Erratum
Following the publication of this article [1], it was brought to our attention that due to miscommunications in the production process, Fig. 1 labels were missing and Fig. 4 labelling was incorrect in the original online version.
Fig. 1.
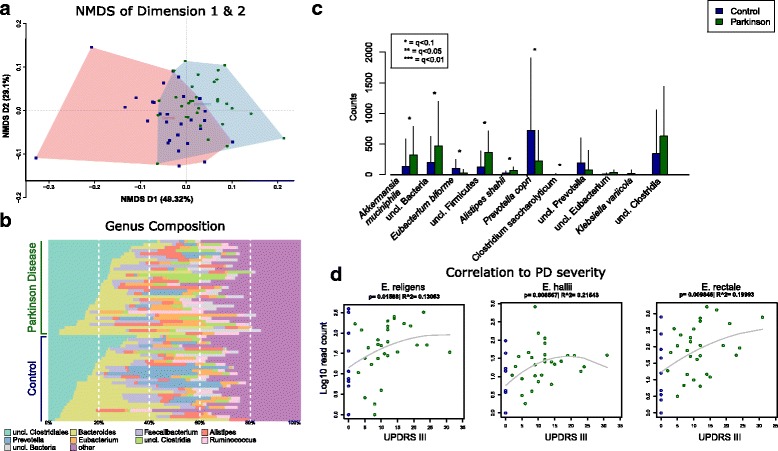
Genus and species level differences in PD participants and controls. a NMDS ordination of all samples used in this study, using a Bray–Curtis between-sample distance at genus level. This shows the composition relatedness of samples and that PD samples form a subgroup. Outliers denoted with # took antibiotics in a period of 28–34 days prior to feces sampling. See also Additional file 2 for taxonomic analysis while taking these samples into account. b Genus-level sample composition. c The most significant species or groups of taxa that could not be further classified. Unclassified Prevotella is not significant after multiple testing, but was implied in PD in several studies (see “Discussion”). d Species correlating strongest to PD disease severity (as measured by UPDRS III). Note that after multiple testing correction, these are all q > 0.1
Fig. 4.
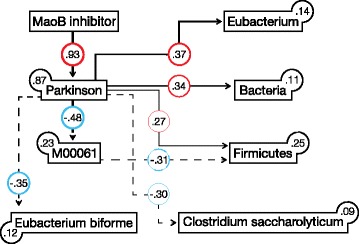
Structural equation modeling (SEM). SEM analysis of PD in relation to key correlating bacterial functions and taxa (MSEA = 0, PCLOSE = 0.79, AIC = 59.385). Values on paths and boxes are standardized regression and determination coefficients (R2), respectively. Dashed lines and red colors denote negative relationships. The thickness of lines is proportional to regression coefficients. All relationships are statistically significant (P < 0.05, Additional file 5). AIC Akaike information criterion, MSEA mean square error of approximation, PCLOSE probability of close fit
The errors:
The x and y axis were accidentally omitted from Fig. 1c and d, as well as the key from 1b. The corrected Fig. 1 is presented below:
MaoB hemmer was erroneously used instead of the English term MaoB inhibitor in Fig. 4. The corrected Fig. 4 is presented below:
The above errors have been corrected in the original version of this article [1].
Footnotes
The online version of the original article can be found under doi:10.1186/s13073-017-0428-y.
Contributor Information
P. Bork, Email: bork@EMBL-Heidelberg.de
U. Wüllner, Email: wuellner@uni-bonn.de
Reference
- 1.Bedarf JR, et al. Functional implications of microbial and viral gut metagenome changes in early stage L-DOPA-naïve Parkinson’s disease patients. Genome Medicine. 2017;9:39. doi: 10.1186/s13073-017-0428-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


