Abstract
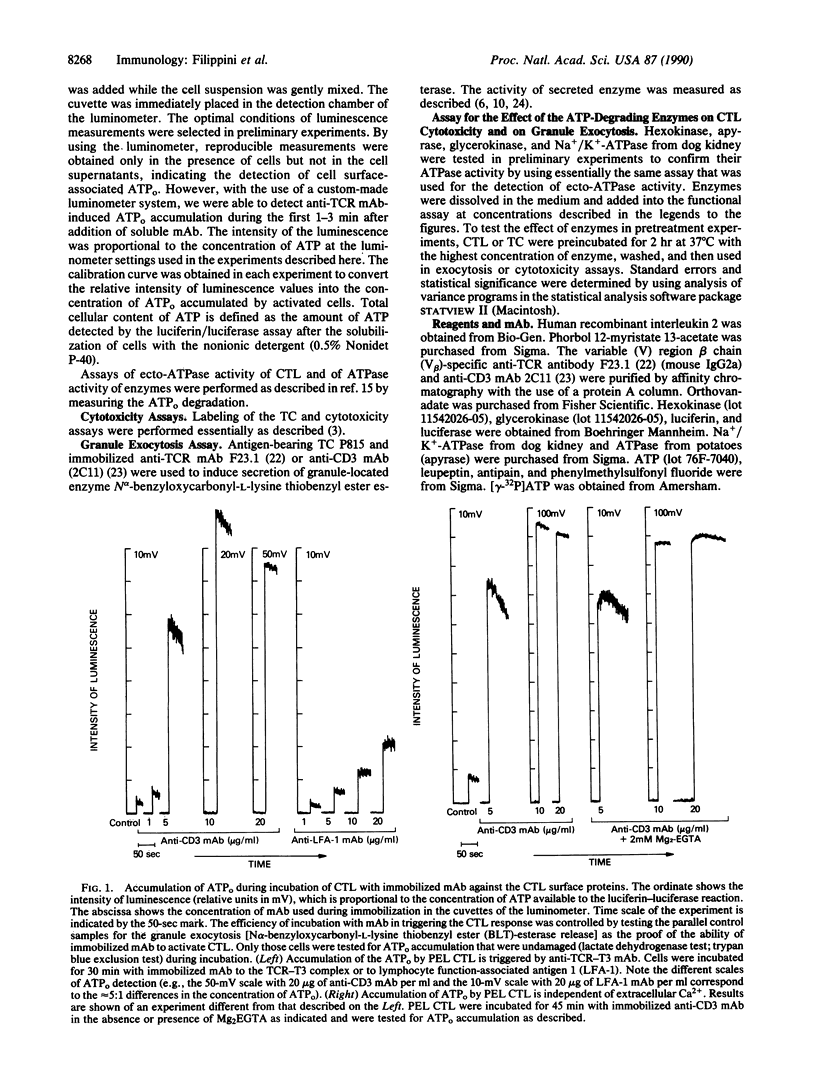
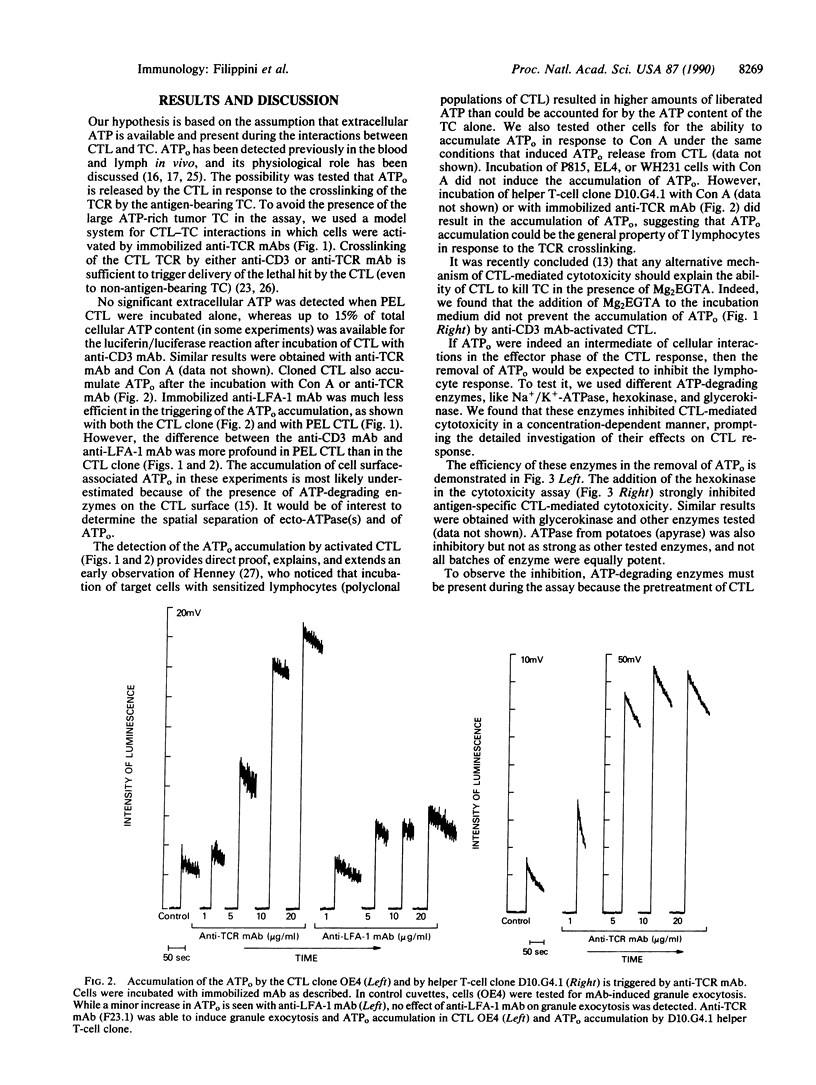
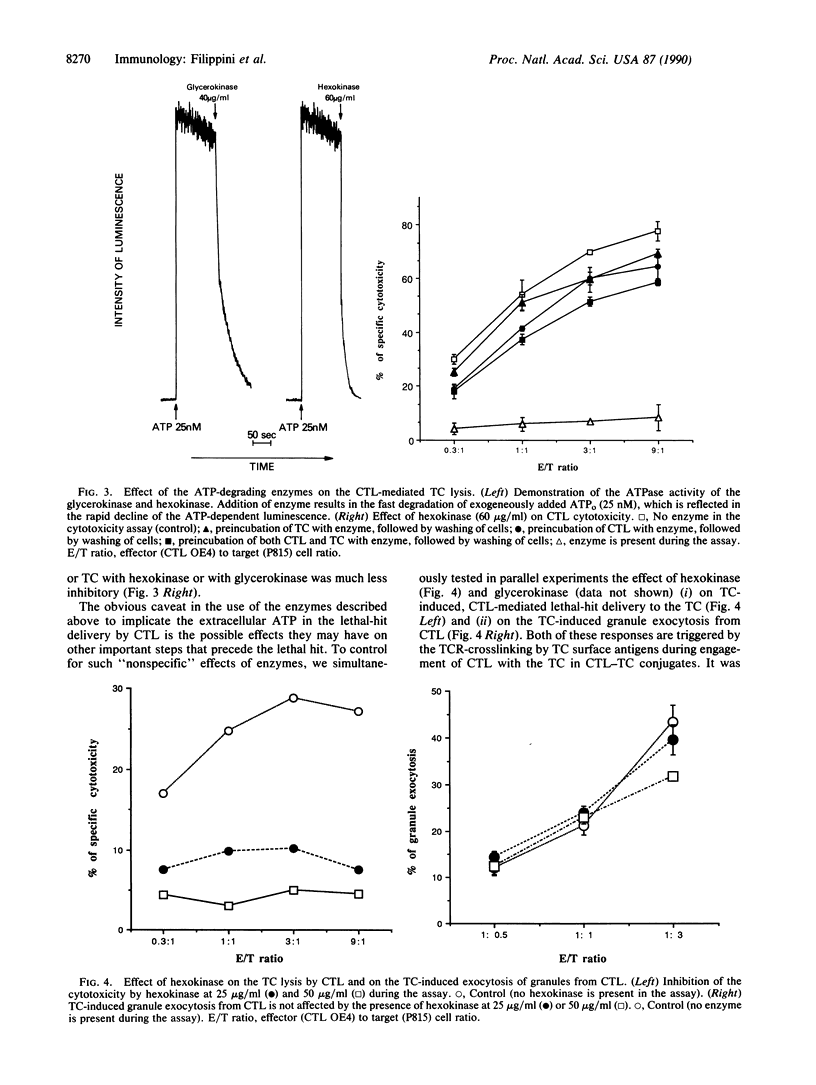
We hypothesized that cytolytic T lymphocytes (CTL) may utilize extracellular ATP (ATPo) during the effector phase of the CTL-target cell interactions and that CTL could be the source of ATPo. It is demonstrated here that incubation of CTL with activating ligands [Con A or monoclonal antibody (mAb) to the T-cell antigen receptor (TCR)] results in the extracellular Ca2(+)-independent accumulation of the ATPo. The addition of the ATP-degrading enzymes into the mixture of CTL and target cells results in a strong inhibition of the CTL-mediated, TCR-triggered lethal-hit delivery to the target cell. In a parallel control experiment, the employed enzymes did not affect target cell-induced, TCR-triggered exocytosis of granules from CTL. Thus, the removal of ATPo with enzymes does not interfere with the activation of CTL by the target cell but does block lytic events. Cloned helper T lymphocytes also accumulate ATPo after incubation with anti-TCR mAb or Con A, suggesting the possibility that ATPo, which acts in concert with ectoprotein kinases and/or purinergic receptors, may be of general use as a messenger in cellular interactions of T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Di Virgilio F., Bronte V., Collavo D., Zanovello P. Responses of mouse lymphocytes to extracellular adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP). Lymphocytes with cytotoxic activity are resistant to the permeabilizing effects of ATP. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1955–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippini A., Taffs R. E., Agui T., Sitkovsky M. V. Ecto-ATPase activity in cytolytic T-lymphocytes. Protection from the cytolytic effects of extracellular ATP. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):334–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Berrebi G. A., Takayama H., Munger W. E., Sitkovsky M. V. Biochemical and functional properties of serine esterases in acidic cytoplasmic granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2398–2405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S. Studies on the mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis. II. The use of various target cell markers to study cytolytic events. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):73–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang N., Wang D. J., Heppel L. A. Extracellular ATP is a mitogen for 3T3, 3T6, and A431 cells and acts synergistically with other growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7904–7908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Porcelli S., Tite J., Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Both a monoclonal antibody and antisera specific for determinants unique to individual cloned helper T cell lines can substitute for antigen and antigen-presenting cells in the activation of T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):836–856. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz D. M., Tonegawa S., Eisen H. N. Attachment of an anti-receptor antibody to non-target cells renders them susceptible to lysis by a clone of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7922–7926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kübler D., Pyerin W., Bill O., Hotz A., Sonka J., Kinzel V. Evidence for ecto-protein kinase activity that phosphorylates Kemptide in a cyclic AMP-dependent mode. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14549–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Sachs D. H., Samelson L. E., Bluestone J. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a murine T3 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Kane K. P., Mescher M. F., Clark W. R. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte mediated lysis without release of serine esterase. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):71–72. doi: 10.1038/330071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. A novel serine esterase expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):743–745. doi: 10.1038/314743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Verret C. R., Liu M. A., Eisen H. N. Serine esterase in cytolytic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):740–743. doi: 10.1038/322740a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R. Molecular mechanisms of cytolysis by complement and by cytolytic lymphocytes. J Cell Biochem. 1986;30(2):133–170. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240300205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport E., Fontaine J. Anticancer activities of adenine nucleotides in mice are mediated through expansion of erythrocyte ATP pools. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1662–1666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Pollard H. B., Heldman E. Real-time measurements of acetylcholine-induced release of ATP from bovine medullary chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 17;185(2):323–327. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80931-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Heppel L. A. Reciprocal control of membrane permeability of transformed cultures of mouse cell lines by external and internal ATP. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):708–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H. Phorbol-ester stimulated lysis of weak and nonspecific target cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):23–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitkovsky M. V. Mechanistic, functional and immunopharmacological implications of biochemical studies of antigen receptor-triggered cytolytic T-lymphocyte activation. Immunol Rev. 1988 Mar;103:127–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staerz U. D., Rammensee H. G., Benedetto J. D., Bevan M. J. Characterization of a murine monoclonal antibody specific for an allotypic determinant on T cell antigen receptor. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3994–4000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Newman A. S., Swanson J. A., Silverstein S. C. ATP4- permeabilizes the plasma membrane of mouse macrophages to fluorescent dyes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8884–8888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama H., Sitkovsky M. V. Antigen receptor-regulated exocytosis in cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):725–743. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama H., Trenn G., Humphrey W., Jr, Bluestone J. A., Henkart P. A., Sitkovsky M. V. Antigen receptor-triggered secretion of a trypsin-type esterase from cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):566–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama H., Trenn G., Sitkovsky M. V. A novel cytotoxic T lymphocyte activation assay. Optimized conditions for antigen receptor triggered granule enzyme secretion. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Nov 23;104(1-2):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama H., Trenn G., Sitkovsky M. V. Locus of inhibitory action of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in the antigen receptor-triggered cytotoxic T lymphocyte activation pathway. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2330–2336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trenn G., Takayama H., Sitkovsky M. V. Exocytosis of cytolytic granules may not be required for target cell lysis by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):72–74. doi: 10.1038/330072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Moatassim C., Dornand J., Mani J. C. Extracellular ATP increases cytosolic free calcium in thymocytes and initiates the blastogenesis of the phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-treated medullary population. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Mar 11;927(3):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



