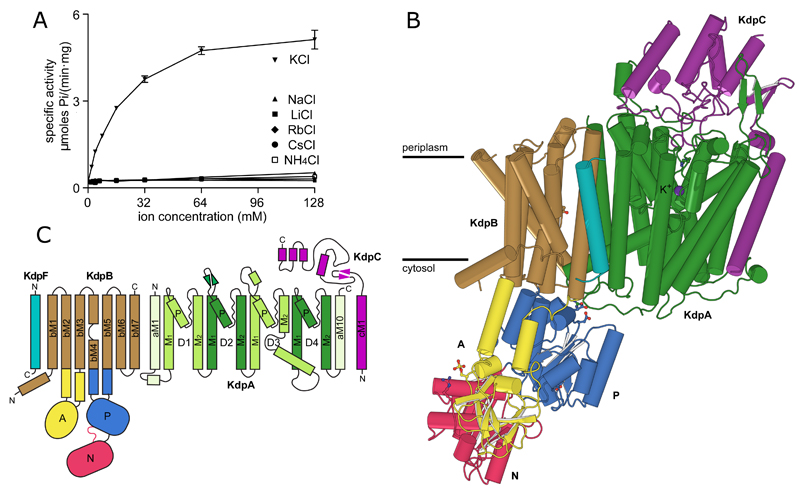
Figure 1. Overview of the KdpFABC complex.
(A) ATPase activity using purified, detergent-solubilized KdpFABC demonstrates robust stimulation by K+ with an apparent affinity of 24.8 mM and Vmax of 6.6 μmoles/(mg*min). There is neglible activity with other ions. Error bars indicate S.E. with n=3. (B) KdpA (green) has a K+ ion bound in the middle of the membrane (purple sphere). KdpB has a transmembrane domain (brown) and three cytoplasmic domains responsible for nucleotide binding (N, red), phosphoenzyme formation (P, blue) and dephosphorylation (A, yellow). KdpC (purple) and KdpF (cyan) have a single transmembrane helix and the soluble domain of KdpC is periplasmic. (C) Transmembrane topology diagram.