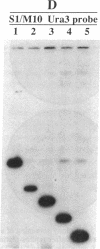
Abstract
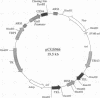
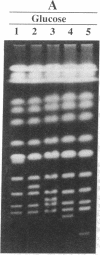
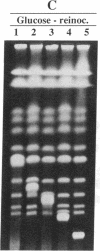
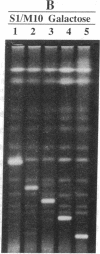
Yeast artificial chromosome cloning is an attractive technology for genomic mapping studies because very large DNA segments can be readily propagated. However, detailed analyses often require the extensive application of blotting-hybridization techniques because artificial chromosomes are normally present at only one copy per haploid genome. We have developed a cloning vector and host strain that alleviate this problem by permitting copy number amplification of artificial chromosomes. The vector includes a conditional centromere that can be turned on or off by changing the carbon source. Strong selective pressure for extra copies of the artificial chromosome can be applied by selecting for the expression of a heterologous thymidine kinase gene. When this system was used, artificial chromosomes ranging from about 100 to 600 kilobases in size were readily amplified 10- to 20-fold. The selective conditions did not induce obvious rearrangements in any of the clones tested. Reactivation of the centromere in amplified artificial chromosome clones resulted in stable maintenance of an elevated copy number for 20 generations. Applications of copy number control to various aspects of artificial chromosome analysis are addressed.
Full text
PDF

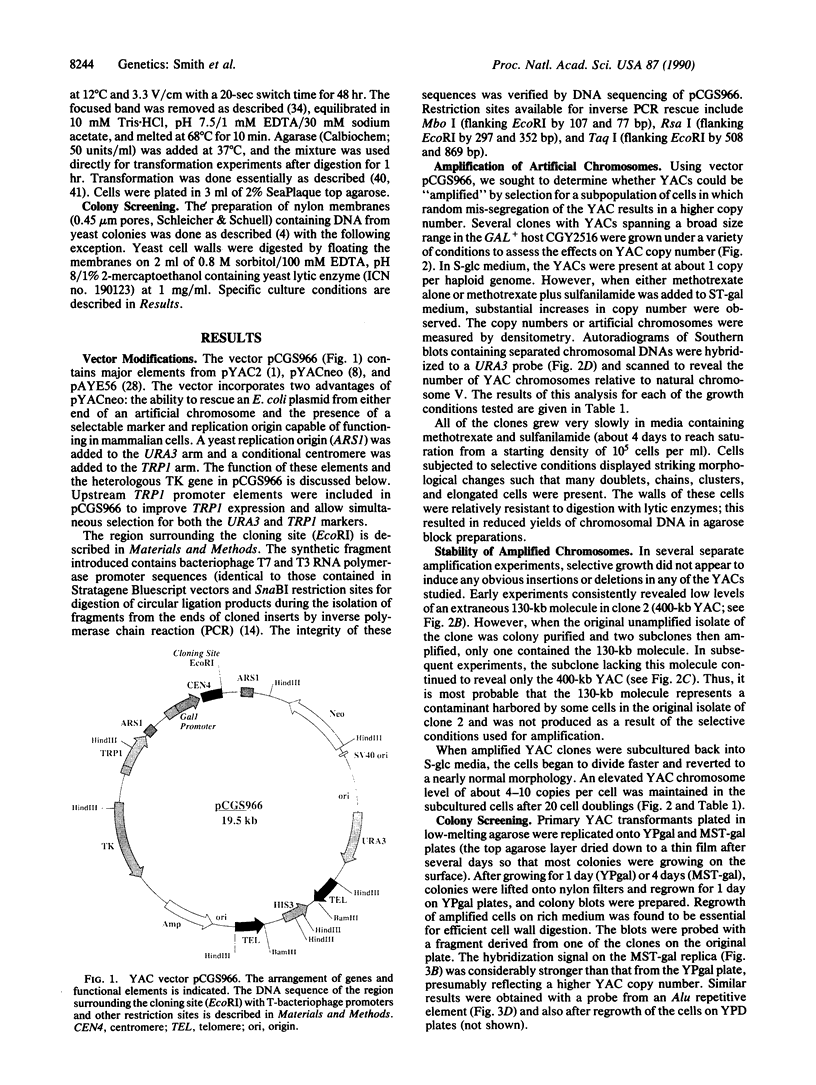
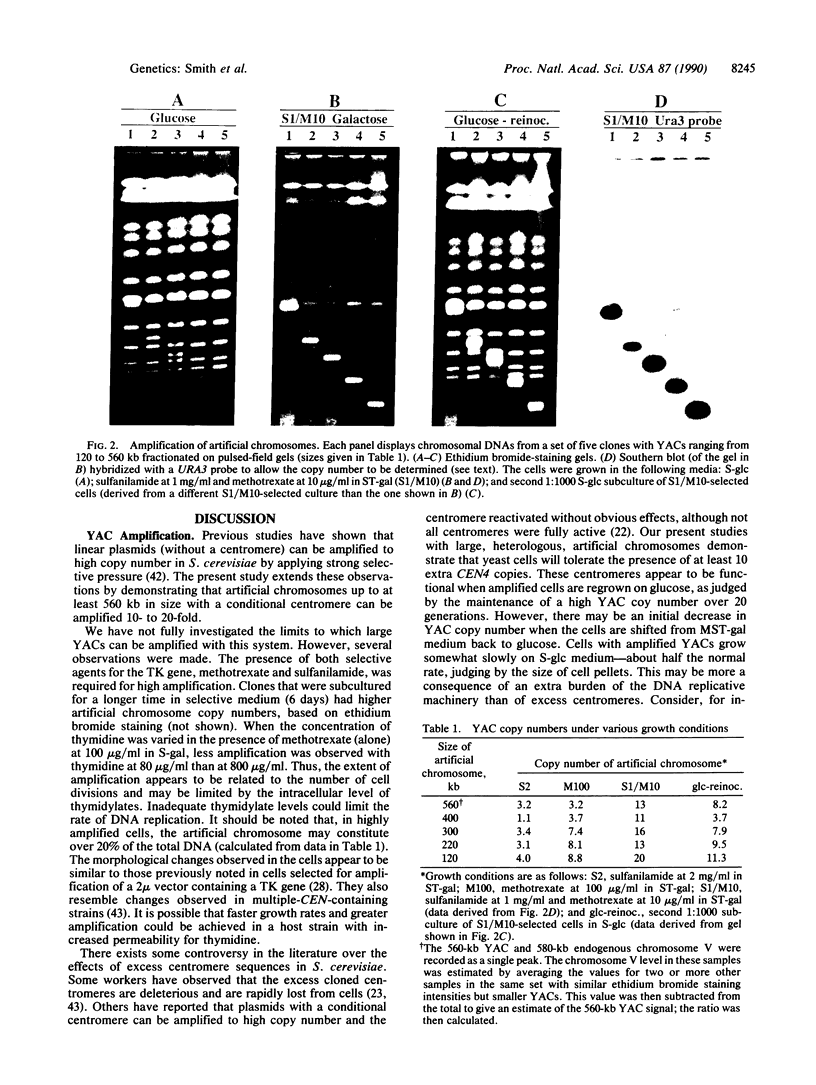

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand R., Villasante A., Tyler-Smith C. Construction of yeast artificial chromosome libraries with large inserts using fractionation by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3425–3433. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs J. D. Transformation of yeast by a replicating hybrid plasmid. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):104–109. doi: 10.1038/275104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein B. H., Silverman G. A., Little R. D., Burke D. T., Korsmeyer S. J., Schlessinger D., Olson M. V. Isolation of single-copy human genes from a library of yeast artificial chromosome clones. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1348–1351. doi: 10.1126/science.2544027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgers P. M., Percival K. J. Transformation of yeast spheroplasts without cell fusion. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jun;163(2):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chlebowicz-Sledziewska E., Sledziewski A. Z. Construction of multicopy yeast plasmids with regulated centromere function. Gene. 1985;39(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Isolation of a yeast centromere and construction of functional small circular chromosomes. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):504–509. doi: 10.1038/287504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H., Cross S. pYAC-4 Neo, a yeast artificial chromosome vector which codes for G418 resistance in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11817–11817. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Waterston R., Kiff J., Sulston J., Kohara Y. Genome linking with yeast artificial chromosomes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):184–186. doi: 10.1038/335184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Urso M., Zucchi I., Ciccodicola A., Palmieri G., Abidi F. E., Schlessinger D. Human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene carried on a yeast artificial chromosome encodes active enzyme in monkey cells. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):531–534. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F., Mellor J., Roberts N. A., King R. M., Burke D. C., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of human interferon-alpha directed by the TRP1 5' region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2287–2302. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erhart E., Hollenberg C. P. The presence of a defective LEU2 gene on 2 mu DNA recombinant plasmids of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is responsible for curing and high copy number. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):625–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.625-635.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fangman W. L., Hice R. H., Chlebowicz-Sledziewska E. ARS replication during the yeast S phase. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):831–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton T. R., Bowcock A. M., Smith D. R., Daneshvar L., Green P., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Donis-Keller H. A 12 megabase restriction map at the cystic fibrosis locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):271–284. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futcher B., Carbon J. Toxic effects of excess cloned centromeres. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2213–2222. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garza D., Ajioka J. W., Burke D. T., Hartl D. L. Mapping the Drosophila genome with yeast artificial chromosomes. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):641–646. doi: 10.1126/science.2510296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Olson M. V. Systematic screening of yeast artificial-chromosome libraries by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán P., Ecker J. R. Development of large DNA methods for plants: molecular cloning of large segments of Arabidopsis and carrot DNA into yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11091–11105. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P., Mann C., Snyder M., Davis R. W. Mitotic stability of yeast chromosomes: a colony color assay that measures nondisjunction and chromosome loss. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Bloom K. Genetic manipulation of centromere function. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2397–2405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Vollrath D., Cheng Y., Kaiser D. Physical mapping of the Myxococcus xanthus genome by random cloning in yeast artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8917–8921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little R. D., Porta G., Carle G. F., Schlessinger D., D'Urso M. Yeast artificial chromosomes with 200- to 800-kilobase inserts of human DNA containing HLA, V kappa, 5S, and Xq24-Xq28 sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1598–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., Collins F. S. pYAC-RC, a yeast artificial chromosome vector for cloning DNA cut with infrequently cutting restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7743–7743. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick M. K., Shero J. H., Cheung M. C., Kan Y. W., Hieter P. A., Antonarakis S. E. Construction of human chromosome 21-specific yeast artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9991–9995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil J. B., Friesen J. D. Expression of the Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):386–393. doi: 10.1007/BF00352510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Schultes N. P., Szostak J. W. Chromosome length controls mitotic chromosome segregation in yeast. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil D. L., Villasante A., Fisher R. B., Vetrie D., Cox B., Tyler-Smith C. Structural instability of human tandemly repeated DNA sequences cloned in yeast artificial chromosome vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1421–1428. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Ledbetter S. A., Corbo L., Victoria M. F., Ramírez-Solis R., Webster T. D., Ledbetter D. H., Caskey C. T. Alu polymerase chain reaction: a method for rapid isolation of human-specific sequences from complex DNA sources. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6686–6690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge K. W., Zakian V. A. Introduction of extra telomeric DNA sequences into Saccharomyces cerevisiae results in telomere elongation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1488–1497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman G. A., Ye R. D., Pollock K. M., Sadler J. E., Korsmeyer S. J. Use of yeast artificial chromosome clones for mapping and walking within human chromosome segment 18q21.3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7485–7489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strich R., Woontner M., Scott J. F. Mutations in ARS1 increase the rate of simple loss of plasmids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):169–178. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traver C. N., Klapholz S., Hyman R. W., Davis R. W. Rapid screening of a human genomic library in yeast artificial chromosomes for single-copy sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5898–5902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Little R. D., Abidi F., Porta G., Labella T., Cooper T., Della Valle G., D'Urso M., Schlessinger D. Human Xq24-Xq28: approaches to mapping with yeast artificial chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;46(1):95–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zealey G. R., Goodey A. R., Piggott J. R., Watson M. E., Cafferkey R. C., Doel S. M., Carter B. L., Wheals A. E. Amplification of plasmid copy number by thymidine kinase expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):155–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00338407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]