple comparison test, as indicated.
Whole‐cell recordings from type II cells
Whole‐cell currents were recorded from type II cells using the nystatin perforated‐patch technique as described previously (Zhang et al. 2000, 2012). The cells were perfused with bicarbonate‐buffered saline warmed to ∼35°C and contained (in mm): 24 NaHCO3, 115 NaCl, 5 KCl, 2 CaCl2, 1 MgCl2, 10 glucose and 12 and sucrose (pH 7.4), as maintained by bubbling with 5% CO2/95% air mixture. The pipette solution contained (mm): 115 potassium gluconate, 25 KCl, 5 NaCl, 1 CaCl2, 10 Hepes and 200 μg ml−1 nystatin (pH 7.2). A fast perfusion system utilizing a double‐barreled pipette assembly was used for rapid application of 5‐HT to the cells (Zhang et al. 2000, 2003, 2012). Voltage clamp data were obtained with the aid of a MultiClamp 700A patch clamp amplifier and a Digidata 1322A analog‐to‐digital converter (Axon Instruments Inc., Union City, CA, USA) and stored on a personal computer. Data acquisition and analysis were performed using pCLAMP, version 9.0 (Axon Instruments Inc.). Multiple comparisons of ionic currents or current density (pA/pF), obtained by dividing peak current by whole cell capacitance, were performed using ANOVA. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Reagents and drugs
Reagents and drugs were obtained from Sigma‐Aldrich (Oakville, ON, Canada): UTP, 5‐HT, ketanserin, carbenoxolone, SB 69955 and BAPTA‐AM. The specific mimetic peptide inhibitor of Panx‐1 channels, 10Panx peptide, and the 10Panx scrambled control peptide, scPanx (Thompson et al. 2008), were kindly provided by Dr Roger Thompson (University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada).
Results
The reported results pertain mainly to isolated ‘solitary’ type II cells to eliminate or minimize cross‐talk as a result of direct stimulation of neighbouring type I cells by 5‐HT (Zhang et al. 2003; Murali & Nurse, 2016). In some cases, intracellular Ca2+ responses were monitored simultaneously in type I cells that were members of a cell cluster and nearby type II cells. In addition to their characteristic spindle shape, type II cells were routinely identified by the presence of a rise in intracellular Ca2+ (Δ[Ca2+]i) following stimulation with the P2Y2R agonist, UTP (Xu et al. 2003; Zhang et al. 2012). The absence of cross‐talk from type I to type II cells was supported by the lack of a Δ[Ca2+]i response in type II cells during exposure to the depolarizing stimulus, high K+ (30 mm) (Murali & Nurse, 2016), which stimulates Ca2+‐dependent neurosecretion from type I cells. For Ca2+ imaging experiments, the reported ‘n’ values refer to the number of culture dishes sampled; typically, 15–30 cells were sampled per dish. In voltage clamp experiments, the ‘n’ value represents the number of cells sampled.
5‐HT evokes intracellular Ca2+ responses in both type I and type II cells
In 2‐day‐old CB cultures, application of 5‐HT (10 μm) via the perfusate elicited a rise in intracellular Ca2+ (Δ[Ca2+]i) in subpopulations of type I and type II cells (Fig. 1 A). In one experimental series, ∼40% (77/190 cells) of type I cells, identified by the presence of a Ca2+ response to the depolarizing stimulus high K+ (Fig. 1 A), were sensitive to 10 μm 5‐HT. This proportion is comparable to that previously reported in electrophysiological studies on the 5‐HT modulation of K+ currents in rat type I cells (∼40%) (Zhang et al. 2003). By contrast, a larger proportion (∼67%; 208/310 cells) of UTP‐sensitive type II cells responded to 10 μm 5‐HT. In general, the peak Ca2+ response in type II cells was more robust than that in type I cells (Fig. 1 A); the relative magnitude of the mean peak Δ[Ca2+]i evoked by 5‐HT was ∼229 nm in type II cells compared to ∼54 nm in type I cells (Mann–Whitney t test; P < 0.01) (Fig. 1 B). Despite the larger peak, Ca2+ responses in type II cells decayed more rapidly compared to the longer‐duration responses in type I cells; when averaged over the time of 5‐HT application, the mean Δ[Ca2+]i was slightly higher in type II than type I cells (Fig. 1 C).
Figure 1. 5‐HT‐evoked intracellular Ca2+ responses in type I vs. type II cells.
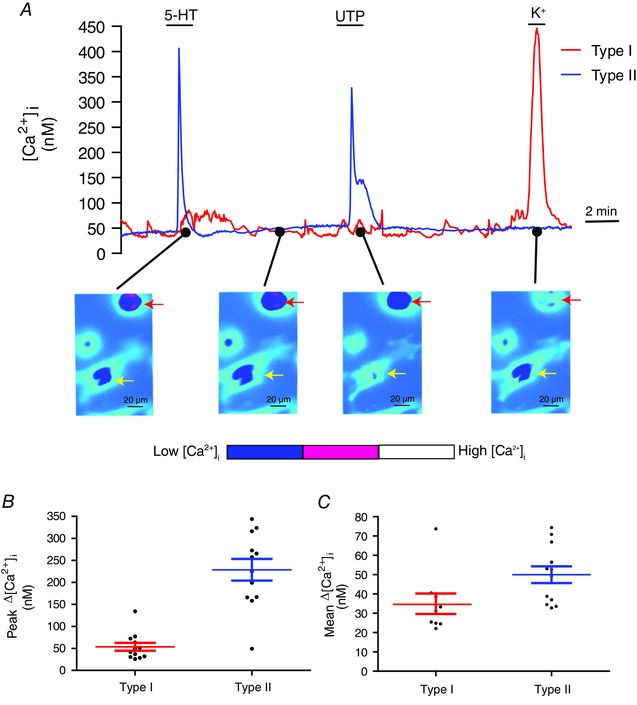
A, 5‐HT (10 μm) causes a rise in intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) in both a type I cell and a type II cell in the same culture. Note that the type II cell (indicated by the yellow arrow, lower) responds to UTP but not high K+ and elicits a more robust Ca2+ response than the type I cell (indicated by the red arrow, lower); the type I cell responds to high K+ but not UTP. Comparison of the peak (mean ± SEM) Δ[Ca2+]i responses in type I vs. type II cells after exposure to 10 μm 5‐HT is shown in (B) (n = 12 dishes; 20–30 cells sampled per dish); the mean Δ[Ca2+]i responses averaged over the time of 5‐HT application are shown in (C) (type I, n = 9 dishes; type II, n = 12 dishes). [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
The effect of 5‐HT on Δ[Ca2+]i in type II cells was dose‐dependent (Fig. 2 A). A plot of the dose–response curve for [5‐HT] vs. Δ[Ca2+]i is shown in Fig. 2 B where the estimated EC50 is ∼183 nm; this value is higher than that reported for 5‐HT acting at 5‐HT2A receptors in other glial cell types (e.g. C6 glioma cells) (EC50 = 100 nm) (Muraoka et al. 1998). There was broad variability in the Δ[Ca2+]i responses among cells in a given dish. For example, in three randomly chosen cells exposed to 10 μm 5‐HT, the mean Δ[Ca2+]i responses were 95.3 ± 5.3 nm (range 64–134 nm; n = 18), 126.1 ± 5.8 nm (range 58–174 nm; n = 25) and 96.5 ± 5.4 nm (range 65–134 nm; n = 15). The 5‐HT receptors on type II cells displayed slight desensitization on repeated application of 10 μm 5‐HT spaced ∼10 min apart; however, only the first and third responses were significantly different from one another (Friedman test, P < 0.001; n = 10 dishes) (Fig. 2 C and D).
Figure 2. Dose–response curve and time‐dependent effects of 5‐HT on intracellular calcium responses in type II cells.
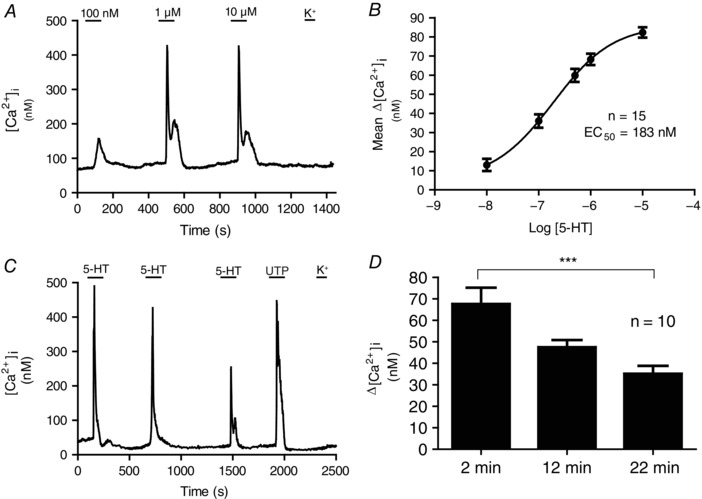
The effect of increasing doses of 5‐HT (100 nm, 1 μm and 10 μm) on intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) is shown in (A), for a type II cell. B, dose–response relation for mean 5‐HT‐induced Δ[Ca2+]i in type II cells; the dose–response curve was fitted with the Hill equation and yielded an EC50 = 183 nm (n = 15 dishes). C, repeated exposure to 10 μm 5‐HT caused a gradual decrease in [Ca2+]i responses in type II cells, presumably as a result of receptor desensitization. D, time‐course of the reduction in Δ[Ca2+]i responses in type II cells after 2, 12 and 22 min exposure to 10 μm 5‐HT; n = 10, *** P < 0.001, Friedman test with Dunn's multiple comparison post hoc test.
Evidence for a role of 5‐HT2A receptors in the 5‐HT‐evoked intracellular Ca2+ responses in both type I and type II cells
Previous studies using different techniques demonstrated that rat type I cells express 5‐HT2AR (Zhang et al. 2003; Peng et al. 2009; Liu et al. 2011; Yokoyama et al. 2015). As expected, the 5‐HT‐induced Ca2+ responses in type I cells were sensitive to the selective 5‐HT2AR antagonist, ketanserin (Fig. 3 A). A scatter plot of Δ[Ca2+]i responses induced by 10 μm 5‐HT in type I cells before, during and after ketanserin is shown in Fig. 3 E. Ketanserin inhibited the mean Δ[Ca2+]i response in type I cells by ∼54%; the mean ± SEM Δ[Ca2+]i response was 28.4 ± 4.8 nm for 5‐HT (10 μm), 13.0 ± 2.26 nm for 5‐HT plus ketanserin (1 μm) and 18.0 ± 6.2 nm for 5‐HT after washout of ketanserin (repeated measures ANOVA, P < 0.01, n = 9 dishes). In previous studies, ketanserin also blocked the 5‐HT‐induced inhibition of K+ currents in rat type I cells (Zhang et al. 2003).
Figure 3. Effects of ketanserin and carbenoxolone on the 5‐HT‐evoked intracellular Ca2+ responses in type I and type II cells.
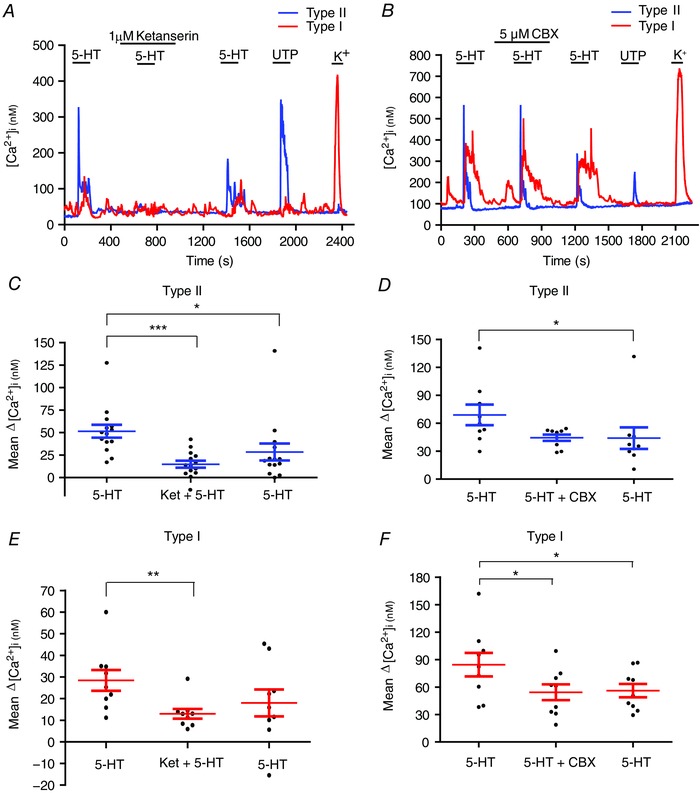
In some cases, as shown in (B), ketanserin (1 μm), a selective 5‐HT2A receptor antagonist, completely blocked the 5‐HT‐induced Ca2+ transients in type I and type II cells within the same cell cluster; note the type I cell was sensitive to high K+ but not UTP, whereas the converse was true for the type II cell. In other cases, inhibition by ketanserin was incomplete, as shown in the summary data for both cell types in (C) and (E). In (B) and (F), the Panx‐1 channel inhibitor carbenoxolone (CBX; 5 μm) failed to block the 5‐HT‐evoked intracellular Ca2+ response in type I cells, although the overall mean response was reduced (F; n = 9). This suggests that the type I cell response to 5‐HT was not primarily a result of cross‐talk between type II and type I cells, which can occur via Panx‐1 channels (Murali & Nurse, 2016). Note that carbenoxolone had no significant effect on the mean 5‐HT ‐evoked ΔCa2+ responses in type II cells (D; n = 9). * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
By contrast to the present findings, 5‐HT‐evoked Ca2+ responses were not detectable in clustered rat type I cells in a recent study by Yokoyama et al. (2015). Given the possibility of cross‐talk between type II and type I cells (Murali & Nurse, 2016), we considered whether the type I cell Ca2+ responses seen in the present study arose indirectly (i.e. consequent to type II cell stimulation). This did not appear to be the case because perfusion with 5 μm carbenoxolone, a Panx‐1 channel inhibitor that blocks type II to type I cross‐talk (Murali & Nurse, 2016), did not abolish the 5‐HT‐evoked Ca2+ responses in type I cells, although the mean response was slightly reduced (Fig. 3 B and F). Note that carbenoxolone did not significantly affect 5‐HT‐evoked Ca2+ responses in type II cells (Fig. 3 B and D). These data support the notion that 5‐HT can evoke direct Ca2+ responses in at least a subpopulation of type I cells via 5‐HT2A receptors.
Because 5‐HT2A receptors are commonly linked to the generation of intracellular Ca2+ signals in glial cells (Verkhratsky & Kettenmann, 1996), we tested whether those receptors might also contribute to the type II cell Ca2+ responses using ketanserin. Indeed, the 5‐HT‐evoked Δ[Ca2+]i was reversibly inhibited by ketanserin (1 μm) in the majority of responsive type II cells (180/252; 70%) (Fig. 3 A). The mean Δ[Ca2+]i response induced by 10 μm 5‐HT in the absence and presence of ketanserin was 52 nm and 15 nm, respectively, corresponding to ∼71% inhibition (n = 14 dishes; Friedman test with Dunn's post hoc multiple comparison test; P < 0.01) (Fig. 3 C). In general, there was only partial recovery of 5‐HT‐induced responses after washout of ketanserin; the mean Δ[Ca2+]i response after ketanserin was 28.5 nm compared to 52 nm before (n = 14 dishes; Friedman test with Dunn's post hoc multiple comparison test, P < 0.001). This effect may be related to the gradual run‐down in 5‐HT‐evoked responses with repeated 5‐HT application (Fig. 2 C and D).
The persistence of a residual Ca2+ response in some type II cells exposed to 5‐HT plus ketanserin, together with the observation that ketanserin had a negligible effect on a minority population of type II cells, raised the question of whether other 5‐HT receptors were involved. The expression of mRNA for a broad variety of G‐protein coupled 5‐HT receptors was recently reported in extracts of the rat CB (Yokoyama et al. 2015). Although controversial (Yokoyama et al. 2015), expression of 5‐HT5A receptor mRNA was reported in the rat CB and 5‐HT5AR immunoreactivity has been localized to type I clusters (Wang et al. 2000). Moreover, rat 5‐HT5A receptors typically display submicromolar affinity for 5‐HT (EC50 ∼ 0.6 μm) (Goodfellow et al. 2012), which is not dissimilar to that observed for the 5‐HT‐induced Ca2+ responses in type II cells (EC50 ∼ 0.2 μm) (Fig. 2 B). In the present study, the putative 5‐HT5AR blocker SB 699551 at 10 μm, a concentration expected to inhibit rat 5‐HT5A receptors (Thomas et al. 2006; Goodfellow et al. 2012), had no significant effect on the 5‐HT ‐induced Ca2+ response; the mean Δ[Ca2+]i response induced by 10 μm 5‐HT was 50.9 ± 4.9 nm (control), 45.3 ± 5.5 nm in the presence of SB 699551 and 34.2 ± 4.6 nm after washout of SB 699551 (P > 0.05; n = 11 dishes). These data do not support a significant contribution of 5‐HT5AR to the intracellular Ca2+ responses induced by 5‐HT in type II cells.
5‐HT‐induced Ca2+ transients in type II cells originate from intracellular stores
In most cases, 5HT2AR activation leads to an increase in Ca2+ i from an intracellular source via the Gαq‐PLC‐IP3 signalling pathway (Peng et al. 2009; Liu et al. 2011). Therefore, to confirm that the 5‐HT‐evoked [Ca2+]i transients in type II cells arose from an intracellular source, we monitored Ca2+ responses in a nominally ‘Ca2+‐free’ solution (0 Ca2+ plus 1 mm EGTA). In some experiments, the order of presenting normal Ca2+ and 0 Ca2+ solutions was reversed to account for the desensitization properties of the receptor. A high proportion (86%; n = 133/154) of type II cells that initially responded to 5‐HT in normal Ca2+ continued to do so in Ca2+‐free solution. Indeed, as shown in Fig. 4 A, type II cell Ca2+‐ transients evoked by 10 μm 5‐HT were not significantly altered on switching from normal to Ca2+‐free medium, suggesting the predominant source of Ca2+ was intracellular. Figure 4 B provides a scatter plot comparison of 5‐HT‐induced Δ[Ca2+]i in normal (2 mm) and Ca2+‐free solutions; the mean ± SEM Δ[Ca2+]i in normal calcium was 77.5 ± 7.2 nm compared to 74.8 ± 13.4 in zero calcium (unpaired t test with Welch's correction, P = 0.8644; n = 9 dishes). In support of an intracellular Ca2+ source, application of the store depleting agent thapsigargin (1 μm) prevented the 5‐HT‐induced Δ[Ca2+]i (Fig. 4 C). Of 431 5‐HT‐responsive type II cells tested, only nine cells (i.e. ∼2%) elicited a significant rise in Ca2+ in the presence of 5‐HT plus thapsigargin; in Fig. 4 D, thapsigargin dramatically reduced the mean Δ[Ca2+]i from 77.8 ± 6.98 to –16.1 ± 3.61 nm (n = 12 dishes; Friedman test with Dunn's post hoc multiple comparison test, P < 0.001). In these experiments, the effects of thapsigargin were not reversible (Fig. 4 C and D).
Figure 4. Role of intracellular stores in the 5‐HT‐induced rise in [Ca2+]i in type II cells.
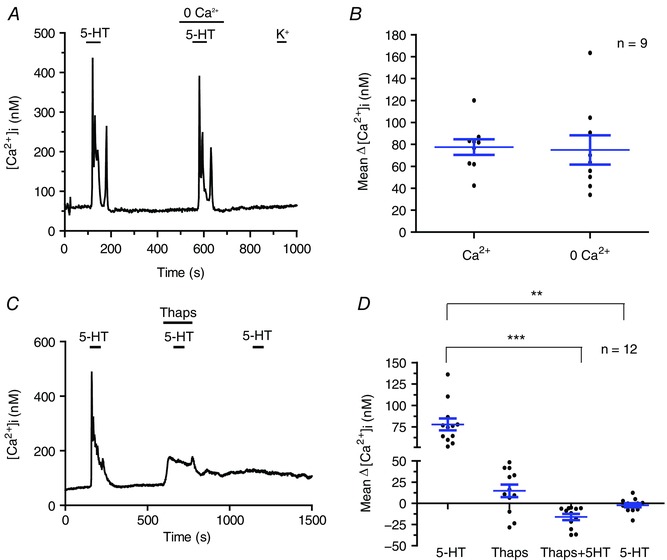
A, 5‐HT‐induced rise in [Ca2+]i persisted in solution containing nominally‐free extracellular Ca2+ (0 Ca2+); summary data of the mean ± SEM Δ[Ca2+]i responses from nine dishes are shown in (B). Consistent with an intracellular source of Ca2+, the 5‐HT‐induced Δ[Ca2+]i was inhibited in the presence of the store‐depleting agent, thapsigargin (Thaps; 1 μm) in (C) and (D); note the effects of thapsigargin were irreversible in (C) and (D) (n = 12 dishes; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001). [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
5‐HT activates a carbenoxolone‐sensitive inward current in type II cells
We previously demonstrated that other CB neurotransmitters such as ATP and angiotensin II activated an inward current in type II cells via P2Y2 and AT1 receptors, respectively (Zhang et al. 2012; Murali et al. 2014); the sensitivity of this current to low doses of carbenoxolone (5 μm) was consistent with the proposed involvement of Panx‐1 channels. Similarly, in voltage clamp studies, 5‐HT activated a dose‐dependent inward current (EC50 = 0.21 μm) at a holding potential of ‐60 mV in responsive type II cells (Fig. 5 A and B). The latency of the current response decreased with increasing 5‐HT concentrations over the range 0.02–10 μm and varied typically between 4 and 12 s (Fig. 5 A and C). Consistent with activation of a non‐selective cation current, the 5‐HT‐induced current showed a mean ± SEM reversal potential of –10.8 ± 3.2 mV (n = 5) (Fig. 6 A and B).
Figure 5. Dose‐ and time‐dependent activation of an inward current in type II cells by 5‐HT.
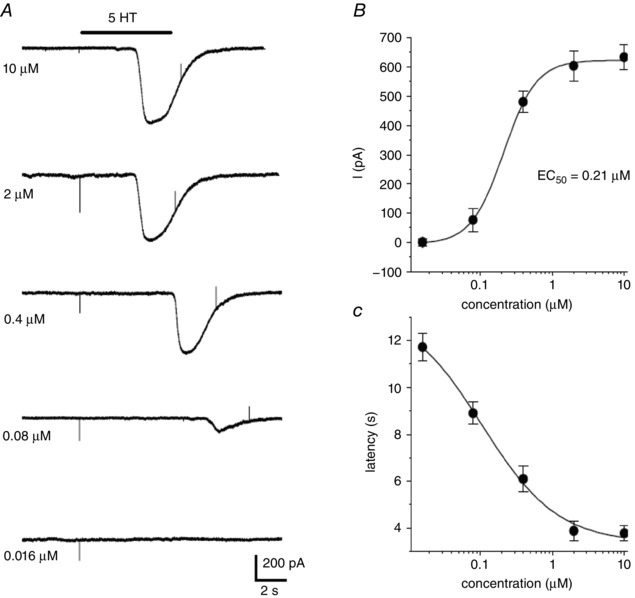
Application of varying doses of 5‐HT by rapid perfusion during the period indicated by upper horizontal bar evokes a delayed inward current in a type II cell (A); holding potential = –60 mV. B, a fit of the dose–response curve for the effects of 5‐HT on the peak inward current yields an EC50 of 0.21 μm using the Hill equation (data points represent the mean ± SEM; n = 5 cells). The mean ± SEM latency of the current response vs. 5‐HT concentration is shown in (C) (n = 5 cells).
Figure 6. Reversal potential of the 5‐HT‐activated current in type II cells.
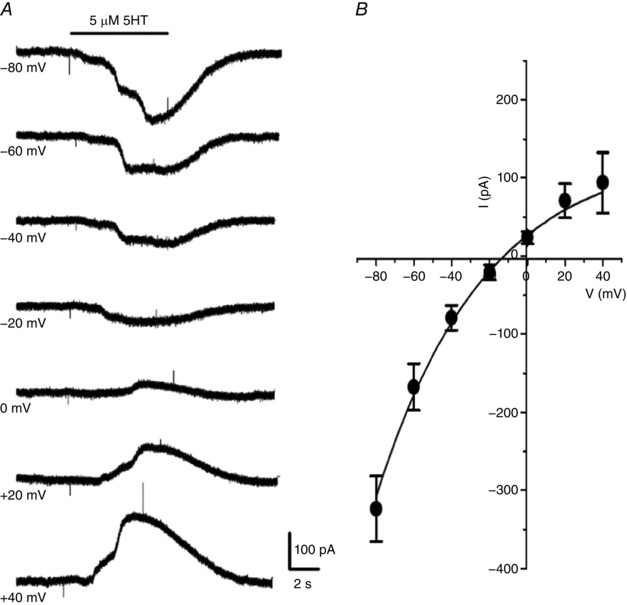
A, the current evoked by 5 μm 5‐HT (I5‐HT) was inward at more negative holding potentials and outward at more positive potentials; note that I 5‐HT sometimes showed multiple peaks (e.g. at −80 and +40 mV), which may reflect different conductance states. The reversal potential of I 5‐HT for a group of five cells was approximately –11 mV (B), which is consistent with activation of non‐selective ion channels.
We next investigated whether the 5‐HT‐induced inward current in type II cells was sensitive to the putative Panx‐1 channel inhibitor, carbenoxolone. As shown in Fig. 7 A, the 5‐HT‐induced inward current (at −60 mV holding potential) was reversibly inhibited by 5 μm carbenoxolone, which is an effect similar to that previously observed when ATP/UTP or ANG II was used to stimulate type II cells (Zhang et al. 2012; Murali et al. 2014). The onset of current blockade was slow, developing gradually over a period of 6 min (Fig. 7 A); summary data for a group of four cells treated in this way are illustrated in Fig. 7 B.
Figure 7. Inhibition of the 5‐HT‐induced inward current in type II cells by the Panx‐1 channel blocker carbenoxolone.
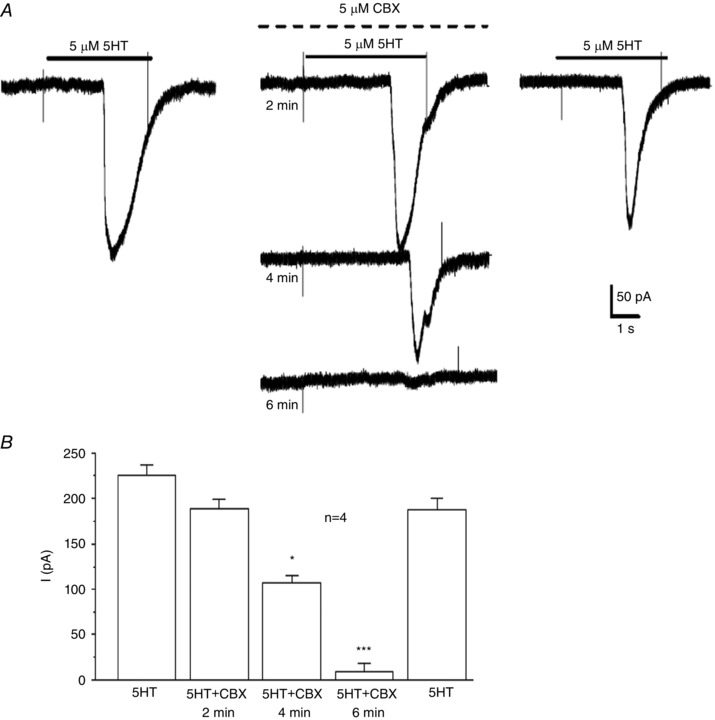
A, the 5‐HT‐induced inward current was reversibly inhibited by 5 μm carbenoxolone (CBX), a Panx‐1 channel blocker (upper dotted line above middle traces); note the block developed gradually over a period of ∼6 min (middle traces). B, summary data for a group of four cells exposed to 5‐HT before, during and after CBX; * P < 0.05; *** P < 0.001.
Sensitivity of the inward current in type II cells to the specific Panx‐1 channel blocker, 10Panx peptide
There is increasing skepticism over the use of carbenoxolone, even at low concentrations, as a reliable tool for the positive identification of Panx‐1 channels (Lohman & Isakson, 2014). Therefore, to obtain more compelling evidence for Panx‐1 channel involvement, we tested the effects of the specific mimetic peptide inhibitor of Panx‐1 channels, 10Panx peptide, and its scrambled control peptide, scPanx (Thompson et al. 2008). Figure 8 A illustrates the similarity of the carbenoxolone‐sensitive, inward current activated by 50 μm UTP and 5 μm 5‐HT in the same type II cell. Perfusion with an extracellular solution containing 10Panx peptide (100 μm) resulted in a reversible blockade of the UTP‐activated inward current in this cell (Fig. 8 Aa). On the other hand, perfusion with scrambled control peptide scPanx (100 μm) was ineffective in the same cell (Fig. 8 Ab);scPanx was similarly ineffective on the UTP‐activated inward current in two other type II cells (data not shown). As shown in Fig. 8 B for a different cell, blockade of the UTP‐activated inward current with 10Panx peptide developed gradually over several minutes, similar to the effect of carbenoxolone (Fig. 7 A). A histogram of UTP‐activated inward current density measurements for three different type II cells before, during and after exposure to 10Panx peptide is shown in Fig. 8 C; note almost complete inhibition of the current by 10Panx peptide in all cases and a full recovery of the response after washout of the blocker. Taken together, these data strongly support a role of Panx‐1 channels in the generation of the inward current in type II cells.
Figure 8. Effects of the specific mimetic peptide inhibitor of Panx‐1 channels (10Panx peptide) and of scrambled control peptide (scPanx) on the inward current in type II cells.
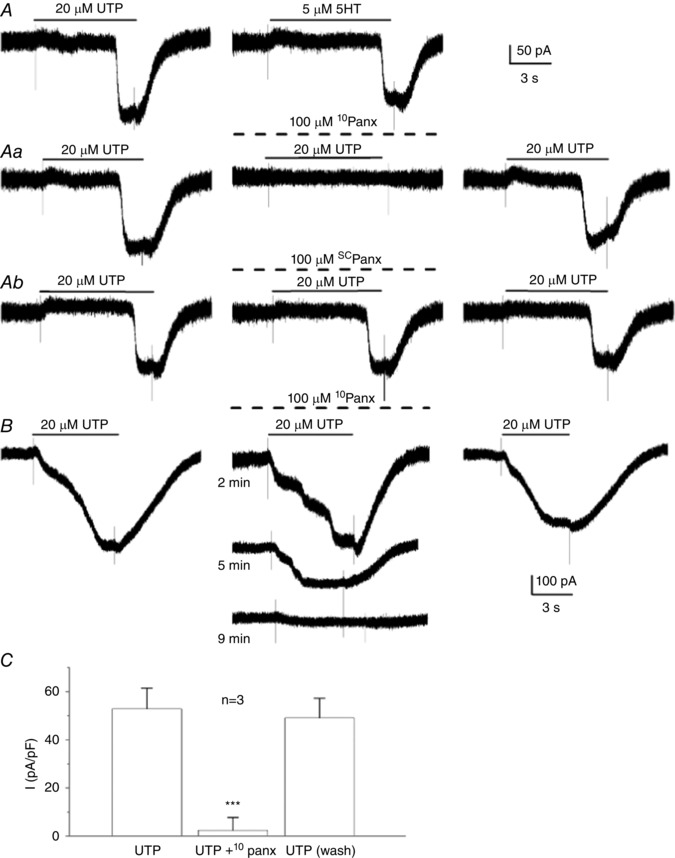
A, showing the similarity of the inward current activated by UTP and 5‐HT in the same cell; holding potential –60 mV. The UTP‐activated inward current was reversibly inhibited by 10Panx peptide (100 μm) in (Aa) but not by 100 μm scPanx peptide in (Ab); all recordings from in (A), (Aa) and (Ab) were from same cell. The time course of current blockade by 10Panx peptide is shown in (B) for a different cell. C, showing UTP‐activated inward current (plotted as current density pA/pF) for three cells before, during and after (wash) treatment with 100 μm 10Panx peptide; *** P < 0.001.
Effects of 5‐HT receptor blockers on the 5‐HT‐activated inward current in type II cells
Given the sensitivity of the 5‐HT‐induced Ca2+ transients to the 5‐HT2A receptor blocker ketanserin (Fig. 3), we first tested the effects of ketanserin on the inward current induced by 5 μm 5‐HT in type II cells. As shown in Fig. 9 A, low doses of ketanserin (1–10 nm) (i.e. values near its IC50 at 5‐HT2A receptors; IC50 = 1.58 nm) (Barnes & Sharp, 1999) reversibly inhibited the 5‐HT‐induced inward current at –60 mV holding potential. An illustration of the concentration‐dependent inhibition of this inward current (plotted as current density, pA/pF) is shown in Fig. 9 B (n = 5 cells).
Figure 9. Sensitivity of the 5‐HT‐induced inward current in type II cells to ketanserin.
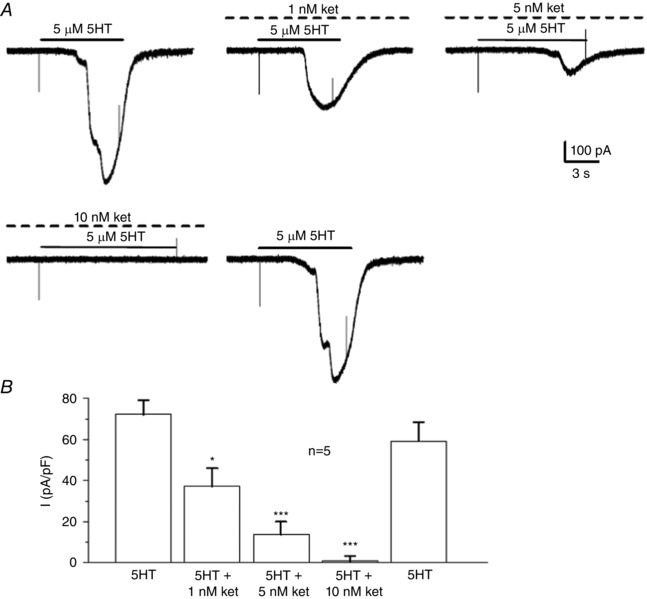
A (upper and lower traces), increasing doses of ketanserin (ket), a selective blocker of 5HT2A receptors, over the dose range 1, 5 and 10 nm, caused a progressive inhibition of the 5‐HT‐induced inward current in type II cells; note complete blockade was apparent at 10 nm ket and that the 5‐HT‐induced response recovered completely after washout of ket. B, summary data for a group of five cells; * P < 0.05; *** P < 0.001.
Interestingly, in contrast to the Ca2+ imaging data (see above), application of the 5‐HT5A receptor antagonist SB 699551 at concentrations of 1 , 5 and 10 μm caused ∼4%, 50% and 97% inhibition of the inward current, respectively; for a group of seven cells, the mean peak current evoked 5 μm 5‐HT was 379 ± 47 pA initially, compared to 364 ± 52 pA for 5‐HT plus 1 μm SB 699551 (P > 0.05), 193 ± 38 pA for 5‐HT plus 5 μm SB 699551 (P < 0.05), 13 ± 9 pA for 5‐HT plus 10 μm SB 699551 (P < 0.001) and 359 ± 43 pA for 5‐HT alone (P > 0.05), after washout of the drug. Although these data are consistent with the blockade of rodent 5‐HT5AR (Thomas et al. 2006), they are inconclusive because, in parallel experiments, we found that 10 μm SB 699551 caused > 90% blockade of the inward current when it was activated by ATP. In the latter experiments, the mean peak current evoked by 20 μm ATP was 716 ± 78 pA before, 43 ± 41 pA during (P < 0.001) and 634 ± 83 pA (P > 0.01) after perfusion with 10 μm SB 699551, corresponding to ∼95% inhibition (n = 8). These data suggest that SB 699551 may cause non‐specific blockade of the Panx‐1‐like channels and, together with the Ca2+ imaging data (see above), do not support a significant contribution of 5‐HT5A receptors in the type II cell response.
Role of intracellular Ca2+ in the activation of the inward current by 5‐HT in type II cells
We previously showed that, in type II cells, a rise in cytosolic Ca2+ was necessary for the activation of Panx‐1 current by ATP and angiotensin II (Murali et al. 2014). To determine whether this was also the case for 5‐HT, we used the membrane‐permeable Ca2+ chelator, BAPTA‐AM (5 μm). As shown in Fig. 10, the inward current evoked by 5 μm 5‐HT was almost completely inhibited in the presence of BAPTA‐AM and the effect was reversible (∼95% inhibition; P < 0.001). This blockade by BAPTA‐AM typically occurred within 4–5 min of exposure and recovery of the initial response was complete some 10–14 min after washout of the drug. These data suggest that a rise in intracellular Ca2+ is necessary for activation of the inward current by 5‐HT.
Figure 10. Effects of the Ca2+ chelator BAPTA‐AM on the 5‐HT‐induced inward current in type II cells.
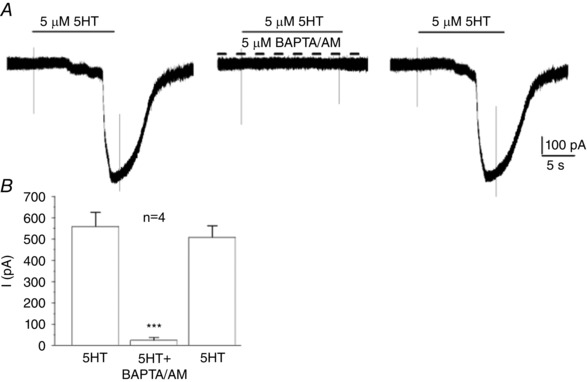
A, chelating intracellular Ca2+ with BAPTA‐AM (5 μm) reversibly abolished the 5‐HT‐induced inward current in a type II cell; summary data for a group of four cells are shown in (B) (*** P < 0.001).
Discussion
In the present study, we demonstrate for the first time that glial‐like sustentacular or type II cells of the juvenile rat CB express functional receptors for 5‐HT, an endogenous neuromodulator known to be synthesized and released by neighbouring chemoreceptor (type I) cells. This finding adds further support to the proposal that several paracrine signalling pathways help shape the integrated sensory response of the CB during chemotransduction (Nurse, 2010; Kumar & Prabhakar, 2012; Tse et al. 2012; Nurse, 2014). Using ratiometric fura‐2 imaging, we found that 5‐HT evoked a marked elevation in intracellular Ca2+ (Δ[Ca2+]i) in ∼67% of type II cells and the source of this Ca2+ was mainly intracellular. By comparison, a smaller proportion (∼40%) of type I cells responded to 5‐HT with an elevation of intracellular Ca2+ and their peak responses were generally smaller, although longer lasting, than those seen in type II cells. In voltage clamp studies, we found a subpopulation of isolated type II cells in which 5‐HT activated a delayed, inward current (I 5‐HT) at holding voltages near the resting potential. This current had a reversal potential of approximately –11 mV and was reversibly inhibited by the Panx‐1 channel blocker, carbenoxolone (5 μm), and was also indistinguishable from the current that was activated during ATP/UTP and angiotensin II stimulation of type II cells in previous studies (Zhang et al. 2012; Murali et al. 2014). Consistent with a role for intracellular Ca2+, application of the Ca2+ chelator BAPTA‐AM (5 μm) prevented activation of the inward current by 5‐HT, which is a property similar to that previously reported for ATP and angiotensin II (Murali et al. 2014). The effect of BAPTA‐AM was probably not the result of non‐specific external blockade of the underlying channels because intracellular application of BAPTA via the patch pipette during whole‐cell recording also caused inhibition of the ATP‐activated inward current (M. Zhang and C. A. Nurse, unpublished observations). Both the 5‐HT‐evoked Δ[Ca2+]i and inward current were sensitive to low doses of ketanserin, suggesting involvement of the 5‐HT2 receptor. More compelling evidence for the role of Panx‐1 channels as the carriers of the inward current was obtained in experiments using UTP. Although the UTP‐activated current (I UTP) in type II cells was previously shown to be sensitive to low doses of carbenoxolone (5 μm) (Zhang et al. 2012), the ability of this drug to distinguish Panx‐1 channels from connexin hemichannels is increasingly being challenged (Lohman & Isakson, 2014). In the present study, we found that I UTP was also reversibly abolished by the specific mimetic peptide inhibitor of Panx‐1 channels, 10Panx peptide (Thompson et al. 2008; Lohman & Isakson, 2014), whereas its scrambled control peptide scPanx was ineffective. These data, together with the previous immunohistochemical evidence that Panx‐1 is expressed in rat type II cells, provide strong support for the proposal that Panx‐1 channels are the mediators of the inward current and the conduits for ATP release from these cells, as reported previously (Zhang et al. 2012).
Evidence for a role of 5‐HT2A receptors in the type II cell response
Expression of mRNA for multiple G‐protein coupled 5‐HT receptor subtypes has been detected in the rat CB, although most functional studies have implicated a role for 5‐HT2AR, localized primarily to type I cells (Wang et al. 2000; Zhang et al. 2003; Jacono et al. 2005; Peng et al. 2006; Liu et al. 2011; Yokoyama et al. 2015). In the present study, the 5‐HT2AR subtype also appeared to be a major contributor to both the 5‐HT‐induced Ca2+ rise and the 5‐HT‐activated inward current in type II cells. Accordingly, both responses were sensitive to low concentrations of the 5‐HT2AR blocker ketanserin and had a submicromolar affinity for 5‐HT (EC50 ∼200 nm), consistent with that for 5‐HT2AR (Muraoka et al. 1998; Okoro, 1999). Minor contributions from other 5‐HT receptors known to be expressed in the rat CB could not be ruled out (Yokoyama et al. 2015) because residual intracellular Ca2+ responses to 5‐HT persisted in the presence of ketanserin in some experiments. However, pharmacological tests did not support a significant contribution from 5‐HT5AR, which display submicromolar affinity for 5‐HT (Noda et al. 2003; Goodfellow et al. 2012), can also signal via IP3‐sensitive Ca2+ stores (Noda et al. 2003) and have been localized to type I cell clusters in a previous study (Wang et al. 2000). In particular, the selective 5‐HT5AR blocker SB 699551 (10 μm) (Thomas et al. 2006; Goodfellow et al. 2012) failed to affect the 5‐HT‐induced intracellular Ca2+ responses in type II cells. We attribute the apparent blockade of the 5‐HT‐induced inward current by SB 699551 to a non‐specific blockade of the channels because similar blockade occurred when ATP was used as the ligand. Additional studies are required to determine whether other 5‐HT receptors in addition to 5‐HT2AR are present on type II cells. Previous immunofluorescence studies demonstrated the expression of 5‐HT2AR in association with type I cell clusters in the rat CB in situ (Zhang et al. 2003; Liu et al. 2011) and, although the evidence was consistent with type I cell staining, the procedures used could not unambiguously exclude type II cell staining as well. Given that rat type I cells in situ have been shown to express not only the 5‐HT biosynthetic enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase and the plasma membrane 5‐HT transporter (Yokoyama et al. 2013), but also endogenous levels of 5‐HT (Liu et al. 2011), the present study adds further support for a paracrine role of 5‐HT possibly also involving 5‐HT2A receptors on type II cells.
Contribution of 5‐HT signalling to carotid body physiology
The present study adds to the complexity of 5‐HT signalling in the CB by proposing an additional paracrine signalling pathway via glial‐like type II cells. Although there is strong evidence that chemoreceptor type I cells possess the machinery for synthesis, storage and release of 5‐HT (Zhang & Nurse, 2000; Peng et al. 2009; Liu et al. 2011; Yokoyama et al. 2013), the role of 5‐HT during CB chemotransduction is still unclear. For example, in one study using cultured CB cells from juvenile rats, exogenous 5‐HT caused a protein kinase C‐dependent depolarization in a subpopulation (∼40%) of type I cells via ketanserin‐sensitive 5‐HT2AR and, moreover, the hypoxia‐induced depolarization in type I cells was partially inhibited by ketanserin (Zhang et al. 2003). This result is consistent with a positive feedback role for 5‐HT acting via 5‐HT2AR on type I cells. Whether or not acute hypoxia releases detectable 5‐HT from CB cells under normal conditions may depend on the method of detection, the sensitivity of the assay, the type of preparation (e.g. whole organ vs. isolated cells) and animal age, or perhaps the level of oxidative stress present (Zhang et al. 2003; Jacono et al. 2005; Peng et al. 2009; Ramirez et al. 2012). In a more recent study, exogenous 5‐HT failed to elicit intracellular Ca2+ responses in adult rat type I cells in normoxia, although it did enhance hypoxia‐induced Ca2+ responses via ketanserin‐sensitive 5‐HT2 receptors (Yokoyama et al. 2015). These data contrast with those of the present study on juvenile rats where a small subpopulation of type I cells did respond to exogenous 5‐HT and may reflect differences in culture conditions, animal age or sampling procedures. In excised intact CB‐nerve preparations from adult rats, exogenous 5‐HT had no effect on the onset or magnitude of the hypoxia‐evoked sinus nerve discharge; however, it did prolong the hypoxic sensory response via ketanserin‐sensitive 5‐HT2 receptors, prompting the suggestion that 5‐HT modulated the dynamics of the sensory discharge (Jacono et al. 2005). It should be noted that the effects of exogenous 5‐HT on sensory discharge are complicated by the fact that 5‐HT can have both postsynaptic and presynaptic effects, and the latter can lead to the release of both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters (Nurse, 2014). A clear role has been demonstrated for 5‐HT in the long‐term facilitation of CB sensory discharge in adult rats exposed to CIH (Peng et al. 2006; Peng et al. 2009). This facilitation is dependent on release of 5‐HT coupled to the 5‐HT2R‐protein kinase C signalling pathway, leading to NADPH oxidase activation and reactive oxygen species generation in type I cells (Peng et al. 2009). Whether or not paracrine 5‐HT‐mediated type II cell signalling, as proposed in the present study, contributes to CB sensory physiology in adult rats, and especially in conditions associated with CIH, remains to be determined. In summary, the ability of 5‐HT to activate Panx‐1 channels in type II cells provides a potential paracrine signalling pathway for enhancing CB excitation via release of the excitatory transmitter ATP (Zhang et al. 2012), combined with the generation of adenosine from the breakdown of extracellular ATP by ectonucleotidases (Conde et al. 2012; Nurse, 2014; Murali & Nurse, 2016). A proposed model of the potential autocrine–paracrine interactions involving 5‐HT at the CB chemosensory synapse is summarized in Fig. 11.
Figure 11. Schematic representation of the proposed autocrine–paracrine role of 5‐HT at the carotid body sensory synapse.
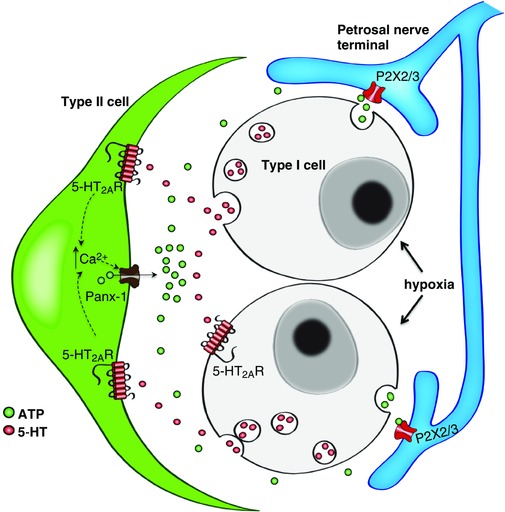
Chemostimuli such as hypoxia cause depolarization of type I cells and the release of several neurotransmitters of which only ATP (green circles) and 5‐HT (red circles) are shown for clarity. 5‐HT may act on autocrine–paracrine 5‐HT2A receptors located on a subpopulation of receptor type I cells and on the majority of adjacent glial‐like type II cells. Stimulation of 5‐HT2A receptors on type I cells may facilitate membrane depolarization and the release of ATP, an excitatory neurotransmitter that acts on P2X2/3 receptors on petrosal afferent terminals. Stimulation of 5‐HT2A receptors on type II cells may cause a rise in intracellular Ca2+, leading to the opening of Panx‐1 channels, which act as conduits for the further release of ATP. Enhanced 5‐HT signalling via type II cells, leading to ATP release, may contribute, in part, to the increased sensory discharge during exposure to chronic intermittent hypoxia. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author contributions
SM helped to prepare the cultures, carried out all the Ca2+ imaging experiments and data analysis, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. MZ performed all of the electrophysiological experiments, analysed the data, and helped prepare the figures. CAN was involved in planning and designing of all the experiments, helped to interpret the data, and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript submitted for publication. All persons designated as authors qualify for authorship, and all those who qualify for authorship are listed.
Funding
This work was supported by an operating grant to CAN from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP 142469). SM held a CIHR/NSERC CGS‐M graduate scholarship award.
Acknowledgements
We thank Cathy Vollmer for expert technical assistance and Drs Erin Leonard and Shaima Salman for assistance with preparation of the figures. We also thank Dr Roger Thompson for providing samples of 10Panx and scPanx peptides.
References
- Barnes NM & Sharp T (1999). A review of central 5‐HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 38, 1083–1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conde SV, Monteiro EC, Rigual R, Obeso A & Gonzalez C (2012). Hypoxic intensity: a determinant for the contribution of ATP and adenosine to the genesis of carotid body chemosensory activity. J Appl Physiol 112, 2002–2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C, Almaraz L, Obeso A & Rigual R (1994). Carotid body chemoreceptors: from natural stimuli to sensory discharges. Physiol Rev 74, 829–898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow NM, Bailey CD & Lambe EK (2012). The native serotonin 5‐HT(5A) receptor: electrophysiological characterization in rodent cortex and 5‐HT(1A)‐mediated compensatory plasticity in the knock‐out mouse. J Neurosci 32, 5804–5809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronblad M, Liesi P & Rechardt L (1983). Serotonin‐like immunoreactivity in rat carotid body. Brain Res 276, 348–350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang YJ, Maruyama Y, Dvoryanchikov G, Pereira E, Chaudhari N & Roper SD (2007). The role of pannexin 1 hemichannels in ATP release and cell‐cell communication in mouse taste buds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 6436–6441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iturriaga R & Alcayaga J (2004). Neurotransmission in the carotid body: transmitters and modulators between glomus cells and petrosal ganglion nerve terminals. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 47, 46–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iturriaga R, Del Rio R, Idiaquez J & Somers VK (2016). Carotid body chemoreceptors, sympathetic neural activation, and cardiometabolic disease. Biol Res 49, 13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacono FJ, Peng YJ, Kumar GK & Prabhakar NR (2005). Modulation of the hypoxic sensory response of the carotid body by 5‐hydroxytryptamine: role of the 5‐HT2 receptor. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 145, 135–142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby GC & McQueen DS (1984). Effects of the antagonists MDL 72222 and ketanserin on responses of cat carotid body chemoreceptors to 5‐hydroxytryptamine. Br J Pharmacol 83, 259–269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar P & Prabhakar NR (2012). Peripheral chemoreceptors: function and plasticity of the carotid body. Compr Physiol 2, 141–219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J, Wei X, Zhao C, Hu S, Duan J, Ju G, Wong‐Riley MT & Liu Y (2011). 5‐HT induces enhanced phrenic nerve activity via 5‐HT(2A) receptor/PKC mechanism in anesthetized rats. Eur J Pharmacol 657, 67–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locovei S, Wang J & Dahl G (2006). Activation of pannexin 1 channels by ATP through P2Y receptors and by cytoplasmic calcium. FEBS Lett 580, 239–244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman AW & Isakson BE (2014). Differentiating connexin hemichannels and pannexin channels in cellular ATP release. FEBS Lett 588, 1379–1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murali S & Nurse CA (2016). Purinergic signalling mediates bidirectional crosstalk between chemoreceptor type I and glial‐like type II cells of the rat carotid body. J Physiol 594, 391–406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murali S, Zhang M & Nurse CA (2014). Angiotensin II mobilizes intracellular calcium and activates pannexin‐1 channels in rat carotid body type II cells via AT1 receptors. J Physiol 592, 4747–4762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murali S, Zhang M & Nurse CA (2015). Paracrine signaling in glial‐like type II cells of the rat carotid body. Adv Exp Med Biol 860, 41–47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraoka S, Kamei K, Muneoka K & Takigawa M (1998). Chronic imipramine administration amplifies the serotonin2A receptor‐induced intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in C6 glioma cells through a calmodulin‐dependent pathway. J Neurochem 71, 1709–1718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M, Yasuda S, Okada M, Higashida H, Shimada A, Iwata N, Ozaki N, Nishikawa K, Shirasawa S, Uchida M, Aoki S & Wada K (2003). Recombinant human serotonin 5A receptors stably expressed in C6 glioma cells couple to multiple signal transduction pathways. J Neurochem 84, 222–232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse CA ( 2010). Neurotransmitter and neuromodulatory mechanisms at peripheral arterial chemoreceptors. Exp Physiol 95, 657–667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse CA (2014). Synaptic and paracrine mechanisms at carotid body arterial chemoreceptors. J Physiol 592, 3419–3426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okoro EO (1999). Overlap in the pharmacology of L‐type Ca2+‐channel blockers and 5‐HT2 receptor antagonists in rat aorta. J Pharm Pharmacol 51, 953–957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oomori Y, Nakaya K, Tanaka H, Iuchi H, Ishikawa K, Satoh Y & Ono K (1994). Immunohistochemical and histochemical evidence for the presence of noradrenaline, serotonin and gamma‐aminobutyric acid in chief cells of the mouse carotid body. Cell Tissue Res 278, 249–254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng YJ, Nanduri J, Yuan G, Wang N, Deneris E, Pendyala S, Natarajan V, Kumar GK & Prabhakar NR (2009). NADPH oxidase is required for the sensory plasticity of the carotid body by chronic intermittent hypoxia. J Neurosci 29, 4903–4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng YJ, Yuan G, Jacono FJ, Kumar GK & Prabhakar NR (2006). 5‐HT evokes sensory long‐term facilitation of rodent carotid body via activation of NADPH oxidase. J Physiol 576, 289–295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piskuric NA & Nurse CA (2012). Effects of chemostimuli on [Ca2+]i responses of rat aortic body type I cells and endogenous local neurons: Comparison with carotid body cells. J Physiol 590, 2121–2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar NR ( 2011). Sensory plasticity of the carotid body: role of reactive oxygen species and physiological significance. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 178, 375–380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar NR, Peng YJ, Kumar GK & Nanduri J (2015). Peripheral chemoreception and arterial pressure responses to intermittent hypoxia. Compr Physiol 5, 561–577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez M, Gallego‐Martin T, Olea E, Rocher A, Obeso A & Gonzalez C (2012). Serotonin dynamics and actions in the rat carotid body: preliminary findings. Adv Exp Med Biol 758, 255–263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz HD, Marcus NJ & Del Rio R (2015). Mechanisms of carotid body chemoreflex dysfunction during heart failure. Exp Physiol 100, 124–129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas DR, Soffin EM, Roberts C, Kew JN, de la Flor RM, Dawson LA, Fry VA, Coggon SA, Faedo S, Hayes PD, Corbett DF, Davies CH & Hagan JJ (2006). SB‐699551‐A (3‐cyclopentyl‐N‐[2‐(dimethylamino)ethyl]‐N‐[(4′‐{[(2‐phenylethyl)amino]methyl}‐4 ‐biphenylyl)methyl]propanamide dihydrochloride), a novel 5‐ht5A receptor‐selective antagonist, enhances 5‐HT neuronal function: Evidence for an autoreceptor role for the 5‐ht5A receptor in guinea pig brain. Neuropharmacology 51, 566–577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson RJ, Jackson MF, Olah ME, Rungta RL, Hines DJ, Beazely MA, MacDonald JF & MacVicar BA (2008). Activation of pannexin‐1 hemichannels augments aberrant bursting in the hippocampus. Science 322, 1555–1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse A, Yan L, Lee AK & Tse FW (2012). Autocrine and paracrine actions of ATP in rat carotid body. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 90, 705–711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkhratsky A & Kettenmann H (1996). Calcium signalling in glial cells. Trends Neurosci 19, 346–352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang ZY, Keith IM, Beckman MJ, Brownfield MS, Vidruk EH & Bisgard GE (2000). 5‐HT5a receptors in the carotid body chemoreception pathway of rat. Neurosci Lett 278, 9–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J, Tse FW & Tse A (2003). ATP triggers intracellular Ca2+ release in type II cells of the rat carotid body. J Physiol 549, 739–747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama T, Misuzu YY & Yamamoto Y (2013). Immunohistochemical localization of tryptophan hydroxylase and serotonin transporter in the carotid body of the rat. Histochem Cell Biol 140, 147–155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama T, Nakamuta N, Kusakabe T & Yamamoto Y (2015). Serotonin‐mediated modulation of hypoxia‐induced intracellular calcium responses in glomus cells isolated from rat carotid body. Neurosci Lett 597, 149–153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M, Fearon IM, Zhong H & Nurse CA (2003). Presynaptic modulation of rat arterial chemoreceptor function by 5‐HT: role of K+ channel inhibition via protein kinase C. J Physiol 551, 825–842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M & Nurse CA (2000). Does endogenous 5‐HT mediate spontaneous rhythmic activity in chemoreceptor clusters of rat carotid body? Brain Res 872, 199–203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M, Piskuric NA, Vollmer C & Nurse CA (2012). P2Y2 receptor activation opens pannexin‐1 channels in rat carotid body type II cells: potential role in amplifying the neurotransmitter ATP. J Physiol 590, 4335–4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M, Zhong H, Vollmer C & Nurse CA (2000). Co‐release of ATP and ACh mediates hypoxic signalling at rat carotid body chemoreceptors. J Physiol 525, 143–158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


