Abstract
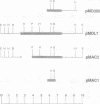
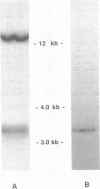
The DNA sequence of the gene encoding the protective surface protein antigen (SPA) of Rickettsia prowazekii has been determined. The open reading frame of 4836 nucleotides with promoter and ribosome-binding site is present on a 10.1-kilobase EcoRI fragment. The encoded carboxyl terminus of the 169-kDa protein contains a potential transmembrane region and hydrophilic regions with many lysine and arginine residues potentially accessible to proteolytic cleavage. Because the rickettsia-derived SPA has an estimated molecular mass of only 120 kDa and does not contain several predicted large carboxyl-region CNBr fragments, the SPA product appears to be processed by the rickettsiae. Eight other CNBr fragments were identical in sequence to those predicted from the encoded gene. A complementary 8.7-kilobase EcoRI fragment of Rickettsia typhi DNA was cloned. This fragment lacked a 1433-base-pair region that included the promoter, ribosome-binding site, and the initial 1162 base pairs of the open reading frame encoding the R. prowazekii SPA but had a 3674-base-pair region identical with the remainder of the R. prowazekii SPA gene sequence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumeister W., Karrenberg F., Rachel R., Engel A., ten Heggeler B., Saxton W. O. The major cell envelope protein of Micrococcus radiodurans (R1). Structural and chemical characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jul;125(3):535–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Smith P. F., Repine J. E., Joiner K. A. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter fetus infections. Failure of encapsulated Campylobacter fetus to bind C3b explains serum and phagocytosis resistance. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1434–1444. doi: 10.1172/JCI113474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl M., Dasch G. A. Characterization of human cytotoxic lymphocytes directed against cells infected with typhus group rickettsiae: evidence for lymphokine activation of effectors. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2654–2661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl M., Tibbs C. W., Dobson M. E., Paparello S., Dasch G. A. Diagnosis of acute typhus infection using the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):791–793. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl M., Vaidya S., Robbins F. M., Ching W. M., Hartzman R. J., Dasch G. A. Heterogeneity of CD4-positive human T-cell clones which recognize the surface protein antigen of Rickettsia typhi. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1276-1280.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching W. M., Dasch G. A., Carl M., Dobson M. E. Structural analyses of the 120-kDa serotype protein antigens of typhus group rickettsiae. Comparison with other S-layer proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:334–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A. Isolation of species-specific protein antigens of Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia prowazekii for immunodiagnosis and immunoprophylaxis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):333–341. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.333-341.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Samms J. R., Williams J. C. Partial purification and characterization of the major species-specific protein antigens of Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia prowazekii identified by rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):276–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.276-288.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. G., Boeke J. D., Model P. Fine structure of a membrane anchor domain. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90329-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D. Three-dimensional structure of membrane and surface proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:595–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. A., Smit J., Agabian N. Transcriptional analysis of the major surface array gene of Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4706–4713. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4706-4713.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS E., WITKOP B. Nonenzymatic cleavage of peptide bonds: the methionine residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1856–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovmöller S., Sjögren A., Wang D. N. The structure of crystalline bacterial surface layers. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1988;51(2):131–163. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(88)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koval S. F., Murray R. G. The isolation of surface array proteins from bacteria. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;62(11):1181–1189. doi: 10.1139/o84-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner J., Sumper M. The primary structure of a procaryotic glycoprotein. Cloning and sequencing of the cell surface glycoprotein gene of halobacteria. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9724–9729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepault J., Pitt T. Projected structure of unstained, frozen-hydrated T-layer of Bacillus brevis. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):101–105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01768.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misiti J., Dasch G. A. In vitro antigen-specific antibody response to the species-specific surface protein antigens of typhus group rickettsiae by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: generation of an antigen-dependent suppressor T cell. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2689–2694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E. L., Mallavia L. P., Tzianabos T., Obijeski J. F. Electron microscopy of the cell wall of Rickettsia prowazeki. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):1158–1166. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.1158-1166.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J., Peters M., Lottspeich F., Schäfer W., Baumeister W. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the gene encoding the Deinococcus radiodurans surface protein, derived amino acid sequence, and complementary protein chemical studies. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5216–5223. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5216-5223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Dasch G. A. The line blot: an immunoassay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Its application to the serotyping of gram-negative bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Dec 20;125(1-2):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D., Jones M. External layers of Rickettsia prowazekii and Rickettsia rickettsii: occurrence of a slime layer. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):233–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.233-246.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers in procaryotes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2891–2897. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2891-2897.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers on bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:311–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. K., Winkler H. H. Separation of inner and outer membranes of Rickettsia prowazeki and characterization of their polypeptide compositions. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):963–971. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.963-971.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi A., Uchihi R., Adachi T., Sasaki T., Hayakawa S., Yamagata H., Tsukagoshi N., Udaka S. Characterization of the genes for the hexagonally arranged surface layer proteins in protein-producing Bacillus brevis 47: complete nucleotide sequence of the middle wall protein gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):935–945. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.935-945.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi A., Uchihi R., Tabata R., Takahashi Y., Hashiba H., Sasaki T., Yamagata H., Tsukagoshi N., Udaka S. Characterization of the genes coding for two major cell wall proteins from protein-producing Bacillus brevis 47: complete nucleotide sequence of the outer wall protein gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):365–373. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.365-373.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. O., Williamson L. R., Winkler H. H., Krause D. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Rickettsia prowazekii citrate synthase gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3564–3572. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3564-3572.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata H., Adachi T., Tsuboi A., Takao M., Sasaki T., Tsukagoshi N., Udaka S. Cloning and characterization of the 5' region of the cell wall protein gene operon in Bacillus brevis 47. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1239–1245. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1239-1245.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]