Abstract
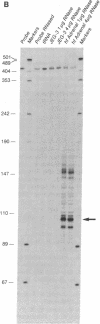
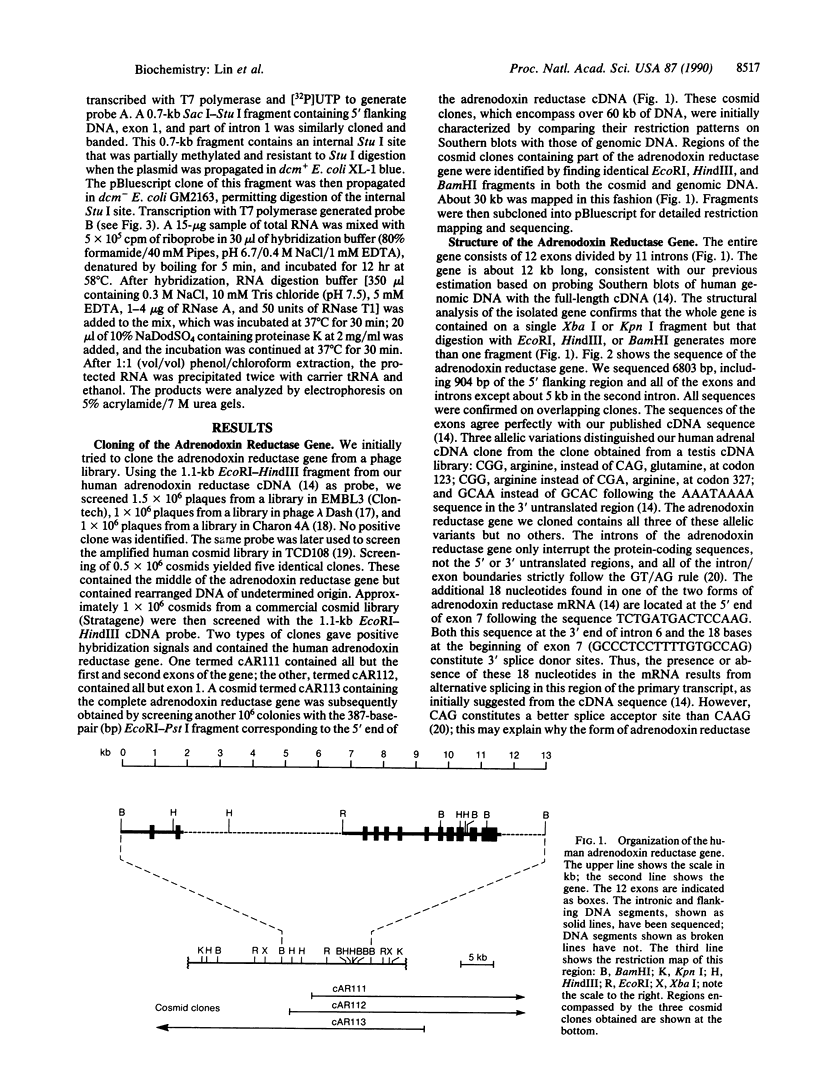
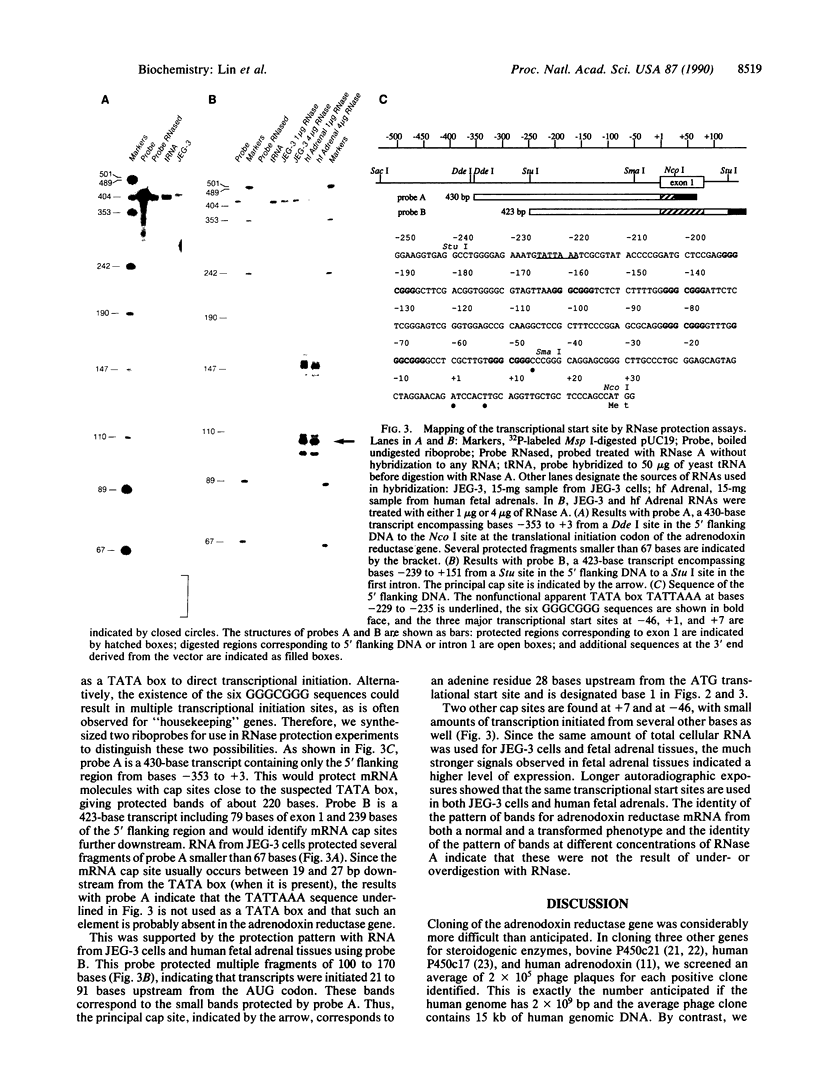
Adrenodoxin reductase (ferrodoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase, EC 1.18.1.2) is a flavoprotein mediating electron transport to all mitochondrial forms of cytochrome P450. We cloned the human adrenodoxin reductase gene and characterized it by restriction endonuclease mapping and DNA sequencing. The entire gene is approximately 12 kilobases long and consists of 12 exons. The first exon encodes the first 26 of the 32 amino acids of the signal peptide, and the second exon encodes the remainder of signal peptide and the apparent FAD binding site. The remaining 10 exons are clustered in a region of only 4.3 kilobases, separated from the first two exons by a large intron of about 5.6 kilobases. Two forms of human adrenodoxin reductase mRNA, differing by the presence or absence of 18 bases in the middle of the sequence, arise from alternate splicing at the 5' end of exon 7. This alternately spliced region is directly adjacent to the NADPH binding site, which is entirely contained in exon 6. The immediate 5' flanking region lacks TATA and CAAT boxes; however, this region is rich in G + C and contains six copies of the sequence GGGCGGG, resembling promoter sequences of "housekeeping" genes. RNase protection experiments show that transcription is initiated from multiple sites in the 5' flanking region, located about 21-91 base pairs upstream from the AUG translational initiation codon.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björkhem I., Holmberg I., Oftebro H., Pedersen J. I. Properties of a reconstituted vitamin D3 25-hydroxylase from rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5244–5249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R., Lee E. Y., To H., Young L. J., Sery T. W., Hayes R. C., Friedmann T., Lee W. H. Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: genomic organization and analysis of heterozygous intragenic deletion mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2210–2214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. Y., Wu D. A., Lai C. C., Miller W. L., Chung B. C. Cloning and structure of the human adrenodoxin gene. DNA. 1988 Nov;7(9):609–615. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. Y., Wu D. A., Mohandas T. K., Chung B. C. Structure, sequence, chromosomal location, and evolution of the human ferredoxin gene family. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;9(3):205–212. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Miller W. L. Cloning and characterization of the bovine gene for steroid 21-hydroxylase (P-450c21). DNA. 1985 Jun;4(3):211–219. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Miller W. L. Structure of a bovine gene for P-450c21 (steroid 21-hydroxylase) defines a novel cytochrome P-450 gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Voutilainen R., Mohandas T. K., Miller W. L. Human cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc: cDNA cloning, assignment of the gene to chromosome 15, and expression in the placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8962–8966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill P. F., deAlvare L. R., Kimura T. Topological studies of the steroid hydroxylase complexes in bovine adrenocortical mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4924–4929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Gutfinger T. cDNA sequence of adrenodoxin reductase. Identification of NADP-binding sites in oxidoreductases. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):479–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Jefcoate C. R. Mitochondrial cytochrome P-450scc. Mechanism of electron transport by adrenodoxin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3057–3061. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)85851-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambeth J. D., Seybert D. W., Kamin H. Ionic effects on adrenal steroidogenic electron transport. The role of adrenodoxin as an electron shuttle. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7255–7264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Kan Y. W. Versatile cosmid vectors for the isolation, expression, and rescue of gene sequences: studies with the human alpha-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5225–5229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luu-The V., Labrie C., Simard J., Lachance Y., Zhao H. F., Couët J., Leblanc G., Labrie F. Structure of two in tandem human 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase genes. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Feb;4(2):268–275. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-2-268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson K. J., Chung B. C., Urdea M. S., Miller W. L. Study of cholesterol side-chain cleavage (20,22 desmolase) deficiency causing congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia using bovine-sequence P450scc oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1296–1305. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon S. H., Miller W. L. Extraadrenal steroid 21-hydroxylation is not mediated by P450c21. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1497–1502. doi: 10.1172/JCI114325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Leisti S., Johnson L. K. Synthesis of growth hormone, prolactin, and proopiomelanocortin by intact adult ovine pituitary tissue in vitro. Endocrinology. 1982 Oct;111(4):1358–1367. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-4-1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L. Molecular biology of steroid hormone synthesis. Endocr Rev. 1988 Aug;9(3):295–318. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-3-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel Y., Picado-Leonard J., Wu D. A., Chang C. Y., Mohandas T. K., Chung B. C., Miller W. L. Assignment of the functional gene for human adrenodoxin to chromosome 11q13----qter and of adrenodoxin pseudogenes to chromosome 20cen----q13.1. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;43(1):52–59. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morioka H., Magnuson M. A., Mitsuhashi T., Song M. K., Rall J. E., Nikodem V. M. Structural characterization of the rat malic enzyme gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4912–4916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohashi K., Sogawa K., Omura T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Gene structure of human cytochrome P-450(SCC), cholesterol desmolase. J Biochem. 1987 Apr;101(4):879–887. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. I., Framson P. E., Caskey C. T., Chinault A. C. Fine structure of the human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):393–403. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picado-Leonard J., Miller W. L. Cloning and sequence of the human gene for P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase): similarity with the gene for P450c21. DNA. 1987 Oct;6(5):439–448. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picado-Leonard J., Voutilainen R., Kao L. C., Chung B. C., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Miller W. L. Human adrenodoxin: cloning of three cDNAs and cycloheximide enhancement in JEG-3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3240–3244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice D. W., Schulz G. E., Guest J. R. Structural relationship between glutathione reductase and lipoamide dehydrogenase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 15;174(3):483–496. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90332-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton N. S., Berry A., Perham R. N. Redesign of the coenzyme specificity of a dehydrogenase by protein engineering. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):38–43. doi: 10.1038/343038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solish S. B., Picado-Leonard J., Morel Y., Kuhn R. W., Mohandas T. K., Hanukoglu I., Miller W. L. Human adrenodoxin reductase: two mRNAs encoded by a single gene on chromosome 17cen----q25 are expressed in steroidogenic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su P., Rennert H., Shayiq R. M., Yamamoto R., Zheng Y. M., Addya S., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Avadhani N. G. A cDNA encoding a rat mitochondrial cytochrome P450 catalyzing both the 26-hydroxylation of cholesterol and 25-hydroxylation of vitamin D3: gonadotropic regulation of the cognate mRNA in ovaries. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;9(9):657–667. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Terpstra P., Hol W. G. Prediction of the occurrence of the ADP-binding beta alpha beta-fold in proteins, using an amino acid sequence fingerprint. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]