Abstract
LIM-Homeodomain (LIM-HD) transcription factors are highly conserved in animals where they are thought to act in a transcriptional ‘LIM code’ that specifies cell types, particularly in the central nervous system. In chick and mammals the interaction between two LIM-HD proteins, LHX3 and Islet1 (ISL1), is essential for the development of motor neurons. Using yeast two-hybrid analysis we showed that the Caenorhabditis elegans orthologs of LHX3 and ISL1, CEH-14 and LIM-7 can physically interact. Structural characterisation of a complex comprising the LIM domains from CEH-14 and a LIM-interaction domain from LIM-7 showed that these nematode proteins assemble to form a structure that closely resembles that of their vertebrate counterparts. However, mutagenic analysis across the interface indicates some differences in the mechanisms of binding. We also demonstrate, using fluorescent reporter constructs, that the two C. elegans proteins are co-expressed in a small subset of neurons. These data show that the propensity for LHX3 and Islet proteins to interact is conserved from C. elegans to mammals, raising the possibility that orthologous cell specific LIM-HD-containing transcription factor complexes play similar roles in the development of neuronal cells across diverse species.
Introduction
LIM-containing proteins are commonly found in eukaryotes of all types, but LIM-homeodomain (LIM-HD) transcription factors are unique to and highly conserved in animals. The proteins are characterised by two closely-spaced LIM domains (zinc fingers that mediate protein-protein interactions) at or near their N-termini, a central homeodomain (which binds DNA) and a C-terminal domain, the functions of which are usually unknown. There are six subfamilies of LIM-HD proteins (Fig. 1A). Vertebrates have two representatives from each subfamily (except teleost fish, which have up to four representatives from each subfamily), whereas most invertebrates have only one gene from each, or lack representation from one or more subfamilies1. Basal metazoans, which have simpler body plans, also contain genes for LIM-HD proteins, but none have been identified in plants or unicellular organisms suggesting that this family of proteins expanded and diversified early in metazoan evolution2, 3 (Fig. 1B). The contribution of LIM-HD proteins to cell specification and tissue patterning has been well studied in vertebrate neuronal development. Early observations that different combinations of LIM-HD proteins were expressed in different neurons4, 5, led to suggestions that a combinatorial transcriptional code (the “LIM-code”) involving these proteins was responsible for neuronal subtype specification6.
Figure 1.
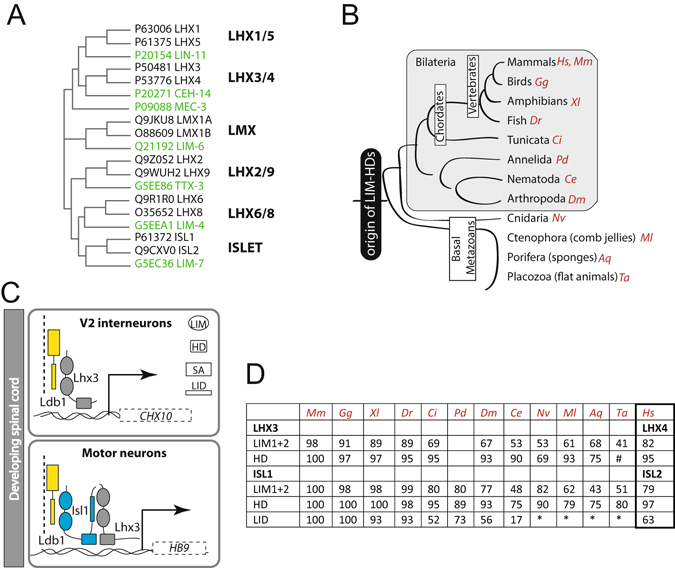
Islet- and LHX3-family LIM-HD proteins and interactors. (A) Simple phylogenetic tree diagram of LIM-HD proteins from mouse (black) and C. elegans (green) illustrating the LIM-HD families; Uniprot accession codes are provided. Branches and relationships are derived from analysis of these proteins using CLUSTAL OMEGA and CLUSTAL PHYLOGENY. Distances are not to scale. (B) Schematic of evolutionary relationships in metazoans. Hs – Homo sapiens; Ms – Mus musculus; Gg – Gallus gallus, Xl – Xenopus laevis, Dr – Danio rerio, Ci – Ciona intestinalis, Pd - Platynereis dumerilii, Ce -Caenorhabditis elegans, Dm – Drosophila melanogasta, Nv - Nematostella vectensis, Ml - Mnemiopsis leidyi, Aq- Amphimedon queenslandica, Ta - Trichoplax adhaerens. The branchpoints between some basal metazoans are controversial70, 71 and not indicated here. (C) Distinct transcriptional complexes drive different transcription programs in adjacent cell types in the developing ventral spinal cord in vertebrates. (D) Sequence identity (% compared to Hs proteins) between domains in metazoan LHX3 and ISL1 proteins. No domain identified (*), substantially truncated domain identified (#). No PdLHX3 gene was found.
The best characterised example of the LIM code relates to the developing ventral spinal cord in vertebrates. It involves LIM-HD factors LIM homeobox protein 3 (LHX3) and Islet 1 (ISL1). The expression of LHX3 in the absence of ISL1 in one population of post-mitotic cells results in V2 interneuron formation, whereas the expression of both LHX3 and ISL1 in an adjacent set of cells leads to motor neuron formation7. The alternate differentiation outcomes result from the formation of cell-specific transcription complexes. In developing V2 interneurons LHX3 binds to LIM-domain binding protein 1 (LDB1), which is an essential cofactor for LIM-HD proteins8, and this binary complex binds to LHX3 recognition elements on DNA, including those in the promoter region of Chx10, a V2 interneuron marker9 (Fig. 1C). In developing motor neurons ISL1 binds directly to LDB1, while LHX3 binds instead to ISL1. This ternary complex binds to ISL1/LHX3 recognition sites, including those in the promoter region of Hb9, which is a marker of motor neurons (Fig. 1C). The interaction between LHX3 and ISL1, first noted by Jurata and colleagues10, is mediated by the tandem LIM domains of LHX3 and a ~30-residue region in the C-terminal domain of ISL1 that was designated as the LHX3-binding domain in ISL111, but is hereafter referred to as a LIM interaction domain (LID). The structures of LHX3 in complex with each of ISL1 and LDB1 revealed that both proteins bind LHX3 in the same manner, despite considerable sequence variation in the interaction domains11.
Members of the same LIM-HD protein subfamily are often expressed in the same neural cell type. For example, ISL1/ISL2 and LHX3/LHX4 pairs are all expressed in developing motor neurons. Interactions between ISL1/LHX4, ISL2/LHX3 and ISL2/LHX4 have all been detected in vivo 10, 12, and the structures of the complexes are highly similar11, 12. Equivalent complexes are likely to exist in zebrafish and Drosophila, although the molecular details and functional roles of such complexes are less well documented7, 10, 11, 13–16. To determine if LHX3/ISL1-type interactions are widely conserved in metazoans, we focussed on the more divergent but highly characterised nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. These nematodes have seven LIM-HD proteins (one member from six subfamilies, and an additional member that is most closely related to the LHX3/LHX4 and LHX1/LHX5 families17, 18, Fig. 1A), all of which are expressed in neurons18–25. Early observations of expression patterns of LIM-HD proteins found little or no overlapping expression in C. elegans, suggesting that interactions between LIM-HD proteins might not be an evolutionarily conserved feature18. The C. elegans orthologs of ISL1 and LHX3 are LIM-7 and CEH-14, respectively. We hypothesised that these two LIM-HD proteins can interact to form cell-specific transcription complexes like their vertebrate counterparts. We identified an ISL1LID-like domain in LIM-7 and tested the ability of this domain to interact with CEH-14. The LIM interaction domain of LIM-7 (LIM-7LID) interacts with the tandem LIM domains of CEH-14 (CEH-14LIM1+2) in a similar fashion to ISL1LID contacting LHX3LIM1+2. Biophysical characterisation of a tethered complex of LIM-7LID with CEH-14LIM1+2, revealed that this complex is identical to the mouse counterpart and to other LIM/LID transcriptional assemblies that we have previously reported. We also demonstrate that the cellular expression patterns of fluorescently tagged reporter constructs of these genes, lim-7::mcherry and ceh-14::gfp, overlap in a restricted number of head and tail neurons. These data suggest that LHX3/ISL1 family interactions also exist in nematodes and have been conserved from early animal evolution.
Results
Identification of the LIM interaction domain of LIM-7
A comparison of sequences of ISL and LHX3 family proteins from a range of metazoan species that represent different evolutionary branches (Supplemental Data 1) indicates that there is high conservation of HDs and LIM domains, but the ISLLID is less conserved (Fig. 1D). A BLAST search using a 31-residue sequence of murine ISL1LID detected similar domains in ISL-proteins in vertebrates, arthropods and chordata, but failed to identify any similar sequences within LIM-7. However, a manual alignment of the C-terminal regions of ISL1 and LIM-7 that used the spacing of the HD and LID domains as well as the structurally conserved LIM-binding motifs in the LID domains26 as a guide, revealed a putative LIM interaction domain encompassing residues 347–376 of LIM-7 (LIM-7LID; Fig. 2A). This region shares only 17% sequence identity with mammalian ISL1LID compared with higher levels of identity in the LIM domain (48%) and HD (75%) regions. Similar sequences could not be identified in basal metazoans that contain both ISL- and LHX3-like proteins.
Figure 2.
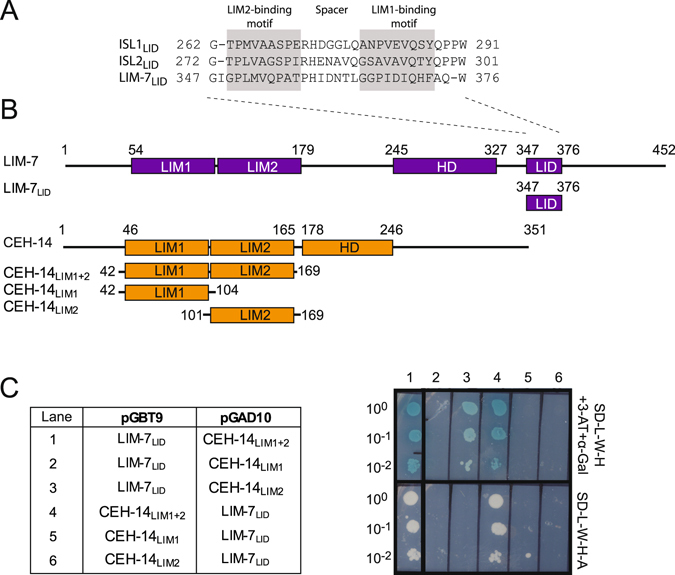
Islet- and LHX3-family LIM-HD proteins from C. elegans interact. (A) Manual alignment of experimentally determined LIM-interaction domains from mouse ISL1 and ISL2 and a predicted LID from LIM-7. The LIM1 and LIM2 binding motifs as previously identified for ISL1 and ISL2 are indicated; the spacer is the sequence between the binding motifs. (B) Schematics of LIM-7 and CEH-14 and constructs used in yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) assays showing the LIM1 and LIM2, homeodomain (HD) and predicted LIM interaction domain (LID). (C) Y2H data indicate a direct interaction between LIM-7LID and CEH-14LIM1+2. The original images for the yeast plates, including additional controls are shown in Supplemental data Figure S1.
We predicted that an interaction between CEH-14 and LIM-7 would occur via the LIM domains of CEH-14 (CEH-14LIM1+2) and the putative LIM-7LID, by analogy with the previously-observed interactions between LHX3/4 and ISL1/2 proteins11, 12. We used yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) analysis to investigate whether CEH-14 and LIM-7 could physically interact. Control experiments, in which the full length LIM-HD proteins in pGBT9 plasmids were paired with ‘empty’ pGAD10 vectors, gave rise to yeast growth indicating autoactivation of the reporter genes as described previously27. This is not unexpected due to the presence of the DNA-binding homeodomains and possible activation domains in the C-terminal domains for these proteins. However, by focussing on smaller constructs (Fig. 2B) in the assays, an interaction between LIM-7LID and CEH-14LIM1+2 was observed as evidenced by yeast growth on moderate (-L-W-H + 3-AT) and high (-L-W-H-A) stringency media (Fig. 2C and Supplemental data Figure S2). LIM-7LID was also tested for binding to each of the individual LIM domains of CEH-14, CEH-14LIM1 and CEH-14LIM2. In those experiments, LIM-7LID could not bind with CEH-14LIM1 alone but could bind weakly (yeast growth under moderate but not high affinity selection conditions) to CEH-14LIM2, only when the latter was expressed from a pGAD10 plasmid. Note that it is not unusual to see apparent differences in strength of binding for Y2H interactions with the bait and prey proteins in alternate vector combination as was seen here; differences in yeast growth may originate from differences in protein stability in the different constructs11, 12. Thus, whereas both LIM domains from CEH-14 are required for high affinity binding to LIM-7, CEH-14LIM2 is able to bind with LIM-7 independently.
Biophysical analysis of a CEH-14/LIM-7 complex
Having obtained evidence of a direct interaction between LIM-7 and CEH-14, we set out to examine whether the association of these proteins is structurally analogous to that of LHX3 and ISL1 using biophysical analyses. When recombinant forms of LIM domains from LIM-HD proteins are expressed in bacteria, they tend to aggregate and/or be expressed in inclusion bodies, but they can be stabilised through tethering to an interaction partner such as LDB1LID or ISL1/2LID 28–31. The same approach was used here such that the C-terminus of the LIM domains from CEH-14 was tethered to the N-terminus of the LIM-7LID using an 11-residue Gly/Ser linker to form CEH-14–LIM-7 (Fig. 3A). This construct expressed as a predominantly soluble protein in E. coli. SEC-MALLS data showed that purified CEH-14–LIM-7 is largely monomeric at high micromolar concentrations (200 μM loading concentration, ~25 μM at the maximum of the monomer elution peak based on refractive index), with an average molecular weight of 19.8 ± 0.5 kDa (Fig. 3B) which is in close agreement with the calculated molecular weight (19.4 kDa) based on amino acid sequence composition.
Figure 3.
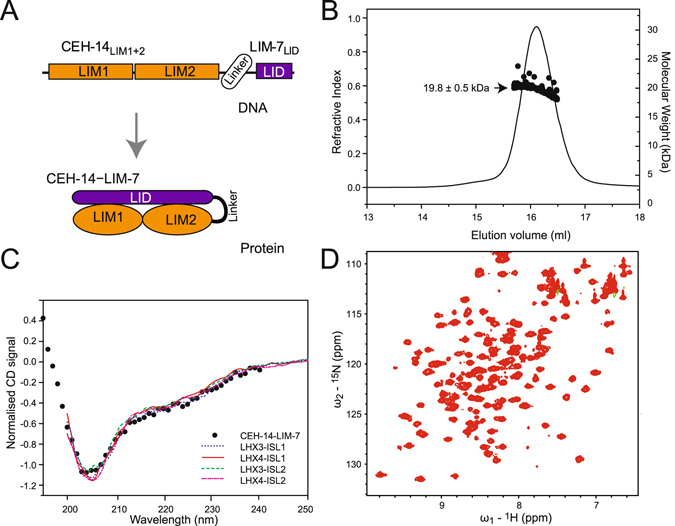
A ‘tethered’ CEH-14–LIM-7 complex. (A) Schematic of the CEH-14–LIM-7 tethered complex. Based on data from similar complexes, introducing a tether between the LIM1+2 domains from CEH-14 and the LID from LIM-7 was expected to stabilise the complex and facilitate structural characterisation. This engineering approach takes advantage of the close positioning of C-and N-termini in the native complexes. (B) SEC-MALLS data for CEH-14–LIM-7 in 20 mM Tris, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT at 0.5 ml/min at 25 °C (black line, refractive index profile; black dots, MW distribution). (C) Far UV-CD profile of CEH-14–LIM-7 (5 μM black dots) in 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.5, 150 mM NaF, 0.5 mM TCEP at 20 °C, compared to the spectra of related LHX3/4–ISL1/2 tethered complexes as indicated. Data for those complexes were published previously12. (D) 1H-15N HSQC spectrum of CEH-14–LIM-7 (37 μM) in 20 mM HEPES pH 7.0, 1 mM DTT at 25 °C recorded at 600-MHz.
The solution structure of a CEH-14/LIM-7 complex
Given that the sequences of LIM-7LID are quite different from those of ISL1/2LID we sought to determine the structure of the CEH-14/LIM-7 complex. The far-UV circular dichroism spectrum of CEH-14–LIM-7 is characteristic of a folded protein, and closely resembles the spectra of related LHX3/4-ISL1/2 complexes (Fig. 2C)12. Various attempts were made to determine the high resolution structure of CEH-14–LIM-7. 1H-15N-HSQC data showed that the protein was well folded (Fig. 3D), but limited sample solubility meant that it was not feasible to use NMR methods to determine the solution structure of CEH-14–LIM-7 (data not shown). Although crystals of the tethered complex formed under several conditions, they diffracted only to low resolution and/or displayed high levels of anisotropy, preventing structure determination. Fortunately, however, the low resolution structure of the complex could be derived using small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). When combining the structural parameters extracted from the SAXS data (Fig. 4 and Table 1) with a priori shape classification and subsequent structural modelling, the SAXS results show that CEH-14–LIM-7 adopts an overall extended conformation that is structurally very similar to the LHX3-ISL1 homologue12. The SAXS-based molecular weight (M r) estimates of ~17–20 kDa, assessed from concentration-dependent and concentration-independent methods32–34, lie close to the expected value of 19.4 kDa for a monomeric complex and are commensurate with the experimental M r results obtained from MALLS (19.8 kDa). These M r values, an obtained Porod volume of ~26 nm3 (expected dry volume = 23 nm3) and the linear Guinier plot of the data at very-low angles (lnI(s) vs s 2, s 2 < 0.26 nm−2, R 2 = 0.985; Fig. 4B)35, indicate that the complex is homogeneous and unaffected by self-association/oligomerisation, aggregation or repulsive interparticle interference effects. In summary, the SAXS data indicate that CEH-14–LIM-7 is a monomeric tethered complex in solution.
Figure 4.
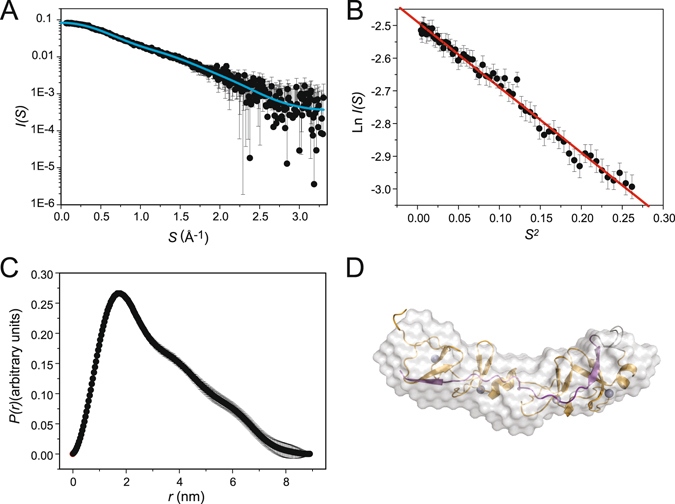
SAXS analysis for CEH-14–LIM-7. (A) Buffer-corrected, desmeared SAXS scattering curve of CEH-14–LIM-7 (circles; 5.2 mg mL−1) in 20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM TCEP, overlaid with the theoretical scattering profiles of an homology model of CEH-14–LIM-7 based on the template of the LHX3-ISL1 crystal structure (1RGT Chain B; cyan line) calculated by CRYSOL. (B) Guinier plot showing linearity of low Q data. (C) The pairwise distribution P(r) profile. (D) Shape restoration model of CEH-14–LIM-7 (white surface) superimposed with an homology model based on the template of the LHX3-ISL1 crystal structure (orange and purple; zinc ions are shown as grey spheres).
Table 1.
Small angle scattering parameters for CEH-14–LIM-7.
| Data-collection parameters | |
| Instrument | SAXSess (Anton Paar) |
| Beam geometry | 10 mm slit |
| X-ray wavelength (nm) | 0.1542 |
| Measured s-range (nm−1) | 0.07–4.0 |
| Shannon-channel limited s-range (nm−1)a | 0.07–3.3 |
| Exposure time (min) | 4 × 15 min |
| Protein Concentration (mg ml−1)b | 5.2 (±0.3) |
| Temperature (°C) | 10 |
| Structural parameters | |
| I(0) (cm−1) [from p(r)] | 0.0833 ± 0.002 |
| Real-space R g (nm) [from p(r)] | 2.5 ± 0.09 |
| I(0) (cm−1) (from Guinier) | 0.083 ± 0.0002 |
| R g (nm) (from Guinier) | 2.4 ± 0.03 |
| D max (nm) | 8.9 |
| Porod volume estimate (Vp, nm3) | 25.6 |
| Molecular-mass determination | |
| Partial specific volume (cm3 g−1)c | 0.718 |
| Contrast (Δρ × 1010 cm−2)c | 3.345 |
| Molecular mass M r, kDa [from I(0)]d | 16.7 ± 0.9 |
| Molecular mass M r, kDa [from SAXSMOW]d | 20 |
| Molecular mass M r, kDa [from Vc]d | 18 |
| Expected monomeric M r calculated from sequence, kDa | 19.4 |
| Software employed | |
| Primary data reduction | SAXSquant 1D |
| Data processing | PrimusQT/GNOM |
| Ab initio analysis | DAMMIF |
| Spatial averaging and resolution estimates | DAMAVER/SASRES |
| Computation of model intensities | CRYSOL |
aThe information content of the scattering data and corresponding s-range were evaluated using SHANUM62. bThe protein concentration was determined at A280 nm using the extinction coefficient calculated by ProtParam59 from the primary amino acid sequence. cObtained from the Contrast module of MULCH61. dMolecular mass estimates were determined from I(0) and protein concentration (M r = I(0)NA/[protein](Δρυ)2) as well as concentration-independent methods (SAXSMOW32 and the volume of correlation, Vc33).
A qualitative assessment of the Kratky plot obtained from the SAXS data (I(s)s 2 vs s) indicates that the protein is mainly folded36, while the model-independent shape classification and the shape topology determined from the data using automated shape-categorization and ambiguity assessments37 suggest that the complex is structurally anisotropic and extended (Supplemental data Figure S3). The conclusion that CEH-14–LIM-7 forms an extended particle is borne out in the resulting scattering-pair distance distribution (p(r) vs r profile) that shows a skewed distribution of real-space vector lengths for r > 1.8 nm which extends to a maximum particle dimension, D max, of ~9 nm with a radius of gyration, R g, of 2.5 nm (Fig. 4C).
The reconstruction of the low-resolution shape of the CEH-14–LIM-7 complex was calculated using ab initio dummy atom bead modelling38. Ten individual models were generated that each fit the experimental data (χ 2 = 0.3). Although the χ 2 discrepancy of the individual model-fits to the data is somewhat low, likely due to the misspecification of experimental errors, no statistically significant systematic deviations between the data and the fits were identified using variance/co-variance analysis (Correlation Map, or CorMap, p > 0.01)39. The spatial alignment and averaging of the individual models produces a mean normalised spatial discrepancy of 0.640, indicating spatial consistency between the ten reconstructions, with an ensemble resolution estimate of 2.8 nm41. The final averaged representation of the low-resolution structure of CEH-14–LIM-7 (corrected for volume and spatial occupancy) is presented in Fig. 4D and shows that the complex adopts a subtly bent and extended conformation in solution with approximate dimensions of ~3 × 2 × 9 nm. This global conformation is very similar to that previously observed for the neuronal-type specification complex LHX3-ISL112. Indeed, the scattering profile of LHX3-ISL1 calculated from the X-ray crystal structure (PDB: 2RGT chain B) fits the CEH-14–LIM-7 SAXS data surprisingly well (χ 2 = 0.3; CorMap p = 0.025; Supplementary data Figure S4A) and was thus used as a template to develop an atomistic homology model of CEH-14–LIM-7 (see below) that fits that solution scattering data (χ 2 = 0.3; CorMap p = 0.05). Both the CEH-14–LIM-7 homology model and the LHX3–ISL1 X-ray crystal structure spatially superpose very well into the low-resolution ab initio bead model of the complex (Fig. 4D and Supplemental data Figure S4B).
Binding determinants on CEH-14LIM1+2 and LIM-7LID
Several series of LIM-7LID mutants were generated and tested for binding with CEH-14 in yeast two-hybrid assays in order to identify which residues from LIM-7LID are critical for binding to CEH-14 (Table 2). Initially the LIM-7 residues P350, L351, M352 and V353, were mutated to alanine as single or double mutations, as equivalent residues have previously been shown to be important for the interaction between LHX3 and ISL111. However, none of these mutations had any significant effect on the interaction with CEH-14LIM1+2 in this assay. Thus, an alanine scan covering the entire LIM-7LID peptide was used to probe for key regions of binding. Sets of three consecutive residues were mutated to alanine (or glycine, if the wildtype residue was alanine) and tested for binding. Only one mutant LIM-7(H359A/I360A/D361A) completely abolished the interaction of the peptide with CEH-14LIM1+2 under both moderate and strong selection conditions. Two other mutants, LIM-7(P350A/L351A/M352A) and LIM-7(A374G/Q375A/W376A), showed some evidence of a reduced interaction as yeast growth was observed only under moderate (but not high) affinity selection conditions. Residues H359, I360 or D361 were individually targeted for mutation, with no major effect on binding, but when mutated in combination with the P350A/L351A/M352A triple mutant, each mutation was sufficient to abolish binding in this assay. Overall, these data indicate that residues H359, I360 and D361 in LIM-7 are the most important for the interaction, whereas residues within P350-M352 and A374-W376 also play a more modest role.
Table 2.
Yeast two-hybrid mutagenic screens for CEH-14 and LIM-7 interactions.
| pGBT9 | Sequence | pGAD10 |
|---|---|---|
| Construct | ||
| LIM-7LID | CEH-14 LIM1+2 | |
| WT LIM-7LID | GIGPLMVQPATPHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| P350A | GIGALMVQPATPHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| L351A | GIGPAMVQPATPHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| M352A | GIGPLAVQPATPHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| V353A | GIGPLMAQPATPHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| P350A/L351A | GIGAAMVQPATPHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/++ |
| L351A/M352A | GIGPAAVQPATPHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| G347A/I348A/G349A | AAAPLMVQPATPHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| P350A/L351A/M352A | GIGAAAVQPATPHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/− |
| V353A/Q354A/P355A | GIGPLMAAAATPHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| A356G/T357A/P358A | GIGPLMVQPGAAHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| H359A/I360A/D361A | GIGPLMVQPATPAAANTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | −/− |
| N362A/T363A/L364A | GIGPLMVQPATPHIDAAAGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| G365A/G366A/P367A | GIGPLMVQPATPHIDNTLAAAIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| I368A/D369A/I370A | GIGPLMVQPATPHIDNTLGGPAAAQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| Q371A/H372A/F373A | GIGPLMVQPATPHIDNTLGGPIDIAAAAQW | +++/+++ |
| A374G/Q375A/W376A | GIGPLMVQPATPHIDNTLGGPIDIQHFGAA | +++/− |
| H359A | GIGPLMVQPATPAIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| I360A | GIGPLMVQPATPHADNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| D361A | GIGPLMVQPATPHIANTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | +++/+++ |
| P350A/L351A/M352A/H359A | GIGAAAVQPATPAIDNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | −/− |
| P350A/L351A/M352A/I360A | GIGAAAVQPATPHADNTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | −/− |
| P350A/L351A/M352A/D361A | GIGAAAVQPATPHIANTLGGPIDIQHFAQW | −/− |
Y2H assay summary for alanine mutagenic screening of LIM-7LID against CEH-14LIM1+2. Results are reported as yeast growth on moderate (SD-H-L-W+1mM 3-AT)/strong (SD-H-L-W-A) selective media. Yeast growth is represented as either ‘+++’, ‘++’ or ‘+’ for robust growth at all three dilution points (10°, 10−1, 10−2), two dilution points (10°, 10−1) or only on the first dilution point (100), respectively. ‘−’ represents no detectable yeast growth. LIM-7LID and CEH-14LIM1+2 constructs were in the vectors pGBT9 and pGAD10, respectively.
Homology Modelling of CEH-14–LIM-7
Given that the far-UV CD and SAXS data for LHX3LIM1+2–ISL1LID and CEH-14LIM1+2–LIM-7LID complexes indicate that the structures are very similar, we generated a simple homology model of the C. elegans complex using SwissModel. As with homology models in general this model closely resembles the template (Fig. 5A) and may not reflect minor differences in conformation between the two complexes. Per residue QMEAN scores from SwissModel indicate that the model is of higher quality around the core part of each LIM domain-binding motif interaction module, and is less likely to be accurate in the Gly/Ser linker and ends of the domains (which were not present in the X-ray coordinates), loops, and around the spacer between the LIM-binding motifs (Supplemental Data 5). However, it fits the acquired SAXS data from the CEH-14LIM1+2–LIM-7LID complex in solution (Fig. 4D) and allows a reasonable physical interpretation of the mutational data above. LIM domains share a highly conserved structure with some variations in the spacing between zinc-ligating residues, which generally just change loop lengths. For the LIM domains from CEH-14 and LHX3, the spacing of the zinc-coordinating residues are identical, apart from a single loop where CEH-14 has an extra residue (CEH-14A152) in the bend of the final β-hairpin of the LIM2 domain, which should have a very minor effect on the local structure (Fig. 5A). In terms of the LIDs from LIM-7 and ISL1, the sequence identity is low, and it is not easy to confidently predict binding registers for LIM-LID interactions43, 44. However, the SWISS-MODEL prediction was identical to our manual alignment (Fig. 2A), and indicates that the most important residues for binding (H359–D361), as identified by mutagenesis, lie in the spacer region between the two predicted LIM-binding motifs (Fig. 5B). In the CEH-14–LIM-7 model and the LHX3–ISL1 structure, equivalent residues LIM-7H359 and ISL1H272 sit in pockets in the LIM2 domain of the partner protein such that the imidazole groups of those residues make complementary interactions with the sidechain Oγ atoms of CEH-14T105 and LHX3T91, respectively (Fig. 5B). The sidechain of LIM-7I360 appears to make intramolecular hydrophobic contacts with the backbone of LIM-7N362, while the sidechain of LIM-7D361 appears to sit between the two LIM domains of CEH-14, and could make favourable intermolecular interactions with the imidazole sidechain of LIM-7H359 and backbone N of CEH-14T105. Of the two other regions in LIM-1LID that were identified as making moderate contributions to binding, one (P350/L351/M352) lies in the putative LIM2-binding motif and is similar to the main binding-hotspots previously identified for ISL1/2 binding to LHX3/411, 12; all three sidechains in this cluster appear to make hydrophobic contacts with the surface of the LIM domains. In contrast, the second binding hotspot, A374G/Q375A/W376A, lies outside of the structured regions. It is possible that mutation of A374 to glycine introduces too much flexibility, destabilising the peptide, and/or that W376 makes additional hydrophobic or other interactions with CEH-14 (e.g., π-cation interactions with CEH-14R56/R58). Another characteristic feature of LIM-LID interactions26 that is conserved in this model is the burial of the LIM-7V353 and LIM-7I368 sidechains in between the two zinc-binding modules in each LIM domain of CEH-14. Note that although these features are structurally conserved, mutation of these buried residues can have surprisingly little effect, possibly due to plasticity in the hydrophobic pockets31, 44.
Figure 5.
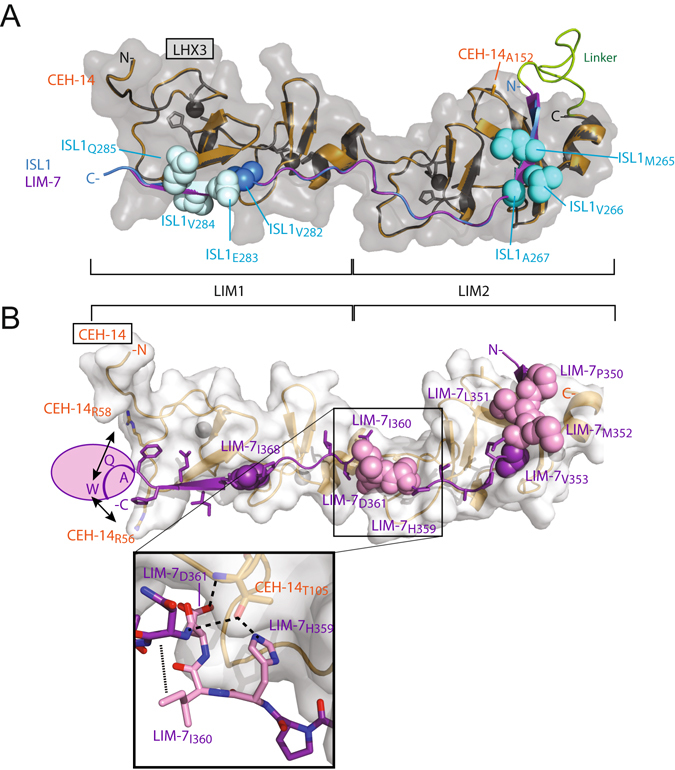
Conserved and unusual features of LHX3-Islet family LIM-HD interactions in C. elegans proteins. (A) Overlay of the LHX3LIM1+2 (black ribbon/transparent grey surface representation)–ISL1LID(cyan) crystal structure (1RGT Chain B) and a simple homology model of CEH-14(orange)–LIM-7(purple). The N- and C-termini from the domains in LHX3 and ISL1 are indicated. A small insertion in CEH-14 (residue A152) is likely to have little effect apart from a short β-hairpin extension. The binding hotspots for ISL1 for LHX3 and LHX4 as determined by alanine scanning mutagenesis and Y2H are shown (cyan spheres), an additional hotspot for ISL2 binding to LHX3 and LHX4 is also indicated (light cyan spheres) and a conserved residue (ISL1V282) that is buried between the two zinc binding modules is indicated (blue spheres). (B) Predicted binding features of CEH-14 (orange ribbon; white surface representation) and LIM-7 (purple ribbon and stick representation). The binding hotspots are indicated (pink circles/spheres). LIM-7V353/I368 (purple spheres) are buried between the two zinc binding modules of each LIM domain in CEH-14. Inset shows possible stabilising interactions within the main hotspot with residues in stick representation. Possible stabilising interactions between LIM-7W376 and CEH-14R56/R58 are indicated. Nitrogen atoms (blue) and oxygen atoms (red) are shown where appropriate.
ceh-14 and lim-7 expression patterns
To assess whether the nematode LIM-HD proteins CEH-14 and LIM-7 might function together like their vertebrate counterparts, we investigated the expression patterns of the ceh-14 and lim-7 genes in C. elegans using fluorescent reporter constructs. The ceh-14 reporter construct contains 4 kbp immediately upstream of ceh-14 and the first exon of ceh-14, which encodes the first 16 amino acids of CEH-14, fused to the gfp coding sequence (Fig. 6A). As there is no nuclear localisation sequence in this construct, expressing cells are fluorescent throughout the nucleus and cytoplasm. The ceh-14::gfp reporter has previously been reported to be expressed in the nematode spermatheca and in the nervous system. In the latter, expressing neurons in the head have been identified as the sensory neurons AFDL/R, the interneurons BDUL/R, and the interneuron ALA45. Neurons in the tail that express ceh-14 have been identified as PVT, PVQL/R, DVC, PVNL/R, PVWL/R, PVR, PHAL/R, PHBL/R and PHCL/R45.
Figure 6.
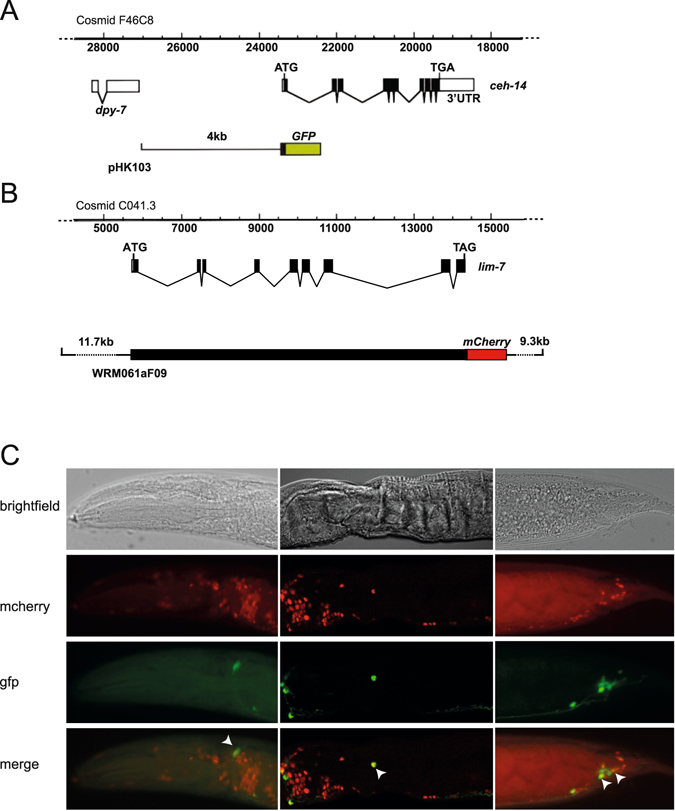
CEH-14 and LIM-7 are co-expressed in several C. elegans neurons. (A) The ceh-14 locus within cosmid F46C8 is shown with exons indicated by black boxes and introns by lines. The ceh-14::GFP reporter construct in plasmid pHK103 is shown underneath. The diagram was modified from27. (B) The lim-7 locus within cosmid C04F1 is shown with exons indicated by black boxes and introns by lines. The structure of the lim-7::mCherry reporter construct created by recombineering fosmid WRM061aF09 is shown underneath. (C) Fluorescence micrographs depict expression of the ceh-14::GFP (chIs513) and lim-7::mcherry (stIs10289) reporters in the head (left panels) and tail (right panels) of adult hermaphrodites of strain HRN073. The corresponding brightfield image is shown above and a merged image is shown below. Representative cells in which both gfp and mcherry fluorescence was observed are indicated by arrowheads.
The lim-7 reporter construct was made by recombineering of fosmid WRM061aF09 to fuse an mCherry tag and 3xFLAG epitope to the C-terminus of the LIM-7 protein (Fig. 6B)21. This construct thus encompasses the complete lim-7 genomic locus and is expected to contain all relevant regulatory elements. In nematodes carrying this reporter construct, mcherry fluorescence has been reported in the gonadal sheath cells, in the URA neurons in the head, and in 10 additional cells near the isthmus and terminal bulb of the pharynx. Although the precise identities of the latter cells have not been defined, they are presumed to be neurons21.
We performed confocal microscopy on a strain carrying both the ceh-14 and the lim-7 reporter constructs described above (HRN073 stIs10289; chIs513) to further examine the expression patterns of ceh-14 and lim-7 and to assess whether there are any cells in which CEH-14 and LIM-7 are co-expressed. In this strain, ceh-14 was only consistently observed in one cell in the head, which appears to correspond to the ALA cell. In the tail, expression of ceh-14 matched previous reports. Expression of lim-7 was observed in the gonadal sheath cells and in a number of cells surrounding the pharynx as previously reported. In addition, we observed expression in at least 12 cells in the tail.
GFP and mCherry images were acquired and overlayed using ImageJ software to identify cells expressing both lim-7 and ceh-14. Co-expression was observed in one cell in the head, ALA (Fig. 6C left panels) and one cell positioned posterior to the pharynx, BDU (Fig. 6C middle panels). Co-expression was also observed in five cells in the tail, which are appropriately positioned to be PHAL/R, PHBL/R and PVT (Fig. 6C right panels).
Discussion
Through yeast two-hybrid analyses, complemented by biophysical and structural characterisation, we have shown that the tandem LIM domains of CEH-14 and the LIM interaction domain of LIM-7 form a complex analogous to that of their mammalian counterparts, LHX3 and ISL1. Moreover, our in vivo data indicate that CEH-14 and LIM-7 are co-expressed in a subset of neurons in C. elegans suggesting that transcriptional events in these neurons could be regulated by interactions between the nematode Islet and LHX3-family LIM-HD transcription factors.
Interactions among the mammalian LIM-HD transcription factors as well as interactions between the LIM-HD transcription factors and other binding partners such as the LIM only proteins (LMO) and the LIM domain binding protein (LDB1) have been extensively investigated (reviewed in ref. 26). Mutagenic and structural studies of LHX3/4LIM1+2-ISL1/2LID complexes as well as LMOLIM1+2-LDB1LID and other LMO-LID complexes have shown that binding is modular. That is, binding is mediated by two distinct linear motifs (~8–10 residues each) in the LIDs (Fig. 2A), which contact equivalent faces on each of the partner LIM domains. The linear motifs in the LIDs are specific for their cognate LIM domains (i.e., the LIM2 domain does not bind the LIM1-binding motif and vice versa) and the variable length spacer that lies between the linear motifs tends to be plastic or disordered and makes little or no contribution to binding11, 12, 31, 43, 46.
In the case of the interaction between the LIM domains of CEH-14 and the LID of LIM-7, we observed that both LIM domains of CEH-14 are required for high affinity binding to LIM-7 (Fig. 2C). This requirement is a common feature of tandem LIM/LID interactions in which it has also been demonstrated that contributions to binding tend to be dominated by one or the other LIM domain, as evidenced by independent binding and/or abrogation of binding by mutagenesis10, 11, 31, 47–49. For example, mouse LHX3/4-ISL1/2 interactions are dominated by the association of the LIM2 domain of LHX3 with its cognate binding sequence11, 12; mutagenesis indicates that contacts with the LIM1 domain play an additional minor role in LHX3/4 interaction with ISL212 (Fig. 5A). In line with these typical features of LIM/LID interactions, the LIM2 domain of CEH-14 showed weak independent binding to the LID of LIM-7 (Fig. 2C).
Consistent with the LIM2 domain of CEH-14 being the dominant binder, our mutagenesis experiments identified residues P350-M532 of the LIM-7 LID, which interface with LIM2 of CEH-14 in the homology model, as contributors to high affinity binding. In contrast with other characterised LIM/LID interactions, in which the spacer between the two linear motifs of the LID make minimal contributions to binding11, 12, 31, 43, 46, these same mutagenesis experiments also revealed an even more important role for the spacer region of the LIM-7 LID (H359-D361; Table 2; Fig. 2A). However, inspection of the homology model indicates that these hotspot residues predominately make contact with the LIM2 domain (which is consistent with that domain being the dominant binder), or form intramolecular interactions that could stabilise the structure of the LIM-7LID (Fig. 5B). These data suggest that precise mechanisms for stabilisation of the interaction may have diverged for the mouse versus nematode LHX-Islet interactions. Other LIM-LID interactions are consistent with minor variation in modes of binding. For example, an extended or bipartite binding hotspot at the LIM2 interface is seen for LMOLIM2-partner interactions26, and the main binding hotspot for TESLIM2+3-ARP7ALID completely overlaps the very short spacer in ARP7ALID 50.
Beyond our biophysical data confirming the interaction of CEH-14 and LIM-7 in vitro, our expression analysis indicates that these two proteins are co-expressed in several neurons, presenting the possibility that CEH-14 and LIM-7 may co-ordinately regulate gene expression in nematode neuronal development. Although the neuronal expression of LIM-7 was previously reported, specific roles for LIM-7 in neuronal development or function have not yet been described. An important role for LIM-7 in the developing nervous system is suggested by the observation that the majority of lim-7 mutant animals, which arrest at the first larval (L1) stage of development, show an uncoordinated phenotype21. In the case of CEH-14, specific developmental functions in several neurons have been described, including the AFD thermosensory neuron, the ALA sleep neuron and the BDU interneuron20, 51, 52. The latter two are of particular interest here since we have identified co-expression of CEH-14 and LIM-7 in these two cell types. In the ALA, CEH-14 regulates expression of several ALA-specific genes and the absence of CEH-14 renders worms unable to respond to sleep cues in the form of the epidermal growth factor LIN-3. In the BDU interneuron, CEH-14 regulates expression of a battery of neuropeptides. It remains to be determined whether LIM-7 works together with CEH-14 in these gene regulatory events. Nonetheless, our finding that these two proteins are co-expressed in these two cells and others suggests the possibility of coordinate activity.
As outlined earlier, the vertebrate homologues of LIM-7 and CEH-14 interact with distinct binding partners to regulate specific developmental programs. In V2 interneurons, a binary complex of LHX3 and LDB1 regulate expression of chx10 while in motor neurons a ternary complex of LDB1, LHX3 and ISL1 targets Hb9 7, 9. The two cell populations possess additional mechanisms that suppress the alternative differentiation program through both protein-DNA and protein-protein interactions. For example, in chick and mice, chx10 and Hb9 encode homeodomain proteins that are thought to block the binding site of the ternary and binary complexes, respectively, thereby repressing inappropriate transcriptional activity9. In addition, in developing motor neurons the LIM only protein LMO4 appears to compete with LHX3 for binding of LDB1 to prevent formation of the binary complex9, 53. A similar regulatory mechanism was observed in Drosophila, in which dLMO antagonises the formation of a transcriptional complex comprising Apterous (the fly homologue of mammalian LHX2) and Chip (the fly homologue of LDB1) by competing for binding to Chip protein14, 54.
Analogous LIM-HD/LDB binary and ternary complexes involving CEH-14 and LIM-7 may similarly regulate neuronal development in C. elegans. Like mammalian LDB1, which is widely expressed in both embryonic and adult tissues17, the C. elegans homologue called LDB-1 is expressed broadly during nematode embryogenesis, with expression persisting into adulthood in some tissues including the gonadal sheath cells and body wall muscle cells27. Of particular relevance here is the observation that LDB-1 is expressed throughout the nervous system in both larvae and adults, and is therefore present with CEH-14 and LIM-7 in a subset of neurons. The LIM interacting domain of LDB-1 shares ~60–65% sequence identity with its mammalian homologues, suggesting functional conservation27. Consistent with this, LDB-1LID was shown to interact with CEH-14LIM1+2 in Y2H assays27.
Binary and ternary complexes involving CEH-14, LIM-7 and LDB-1, similar to those in mammals and Drosophila, may thus regulate analogous biological processes in C. elegans. However, the regulation of complex assembly that has been exhibited previously by LMO proteins is unlikely to be relevant in the nematode as C. elegans lacks LMO orthologs.
Downstream of the LHX3/LDB1 and LHX3/ISL1/LDB1 transcriptional complexes are the target genes Hb9 and Chx10. The C. elegans homologue of Hb9, CEH-12, is expressed in the VB subclass of motor neurons55 and the Chx10 homologue, CEH-10, is expressed in distinct group of neurons that includes several interneurons and motor neurons56. Whether expression of CEH-12 and CEH-10 is regulated by the analogous nematode LIM-HD/LDB binary and ternary complexes has not yet been examined.
In conclusion, this study has shown that a LIM-HD transcriptional complex that regulates differentiation of post-mitotic motor neurons in vertebrates is likely to also exist in C. elegans. The physical characteristics of protein-protein interactions within a CEH-14/LIM-7 assembly are essentially identical to that of vertebrate LHX3/ISL1 complexes. Although the function of that complex in driving cell fate decisions is likely similar to its mammalian counterpart, it is yet to be confirmed if mammals and nematode share regulatory mechanisms of cell-specific transcriptional complex assembly. The nematode and mammalian families of LIM-HD factors are very distantly related making it likely that Islet/LHX3 transcriptional assemblies are strongly conserved throughout bilateral metazoans and developed at an early stage of evolution of multicellular organisms.
Materials and Methods
Cloning and mutagenesis
All constructs were generated via standard or overlap extension PCR methods and cloned into pGBT9 and pGAD10 for yeast two-hybrid experiments, or pGEX-2T for biophysical in vitro work. All plasmids were sequenced to confirm identity (SUPAMAC, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Sydney). Constructs for protein expression were generated as fusions of CEH-14LIM1+2(CEH-14 residues 42–168; UniProt accession P20271) and LIM-7LID (LIM-7 residues 347–376; UniProt accession G5EC36) where the two domains are connected by an 11-residue glycine-serine linker as previously described for LHX3LIM1+2-ISL1LID fusion constructs29, 57.
Recombinant protein expression and purification
Proteins were expressed with a glutathione S-transferase (GST) tag using a pGEX-2T vector in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells. Bacterial cell cultures in Luria broth supplemented with 100 μg/mL ampicillin were induced at mid-log phase (OD600nm = 0.5–0.6) by the addition of 0.4 mM IPTG and incubated at 20 °C for 16–20 h. The proteins were purified by glutathione (GSH) affinity chromatography using the Sepharose4B resin (GE Healthcare) in 50 mM Tris (pH 8.0), 200 mM NaCl, 7 mM β-mercaptoethanol. The GST-tag was removed by mixing the beads overnight at 4 °C in the same buffer supplemented with 2.5 mM CaCl2 and 50U thrombin (Sigma-Aldrich). The eluted protein was further purified by size exclusion chromatography using a HiLoadTM SuperdexTM S75 16/60 size exclusion column (GE Healthcare) equilibrated in 20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT (pH 8.0) or 50 mM Tris, 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM TCEP (pH 8.0).
Yeast two-hybrid analysis
pGBT9 and pGAD10 plasmids were co-transformed into AH109 cells (Clontech), as described previously31. All selective media lacked leucine and tryptophan (-L-W) to ensure co-transformation of bait and prey plasmids was maintained. For screening of interactions, media were further deficient in histidine (-H-L-W) but contained or lacked additional reagents for detection of different affinity interactions. Selective media supplemented with 40 μg/mL X-α-gal (Progen), further supplemented with 1 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (3-AT; Sigma), or, additionally deficient in adenine, were used to probe for weak, moderate and high affinity interactions. Transformed yeast colonies were cultured in the appropriate media, adjusted to A600 nm = 0.2, and two serial 1:10 dilution suspensions prepared designated as 100, 10−1, and 10−2, respectively. 2-μL aliquots of all three dilutions were spotted onto plates and incubated at 30 °C for 72 h.
Circular dichroism analysis
Far UV-CD used a sample concentration of 5 μM protein in 10 mM Tris pH 8.5, 150 mM NaFl, 0.5 mM TCEP in a 1-mm path length quartz cell seated in a water-jacketed cell holder. Spectra were recorded at 20 °C on a Jasco J-720 spectropolarimeter equipped with a Neslab RTE-111 temperature controller. CD data were collected over the wavelength range 195–240 nm, with a speed of 20 nm/min, step resolution of 1 nm, bandwidth of 1 nm and a response time of 1 s. The final spectrum was the average of five scans, and was baseline corrected. Spectra collected previously12 were further normalised at 207 nm to account for small variations in protein concentration for comparison.
Multiple angle laser light scattering
Size exclusion chromatography multiple angle laser light scattering (SEC-MALLS) analysis was performed using a SuperoseTM Peptide column attached to the AKTA HPLC system at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min in 20 mM Tris.HCl, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT). A protein sample of 200 μM was used. The size exclusion chromatography column was followed in-line by a miniDAWN light scattering detector and an interometric refractometer (Wyatt Technologies, Santa Barbara, CA). Light scattering analysis was performed using a 690 nm wavelength laser. Voltage and light scattering intensity were calibrated with toluene yielding a constant of 8.534 × 10−6 for this study. A refractive index increment (dn/dc) estimate of 0.19 mL/g was used for protein concentration determination58 and data were analysed using ASTRA software (Wyatt Technologies).
Small angle X-ray scattering
Small-angle X-ray scattering data I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinΘ/λ nm−1; 2Θ is the scattering angle and λ is the X-ray wavelength were collected from a sample of CEH-14–LIM-7 at 5.2 mg/mL in 50 mM Tris, 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM TCEP (pH 8.0) and a corresponding matched solvent blank that was prepared via dialysis34. The final post-dialysis sample concentration was determined using an A280nm extinction coefficient of 14878 M−1 cm−1 calculated from the amino acid sequence of the protein using ProtParam59. SAXS data were recorded on a SAXSess (Anton Paar) Kratky camera (line collimation, 10 mm slit) equipped with a sealed tube source (Cu-Kα, λ = 1.5418 Å) and a CCD detector60, 61 through an s-range of 0.07–6 nm−1. The protein sample or matched solvent blank (30 μL) were mounted in the same quartz capillary (1 mm diameter), and irradiated at 10 °C for at total exposure time of 1 h (4 × 15 min blocks). The 2D scattering data were reduced to 1D I(s) vs s profiles using the SAXSQuant 2.0 software package (Anton Paar, Austria) taking into account sample absorbance and detector sensitivity. The scattering from the matched solvent was subtracted from the sample scattering to generate the smeared I(s) vs s profile of the protein in solution. The information content of the resulting scattering profile and effective s-range were assessed using SHANUM 62 and data were accordingly truncated to working s max of 3.5 nm−1. All data were placed on an absolute scale (I(s), cm−1) using the scattering from water as a reference63. The partial specific volume and X-ray contrast were calculated using MULCh61.
The indirect Fourier transform of the SAXS data and subsequent calculation of the real-space p(r) vs r profile was performed using GNOM 64 in PRIMUSQT as part of the ATSAS 2.8 software package (https://www.embl-hamburg.de/biosaxs/software.html)65. The effects of the 10 mm slit beam geometry were taken into account using the prepared experimental beam profile as input to generate desmeared (i.e., beam-geometry corrected) p(r) vs r and SAXS profiles. The R g and forward scattering intensity at zero angle, I(0), were evaluated from both p(r) and Guinier analysis (in the Guinier limit 0.16 < sR g < 1.25)35. Porod volume estimation from the data was performed using DATPOROD 65 while the expected dry volume was calculated from the amino acid sequence using SEQSTAT (ATSAS 2.8). Concentration independent M r estimates were evaluated using the methods of Fischer et al. (SAXSMOW)32 and Rambo and Tainer (volume of correlation, Vc)33. Automated shape classification of the p(r) vs r profile was calculated using DATCLASS (ATSAS 2.8). The a priori assessment of the non-uniqueness of the SAXS data was calculated suing AMBIMETER 37 which also produced a likely model-independent shape topology of the protein. Subsequent dummy atom bead model refinements were performed using DAMMIF 38. As shape restoration from SAXS data may be ambiguous (CEH-14–LIM-7 AMBIMETER score = 2.5; highly ambiguous), DAMMIF was run 10 times and the resulting individual models were assessed for consistency using the DAMAVER set of programs40 that calculate all pair-wise spatial superpositions, the normalised spatial discrepancy of the alignments (where NSD < 0.7 are spatially similar) and a final averaged 3D-representation of the protein (corrected for volume and bead-occupancy). The resolution of the individual bead-model cohort was assessed using SASRES 41. CRYSOL 66 was employed to calculate the SAXS profiles and evaluate the fits to the desmeared SAXS data of the LHX3-ISL1 X-ray crystal structure or the CEH-14–LIM-7 homology model and the discrepancy was assessed using the reduced χ 2 test. Additional data-model comparisons were performed using the Correlation Map method39 (set to a significance threshold α of 0.01) which is independent of correct error estimation and propagation.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Spectra were acquired at 298 K on a 600 MHz Bruker Avance III spectrometer equipped with a 5-mm TCI CryoProbe (Bruker). 15N-labelled67 CEH-14–LIM-7 was generated and buffer-exchanged into 20 mM HEPES pH 7.0, 1 mM DTT supplemented with 10% D2O and 20 μM DSS (4,4-dimethyl-4-silapentane-1-sulfonic acid). 15N- HSQC experiments were performed using the standard pulse sequence hsqcf3gpsi from the Bruker library. Spectra were processed with TopSpin (Bruker) and analysed with Sparky (T.D. Goddard and D.G. Kneller, SPARKY 3, University of California, San Francisco).
Homology Modelling
The CEH-14–LIM-7 model was generated in SwissModel68 using the sequence of the CEH-14–LIM-7 construct as the target and 2RGT Chain B as the template. The sequence identity based on the structured regions of ISL1-LHX3 was 46%.
Analysis of fluorescent reporter genes in C. elegans
C. elegans strains were cultured and maintained using standard protocols69. Strain RW10289 stIs10289[lim-7(+)::GL-mCherry-3XFLAG, unc-119(+)] was provided by Dr Laura G. Vallier (Department of Biology, Hofstra University, NY, USA)21. Strain TB513 chIs513[pHK103(ceh-14::gfp), pMH86 (dpy-20(+))]; dpy-20(e2071) was provided by Hiroshi Kagoshima (National Institute of Genetics, Mishima, Japan)45. Strain HRN073 stIs10289; chIs513 was generated by crossing strains RW10289 and TB513. Reporter gene expression in nematode strain HRN073 was visualised using an Olympus FluoViewTM FV1000 confocal microscope (GFP, 488 nm; mcherry, 568 nm) (Australian Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis, University of Sydney).
Data Availability
The homology model, bead model and SAXS data for CEH-14–LIM-7 have been deposited to the Small Angle Scattering Biological Database (SASBDB)42 under the accession code SASDC22. All other data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its Supplementary Information files or are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request).
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
MB was supported by an Australian Postgraduate Award from the Australian Government, JMM was supported by a Senior Research Fellowship from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC). The work was supported by grants DP098502 and DP140102318 from the Australian Research Council. The authors thank Jill Trewhella for access to the SAXSess instrument and Don Parkin for help with SAXS data collection.
Author Contributions
M.B., E.L., D.J., S.D., N.R., and H.N. carried out experiments. M.B., E.L., D.J., C.J., H.N. and J.M.M. analysed the data. H.N. and J.M.M. conceived and directed the project overall. M.B., H.N., J.M.M. wrote the manuscript. All authors edited the manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at doi:10.1038/s41598-017-04587-8
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Hannah R. Nicholas, Email: hannah.nicholas@sydney.edu.au
Jacqueline M. Matthews, Email: jacqui.matthews@sydney.edu.au
References
- 1.Bachy I, Failli V, Retaux S. A LIM-homeodomain code for development and evolution of forebrain connectivity. Neuroreport. 2002;13:A23–27. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200202110-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Srivastava M, et al. Early evolution of the LIM homeobox gene family. BMC Biol. 2010;8:4. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Simmons DK, Pang K, Martindale MQ. Lim homeobox genes in the Ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi: the evolution of neural cell type specification. Evodevo. 2012;3:2. doi: 10.1186/2041-9139-3-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tsuchida T, et al. Topographic organization of embryonic motor neurons defined by expression of LIM homeobox genes. Cell. 1994;79:957–970. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tanabe Y, Jessell TM. Diversity and pattern in the developing spinal cord. Science. 1996;274:1115–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5290.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lumsden A. Neural development. A ‘LIM code’ for motor neurons? Curr Biol. 1995;5:491–495. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(95)00100-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Thaler JP, Lee SK, Jurata LW, Gill GN, Pfaff SL. LIM factor Lhx3 contributes to the specification of motor neuron and interneuron identity through cell-type-specific protein-protein interactions. Cell. 2002;110:237–249. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00823-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Matthews, J. M. & Visvader, J. E. LIM domain binding protein 1 (Ldb1): a multifunctional cofactor that interacts with diverse proteins. EMBO Rep 1132–1137 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 9.Lee S, et al. A regulatory network to segregate the identity of neuronal subtypes. Dev Cell. 2008;14:877–889. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.03.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jurata LW, Pfaff SL, Gill GN. The nuclear LIM domain interactor NLI mediates homo- and heterodimerization of LIM domain transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:3152–3157. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.6.3152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bhati M, et al. Implementing the LIM code: the structural basis for cell type-specific assembly of LIM-homeodomain complexes. EMBO J. 2008;27:2018–2029. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gadd MS, et al. The structural basis for partial redundancy in a class of transcription factors, the LIM homeodomain proteins, in neural cell type specification. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:42971–42980. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.248559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Thor S, Andersson SG, Tomlinson A, Thomas JB. A LIM-homeodomain combinatorial code for motor-neuron pathway selection. Nature. 1999;397:76–80. doi: 10.1038/16275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.van Meyel DJ, et al. Chip and apterous physically interact to form a functional complex during Drosophila development. Mol Cell. 1999;4:259–265. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Appel B, et al. Motoneuron fate specification revealed by patterned LIM homeobox gene expression in embryonic zebrafish. Development. 1995;121:4117–4125. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.12.4117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jurata LW, Gill GN. Functional analysis of the nuclear LIM domain interactor NLI. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:5688–5698. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.10.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bach I. The LIM domain: regulation by association. Mech Dev. 2000;91:5–17. doi: 10.1016/S0925-4773(99)00314-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hobert O, Westphal H. Functions of LIM-homeobox genes. Trends Genet. 2000;16:75–83. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(99)01883-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hobert O, D’Alberti T, Liu Y, Ruvkun G. Control of neural development and function in a thermoregulatory network by the LIM homeobox gene lin-11. J Neurosci. 1998;18:2084–2096. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-06-02084.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cassata G, et al. The LIM homeobox gene ceh-14 confers thermosensory function to the AFD neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans. Neuron. 2000;25:587–597. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Voutev R, Keating R, Hubbard EJ, Vallier LG. Characterization of the Caenorhabditis elegans Islet LIM-homeodomain ortholog, lim-7. FEBS Lett. 2009;583:456–464. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.12.046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hobert O, et al. Regulation of interneuron function in the C. elegans thermoregulatory pathway by the ttx-3 LIM homeobox gene. Neuron. 1997;19:345–357. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80944-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Burglin TR, Finney M, Coulson A, Ruvkun G. Caenorhabditis elegans has scores of homoeobox-containing genes. Nature. 1989;341:239–243. doi: 10.1038/341239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hobert O, Tessmar K, Ruvkun G. The Caenorhabditis elegans lim-6 LIM homeobox gene regulates neurite outgrowth and function of particular GABAergic neurons. Development. 1999;126:1547–1562. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.7.1547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sagasti A, Hobert O, Troemel ER, Ruvkun G, Bargmann CI. Alternative olfactory neuron fates are specified by the LIM homeobox gene lim-4. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1794–1806. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.14.1794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Matthews JM, Potts JR. The tandem β-zipper: modular binding of tandem domains and linear motifs. FEBS Lett. 2013;587:1164–1171. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cassata G, et al. The Caenorhabditis elegans Ldb/NLI/Clim orthologue ldb-1 is required for neuronal function. Dev Biol. 2000;226:45–56. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gadd MS, Langley DB, Guss JM, Matthews JM. Crystallization and diffraction of an Lhx4-Isl2 complex. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2009;65:151–153. doi: 10.1107/S1744309108043431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bhati M, et al. Crystallization of an Lhx3-Isl1 complex. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2008;64:297–299. doi: 10.1107/S174430910800691X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee C, Nancarrow AL, Bach I, Mackay JP, Matthews JM. Letter to the Editor: 1H, 15N and 13C assignments of an intramolecular Lhx3:ldb1 complex. J Biomol NMR. 2005;33:198. doi: 10.1007/s10858-005-3209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Deane JE, et al. Tandem LIM domains provide synergistic binding in the LMO4:Ldb1 complex. EMBO J. 2004;23:3589–3598. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fischer H, de Oliveira Neto M, Napolitano HB, Polikarpov I, Craievich AF. Determination of the molecular weight of proteins in solution from a single small-angle X-ray scattering measurement on a relative scale. J Appl Crystallogr. 2010;43:101–109. doi: 10.1107/S0021889809043076. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rambo RP, Tainer JA. Accurate assessment of mass, models and resolution by small-angle scattering. Nature. 2013;496:477–481. doi: 10.1038/nature12070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jeffries CM, et al. Preparing monodisperse macromolecular samples for successful biological small-angle X-ray and neutron-scattering experiments. Nat Protoc. 2016;11:2122–2153. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Guinier A. La diffraction des rayons X aux tres petits angles; application a l’etude de phenomenes ultramicroscopiques. Ann Phys (Paris) 1939;12:161–237. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jeffries CM, Svergun DI. High-throughput studies of protein shapes and interactions by synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1261:277–301. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2230-7_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Petoukhov MV, Svergun DI. Ambiguity assessment of small-angle scattering curves from monodisperse systems. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015;71:1051–1058. doi: 10.1107/S1399004715002576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Franke D, Svergun DI. DAMMIF, a program for rapid ab-initio shape determination in small-angle scattering. J Appl Crystallogr. 2009;42:342–346. doi: 10.1107/S0021889809000338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Franke D, Jeffries CM, Svergun DI. Correlation Map, a goodness-of-fit test for one-dimensional X-ray scattering spectra. Nat Methods. 2015;12:419–422. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Volkov VV, Svergun DI. Uniqueness of ab initio shape determination in small-angle scattering. J App Crystallogr. 2003;36:860–864. doi: 10.1107/S0021889803000268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tuukkanen AT, Kleywegt GJ, Svergun DI. Resolution of ab initio shapes determined from small-angle scattering. IUCr J. 2016;3:440–447. doi: 10.1107/S2052252516016018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Valentini E, Kikhney AG, Previtali G, Jeffries CM, Svergun DI. SASBDB, a repository for biological small-angle scattering data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D357–363. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Joseph S, et al. The structure of an LIM-only protein 4 (LMO4) and Deformed epidermal autoregulatory factor-1 (DEAF1) complex reveals a common mode of binding to LMO4. PLOS One. 2014;9:e109108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Stokes PH, et al. Structural basis of the interaction of the breast cancer oncogene LMO4 with the tumour suppressor CtIP/RBBP8. J Mol Biol. 2013;425:1101–1110. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kagoshima H, et al. The LIM homeobox gene ceh-14 is required for phasmid function and neurite outgrowth. Dev Biol. 2013;380:314–323. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Gadd MS, et al. A structural basis for the regulation of the LIM-homeodomain protein islet 1 (Isl1) by intra- and intermolecular interactions. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:21924–21935. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.478586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Breen JJ, Agulnick AD, Westphal H, Dawid IB. Interactions between LIM domains and the LIM domain-binding protein Ldb1. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:4712–4717. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.8.4712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jurata LW, Kenny DA, Gill GN. Nuclear LIM interactor, a rhombotin and LIM homeodomain interacting protein, is expressed early in neuronal development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:11693–11698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.21.11693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Deane JE, et al. Structural basis for the recognition of ldb1 by the N-terminal LIM domains of LMO2 and LMO4. EMBO J. 2003;22:2224–2233. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Boeda B, et al. Molecular recognition of the Tes LIM2-3 domains by the actin-related protein Arp7A. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:11543–11554. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.171264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Van Buskirk C, Sternberg PW. Paired and LIM class homeodomain proteins coordinate differentiation of the C. elegans ALA neuron. Development. 2010;137:2065–2074. doi: 10.1242/dev.040881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gordon PM, Hobert O. A competition mechanism for a homeotic neuron identity transformation in C. elegans. Dev Cell. 2015;34:206–219. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.04.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Song MR, et al. Islet-to-LMO stoichiometries control the function of transcription complexes that specify motor neuron and V2a interneuron identity. Development. 2009;136:2923–2932. doi: 10.1242/dev.037986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Milan M, Cohen SM. Regulation of LIM homeodomain activity in vivo: a tetramer of dLDB and apterous confers activity and capacity for regulation by dLMO. Mol Cell. 1999;4:267–273. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80374-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Von Stetina SE, et al. UNC-4 represses CEH-12/HB9 to specify synaptic inputs to VA motor neurons in C. elegans. Genes Dev. 2007;21:332–346. doi: 10.1101/gad.1502107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Svendsen PC, McGhee JD. The C. elegans neuronally expressed homeobox gene ceh-10 is closely related to genes expressed in the vertebrate eye. Development. 1995;121:1253–1262. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.5.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Deane JE, et al. Design, production and characterization of FLIN2 and FLIN4: the engineering of intramolecular ldb1:LMO complexes. Protein Eng. 2001;14:493–499. doi: 10.1093/protein/14.7.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Folta-Stogniew E, Williams KR. Determination of molecular masses of proteins in solution: Implementation of an HPLC size exclusion chromatography and laser light scattering service in a core laboratory. J Biomol Tech. 1999;10:51–63. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gasteiger, E. et al. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook (ed John M. Walker) 571–607 (Humana Press 2005).
- 60.Bhati M, et al. Solution Structure of the LIM-Homeodomain Transcription Factor Complex Lhx3/Ldb1 and the Effects of a Pituitary Mutation on Key Lhx3 Interactions. PLOS One. 2012;7:e40719. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Jeffries CM, Whitten AE, Harris SP, Trewhella J. Small-angle X-ray scattering reveals the N-terminal domain organization of cardiac myosin binding protein C. J Mol Biol. 2008;377:1186–1199. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.01.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Konarev PV, Svergun DI. A posteriori determination of the useful data range for small-angle scattering experiments on dilute monodisperse systems. IUCr J. 2015;2:352–360. doi: 10.1107/S2052252515005163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Orthaber D, Bergmann A, Glatter O. SAXS experiments on absolute scale with Kratky systems using water as a secondary standard. J Appl Crystallogr. 2000;33:218–225. doi: 10.1107/S0021889899015216. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Svergun DI. Determination of the regularization parameter in indirect-transform methods using perceptual criteria. J Appl Crystallogr. 1992;25:495–503. doi: 10.1107/S0021889892001663. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Petoukhov MV, et al. New developments in the ATSAS program package for small-angle scattering data analysis. J Appl Crystallogr. 2012;45:342–350. doi: 10.1107/S0021889812007662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Svergun DI, Barberato C, Koch MHJ. CRYSOL - a program to evaluate X-ray solution scattering of biological macromolecules from atomic coordinates. J Appl Crystallogr. 1995;28:768–773. doi: 10.1107/S0021889895007047. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Marley J, Lu M, Bracken C. A method for efficient isotopic labeling of recombinant proteins. J Biomol NMR. 2001;20:71–75. doi: 10.1023/A:1011254402785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Biasini M, et al. SWISS-MODEL: modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:W252–258. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974;77:71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Whelan NV, Kocot KM, Moroz LL, Halanych KM. Error, signal, and the placement of Ctenophora sister to all other animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:5773–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1503453112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pisani D, et al. Genomic data do not support comb jellies as the sister group to all other animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:15402–15407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1518127112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The homology model, bead model and SAXS data for CEH-14–LIM-7 have been deposited to the Small Angle Scattering Biological Database (SASBDB)42 under the accession code SASDC22. All other data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its Supplementary Information files or are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request).


